Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Competency Mapping Model For HR Professionals in India: Vikram Singh Chouhan & Sandeep Srivastava
Hochgeladen von
sunru24Originaltitel
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Competency Mapping Model For HR Professionals in India: Vikram Singh Chouhan & Sandeep Srivastava
Hochgeladen von
sunru24Copyright:
Verfügbare Formate
International Journal of Human Resource Management and Research (IJHRMR) ISSN 2249-6874 Vol.
3, Issue 1, Mar 2013, 113-118 TJPRC Pvt. Ltd.
COMPETENCY MAPPING MODEL FOR HR PROFESSIONALS IN INDIA
VIKRAM SINGH CHOUHAN & SANDEEP SRIVASTAVA JUET, AB Road, Raghogarh, Guna, Madhya Pradesh, India
ABSTRACT
As the HR profession has increasingly earned its seat at the strategic table and become a business partner, the need to develop the foundational competency has become more pronounced. Every well-managed firm should have well defined roles and list of competencies required to perform each role effectively for all HR jobs. Competency is a set of knowledge, skills and attitudes required to perform a job effectively and efficiently. Competency mapping identifies an individuals strengths and weaknesses in order to help them better understand themselves and to show them where career development efforts need to be directed. There is a need for multi skill development. Competency Mapping is a process of identifying key competencies for an organization, the jobs and functions within it. Competency mapping is one of the most accurate means in identifying the job and behavioral competencies of an individual in an organization. This paper is an attempt to develop a competency mapping model for HR professionals in Indian context. At the top of the competency model are five roles, or lenses, through which HR practitioners can view the model: Strategic partners, Administrative experts, Employee champions, Change agents and HR experts.
KEYWORDS: Competencies, Competency Mapping, Competency Mapping Model, Competency Management, HR
Roles
INTRODUCTION
Competency mapping analyzes individuals SWOT for better understanding and this helps to improve his career growth. This identifies the gap for improving knowledge to develop. Companies are vastly shifting their approach of having multi-skilled employees with knowledge of only one skill. Companies are interested in knowing the present skill level of their employees so that training can be given to improve their performance. The competence approach focuses on linking business strategies to individual performance efforts. It also encourages employees to develop competencies which can be used in diverse work situations rather than being boxed into the job. Development of employees focuses on enhancing their competencies rather than preparing them for moving to jobs. In this way they can develop capabilities useful throughout the organization as it changes and evolves. Competency models thus not only help the organizations in providing a Blue print for the entire gamut of behavior that produce excellent performance but can also provide an important and useful tool to guide individual development.
STATEMENT OF THE PROBLEM
It appears necessary to investigate if a difference exists in job competency expectations held for their employees between the required competency levels to the existing level of working. Research indicates that the closer of the employer job competency expectations i.e, the required competency level to the actual job competency level of the employees brings the better chance for productivity improvement, waste elimination, multi skill development and the higher employees will rate overall job satisfaction.
114
Vikram Singh Chouhan & Sandeep Srivastava
In order to ascertain accurate and current job competency expectations i.e, the required competency to work in a particular industry, professionals, supervisors and production heads are asked to rate the importance of the specific job competencies for the workforce. The managers are asked to list the required competency to perform a job and they were also asked to fix the required level of competencies in the specific competency. Thus Competency models are prepared.
MAIN OBJECTIVES
To map the competencies for the professionals in HR departments in India. To develop the competency mapping model for employees in a particular industry. To find out the ranking of competencies required for different HR roles.
CONCEPTUAL FRAMEWORK
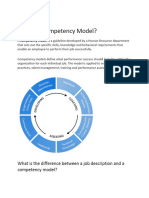
The competency model has five roles, or lenses, through which HR practitioners can view the model: Strategic Partners translate business strategy into action.. Building new organizational capabilities call for performance management programs aligned with the desired outcomes. Administrative Experts improve processes, apply the principles of reengineering business processes to human resources processes, rethink value creation, rethink how work is performed, and measure human resources results in terms of efficiency (cost) and effectiveness (quality). Employee Champions listen and respond to employees and find the right balance between demands on employees and resources available to employees. They promote employee contributions. Change Agents understand the theory and apply the tools of change. They serve as catalysts for change, facilitators of change, and designers of systems for change. HR Experts are the technical specialists and they deal in areas like recruitment, selection, training, performance appraisal etc. To perform these roles, HR professionals must possess a set of competencies, which are divided into 6 categories. HR jobs have different role to play and each role requires different dimensions of behavior, to achieve a particular outcome as explained in Figure 1.
Five HR Roles 1. Strategic partners 2. Administrative experts 3. Employee champions 4. Change agents 5. HR Experts
Five Competency Groups 1. Analytical 2. Technical 3. Leadership 4. Interpersonal 5. Business
Desired Outcomes Foresee future challenges Developing individual capabilities Achieving organizational Increase in efficiency Training Need Assessment
Figure 1: Conceptual Framework
Competency Mapping Model for HR Professionals in India
115
RESEARCH MODEL
Figure 2 : Competency Mapping Model for Increasing Efficiency
WHAT METHODOLOGY IS USED?
The following methods are used in combination for competency mapping: Questionnaire, Use of Job descriptions, Performance Appraisal Formats etc.
STEPS INVOLVED IN COMPETENCY MAPPING
The steps involved in competency mapping to identify the key competencies for an organization and the job within the function Indentify the department for mapping. Identify the Structure of the organization and select the grades & levels. Job Description from individuals and departments. Conducting Semi-Structured interviews. Collecting interview datas. Classify the required Skill list. Identify the skill levels. Evaluate identified competencies and skill levels with immediate superiors and other heads of concerned departments. Preparation of Competency calendar. Mapping of Competencies. 11.Development of competency model.
CONCLUSIONS
There is a strong and positive relationship between possession of competencies and successful job performance. This can be explained by the fact that HR jobs have different role to play and each role requires different dimensions of behavior. Thus, competencies and competency models are a viable tool that can be utilized to prepare the current and future workforce and retain skilled incumbent workers to meet the job requirements and other needs of employers.
116
Vikram Singh Chouhan & Sandeep Srivastava
Future research may examine different factors of competency model for different needs of the industry and can find out that is there any consensus for the factors of competency model that we can arrive for the same industry.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
1. 2. Ashworth, P.D. & Saxton, J. (1990), On competence. Journal of Further and Higher Education, - 27. Banger, J., and Sharma, A. (2005), The Indian Perspective of Strategic HR Roles and Organizational Learning Capability, International Journal of Human Resource Management, 16, 9, 17111739. 3. Bowden, J.A. & Masters G.N. (1993), Implications for higher education of a competency-based approach to education and training. 4. 5. 6. Boyatzis. R (1982), The Competent Manager: A model for effective Performance. New York Wiley 6. Cairns, L. (1996), Capability: going beyond competence. Cascio. W.F. (1998), Applied Psychology in Human Resource Management. Englefield Cliffs; N.J. Prentice Hall 9 7. Cockerels, T., Hunt, J., & Schroder, H. (1995), Managerial competencies: Fact or fiction? Business Strategy Review 26 8. 9. David C McClelland (1973), Testing for Competence Rather than for Intelligence. American Psychologist 2 Dubois (1993), Competency Based performance improvement: a Strategy for organizational Change.Amherst: HRD- 12. 10. Dulewicz, V. (1989), Performance appraisal and counseling. John Wiley & Sons. New York, pp. 645- 649. 11. Evarts H F (1988), The Competency Programme of the American Management Association. Journal of Management Development. 12. Fogg, CD (1994), Implementing your strategic plan: How to turn intent into effective action for sustainable change. New York. American Management Association 10 13. Furnham (1970), A question of time Competency. Personnel Management. P. 37 -1. 14. Garret, S. (2007), Competency Mapping: What is it and How It Can Be Done by Individuals? 15. Hase, S. & Davis L. (1999), From competence to capability-Implications for human resource development and management. Association of International Management, 17th annual conference. 16. Hoffman T (1999), The Meaning of Competency. Journal of European Industrial Training. 17. Lucia, A. D., & Lepsinger, R. (1999), The art and science of competency models: Pinpointing critical success factors in organizations. New York: Pfeiffer 28 18. Lucian Cernusca and Cristina Dima (2007), Competency and Human Resource Management. International journal of psychology, Vol.II. 19. McClelland D C (1975), A Competency Model for HR Management specialists to be used in the delivery of Human Resource Management Cycle, McBer, Boston. 20. Patty Grigorgev (2006), Hiring by Competency Models. The Journal for Quality and Participation. 16
Competency Mapping Model for HR Professionals in India
117
21. Phelps, R., Hase, S. & Ellis, A. (2005), Competency, capability, complexity and computers: exploring a new model for conceptualizing enduser computer education. 22. Richard Montier, David Alai (2008), Competency Models: Develops Top Performers. ASTD 20 23. Robert M Fulmera and Jay A Conger (2004), Identifying Talent. Executive Excellence 15 24. Shipman, J S Ash; R A (2000), The practice of competency modeling. Personnel Psychology. 11 25. Shippmann, J. S., Ash, R. A., Battista, M., Carr. L., Eyde, L. D., Hesketh, B., Kehoe, J., Suri, G. and Vohra, N. (2004), Competency Mapping in Performance Management. 26. Spencer, L.M and Spencer, S.G (1993), Competence at work: Models for superior performance. New York: Wiley 7 27. Tucker, Sharon A., and Kathryn M. Cofsky (1994), Competency-Based Pay on a Banding Platform. CA Journal.1994, Volume 3, Number 1. 28. William Rothwell (2004), Mapping the future: Shaping new workplace learning and performance competencies. American Society for Training & Development 25
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Defining HR Success: 9 Critical Competencies for HR ProfessionalsVon EverandDefining HR Success: 9 Critical Competencies for HR ProfessionalsBewertung: 5 von 5 Sternen5/5 (1)
- A Study of Competency Mapping of Employees in Banking SectorDokument11 SeitenA Study of Competency Mapping of Employees in Banking SectorVinothNoch keine Bewertungen
- Summary of Dave Ulrich, David Kryscynski, Wayne Brockbank & Mike Ulrich's Victory Through OrganizationVon EverandSummary of Dave Ulrich, David Kryscynski, Wayne Brockbank & Mike Ulrich's Victory Through OrganizationNoch keine Bewertungen
- Competency Mapping - A Managerial Perception (A Study of HDFC Bank LTD.)Dokument12 SeitenCompetency Mapping - A Managerial Perception (A Study of HDFC Bank LTD.)Vinoth KannanNoch keine Bewertungen
- AbstractDokument3 SeitenAbstractChitra SahuNoch keine Bewertungen
- The HR Scorecard (Review and Analysis of Becker, Huselid and Ulrich's Book)Von EverandThe HR Scorecard (Review and Analysis of Becker, Huselid and Ulrich's Book)Bewertung: 5 von 5 Sternen5/5 (1)
- Need of Competency Mapping in Modern EraDokument7 SeitenNeed of Competency Mapping in Modern EraHappy SinghNoch keine Bewertungen
- Researchpaper Competency MappingDokument7 SeitenResearchpaper Competency MappingGhansham PanwarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hope - Holistic & Objective Psychometric Effectiveness in Competency MappingDokument18 SeitenHope - Holistic & Objective Psychometric Effectiveness in Competency MappingTJPRC Publications100% (1)
- Competency Mapping - A Strategic Approach in Talent ManagementDokument20 SeitenCompetency Mapping - A Strategic Approach in Talent ManagementAnonymous 0zM5ZzZXCNoch keine Bewertungen
- 10 - 12 - HR PolyclinicDokument22 Seiten10 - 12 - HR PolyclinicPratiksha MaturkarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Competency MappingDokument109 SeitenCompetency MappingkartikNoch keine Bewertungen
- Full Project Sumit Ninawe 2022Dokument53 SeitenFull Project Sumit Ninawe 2022Sagar KhursangeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Competency Mapping in Indian Industries - A Case Study: Research ArticleDokument13 SeitenCompetency Mapping in Indian Industries - A Case Study: Research ArticleSameera SyedNoch keine Bewertungen
- A Study On Competency MappingDokument12 SeitenA Study On Competency MappingAnonymous CwJeBCAXpNoch keine Bewertungen
- Competency Mapping of The EmployeesDokument7 SeitenCompetency Mapping of The EmployeesJijo Abraham100% (1)
- Synopsis Sumit Ninawe 2022Dokument8 SeitenSynopsis Sumit Ninawe 2022Sagar KhursangeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Competancy Mapping With Axis BankDokument71 SeitenCompetancy Mapping With Axis Bankcharu100% (1)
- Competency Mapping in Indian IndustriesDokument13 SeitenCompetency Mapping in Indian IndustriesVignesh MhatreNoch keine Bewertungen
- Synopsis On Competency GAP AnalysisDokument21 SeitenSynopsis On Competency GAP AnalysisRajesh BathulaNoch keine Bewertungen
- ComptDokument6 SeitenComptTanya SachdevaNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Competency Modeling ApproachDokument4 SeitenThe Competency Modeling ApproachsaospieNoch keine Bewertungen
- Competency ModelDokument23 SeitenCompetency ModelShreyash PatilNoch keine Bewertungen
- Project Report On: Management of Human ResourcesDokument12 SeitenProject Report On: Management of Human ResourcesAkhil ThakurNoch keine Bewertungen
- Job Analysis DesDokument16 SeitenJob Analysis DesMuhammad NomanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Job Analysis 2Dokument14 SeitenJob Analysis 2Mabe MusicNoch keine Bewertungen
- Performance Appraisal System of HDFC Bank.: Chapter No. 05Dokument34 SeitenPerformance Appraisal System of HDFC Bank.: Chapter No. 05Shubham utekarNoch keine Bewertungen
- HR Strategies To Retain Employees and Building Their CompetencyDokument7 SeitenHR Strategies To Retain Employees and Building Their CompetencyEditor IJTSRDNoch keine Bewertungen
- HR Project TopicsDokument13 SeitenHR Project TopicsthariniadmiresNoch keine Bewertungen
- Assignment 1 Research ProjectDokument25 SeitenAssignment 1 Research ProjectRoni AliNoch keine Bewertungen
- Competency MappingDokument10 SeitenCompetency Mappingjyothsna19Noch keine Bewertungen
- Documents MX Sudhir Internship On Tata Steel Jamshedpur Skills MappingDokument4 SeitenDocuments MX Sudhir Internship On Tata Steel Jamshedpur Skills MappingParixit DasNoch keine Bewertungen
- HR PolicyDokument12 SeitenHR PolicyEva AliceNoch keine Bewertungen
- Final Chapter 1Dokument17 SeitenFinal Chapter 1abdfaz951Noch keine Bewertungen
- HRM Mid Sem AnswerDokument10 SeitenHRM Mid Sem AnswerApril ReynoldsNoch keine Bewertungen
- MS 02Dokument7 SeitenMS 02Rajni KumariNoch keine Bewertungen
- Competency MappingDokument7 SeitenCompetency MappingDR K DHAMODHARANNoch keine Bewertungen
- The HR Manager As A LeaderDokument10 SeitenThe HR Manager As A LeaderJosenia Constantino100% (2)
- Roles and Responsibilities of HR Manager Assignment-1: Bavya.R 19EPMB013 Mba-ADokument4 SeitenRoles and Responsibilities of HR Manager Assignment-1: Bavya.R 19EPMB013 Mba-ABavya RajNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Role of Human Resource Development in Enhancing The Firm Capabilities in Pakistani OrganizationDokument8 SeitenThe Role of Human Resource Development in Enhancing The Firm Capabilities in Pakistani OrganizationTallalBaigLalaNoch keine Bewertungen
- For Competency Mapping ProjectDokument19 SeitenFor Competency Mapping ProjectAchu ThiruNoch keine Bewertungen
- HR CombineDokument23 SeitenHR CombineroshanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Performance Appraisal and Human Resource PDFDokument6 SeitenPerformance Appraisal and Human Resource PDFPratik LokhandeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Performance Appraisal HR ProjectDokument87 SeitenPerformance Appraisal HR Projecteeshwer84% (291)
- What Is CompetencyDokument3 SeitenWhat Is Competencysureshdwivedi2482Noch keine Bewertungen
- Introduction of HRM HDFC BankDokument25 SeitenIntroduction of HRM HDFC BankAnonymous ty7mAZ50% (2)
- TVS ProfileDokument29 SeitenTVS ProfileMohan RajNoch keine Bewertungen
- HRM Assignment - Angshu GurungDokument14 SeitenHRM Assignment - Angshu GurungGurung AnshuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lesson No. 8 - Organizing (Managing Human Resource)Dokument44 SeitenLesson No. 8 - Organizing (Managing Human Resource)jun junNoch keine Bewertungen
- Exam TopicsDokument3 SeitenExam TopicsNoha YamanyNoch keine Bewertungen
- A Study On Performance Appraisal System in Stanley Material and Metallurgical Pipe and Tube Manufacturing Industry at CoimbatoreDokument36 SeitenA Study On Performance Appraisal System in Stanley Material and Metallurgical Pipe and Tube Manufacturing Industry at Coimbatorek eswariNoch keine Bewertungen
- Talent.: Talent Management Refers To The Anticipation of RequiredDokument3 SeitenTalent.: Talent Management Refers To The Anticipation of RequiredshyamgopiNoch keine Bewertungen
- HRM Discusssion ReferencesDokument19 SeitenHRM Discusssion ReferencesAAPHBRSNoch keine Bewertungen
- Talent ManagementDokument8 SeitenTalent ManagementAnthony Dela TorreNoch keine Bewertungen
- Competency Mapping: Asst Professor, Amity University Noida Asst Professor, Amity University NoidaDokument3 SeitenCompetency Mapping: Asst Professor, Amity University Noida Asst Professor, Amity University NoidaVirah RNoch keine Bewertungen
- Competency MappingDokument71 SeitenCompetency MappingnithiNoch keine Bewertungen
- HRD Matrix: Submitted byDokument21 SeitenHRD Matrix: Submitted bykusumNoch keine Bewertungen
- Competency Based HRM ModuleDokument4 SeitenCompetency Based HRM ModuleErlene LinsanganNoch keine Bewertungen
- HRD AssignmentDokument17 SeitenHRD AssignmentKarpagam Chandrasekaran67% (3)
- Brochure - Workshop On RDokument5 SeitenBrochure - Workshop On Rsunru24Noch keine Bewertungen
- SHRM (4th) May2017Dokument2 SeitenSHRM (4th) May2017sunru24Noch keine Bewertungen
- Job Satisfaction and Turnover Intentions: The Moderating Role of Positive AffectDokument4 SeitenJob Satisfaction and Turnover Intentions: The Moderating Role of Positive Affectsunru24Noch keine Bewertungen
- The Validation of The Turnover Intention ScaleDokument138 SeitenThe Validation of The Turnover Intention Scalesunru24Noch keine Bewertungen
- The Validation of The Turnover Intention Scale Bothma y Roodt 2013Dokument12 SeitenThe Validation of The Turnover Intention Scale Bothma y Roodt 2013Pedro Alberto Herrera LedesmaNoch keine Bewertungen
- A Qualitative Study On The Causes of Stress and Management Mechanisms at Volvo Trucks AB, Umeå PDFDokument67 SeitenA Qualitative Study On The Causes of Stress and Management Mechanisms at Volvo Trucks AB, Umeå PDFSoumya SunishNoch keine Bewertungen
- Entry of Jio in Telecommunication Sector in A Competitive EnvironmentDokument4 SeitenEntry of Jio in Telecommunication Sector in A Competitive Environmentsunru24Noch keine Bewertungen
- QP SHRM Old PaperDokument2 SeitenQP SHRM Old Papersunru24Noch keine Bewertungen
- Case StudyDokument28 SeitenCase Studysunru24Noch keine Bewertungen
- Medi Caps University Indore: Form IDokument1 SeiteMedi Caps University Indore: Form Isunru24Noch keine Bewertungen
- 2020 International Conference On Partial Least Squares Structural Equation Modeling (PLS-SEM)Dokument1 Seite2020 International Conference On Partial Least Squares Structural Equation Modeling (PLS-SEM)sunru24Noch keine Bewertungen
- Summer Training Project Report ON: Master of Business AdministrationDokument25 SeitenSummer Training Project Report ON: Master of Business Administrationsunru24Noch keine Bewertungen
- BSXIDokument183 SeitenBSXIsunru24Noch keine Bewertungen
- 1 s2.0 S0897189717302410 Main PDFDokument11 Seiten1 s2.0 S0897189717302410 Main PDFsunru24Noch keine Bewertungen
- Assess Whole SEM Model - Fit IndexDokument14 SeitenAssess Whole SEM Model - Fit Indexsunru24Noch keine Bewertungen
- Serial Key For SmartPLSDokument1 SeiteSerial Key For SmartPLSsunru2450% (4)
- Employment Downsizing PDFDokument48 SeitenEmployment Downsizing PDFEmperorr Tau MtetwaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sip Mentees Details - DTDokument3 SeitenSip Mentees Details - DTsunru24Noch keine Bewertungen
- Sample Paper 3Dokument8 SeitenSample Paper 3Aswajith K BabuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Strategic Human Resource DevelopmentDokument3 SeitenStrategic Human Resource Developmentsunru24Noch keine Bewertungen
- BOOK Presentation Schedule (F)Dokument1 SeiteBOOK Presentation Schedule (F)sunru24Noch keine Bewertungen
- International Conference Brochure IIT Roorkee 2017Dokument2 SeitenInternational Conference Brochure IIT Roorkee 2017sunru24Noch keine Bewertungen
- AttestationSheet MBA IV 105 StudentsDokument106 SeitenAttestationSheet MBA IV 105 Studentssunru24Noch keine Bewertungen
- Punjabi University Patiala 4th Sem Syllabus, 2010.Dokument43 SeitenPunjabi University Patiala 4th Sem Syllabus, 2010.Hardeep SharmaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Dynamic Student Report 30-12-2016Dokument63 SeitenDynamic Student Report 30-12-2016sunru24Noch keine Bewertungen
- Dynamic Student Report 30-12-2016Dokument63 SeitenDynamic Student Report 30-12-2016sunru24Noch keine Bewertungen
- Attempt All QuestionsDokument3 SeitenAttempt All Questionssunru24Noch keine Bewertungen
- Dynamic Student Report 30-12-2016Dokument63 SeitenDynamic Student Report 30-12-2016sunru24Noch keine Bewertungen
- User Manual - AQIS Application - TGS - Version 1.0Dokument35 SeitenUser Manual - AQIS Application - TGS - Version 1.0sunru24Noch keine Bewertungen
- ICP - Abstract SubmissionDokument1 SeiteICP - Abstract Submissionsunru24Noch keine Bewertungen
- Strategic Managing The Human Resources FunctionDokument3 SeitenStrategic Managing The Human Resources FunctionPrincess Joy MoralesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Content Theories - Maslow, Herzberg, AlderferDokument3 SeitenContent Theories - Maslow, Herzberg, Alderferfaltumail379Noch keine Bewertungen
- Strategic Human Resource ManagementDokument66 SeitenStrategic Human Resource ManagementHarshita Rajput HarshuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Effects of Workplace Friendship On Employee Job Satisfaction Org PDFDokument5 SeitenEffects of Workplace Friendship On Employee Job Satisfaction Org PDFanon_212220538100% (1)
- Quality of Work LifeDokument13 SeitenQuality of Work LifeMarc Eric RedondoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Introduction To Industrial SociologyDokument7 SeitenIntroduction To Industrial Sociologyamitsharma1882006Noch keine Bewertungen
- Lesson 11Dokument28 SeitenLesson 11Marisol TiempoNoch keine Bewertungen
- ORR-Participant Guide, FillableDokument29 SeitenORR-Participant Guide, FillableVadim FattakhovNoch keine Bewertungen
- HRM & Motivational TheoriesDokument21 SeitenHRM & Motivational TheoriesDalila MatakovaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 607c080d 1597126909187Dokument41 Seiten607c080d 1597126909187Jyoti Arvind PathakNoch keine Bewertungen
- Application of Motivation ConceptsDokument21 SeitenApplication of Motivation ConceptsRaghav ArroraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Industrial PsychologyDokument66 SeitenIndustrial Psychologyvikas prachetaNoch keine Bewertungen
- HR Group Assignment 2 TALENT RETENTIONDokument25 SeitenHR Group Assignment 2 TALENT RETENTIONfaeeezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Importance of Personality Tests in AssessmentDokument12 SeitenImportance of Personality Tests in AssessmentApar PanchalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Aman Nailwal: Erp ExecutiveDokument2 SeitenAman Nailwal: Erp ExecutiveAman NailwalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Human Resource Planning ProcessDokument3 SeitenHuman Resource Planning ProcessG & E Apparel100% (1)
- BMGT4321 - Talent Management Strategies and Legal and Ethical ChallengesDokument13 SeitenBMGT4321 - Talent Management Strategies and Legal and Ethical ChallengesDipan Dutta ChowdhuryNoch keine Bewertungen
- HR Practices of Visakhapatnam Steel Plant - ManjushaDokument3 SeitenHR Practices of Visakhapatnam Steel Plant - ManjushaRam BhargavNoch keine Bewertungen
- Proposal 1Dokument17 SeitenProposal 1Ralph TanNoch keine Bewertungen
- HRM - Unit 2 - PPT - VJDokument14 SeitenHRM - Unit 2 - PPT - VJVijay prasadNoch keine Bewertungen
- Employee Retention Strategies: 2. Open CommunicationDokument3 SeitenEmployee Retention Strategies: 2. Open CommunicationNishika SinghNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 4 Theories of Motivation Edited DTD 9 Sept 2017Dokument19 SeitenChapter 4 Theories of Motivation Edited DTD 9 Sept 2017Ling Meng ChanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Leadership AssignmentDokument18 SeitenLeadership AssignmentHira Mustafa ShahNoch keine Bewertungen
- Antecedents and Consequences of Organisational Citizenship Behaviour (OcbDokument22 SeitenAntecedents and Consequences of Organisational Citizenship Behaviour (Ocbsanjana jatooNoch keine Bewertungen
- Griffin 10e PPTS Ch04Dokument27 SeitenGriffin 10e PPTS Ch04Abigail SubaNoch keine Bewertungen
- List of Recruitment Agencies in DubaiDokument8 SeitenList of Recruitment Agencies in DubaiTeju Ashu100% (1)
- BUS 5511 - Written Assignment 4Dokument4 SeitenBUS 5511 - Written Assignment 4Alen CrossmanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hodgkinson, 2001, Realigning The Stakeholders in ManagementDokument8 SeitenHodgkinson, 2001, Realigning The Stakeholders in ManagementfjsvasconcellosNoch keine Bewertungen
- Performance Management: A Critical Outlook On 360 Degree Performance AppraisalDokument11 SeitenPerformance Management: A Critical Outlook On 360 Degree Performance AppraisalBIPUL BOSENoch keine Bewertungen
- HRP, Recruitment and SelectionDokument14 SeitenHRP, Recruitment and Selectionmohit77778Noch keine Bewertungen
- The Fearless Organization: Creating Psychological Safety in the Workplace for Learning, Innovation, and GrowthVon EverandThe Fearless Organization: Creating Psychological Safety in the Workplace for Learning, Innovation, and GrowthBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (101)
- Coaching and Mentoring: Practical Techniques for Developing Learning and PerformanceVon EverandCoaching and Mentoring: Practical Techniques for Developing Learning and PerformanceBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (4)
- The 5 Languages of Appreciation in the Workplace: Empowering Organizations by Encouraging PeopleVon EverandThe 5 Languages of Appreciation in the Workplace: Empowering Organizations by Encouraging PeopleBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (46)
- The Five Dysfunctions of a Team SummaryVon EverandThe Five Dysfunctions of a Team SummaryBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (59)
- The Power of People Skills: How to Eliminate 90% of Your HR Problems and Dramatically Increase Team and Company Morale and PerformanceVon EverandThe Power of People Skills: How to Eliminate 90% of Your HR Problems and Dramatically Increase Team and Company Morale and PerformanceBewertung: 5 von 5 Sternen5/5 (22)
- Scaling Up: How a Few Companies Make It...and Why the Rest Don't, Rockefeller Habits 2.0Von EverandScaling Up: How a Few Companies Make It...and Why the Rest Don't, Rockefeller Habits 2.0Bewertung: 5 von 5 Sternen5/5 (1)
- 101 Tough Conversations to Have with Employees: A Manager's Guide to Addressing Performance, Conduct, and Discipline ChallengesVon Everand101 Tough Conversations to Have with Employees: A Manager's Guide to Addressing Performance, Conduct, and Discipline ChallengesBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (9)
- Working with AI: Real Stories of Human-Machine Collaboration (Management on the Cutting Edge)Von EverandWorking with AI: Real Stories of Human-Machine Collaboration (Management on the Cutting Edge)Bewertung: 5 von 5 Sternen5/5 (5)
- Goal Setting: How to Create an Action Plan and Achieve Your GoalsVon EverandGoal Setting: How to Create an Action Plan and Achieve Your GoalsBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (9)
- Getting Along: How to Work with Anyone (Even Difficult People)Von EverandGetting Along: How to Work with Anyone (Even Difficult People)Bewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (18)
- The Way of the Shepherd: Seven Secrets to Managing Productive PeopleVon EverandThe Way of the Shepherd: Seven Secrets to Managing Productive PeopleBewertung: 5 von 5 Sternen5/5 (114)
- The Resume and Cover Letter Phrase Book: What to Write to Get the Job That's RightVon EverandThe Resume and Cover Letter Phrase Book: What to Write to Get the Job That's RightBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (9)
- 12 Habits Of Valuable Employees: Your Roadmap to an Amazing CareerVon Everand12 Habits Of Valuable Employees: Your Roadmap to an Amazing CareerNoch keine Bewertungen
- Job Interview: The Complete Job Interview Preparation and 70 Tough Job Interview Questions with Winning AnswersVon EverandJob Interview: The Complete Job Interview Preparation and 70 Tough Job Interview Questions with Winning AnswersBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (7)
- The Manager's Path: A Guide for Tech Leaders Navigating Growth and ChangeVon EverandThe Manager's Path: A Guide for Tech Leaders Navigating Growth and ChangeBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (99)
- Powerful Phrases for Dealing with Difficult People: Over 325 Ready-to-Use Words and Phrases for Working with Challenging PersonalitiesVon EverandPowerful Phrases for Dealing with Difficult People: Over 325 Ready-to-Use Words and Phrases for Working with Challenging PersonalitiesBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (14)
- Organizational Behaviour: People, Process, Work and Human Resource ManagementVon EverandOrganizational Behaviour: People, Process, Work and Human Resource ManagementNoch keine Bewertungen
- Leadership's Perfect Storm: What Millennials Are Teaching Us About Possibilities, Passion and PurposeVon EverandLeadership's Perfect Storm: What Millennials Are Teaching Us About Possibilities, Passion and PurposeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hire With Your Head: Using Performance-Based Hiring to Build Outstanding Diverse TeamsVon EverandHire With Your Head: Using Performance-Based Hiring to Build Outstanding Diverse TeamsBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (5)
- Unbeatable Resumes: America's Top Recruiter Reveals What REALLY Gets You HiredVon EverandUnbeatable Resumes: America's Top Recruiter Reveals What REALLY Gets You HiredBewertung: 5 von 5 Sternen5/5 (2)
- Inspiring Accountability in the Workplace: Unlocking the brain's secrets to employee engagement, accountability, and resultsVon EverandInspiring Accountability in the Workplace: Unlocking the brain's secrets to employee engagement, accountability, and resultsBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (2)
- Profit Works: Unravel the Complexity of Incentive Plans to Increase Employee Productivity, Cultivate an Engaged Workforce, and Maximize Your Company's PotentialVon EverandProfit Works: Unravel the Complexity of Incentive Plans to Increase Employee Productivity, Cultivate an Engaged Workforce, and Maximize Your Company's PotentialBewertung: 5 von 5 Sternen5/5 (1)
- A Joosr Guide to... What Color is Your Parachute? 2016 by Richard Bolles: A Practical Manual for Job-Hunters and Career-ChangersVon EverandA Joosr Guide to... What Color is Your Parachute? 2016 by Richard Bolles: A Practical Manual for Job-Hunters and Career-ChangersBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (1)
- The Essential HR Handbook, 10th Anniversary Edition: A Quick and Handy Resource for Any Manager or HR ProfessionalVon EverandThe Essential HR Handbook, 10th Anniversary Edition: A Quick and Handy Resource for Any Manager or HR ProfessionalBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (3)
- Irresistible: The Seven Secrets of the World's Most Enduring, Employee-Focused OrganizationsVon EverandIrresistible: The Seven Secrets of the World's Most Enduring, Employee-Focused OrganizationsBewertung: 5 von 5 Sternen5/5 (3)
- The Art of Active Listening: How People at Work Feel Heard, Valued, and UnderstoodVon EverandThe Art of Active Listening: How People at Work Feel Heard, Valued, and UnderstoodBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (4)
- How to Be Everything: A Guide for Those Who (Still) Don't Know What They Want to Be When They Grow UpVon EverandHow to Be Everything: A Guide for Those Who (Still) Don't Know What They Want to Be When They Grow UpBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (74)