Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
To Have Higher Data Transfer Speeds and Capacity.: Definition
Hochgeladen von
teosuchinOriginaltitel
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
To Have Higher Data Transfer Speeds and Capacity.: Definition
Hochgeladen von
teosuchinCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
DEFINITION: High-Speed Downlink Packet Access (HSDPA) also known as 3.
5G, 3G+ or turbo 3G, which allows networks based on Universal Mobile Telecommunications System (UMTS) to have higher data transfer speeds and capacity. HSDPA is a protocol for data communications on cellular networks. High Speed Downlink Packet Access (HSDPA) is technology based on the 3G network which can support speeds of up to 7.2 Mbits per second. HSDPA is a downlink enhancement scheme, and thus it improves downlink. It defines a new WCDMA called high-speed downlink shared channel (HS-DSCH). That channel performs contrastingly from other channels and helps to fasten the downlink speeds. IMPORTANT OF HSDPA Many 3G mobile services - such as web browsing or streaming live video - create more traffic coming to the user (downlink) than from the user (uplink). Data traffic on downlink will exceed uplink traffic by a factor of 2:3. HSDPA offers a way to increase downlink capacity within the existing spectrum.
DESCRIBE HSDPA BASIC STRUCTURE Speed - Higher bit rate up to 14 Mbps Capacity -2-3 times improve system thoughput. In the WCDMA downlink, the data transmission is up to 8-10 Megabits/sec over a bandwidth of 5MHZ. The HSDPA use new mechanisms: Adaptive modulation and coding, Hybrid ARQ, Specific scheduling at MAC-hs. Fast adaptation These techniques rely on rapid adaptation of transmission parameters to instantaneous channel conditions.
The mechanisms are implemented in Node B.
DESCRIBE HSDPA CONCEPT HSDPA improves on W-CDMA by using different techniques for modulation and coding. It creates a new channel within W-CDMA called HS-DSCH, or high-speed downlink shared channel. That channel performs differently than other channels and allows for faster downlink speeds. The channel is shared between all users which lets the radio signals to be used most effectively for the fastest downloads. High speed Downlink packet access (HSDPA) is a packet based data service feature of the WCDMA standard. HSDPA, known as 3G Broadband or UMTS Broadband. It is sometimes referred to as a 3.5G technology. HSDPA is an advancement of the WCDMA standard which is created to increase the data rate by a factor of 5 or more. HSDPA improves on W-CDMA by using different techniques for modulation and coding. It defines a new WCDMA called high-speed downlink shared channel (HS-DSCH). That channel performs contrastingly from other channels and helps to fasten the downlink speeds. HS-DSCH is used only for the downlink communication of the mobile. That means that data is sent from the source to the phone. It isn't possible to send data from the phone to a source using HSDPA.
The channel is shared between all users which lets the radio signals to be used most effectively for the fastest downloads. DIFFERENCE BETWEEN LAYERS IN HSDPA AND 3G
HS DPCCH High speed dedicated control channel HS-SCCH High Speed Shared Control Channel DSCH Downlink Shared Channel
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- HSDPA / 3.5G: Download Mobile Phone Adsl Cdma 3G MbpsDokument6 SeitenHSDPA / 3.5G: Download Mobile Phone Adsl Cdma 3G MbpsFendi ChalokNoch keine Bewertungen
- High-Speed Downlink Packet AccessDokument4 SeitenHigh-Speed Downlink Packet Accessflatelecom938Noch keine Bewertungen
- 3G UMTS HSPA - High Speed Packet AccessDokument21 Seiten3G UMTS HSPA - High Speed Packet AccessBikshu KummariNoch keine Bewertungen
- School of Electrical and Computer Engineering Masters of Communication EngineeringDokument14 SeitenSchool of Electrical and Computer Engineering Masters of Communication EngineeringKedir HassenNoch keine Bewertungen
- High-Speed Downlink Packet Access: TechnologyDokument7 SeitenHigh-Speed Downlink Packet Access: Technologyमनीष सिंहNoch keine Bewertungen
- High-Speed Downlink Packet Access (HSDPA) Is An EnhancedDokument9 SeitenHigh-Speed Downlink Packet Access (HSDPA) Is An EnhancedjobertNoch keine Bewertungen
- HSPADokument6 SeitenHSPAmuhcahoNoch keine Bewertungen
- FILE003Dokument52 SeitenFILE003Vikas NigamNoch keine Bewertungen
- Generations of Cellular Technologies: by Yoseph Tenaw 1318/10Dokument5 SeitenGenerations of Cellular Technologies: by Yoseph Tenaw 1318/10Sibhat MequanintNoch keine Bewertungen
- If Everyone Reading This Donated Rs 100, Our Fundraiser Would Be Over Today. Please Read A Personal AppealDokument11 SeitenIf Everyone Reading This Donated Rs 100, Our Fundraiser Would Be Over Today. Please Read A Personal Appealmuthuselvan26Noch keine Bewertungen
- Hspa SeminarDokument20 SeitenHspa SeminarSatish BunnyyNoch keine Bewertungen
- HSDPA PalDokument2 SeitenHSDPA PalChandan PalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hsdpa: High Speed Downlink Packet Access by Alok Sharma (EC 31) Bbdniit, LucknowDokument19 SeitenHsdpa: High Speed Downlink Packet Access by Alok Sharma (EC 31) Bbdniit, LucknowDivyang ShuklaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Understanding HSDPA's Implementation ChallengesDokument6 SeitenUnderstanding HSDPA's Implementation Challengespramod_rfNoch keine Bewertungen
- WCDMA UMTS and CDMA 2000Dokument11 SeitenWCDMA UMTS and CDMA 2000Dhanmeet KaurNoch keine Bewertungen
- HSPA - High Speed Packet Access: Current Trends of Wireless CommunicationsDokument15 SeitenHSPA - High Speed Packet Access: Current Trends of Wireless CommunicationsRasheke Naymantay100% (1)
- 3G Multi CarrierDokument2 Seiten3G Multi CarrierAnonymous mj4J6ZWEWNoch keine Bewertungen
- Multi-Carrier Hspa EvolutionDokument5 SeitenMulti-Carrier Hspa EvolutionAdon A. B. TubieraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Wireless Data Transfer Technologies ExplainedDokument3 SeitenWireless Data Transfer Technologies ExplainedNikhil DharNoch keine Bewertungen
- HSDPA 3G Protocol Provides Faster Mobile Data SpeedsDokument1 SeiteHSDPA 3G Protocol Provides Faster Mobile Data SpeedsHannah MendozaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Group 3Dokument5 SeitenGroup 3Samad AbdusNoch keine Bewertungen
- Diffrence Between HSPA & HSPA+: Broadband Download 3G WcdmaDokument1 SeiteDiffrence Between HSPA & HSPA+: Broadband Download 3G WcdmaAdetayo OnanugaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mipro2006 ConvergenceDokument6 SeitenMipro2006 ConvergenceDamir MuzicNoch keine Bewertungen
- RMCS - Lecture 7 v12 - 1 - Annotated PDFDokument8 SeitenRMCS - Lecture 7 v12 - 1 - Annotated PDFDhanuka AbeysekeraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fast Packet Scheduling for HSDPA Downlink ChannelsDokument2 SeitenFast Packet Scheduling for HSDPA Downlink Channelsqasim78100% (1)
- UMTS - WCDMA Technology OverviewDokument10 SeitenUMTS - WCDMA Technology OverviewsurvivalofthepolyNoch keine Bewertungen
- High Speed Downlink Packet Access (HSDPA) : Cdma 3GDokument14 SeitenHigh Speed Downlink Packet Access (HSDPA) : Cdma 3GAffo AlexNoch keine Bewertungen
- High Speed Downlink Packet AccessDokument2 SeitenHigh Speed Downlink Packet AccessMinto IssacNoch keine Bewertungen
- Wireless Data CommunicationDokument13 SeitenWireless Data CommunicationROBIN SHIRLEY FATCHNoch keine Bewertungen
- 3 5G (Hsdpa)Dokument21 Seiten3 5G (Hsdpa)Sumon Kumar BiswasNoch keine Bewertungen
- WR_BT1011_E01_0 HSDPA Technology P43Dokument41 SeitenWR_BT1011_E01_0 HSDPA Technology P43noumizredhaNoch keine Bewertungen
- High Speed Downlink Packet AccessDokument8 SeitenHigh Speed Downlink Packet AccessNok IssaraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Jaipur National University: High Speed Packet AccessDokument16 SeitenJaipur National University: High Speed Packet AccessPalak KumariNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2 - OWA324030 WCDMA HSPA+ RAN12 Principles ISSUE1.00Dokument45 Seiten2 - OWA324030 WCDMA HSPA+ RAN12 Principles ISSUE1.00MikatechNoch keine Bewertungen
- GPRS 143Dokument10 SeitenGPRS 143Engr. Naveed MazharNoch keine Bewertungen
- Data Transmission Standards Over 2G & 3G NetworksDokument16 SeitenData Transmission Standards Over 2G & 3G NetworksMuneeb Ur RehmanNoch keine Bewertungen
- 5989 2365enDokument36 Seiten5989 2365enTorsion TesnorNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ntroduction: A. Network Architecture and Protocol ImpactDokument2 SeitenNtroduction: A. Network Architecture and Protocol ImpactepriyantonoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Faster SpeedDokument1 SeiteFaster SpeedPriyank KothariNoch keine Bewertungen
- UMTS / WCDMA Basics Tutorial & OverviewDokument3 SeitenUMTS / WCDMA Basics Tutorial & OverviewDiwakar MishraNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1 Hsdpa Concept: Hsdpa, Version 1.1E T.O.P. Businessinteractive GMBH Page 1 of 7Dokument7 Seiten1 Hsdpa Concept: Hsdpa, Version 1.1E T.O.P. Businessinteractive GMBH Page 1 of 7ShahnawazaliNoch keine Bewertungen
- High Speed Circuit Switched Data (HSCSD)Dokument15 SeitenHigh Speed Circuit Switched Data (HSCSD)sunil1978Noch keine Bewertungen
- Concepts of HSDPA: AbstractDokument65 SeitenConcepts of HSDPA: Abstractlegomo81Noch keine Bewertungen
- General Packet Radio ServiceDokument30 SeitenGeneral Packet Radio ServicesamhithaupadhyaNoch keine Bewertungen
- HSPA High Speed Packet AccessDokument23 SeitenHSPA High Speed Packet AccessPrabhat SharmaNoch keine Bewertungen
- General Packet Radio Service (GPRS) Is A: Services OfferedDokument5 SeitenGeneral Packet Radio Service (GPRS) Is A: Services Offeredrenuka_ec694456Noch keine Bewertungen
- Abstract of HSPADokument3 SeitenAbstract of HSPAArju JaimanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hsdpa: 3G Communications Protocol High-Speed Packet AccessDokument2 SeitenHsdpa: 3G Communications Protocol High-Speed Packet AccessBiswajit MohantyNoch keine Bewertungen
- General Packet Radio ServiceDokument4 SeitenGeneral Packet Radio ServiceGouse111Noch keine Bewertungen
- General Packet Radio ServicesDokument8 SeitenGeneral Packet Radio ServicesronyiutNoch keine Bewertungen
- Wireless WAN Advantages of GPRSDokument27 SeitenWireless WAN Advantages of GPRSపుష్ప ఎం ఎస్ డిNoch keine Bewertungen
- General Packet Radio ServicDokument38 SeitenGeneral Packet Radio ServicAmitesh SinghNoch keine Bewertungen
- Analisys of Hsdpa & HsupaDokument3 SeitenAnalisys of Hsdpa & HsupaEmanuela DiakosNoch keine Bewertungen
- WMN Pro NewDokument24 SeitenWMN Pro Newnayan29703Noch keine Bewertungen
- HSDPA Basics: 9:12 PM - byDokument1 SeiteHSDPA Basics: 9:12 PM - byAgus AAANoch keine Bewertungen
- Modeling and Dimensioning of Mobile Wireless Networks: From GSM to LTEVon EverandModeling and Dimensioning of Mobile Wireless Networks: From GSM to LTENoch keine Bewertungen
- How to Use the General Mobile Radio Service for Canadian Business ApplicationsVon EverandHow to Use the General Mobile Radio Service for Canadian Business ApplicationsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Concise Guide to OTN optical transport networksVon EverandConcise Guide to OTN optical transport networksBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (2)
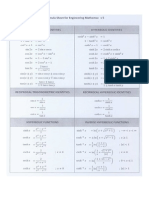
- Formula Ba601 Maths 5 All Dec2013Dokument4 SeitenFormula Ba601 Maths 5 All Dec2013teosuchinNoch keine Bewertungen
- End of ChapterDokument3 SeitenEnd of ChapterteosuchinNoch keine Bewertungen
- GSM ErrorDokument9 SeitenGSM ErrorteosuchinNoch keine Bewertungen
- GSM ErrorDokument9 SeitenGSM ErrorteosuchinNoch keine Bewertungen
- GSM ErrorDokument9 SeitenGSM ErrorteosuchinNoch keine Bewertungen
- End of ChapterDokument3 SeitenEnd of ChapterteosuchinNoch keine Bewertungen
- INSYS - EBW Serie EbookDokument4 SeitenINSYS - EBW Serie EbookJorge_Andril_5370Noch keine Bewertungen
- VxRail Appliance - VxRail Installation Procedures-VxRail P570 - P570FDokument108 SeitenVxRail Appliance - VxRail Installation Procedures-VxRail P570 - P570FbritoalegreNoch keine Bewertungen
- GPON TroubleshootingDokument16 SeitenGPON TroubleshootingAr RasidNoch keine Bewertungen
- CS6301 - Analog and Digital Communication (ADC) PDFDokument122 SeitenCS6301 - Analog and Digital Communication (ADC) PDFparantnNoch keine Bewertungen
- OptiX OSN 8800 6800 3800 Configuration Guide (V100R007)Dokument924 SeitenOptiX OSN 8800 6800 3800 Configuration Guide (V100R007)vladNoch keine Bewertungen
- 03 iBSCDokument36 Seiten03 iBSCYaredNoch keine Bewertungen
- Smc7004awbr ManualDokument50 SeitenSmc7004awbr ManualEric NgNoch keine Bewertungen
- Configure OpenCPN for Garmin radar pluginDokument6 SeitenConfigure OpenCPN for Garmin radar pluginAnonymous yxNRkz1HNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lab 07Dokument9 SeitenLab 07نیان سیف باٹھNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lte19b Ref Bts Parameters Sran20aDokument37 SeitenLte19b Ref Bts Parameters Sran20aAbdourahmane BaNoch keine Bewertungen
- GSM INterview Questions and AnswersDokument2 SeitenGSM INterview Questions and AnswersBromand TurkmaniNoch keine Bewertungen
- (TL-WR885N) How To Set Up A Wireless Router?: Returns TP-LINK HomeDokument4 Seiten(TL-WR885N) How To Set Up A Wireless Router?: Returns TP-LINK HomeJames WoodNoch keine Bewertungen
- PCI device and modem driver modelsDokument320 SeitenPCI device and modem driver modelsomanevNoch keine Bewertungen
- ElecsysDokument19 SeitenElecsysShams ul hassanNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2G and 3G RF Planning ReportDokument242 Seiten2G and 3G RF Planning ReportAshishDevliNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tsunami800+8000 HardwareGuide v5.9-765-00132Dokument163 SeitenTsunami800+8000 HardwareGuide v5.9-765-00132Wael MahmoudNoch keine Bewertungen
- VPC CheatSheet V1.01 PDFDokument2 SeitenVPC CheatSheet V1.01 PDFKanavulagavaasi100% (1)
- XG-PON Definitions and AcronymsDokument26 SeitenXG-PON Definitions and AcronymsAleksandr CherdantsevNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nokia Airscale Wi-Fi Module Ac210M, Release 17ADokument26 SeitenNokia Airscale Wi-Fi Module Ac210M, Release 17Aprashant gauravNoch keine Bewertungen
- Wifisky Wireless AdapterDokument9 SeitenWifisky Wireless AdapterVan HusenNoch keine Bewertungen
- Resolucion Ejercicio Forouzan PDFDokument29 SeitenResolucion Ejercicio Forouzan PDFJAIME FERNANDO TOAQUIZA BALDERRAMONoch keine Bewertungen
- MIMODokument6 SeitenMIMOomer xavi888Noch keine Bewertungen
- Datasheet San Brocade Inter Switch Link TrunkingDokument2 SeitenDatasheet San Brocade Inter Switch Link TrunkingAnkit VashishthNoch keine Bewertungen
- Computer Networks and Operating Systems: Lecture No. 5 by Luminiţa SCRIPCARIUDokument61 SeitenComputer Networks and Operating Systems: Lecture No. 5 by Luminiţa SCRIPCARIUAlexandru IstocNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tfden 122 004 002 EthernetipDokument48 SeitenTfden 122 004 002 EthernetipmfsNoch keine Bewertungen
- RTN 380A&380AX V100R009C10 Commissioning and Configuration Guide 02 PDFDokument313 SeitenRTN 380A&380AX V100R009C10 Commissioning and Configuration Guide 02 PDFSaeed Ashraf KhanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Recent Advances in Information, Communications and Signal ProcessingDokument220 SeitenRecent Advances in Information, Communications and Signal Processingdeltakio@gmail.comNoch keine Bewertungen
- LTE Cell Neighbor ListDokument1.253 SeitenLTE Cell Neighbor ListLenin Alejandro Ramirez HuaypatinNoch keine Bewertungen
- Datafill - RFPar - AREA1 (Sumatera)Dokument1.598 SeitenDatafill - RFPar - AREA1 (Sumatera)Rixson SitorusNoch keine Bewertungen
- Broadband GuideDokument57 SeitenBroadband GuidePrince SinghNoch keine Bewertungen