Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Project Planning, Appraisal and Execution
Hochgeladen von
Omar SiddiquiOriginaltitel
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Project Planning, Appraisal and Execution
Hochgeladen von
Omar SiddiquiCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
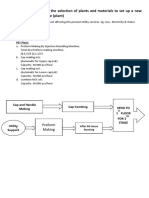
PPAE Discuss briefly the contents of DPR of a hydroelectric project Discuss regarding the various appraisals in the preparation
on of a project report giving reference to construction industry Opportunity study/opportunity report 3 sites cement plant/ crusher plant etc Short notes of DPR Short Notes onTEFR
Project entity or a set of task performed to accomplish some objective Project identification begins in response to the specific need or the objectives Project Selection: Project Identification Project Appraisal Project Selection Collection of all above 3 activites..that is..identification, appraisal and selection is known as a detailed project report
Def. of Project Project ID Project Planning TEFR and DPR Project Appraisal Project Execution Project Organization, Project Mgmr & Project Consultants
Project: Unique process consisting of a set of coordinated and controlled activites with start and finish dates, undertaken to achieve an objective conforming to specific requirements including constraints of time, cost, resources. In other words, project is a complex non-routine, one time effort to complete a particular task within requirements and constraints. Project is a scientifically evolved work plan devised to achieve a specific objectives within specified time limit consuming planned resources. Features of a project: Goal/Objective Uniqueness Beginning and End Complexity Specific time, cost, performance requirements
Project Life Cycle recognizes that project have limited life spans and that there are predictable changes in the level of effort and focus over the life of a project. Although every project is unique, most of them go through 4 phases: defining, planning, executing and delivering.
Life cycle of typical construction project : Each project has a predetermined duration with a definite beginning and an end. Although construction project differe in many way, the life span of the project follows a similar pattern. After conception there is gradual vuild up in the use of resources, and it is followed by a long duration plateau nad towards the end there is a rapid run down completion/ Formulation Mobilization Consturction
The project life cycle phases can be broadly placed In the following categories: o Conception or Identification o Definition or Preparation o Prefeasibility o Feasibility and Financing o Detailed Design o Implementation and Monitoring o Ex post appraisal and impact evaluation
Formulation: Feasibility or inception stage/ Pre investment phase Project Idea Conception Feasibility Studies Investment Appraisal Project Definition ___________________________________
The pre investment phase would usually cover 4 stages: 1. Identification of relevant investment opportunities through appropriate type of opportunity studies 2. Preliminary filtration of the project through pre-feasibility studies 3. Project formulation resulting in Detailed Project Report 4. Techno-Economic Feasibility Report for each project idea conceived worthy for further examination in the previous stage. 5. Final Evaluation & Decision (Appraisal) which is based on technical viablilty, commercial viability, economic viability, environmental viability and managerial viability finally resulting in the evaluation report.
Feasibility Study evaluates project potential o Technical Feasibility o Economic Viability o Financial Implications Contents of Feasibility Report: o Proposed Product Features o Demand Survey Prospective customer; Consumption pattern; Existing market; Govt. Policy; Demand forecast and sale potential o Technical Studies
Process Selection; Construction Methodology; Location Study; Power and local resources availability; Means of transportation; Scope of work; Wastage disposal arrangements; Construction cost estimates; Preliminary time plan o Financial Implications Sales forecast; Project budget; Capital costs; Profitability trend; Payback period; Net present worth; Cash flow forecast; Source of financing o Economic Viability Highlights social implications; Social cost benefit analysis o Summary of Recommendation ________________________________________ Project(investment) Appraisal o Enables client to Decide on the project concept, time and costs Outline the approach needed to taking the project Appoint key person construction project manager or project coordinator to act as his representative Nominate specialist associated agencies such as architect, designer and consultants as per his requirements. The process of formulation of needs, collection of information, critical examination of concepts and re-examination of needs, may have to be repeated several time over before a project inception finally takes shape. Feasibility studies and its appraisal leads to the definition of o Broad scope of work involved; Project objectives o Outline execution methodology o Preliminary time plan; Resource forecasts o Cash flow pattern and source of funding o Potential risk and problem areas
Feasibility of the Projects: 1. Management Appraisal: Management appraisal is related to the technical and managerial competence, integrity, knowledge of the project, managerial competence of promoters etc. The promoters should have the knowledge and ability to plan, implement and operate the entire project effectively. The past record of the promoters is to be appraised to clarify their ability in handling the projects. 2. Technical Feasibility: Technical feasibility analysis is the systematic gathering and analysis of the data pertaining to the technical inputs required and formation of conclusion there from The availability of raw materials. Power. Sanitary and sewerage services, transportation facility, skilled man power, engineering facilities, maintenance, local people etc are coming under technical analysis This feasibility analysis is very important since its significance lies in the planning the exercises, documentation process, risk minimization process and to get approval. 3. Financial Feasibility: One of the very important factors that a project team should meticulously prepare is the financial viability of the entire project. This involves preparation of cost estimates, means of financing, finanicial institutions, financial projection, BEP, ratio analysis etc. The cost of the project includes the land and site development, building, plant and machinery, technical know-how fees, pre-operative expenses, contingency expense etc. The means of finance includes the share capital, term loan, special capital assistance, investment subsidy, margin money loan etc. The financial projections include profitability estimates, cash flow and projected balance sheet
4. Commercial Appraisal: The scope of the project in the market or the beneficiaries, customer friendly process and preferences, future demand of the supply, effectiveness of the selling arrangement, latest information availability and all areas, government control measures etc. The appraisal involves the assessment of the current market scenario, which enables the project to get adequate demand. Estimation, distribution and advertisement scenario also to be here considered into. 5. Economic Appraisal: How far the project contributes to the development of the sector, industrial development, social development, maximizing the growth of employment, etc. are kept in view while evaluating the economic feasibility of the project. 6. Environmental Analysis: Environmental appraisal concerns with the impact of the environment of the project. The factors include the water, air, land sound, geographical locations etc
Feasibility Studies: A project has to pass through three stages of scrutiny and clearance: 1. Pre-feasibility(PF) (PFR) 2. Techno-economic feasibility(TEF) (TEFR) 3. Detailed Project Report(DPR)
Prefeasibility:
2 components of appraisal: Prefeasibility Study and Feasibility Study PF stage is the stage for completing all the preliminary steps for going into detailed feasibility exercise. This PF is the first attempt in identifying the overall potential and viability of the project. The data and information gathered in the preparation stages earlier are utilized here. PF is the first part of conduction project appraisal. Project formulation report or project opportunity study report or Pre-feasibility report(PFR) are the documents which elicits the preliminary sanction or the first stage clearance by the government and/or the board of directors of any enterprise, for further study of a project. The PFR permits determination of whether or not a complete, detailed feasibility study should be made. PFR utilizes the best available information, but cannot contain precise details and accurate figures. Hence, the accuracy of cost estimates is low. Order of magnitude estimate : +/- 25 to 40 percent Preliminary analysis of alternatives: All the available alternatives are compared to ensure: Best financial and economical output Maximum social benefit for the investment Minimum ecological impact PF compromises of following modules: 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Marketing/Demand Module Technical/Engineering Module Environmental Module Manpower & Administrative support module Institutional Module
6. 7. 8. 9.
Financial Module Economic Module Social Appraisal/Distributive and Basic needs analysis Use of Secondary data for Pre-feasibility
PFR Contents: Objective of appraisal in all stage to check if the project is viable from the following angles: Project background & description o Project enterprises name and profile, detailing its experience and performance in project implementation o Project description cost of study/investigations already carried out Market demand and plant capacity o Demand pattern, size of market existing size and capacities in the industry, the project size of future growth, Govt and Private sector dev. Programmes. o Approx. present size of demand, past growth graphs, major determinants and indicators o Sales forecast and market plan anticipated competition for the project from existing and potential local and foreign producers and contractors o Estimated annual cost on marketing and sales promotion Materials and inputs o Details of input requirements, their sources, present and potential supply positions and estimate of annual cost of utilities: Raw materials Processed industrial material; bought out components Power, water and other utilities including transportation services Location and site o Alternative locations, descriptions and area of land selected o Estimated cost of land including its development, for each of the proposed locations alteratives, schedule and cost of soil investigation
o Factors influencing the selection of each of the alternatives Project engineering and investment costs o Preliminary determination of scope of project o Process/technology and equipment cost o Civil engineering works- layout of civil works, arrangement of buildings, description of construction materials to be used Site preparation and development Building & special civil works Outdoor works o Estimate of investment cost of civil engineering work Plant organization and overheads o Organization layout for production, sales, administration and mgmt. o Name, profile and experience of the consultant appointed or proposed to be appointed o Estimated overhead cost on site/factory, administration and financial items cost Manpower o Estimated manpower requirements o Estimated annual salaries and wages including allowances, fringe benefits, and long term social and statutory provisions. o Labour housing plan and estimates Implementation schedule o Proposed time schedule o Estimated implementation cost matching the implementation programme. Financial and economic evaluation o Total investment costs which includes estimated fixed assets o Estimated working capital requirements o Total operation cost classified as fixed costs and variable costs o Project financing arrangement proposed which includes proposed capital structure and finance plan, loan/borrowing planned and interest rates and estimate of interest amounts during construction
o Financial evaluation based on estimates Status of clearance and approvals from various central and state governments and departments
Techno-Economic Feasibility Report:
Techno-economic feasibility refers to the estimation of project demand potential and choice of optimal technology. A project may produce goods/services, it is imperative to know the market for such goods/service produced. TEF makes an analysis of the market and technology TEFR is the second stage of evaluation phases where the project scope is defined, its size and methods determined, suitability of site, the required natural resources and raw materials investigated, and more accurate estimates are made, building, offsite facilities and other assets and their costs; And the total feasibility of the proposal is studied in depth and cleared. After TEFR is cleared, the project proposer can spend money on the preparation of the DPR
Mobilization Stage or Preparation Stage/Investment Phase: 1. 2. 3. 4. Project Preliminary Plan Designs and Drawings Specs and Contract Finalization Resource Mobilization and Earmarking Funds
1. Negotiation and Contracting- in this stage basic specs for a project, plant, equipment are drawn up(help of technical consultants)/ Later on bids/tenders are invited and evaluated and legally enforceable duties and responsibilities of different parties and the one incorporate in the contracts are chalked up. Legal assistance may be taken as well. 2. Detailed Project Design and Engineering this covers detailed site investigations and test, design and approval of plant layout, preparation and approval of engineering drawings and blue prints, time schedules, CPM/PERT charts , final selection of technology and equipment and detailed estimating of costs. Processing the project preliminaries so as to enable the commencement of construction stage Involves: o Compiling detailed design and drawings, specs, BOQ so as the complete all the document necessary for contracting works o Planning project execution resources and mobilization plan o Tendering and appointing contracts Project Team (led by project manager and coordinated by project chief planner) includes o Architects and design engineers o Construction engineers from civil, mechanical, electrical and HVAC disciplines o Tendering Stagg, like contract managers and quantity surveyors o Specialist consultants. o Selection manger, supervisor and connected officials
Construction Stage or Execution Stage: Planning and Controlling execution Inducting Resources Construction and Commissioning Final handing over to the client
Mainly two phases: Construction and Erection this phase involves actual construction, erection, installation , interpretation and follow up of the contracts, project management and making of suitable changes in the design and engineering on account of unforeseen factors and changes in the scope Trial runs, commissioning and optimization this phase entails handing over of the project by the contractors to the management/owners
Project execution through contract system Disputes which may arise during course of the project is addressed by the mechanism detailed out in contract Construction at site is supervised and carried out by two teams: o Client team led by project manager o Contractors workforce managed by his construction manager o Diff. between construction manager and project manager Proper record of operating instructions and as-built drawings is maintained The staff and workers necessary for operating and maintaining the facility are trained prior to its taking over The site is cleared of the left out of the construction Client fully safeguards his interest prior to rendering the completion certificate and making final bill payments\ After handing over the site, team prepares a project completion report which includes
o Scope and schedule of work; Important events; contract executed; contact info about suppliers; equipment maintenance manual; asbuilt drawings; cost involved; problems encountered during execution; lesson learned.
Reasons for Project Time overruns across project lifecycle:
Stages Pre planning
External Issues
# Delay in regulatory approvals # Unavailability/delayed availability of funds # Land/site handover
Internal Issues
# Lack of project managers/commercial managers with adequate planning skills # Lack of liasioning officer/planning engineer # Lack of cost managers # Lack of safety officers/environmental practitioners # Lack of planning engineer/commercial managers #Lack of liaison officer #Lack of MEP engineers
Planning and Design
Execution and Monitoring
Closure and Handover
# Lack of strong R&R policies #Ineffective procurement planning # Design/scope change # Delay in regulatory approvals # Delay in decision making # Weak/ineffective procurement planning # Contractual disputes # Unavailability/delayed availability of funds # Lack of strong R&R policies # Delay Land/site handover # Pre-commissioning teething troubles # Contractual disputes
# Lack of project managers/site managers/planning engineers/quantity supervisors # Lack of awareness of modern equipment and technology #Lack of liaison officer and commercial officers # Lack of commissioning, project and site managers, audit and total quality management professionals
Projects are affected by time overruns. These bottleneck below are divided into two phases: 1) Pre execution phase 2) Execution and Closing Phase Reasons for time overruns in the pre execution phase: 1. Delay in land acquisition and site handover is the primary reason for time overruns in the pre execution phases 2. Manifold regulatory approvals from several agencies leading to delay in construction 3. Poor program management resulting in ineffective coordination with other projects and time delay
4. Other reasons include: a. Lack of strong R&R policies b. Delay in decision making c. Ineffective procurement planning Reasons for time overruns in the Execution and Closing Phase: 1. Change in Project scope/design leads to schedule overruns in the execution stage. 2. Insufficient availability of resources a. Project managers, environmental practitioners and safety officers are top three resources the infrastructure industry faces a shortage of and thereby has considerable effect on time overruns. b. Limited availability of skilled labour c. Shortage of good equipment suppliers/contractors 3. Other reasons for time overruns include: a. Contractual disputes b. Industrial relations and law problems c. Geological surprises d. Pre-commissioning teething troubles e. Coordination issues with Project team/vendors f. Geographical challenges and cultural differences g. Delay in regulatory approvals for commissioning h. Ineffective programme managements i. Ineffective project monitoring j. Lack of awareness of modern technology k. Unavailability of funds
Reasons for Cost overruns across the Project Life Cycle Reasons for cost overruns in the pre execution phase: 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. Scope Creep Inadequate DPR, original estimate and budgeting of the project Acquisition of land at Market price High cost of environmental safeguards Poor selection of consultant Lack of strong R&R policies
Reasons for cost overruns in Execution phase: It is to be noted that any delay in project completion makes the initial cost estimates obsolete leading to cost overruns. 1. Material price escalations beyond projections 2. Escalation in labour costs/ineffective utilization of labour 3. Design changes/iterations 4. Incremental financial costs(foreign exchange, borrowing cost etc.) 5. Location and connectivity of project site 6. Inadequate availability of skilled resources 7. Weak contract administration and claim management 8. Weak procurement planning 9. Contractual disputes due to poor framing of contract document 10.Wrong/poor selection of technology/equipment.
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- 1 - MDV3 Project CharterDokument12 Seiten1 - MDV3 Project CharterOmar Siddiqui100% (1)
- Line of BalanceDokument27 SeitenLine of BalanceOmar Siddiqui100% (1)
- RFP, Ifb, RFQ, RFTDokument3 SeitenRFP, Ifb, RFQ, RFTOmar Siddiqui0% (1)
- Tendering BasicsDokument8 SeitenTendering BasicsOmar SiddiquiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Capital Budgeting: Payback PeriodDokument1 SeiteCapital Budgeting: Payback PeriodOmar SiddiquiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Principles of Safety ManagementDokument70 SeitenPrinciples of Safety ManagementOmar Siddiqui0% (1)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceVon EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (895)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeVon EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (5794)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeVon EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (537)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceVon EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (588)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Von EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Bewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (98)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingVon EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (400)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItVon EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (838)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureVon EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (474)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryVon EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (231)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerVon EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (271)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaVon EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (266)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersVon EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (345)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealVon EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (74)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyVon EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (2259)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnVon EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (234)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaVon EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (45)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreVon EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Von EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Bewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (121)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesVon EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (821)
- Checklist For Pile Foundation: Name of The Project: Specification RemarksDokument2 SeitenChecklist For Pile Foundation: Name of The Project: Specification RemarksDilip Kumar MandalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Unit 2Dokument28 SeitenUnit 2Muhammed Mikhdad K G 21177Noch keine Bewertungen
- Solutions To Selected End-Of-Chapter 4 Problem Solving QuestionsDokument10 SeitenSolutions To Selected End-Of-Chapter 4 Problem Solving QuestionsVân Anh Đỗ LêNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fibonacci 2Dokument27 SeitenFibonacci 2shahzainkhan100% (1)
- Crochet Owl Amigurumi Pattern - MR Murasaki - Craft PassionDokument4 SeitenCrochet Owl Amigurumi Pattern - MR Murasaki - Craft PassionVinícius BaraúnaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Qatar - Civil Material RatesDokument20 SeitenQatar - Civil Material Ratespraveenraj murugadass100% (1)
- ﻲﻟﺎﺣﻟا لوﻻا كﻧﺑﻟ بﺗارﻟا بﺎﺳﺣ Existing Alawwal Bank salary account ﮫﯾﻠﻋ ﻲﺑﺗار ﻊﻓدﻟ دﯾدﺟﻟا بﺎﺳ بﺎﺳﺣ New SABB account to pay my salary toDokument2 Seitenﻲﻟﺎﺣﻟا لوﻻا كﻧﺑﻟ بﺗارﻟا بﺎﺳﺣ Existing Alawwal Bank salary account ﮫﯾﻠﻋ ﻲﺑﺗار ﻊﻓدﻟ دﯾدﺟﻟا بﺎﺳ بﺎﺳﺣ New SABB account to pay my salary tovijai_bhNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Basics - 7 Bankroll Management - 1 Poker Bankroll ManagementDokument5 SeitenThe Basics - 7 Bankroll Management - 1 Poker Bankroll ManagementOpawesomeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Module2 - Economic Tools and Economic SystemsDokument7 SeitenModule2 - Economic Tools and Economic SystemsAleejah QuimsonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sure Repair LectureDokument10 SeitenSure Repair LectureKaye Villaflor80% (5)
- Asme B31.3 Process Piping - Asme B31.3 Process Piping - Allowable Design Pressureallowable Design PressureDokument1 SeiteAsme B31.3 Process Piping - Asme B31.3 Process Piping - Allowable Design Pressureallowable Design PressureRicardo LanderNoch keine Bewertungen
- Audit On ReceivablesDokument7 SeitenAudit On ReceivablesVenus Lyka LomocsoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bottle Plant LineDokument8 SeitenBottle Plant Linekalam23Noch keine Bewertungen
- Tugas Bahasa Inggris Kantor Depan: "Percakapan Tamu Check-In"Dokument5 SeitenTugas Bahasa Inggris Kantor Depan: "Percakapan Tamu Check-In"Agus sukadanaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sterlite NewddDokument2 SeitenSterlite NewddAshok SinghNoch keine Bewertungen
- Riester Stethoscope Set Brochure ENDokument8 SeitenRiester Stethoscope Set Brochure ENAudreyNoch keine Bewertungen
- This Is Your Season Pass Voucher. Exchange For Plastic Card. Instructions BelowDokument3 SeitenThis Is Your Season Pass Voucher. Exchange For Plastic Card. Instructions BelowBhanu GudluruNoch keine Bewertungen
- Deepak Kumar - Hotel Management: United Arab Emirate 971547215363Dokument2 SeitenDeepak Kumar - Hotel Management: United Arab Emirate 971547215363Deepak KumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nitin Intraday Nifty Banknifty Trend FinderDokument11 SeitenNitin Intraday Nifty Banknifty Trend Finderbalaji_resourceNoch keine Bewertungen
- Office of Temporalities: Jerome TenebroDokument2 SeitenOffice of Temporalities: Jerome TenebroJerome TenebroNoch keine Bewertungen
- Centuries of Globalization - J.G. WilliamsonDokument52 SeitenCenturies of Globalization - J.G. WilliamsonLudwigNoch keine Bewertungen
- Practice Problems Ch. 5 Externalities and Public GoodsDokument6 SeitenPractice Problems Ch. 5 Externalities and Public GoodsAyanleNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cost of LivingDokument4 SeitenCost of LivingDhruv ThakkarNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Future of Global MarketingDokument9 SeitenThe Future of Global MarketingBharath Suvarna100% (3)
- Index Number (1) B SC III 16-4Dokument44 SeitenIndex Number (1) B SC III 16-4alcinialbob1234Noch keine Bewertungen
- Drawings Phase IIDokument12 SeitenDrawings Phase IIY Go GltdNoch keine Bewertungen
- Shareholders CorrespondenceDokument5 SeitenShareholders CorrespondenceAtul KumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- MARCH 1st TO 20th Datas VijayDokument13 SeitenMARCH 1st TO 20th Datas VijayHussain ShaikhNoch keine Bewertungen
- MODULAR DESIGN. INFINITE POSSIBILITIES. - Modern Furniture (PDFDrive)Dokument68 SeitenMODULAR DESIGN. INFINITE POSSIBILITIES. - Modern Furniture (PDFDrive)Mee MeeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Although The Sale of Rhinoceros Horns Is Illegal WorldwideDokument1 SeiteAlthough The Sale of Rhinoceros Horns Is Illegal Worldwidezulfiqarali nagriNoch keine Bewertungen