Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Paradigms in Research Research: Grounded Theory Phenomenology Ethnography
Hochgeladen von
Yaj Oliveros PanganOriginaltitel
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Paradigms in Research Research: Grounded Theory Phenomenology Ethnography
Hochgeladen von
Yaj Oliveros PanganCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
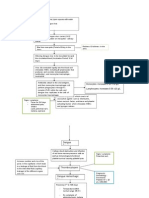
PARADIGMS IN RESEARCH RESEARCH PARADIGM TYPE TRADITION POSITI3IST 6UANTITATI3E NATURA)IST 6UA)ITATI3E
E7PERIMENTA)8 NONE7PERIMENT A)
GROUNDED THEORY PHENOMENO)OGY ETHNOGRAPHY
PURPOSE
IDENTI9ICATION DESCRIPTION E7P)ORATION E7P)ANATION PREDICTION E3A)UATION CONTRO)
IDENTI9ICATION DESCRIPTION E7P)ORATION E7P)ANATION E3A)UATION
QUANTITATIVE RESEARCH RESEARCH: critical investigation of !"ot etical "ro"sitions a#o$t "res$%e& relations of a given " eno%enon' DIMENSIONS OF RESEARCH: (' CONCEPTUA) DIMENSION * +, ! &o ,e &o researc -. / researc is a "rocess t at atte%"ts to see0 sol$tions or ans,ers to "ro#le%s' 1' SU2STANTI3E DIMENSION * +4 at &eter%ines t e contents of researc -. / researc is a "rocess of a""l!ing t e scientific %et o& 5' OPERATIONA) DIMENSION * + Ho, ,e arrive at ans,ers or sol$tions-. / researc is a "rocess of testing #! !"ot esis or verif!ing t eories'
RESEARCH AS A SCIENTIFIC PROCESS: Pro#le% i&entification H!"ot esis for%$lation E:"eri%entation Concl$sion
RESEARCH AS CRITICAL PRAXIS CRITICAL REFLECTION 4HAT;S UP4HAT DO YOU THIN<HO4 SURE ARE YOUSO 4HAT4HAT NO44HAT THENACTION Descri#e t e "ro#le% sit$ation T eori=e #ase& on ass$%"tions 3erif! t eor! Corro#orate fin&ings S!nt esi=e an& generali=e Reco%%en& actions an& interventions OUTPUT 2ac0gro$n& of t e st$&! T eoretical fra%e,or0 Pro#le% > !"ot esis > &esign > anal!sis Revie, of relate& literat$re Concl$sions Reco%%en&ations
PURPOSES OF NURSING RESEARCH 1. Identification: Qualitative research of ten conducts a study to examine phenomena about which little is known. In some cases so little is known that the phenomena has yet to be clearly identified or named or has been inadequately defined or conceptualized. The in depth probing nature or qualitative research is well shifted to the task of answering such questions as what is this phenomena !nd what is its name". In quantitative research by contrast the researcher begins with phenomenon that has been previously studied or defined sometimes in a qualitative study. Thus in quantitative research# identification typically precedes the inquiry. 2. Description: the main ob$ective of many nursing research studies is the description and elucidation of phenomena relating to the nursing profession. The researcher who conducts a description investigation observes# counts# describe and classifies when %henomena that nurse researchers have been interested in describing are varied they include topics such as stress and copping in patients# pain management adaptation processes# health beliefs# rehabilitations success and time patterns of temperature reading. 3. Exploration: &xploratory research begins with some phenomenon of interest' but rather than simply observing and describing the phenomenon# exploratory research is aimed at investigating the full nature of the phenomenon# the manner in which it is manifested and the other factors with which it is related. (or e.g. a descriptive quantities study of patients preoperative stress might seek to document the degree of stress patients experience before surgery and the percentage of patients who actually experience it. !n exploratory study might ask the following. what factors are related to a patients stress level Is a patient)s stress related to behavior of the nursing staff *oes a patients behavior of change in relation to the level of stress experienced. 4. Explanation : The goals of explanatory research are to understand the underpinnings of specific natural phenomena and to explain systematic relationship among phenomena. &xplanatory research is often linked to theories which represent a method of deriving# organizing and integrating ideas about the manner in which phenomena are interrelated where as descriptive research provides new information and exploratory research promising in sign explanatory research attempts to offer understanding of the underlying causes or full nature of a phenomenon. 5. Prediction and Control: +ithout current level of knowledge technology and theoretical progress there are numerous problem that defy absolute
comprehension and explanation yet it is frequently possible to make predications and control phenomena)s based on finding from research user in the observe of complete understanding. Through prediction one can estimate the probability of a specific outcome in a given situation# with predictive knowledge nurses could anticipate the effect that nursing interventions would have a patient and families.
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Understanding Nursing Research Building An Evidence Based Practice 5Th Edition Burns Test Bank Full Chapter PDFDokument34 SeitenUnderstanding Nursing Research Building An Evidence Based Practice 5Th Edition Burns Test Bank Full Chapter PDFMichaelCarrollfdsj100% (9)
- STA630 ResearchMethod Short NotesDokument18 SeitenSTA630 ResearchMethod Short NotesMuhammad Zahid Fareed70% (10)
- 1 Introduction To ResearchDokument31 Seiten1 Introduction To ResearchsoqhNoch keine Bewertungen
- Research Design and Types of ResearchDokument53 SeitenResearch Design and Types of Researchjoshipooja100% (5)
- Ricketts1960 ComunicationDokument28 SeitenRicketts1960 ComunicationKaichou Wa Maid SamaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Study Designs...Dokument16 SeitenStudy Designs...Kizito Lubano100% (1)
- Research Methodology SampleDokument13 SeitenResearch Methodology Samplerewathy100% (2)
- Impaired Physical Mobility Related To Neuromuscular ImpairmentDokument17 SeitenImpaired Physical Mobility Related To Neuromuscular ImpairmentAileen Lopez83% (6)
- Presentation PPT Psychological Research 1543337584 356108Dokument15 SeitenPresentation PPT Psychological Research 1543337584 356108Farooq khanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nursing Research LectureDokument52 SeitenNursing Research LectureKimTot OctavianoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Testing Hypothesis Main PagesDokument32 SeitenTesting Hypothesis Main Pagesneha16septNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hamza-Su-17-01-107-025 - Submitted To DR Rab Nawaz SirDokument9 SeitenHamza-Su-17-01-107-025 - Submitted To DR Rab Nawaz Sirkhan khanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nursing ResearchDokument37 SeitenNursing ResearchGodfrey FrancoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter Review Ch. 1Dokument3 SeitenChapter Review Ch. 1justin5857Noch keine Bewertungen
- Nursing ResearchDokument37 SeitenNursing ResearchIrish Nicole DC100% (8)
- 1-2 Klinik Biyoistatistik 2019 Araştırma Tipleri ENGDokument43 Seiten1-2 Klinik Biyoistatistik 2019 Araştırma Tipleri ENGSalih ÇayırNoch keine Bewertungen
- Frequently Asked Questions F AqsDokument4 SeitenFrequently Asked Questions F AqsMuhammad Zahid FareedNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Research ProcessDokument48 SeitenThe Research ProcessDaniela Marie John RonquilloNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nursing ResearchDokument4 SeitenNursing ResearchJoYCeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hsern Ern's UCS Exam Revision NotesDokument10 SeitenHsern Ern's UCS Exam Revision NotesNanthida AngNoch keine Bewertungen
- Purpose of The Verbal Reasoning SubtestDokument3 SeitenPurpose of The Verbal Reasoning Subtestcoolgeek45Noch keine Bewertungen
- Frameworks For Understanding: Science, Systems, and EthicsDokument9 SeitenFrameworks For Understanding: Science, Systems, and EthicshomamunfatNoch keine Bewertungen
- Researc H Design: Submitted To: Dr. Rajkumar Dean (Imsar, Ihtm, DSW)Dokument22 SeitenResearc H Design: Submitted To: Dr. Rajkumar Dean (Imsar, Ihtm, DSW)Ruchi BansalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Definition and PurposeDokument6 SeitenDefinition and PurposeHerrieGabicaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Timtim Group DiscussionDokument57 SeitenTimtim Group DiscussionMohammed KemalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Several Definitions or Purposes of Descriptive Research Have Been Identified in The LiteratureDokument3 SeitenSeveral Definitions or Purposes of Descriptive Research Have Been Identified in The LiteratureHải myNoch keine Bewertungen
- RM Unit 1Dokument21 SeitenRM Unit 1vivek singhNoch keine Bewertungen
- Clinical Outcome Research ReviewDokument8 SeitenClinical Outcome Research ReviewKu Li ChengNoch keine Bewertungen
- P PP PP P: PP PPPPPPP PPPPPPP P PPPPP P PPPPP PP PP ,"PPPP - PPPP PPPPP P/PPP PPPPP ppp0pp PPP - PPP"P P PPPPPP PPPDokument1 SeiteP PP PP P: PP PPPPPPP PPPPPPP P PPPPP P PPPPP PP PP ,"PPPP - PPPP PPPPP P/PPP PPPPP ppp0pp PPP - PPP"P P PPPPPP PPPGemma Daguioan MendozaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Park 2019Dokument20 SeitenPark 2019Kevin ChowNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Relationship of Theory and ResearchDokument4 SeitenThe Relationship of Theory and ResearchCher TantiadoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Basics in Experimental Research: Editorial-Consultant - Biometrics, Indian Journal, of Urology (IJU)Dokument2 SeitenBasics in Experimental Research: Editorial-Consultant - Biometrics, Indian Journal, of Urology (IJU)Ashok KumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Editorial Preface: The Case For Case-Based ResearchDokument6 SeitenEditorial Preface: The Case For Case-Based Researchammoj850Noch keine Bewertungen
- Vriables OnwardsDokument141 SeitenVriables OnwardsTurko ReparejoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Descriptive Research, Is Used To Describe Characteristics of ADokument2 SeitenDescriptive Research, Is Used To Describe Characteristics of Avijisanji5Noch keine Bewertungen
- RM2Dokument3 SeitenRM2Avinash YadavNoch keine Bewertungen
- Characteristics of ResearchDokument4 SeitenCharacteristics of ResearchAlthea Mae Cardenas PaatNoch keine Bewertungen
- CHAPTER 3: Research MethodologyDokument10 SeitenCHAPTER 3: Research Methodologysaksham sharmaNoch keine Bewertungen
- ShortNotes Research Meth 603Dokument11 SeitenShortNotes Research Meth 603zaiba kiranNoch keine Bewertungen
- M1 LessonDokument8 SeitenM1 LessonBebe LumabaoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Research 8 2019 2022Dokument35 SeitenResearch 8 2019 2022yuhNoch keine Bewertungen
- Identifying The Nature of Inquiry and Research: Prepared By: Mr. Benedict B. DiazDokument57 SeitenIdentifying The Nature of Inquiry and Research: Prepared By: Mr. Benedict B. DiazBenNoch keine Bewertungen
- Beyond Description: An Integrative Model of Content AnalysisDokument15 SeitenBeyond Description: An Integrative Model of Content AnalysistayronagattaNoch keine Bewertungen
- EpidemiologyDokument32 SeitenEpidemiologylanie_jecielNoch keine Bewertungen
- Critique Paper - Level of Satisfaction On The Maternal Health Care Services On Well Family Clinic in Davao CityDokument5 SeitenCritique Paper - Level of Satisfaction On The Maternal Health Care Services On Well Family Clinic in Davao CityAnthony WallNoch keine Bewertungen
- Qualitative and QuantitativeDokument3 SeitenQualitative and QuantitativeAbrar AhmadNoch keine Bewertungen
- Practical Research 2 HANDOUTDokument42 SeitenPractical Research 2 HANDOUTkznethtomale216Noch keine Bewertungen
- Key TermsDokument8 SeitenKey TermsMissMumtazNoch keine Bewertungen
- First Quarter LessonsDokument6 SeitenFirst Quarter LessonsshinnnnkagenouNoch keine Bewertungen
- Master of Business Administration - MBA Semester 3 Mb0050 - 4 Credit Assignment Set - 1Dokument19 SeitenMaster of Business Administration - MBA Semester 3 Mb0050 - 4 Credit Assignment Set - 1pranabk_lenka9589Noch keine Bewertungen
- Final Examination Guide in Experimental Psychology (Research Example)Dokument23 SeitenFinal Examination Guide in Experimental Psychology (Research Example)Ria Joy SorianoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Genes Determine IntelligenceDokument2 SeitenGenes Determine IntelligenceDenizNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lesson 1 Quantitative Research DesignDokument6 SeitenLesson 1 Quantitative Research DesignArt GerNoch keine Bewertungen
- Discussion Guide No. 1Dokument5 SeitenDiscussion Guide No. 1Zara RejusoNoch keine Bewertungen
- What Is Quantitative Research?Dokument7 SeitenWhat Is Quantitative Research?Willyn Grace AgapinNoch keine Bewertungen
- RM NotesDokument4 SeitenRM NotesSahitya RamineniNoch keine Bewertungen
- Definition of Hypothesis in Research StudyDokument6 SeitenDefinition of Hypothesis in Research Studyspqeyiikd100% (2)
- Methods of Research - L1 - The Way of KnowingDokument36 SeitenMethods of Research - L1 - The Way of KnowingRacidon BernarteNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lesson 1Dokument7 SeitenLesson 1Christian David Comilang CarpioNoch keine Bewertungen
- Methods and Biostatistics in Oncology: Understanding Clinical Research as an Applied ToolVon EverandMethods and Biostatistics in Oncology: Understanding Clinical Research as an Applied ToolRaphael. L.C AraújoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Human Atheroma: With Particular Reference to Endocrine Aspects of ÆtiologyVon EverandHuman Atheroma: With Particular Reference to Endocrine Aspects of ÆtiologyNoch keine Bewertungen
- College of Nursing: Family Nursing Care PlanDokument7 SeitenCollege of Nursing: Family Nursing Care PlanYaj Oliveros PanganNoch keine Bewertungen
- Vi. Pathophysiology: Monocytes: Increases 0.10 X 10 G/L Lymphocytes: Increases 0.56 x10 G/LDokument2 SeitenVi. Pathophysiology: Monocytes: Increases 0.10 X 10 G/L Lymphocytes: Increases 0.56 x10 G/LYaj Oliveros PanganNoch keine Bewertungen
- NCP and Drug Study FinalDokument2 SeitenNCP and Drug Study FinalYaj Oliveros PanganNoch keine Bewertungen
- NCP and Drug StudyDokument5 SeitenNCP and Drug StudyYaj Oliveros PanganNoch keine Bewertungen
- NCP and Drug Study FormatDokument3 SeitenNCP and Drug Study FormatYaj Oliveros PanganNoch keine Bewertungen