Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Titration Curves
Hochgeladen von
Ghadeer M HassanOriginalbeschreibung:
Originaltitel
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Titration Curves
Hochgeladen von
Ghadeer M HassanCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
How to Interpret Titration Curves
find the equivalence point
it is the steepest part of the curve where the pH rises the fastest the equivalence point can be used to determine the equivalent weight (molar mass) of the acid
find the mid point
located in the center of the buffer region geometrically halfway between the equivalence point and the beginning of the titration sometimes it is a little more complicated than this - see the example the midpoint determines the pKa of the acid
How to Interpret Titration Curves
things to do first
graph your data as seen in the next slide make sure you turn on the major and minor tick marks on both axes
double click on the axis and click on the patterns tab)
there is enough precision in the tick marks
you should have at least 1 mL or smaller for the minor tick mark on the x-axis you should have at least 0.2 pH units or smaller for the minor tick mark on the y-axis
Two Different Methods
there are two methods of analysis that will be shown
geometric method
requires a ruler, a pencil, and the titration graph
1st derivative method
requires a spreadsheet and some formula entries gives you cool graphs with the 1st derivative pointing to the equivalence and mid points scores you brownie points with the instructors
pick your method (either will work)
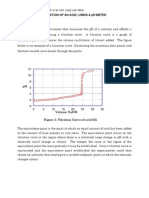
A Typical Titration Curve
Weak Acid Titration Curve
12 10
mid point
pH
8 6 4 2 0 10 20 30
equivalence point
40
50
Buret Volume (mL)
Find the Equivalence Point (Geometric method)
1) using a ruler, draw lines that 12 the flat, follow more horizontal 10 part of the curve
pH
8 6 4 2 0 10 20 30 Buret Volume (mL)
Weak Acid Titration Curve
equivalence point 2) draw a line that follows the flat, more vertical part of the curve
40 50
Find the Equivalence Point (Geometric method)
3) using a ruler, Weak Acid Titration Curve measure the distance 12 the top between intersection and the 10 bottom intersection
pH
8 6 4 2 0 10 20 30 Buret Volume (mL)
equivalence point
4) the geometric center of this line segment is the equivalence point
40 50
Find the Equivalence Point (Geometric method)
Weak Acid Titration Curve
5) draw a vertical line from the 10 equivalence point to the x-axis
12
pH
8 6 4 2 0 10 20 30 Buret Volume (mL)
equivalence point 6) where the line crosses the x-axis is the volume at the equivalence point (28.7 mL in this case)
40 50
Find the Mid Point (Geometric method)
Weak Acid Curve 1) if there is a steep rise in the Titration pH at the beginning of the graph, 12 draw a line that follows the steep part 10 of the curve
pH
8 6 4 2 0 10 20 30 40 50 Buret Volume (mL)
mid point
Find the Mid Point (Geometric method)
Weak Acid 2) using a ruler, measure the Titration Curve distance between the far left and 12 right intersections
10
pH
8 6 4 2 0 10 20 30
equivalence point 3) the geometric center between these points is the mid point
mid point
40
50
Buret Volume (mL)
Find the Mid Point (Geometric method)
Weak Titration Curve 4) draw a horizontal line Acid from the mid point to the y-axis
12 10
pH
8 6 4 2 0 10 20
equivalence point 5) where the line crosses the x-axis is the volume at the equivalence point (pH = 7.2 in this case)
30 40 50
mid point
Buret Volume (mL)
How to Interpret Titration Curves
find the equivalence point
make sure you subtract the initial buret volume! in this case, the initial buret volume was 1.07 mL true equiv. pt. = 28.7 mL - 1.07 mL = 27.63 mL the 3 is the indicate the limit of the significant figures
calculate the equivalent weight (molar mass)
equiv. wt. = (acid mass)/[(NaOH conc)(equiv. pt.)] equiv. wt. = (430.2 mg)/[(0.1139 M)(27.63mL)] equiv. wt. = 136.699 = 137 g/mol
How to Interpret Titration Curves
find the mid point
mid pt = 7.2 = pKa of the acid
For you Excel Aficionados
equivalence point
use the first derivative d pH / d Vol the spike in the graph points to the equiv. pt.
mid point
reverse the axes for the pH curve
x axis = pH values; y-axis = Vol values
use the first derivative d Vol / d pH the spike in the graph points to the mid point
use extra columns in the spreadsheet to make these calcs
1st deriv. (d pH / d Vol) = (pH2 - pH1)/(Vol2 - Vol1) 1st deriv. (d Vol / d pH) = (Vol2 - Vol1)/ (pH2 - pH1)
or just (the first 1st deriv)-1
Find the Equivalence Point (derivative method)
Weak Acid Titration Curve
7
1)1) identify identify volume volume 10 value value atat the the peak peak
pH
pH 1st deriv.
5 4 3 2 1 0
(28.5 mL in this case) 8
6 4 2 0 10 20 30 40 50 Buret Volume (mL)
1st Derivative (mL - 1)
12
Find the Mid Point (derivative method)
Weak Acid Titration Curve
50 identify pH value at the peak 1) 45 (pH 40 = 35 30 25 20 15 10 5 0 2 40 30 25 20 15 10 5 0 4 6 pH 8 10 12 mL 1st deriv. 35
Buret Volume (mL)
1st Derivative (mL)
7.3 in this case)
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- ESPRIT Get StartedDokument182 SeitenESPRIT Get StartedArtur Pereira Leite75% (4)
- Acid-Base Titrations Curve Formal LabDokument9 SeitenAcid-Base Titrations Curve Formal LabAshley StraubNoch keine Bewertungen
- Determination of Ka of Unknown AcidDokument23 SeitenDetermination of Ka of Unknown AcidShasha0% (1)
- Transformation Geometric Cheat SheetDokument1 SeiteTransformation Geometric Cheat Sheetapi-292786124100% (1)
- FprEN 13848-1Dokument48 SeitenFprEN 13848-1Dragana Tranavac100% (1)
- Practical 04 - Estimation of PKa by Half Neutralization MethodDokument10 SeitenPractical 04 - Estimation of PKa by Half Neutralization Methodsandi fernandoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Operacion CNC MAZAKDokument402 SeitenOperacion CNC MAZAKjuventinoNoch keine Bewertungen
- GenMath - q1 - Module3 - For Upload PDFDokument20 SeitenGenMath - q1 - Module3 - For Upload PDFStephanie MinorNoch keine Bewertungen
- CSEC Add Maths Study GuideDokument4 SeitenCSEC Add Maths Study Guider6hNoch keine Bewertungen
- (Nagle, Saff, Snyder) Fundamentals of Differential PDFDokument121 Seiten(Nagle, Saff, Snyder) Fundamentals of Differential PDFFelipe Correa100% (1)
- TitrationCurves 6Dokument3 SeitenTitrationCurves 6JOse ArmentaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Acetic Acid Dissociation Constant S11Dokument7 SeitenAcetic Acid Dissociation Constant S11Ayesha ShahidNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mixture of Carbonate BicarbonateDokument9 SeitenMixture of Carbonate BicarbonateIan Justine SanchezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Weak Acid, Strong Base Titration Lab Chemistry 20 TEACHER NotesDokument3 SeitenWeak Acid, Strong Base Titration Lab Chemistry 20 TEACHER NotesArash JoonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Experiment 6 Titration II - Acid Dissociation ConstantDokument8 SeitenExperiment 6 Titration II - Acid Dissociation ConstantPanneer SelvamNoch keine Bewertungen
- Potentiometric Titration Ex17Dokument10 SeitenPotentiometric Titration Ex17Tien HaminhNoch keine Bewertungen
- 62 Experiment #5. Titration of An Acid Using A PH MeterDokument7 Seiten62 Experiment #5. Titration of An Acid Using A PH MeteryumnatehreemNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lab Report Acid BaseDokument4 SeitenLab Report Acid Basexuni34Noch keine Bewertungen
- Lab Format:: Lab 2: Determination of Carbonate/BicarbonateDokument5 SeitenLab Format:: Lab 2: Determination of Carbonate/BicarbonateAnaya FatimaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chem 112 - Experiment 5 - Simulation - PH Indicators BackgroundDokument5 SeitenChem 112 - Experiment 5 - Simulation - PH Indicators BackgroundnepnepNoch keine Bewertungen
- Titration Strong Weak Acids BasesDokument6 SeitenTitration Strong Weak Acids Basesapi-309713761Noch keine Bewertungen
- Word Version STUDENT NOTES PH (Titration) Curves and IndicatorsDokument12 SeitenWord Version STUDENT NOTES PH (Titration) Curves and IndicatorsQuan nguyen minhNoch keine Bewertungen
- Acids & Bases, Titrations & BuffersDokument6 SeitenAcids & Bases, Titrations & BuffersAhmed KurdishNoch keine Bewertungen
- Acid-Base TitrationDokument19 SeitenAcid-Base TitrationNitin RanaNoch keine Bewertungen
- AP Chemistry - Titration Curves of Strong and Weak Acids and BasesDokument5 SeitenAP Chemistry - Titration Curves of Strong and Weak Acids and BasesJonathan Chen100% (2)
- Lab 10.pdf - 316831Dokument2 SeitenLab 10.pdf - 316831ayaessam392002Noch keine Bewertungen
- Titration Curves of Strong and Weak Acids and BasesDokument3 SeitenTitration Curves of Strong and Weak Acids and BasesMatthew Runyon50% (2)
- ABcurves SP 19Dokument8 SeitenABcurves SP 19Sakshi BangarwaNoch keine Bewertungen
- C2 Lab Manual FinalDokument6 SeitenC2 Lab Manual FinalRafiah JobNoch keine Bewertungen
- KaDokument5 SeitenKaSonu DubeyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lab 3: Introduction To Acids Base Chemistry Part A Experimental Determination of Acid Dissociation Constant, KaDokument10 SeitenLab 3: Introduction To Acids Base Chemistry Part A Experimental Determination of Acid Dissociation Constant, Kaenock yegonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lab 6 Determination of KaDokument11 SeitenLab 6 Determination of KaaddislibroNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lab Experiment 3 - PH TitrationDokument1 SeiteLab Experiment 3 - PH Titrationfive shadowsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Titration NotesDokument3 SeitenTitration Notesshaheer ahmedNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lab 2 Titration sbl1023Dokument10 SeitenLab 2 Titration sbl1023api-385038701Noch keine Bewertungen
- 24 Acid-Base TitrationDokument5 Seiten24 Acid-Base Titrationgardarr11Noch keine Bewertungen
- Liquid-Liquid Extraction (LLE)Dokument28 SeitenLiquid-Liquid Extraction (LLE)IrMuhammadFaizNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lab Techniques: Lab 4 Joint Report PH Measurement and TitrationDokument12 SeitenLab Techniques: Lab 4 Joint Report PH Measurement and TitrationmonarchNoch keine Bewertungen
- Exp 6 - Acid Base Titration-2Dokument9 SeitenExp 6 - Acid Base Titration-2liquidsnake007Noch keine Bewertungen
- WINSEM2022-23 BBIT206P LO VL2022230503900 Reference Material I 23-12-2022 Experiment 2 Acid-Base Titration PH Meter FADokument4 SeitenWINSEM2022-23 BBIT206P LO VL2022230503900 Reference Material I 23-12-2022 Experiment 2 Acid-Base Titration PH Meter FAGravity JaiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Titration Lab ReportDokument5 SeitenTitration Lab ReportvaiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lab 11 Acids, Bases, PH, Hydrolysis, and BuffersDokument10 SeitenLab 11 Acids, Bases, PH, Hydrolysis, and BuffersChing Wai Yong67% (3)
- 7 Titration CurvesDokument10 Seiten7 Titration Curvesryan1230987Noch keine Bewertungen
- TitrationDokument16 SeitenTitrationDeepa DevanathanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chemistry Lab Session N°7: Titration of Vinegar: PurposesDokument12 SeitenChemistry Lab Session N°7: Titration of Vinegar: Purposesjulius_caesar2013Noch keine Bewertungen
- Potentiometric Titration of A Weak Acid: Chemistry 135 Clark CollegeDokument14 SeitenPotentiometric Titration of A Weak Acid: Chemistry 135 Clark CollegeMay LeeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Atq #10Dokument2 SeitenAtq #10JoNoch keine Bewertungen
- BT Tech 28.5Dokument6 SeitenBT Tech 28.5chính NguyễnNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sulfamic Acid Titration C12!5!10Dokument5 SeitenSulfamic Acid Titration C12!5!10Anonymous 1gXoNDYcNoch keine Bewertungen
- 0-Titration Citric Acid.21214247Dokument5 Seiten0-Titration Citric Acid.21214247Bhupendra TiwariNoch keine Bewertungen
- Experiment 1&2Dokument8 SeitenExperiment 1&2Fatima AhmedNoch keine Bewertungen
- Manual - Specific Rotation of Sugar Using L - PolarimeterDokument7 SeitenManual - Specific Rotation of Sugar Using L - PolarimeterMonster DarkNoch keine Bewertungen
- CHEM A 24 COMP Half TitrationDokument4 SeitenCHEM A 24 COMP Half TitrationSung Hoon ParkNoch keine Bewertungen
- Acid Base Titration Experiment 4Dokument10 SeitenAcid Base Titration Experiment 4pokesurfer100% (3)
- Distillation Column DesignDokument17 SeitenDistillation Column Design259Katkar PrathmeshNoch keine Bewertungen
- 3 Lec Volumetric Analysis اولDokument53 Seiten3 Lec Volumetric Analysis اولzaman abadiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lab Report Experiment 2 Determination of Ka Value of A Weak AcidDokument17 SeitenLab Report Experiment 2 Determination of Ka Value of A Weak AcidarisyahariffNoch keine Bewertungen
- Kinetics of Crystal Violet FadingDokument6 SeitenKinetics of Crystal Violet Fadingw_kang50% (2)
- Practical 4Dokument2 SeitenPractical 4vimukthi gunasinghaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Exercise 0 TitrationDokument6 SeitenExercise 0 TitrationMINVILU JUNEN BUSAINGNoch keine Bewertungen
- Biochemistry 2017 2 U1 PHDokument7 SeitenBiochemistry 2017 2 U1 PHOscar DominguezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Experimennt 5 - Examination of BuffersDokument7 SeitenExperimennt 5 - Examination of BuffersMuhammad Riv'at NalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Potentiometric Titration of Strong Acid With Strong Base: ExperimentDokument4 SeitenPotentiometric Titration of Strong Acid With Strong Base: ExperimentBasheer AhammadNoch keine Bewertungen
- Written Report Expt.8Dokument5 SeitenWritten Report Expt.8Nicole NatanauanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Titration Lab ReportDokument13 SeitenTitration Lab Reportapi-341133750Noch keine Bewertungen
- Working Guide to Vapor-Liquid Phase Equilibria CalculationsVon EverandWorking Guide to Vapor-Liquid Phase Equilibria CalculationsBewertung: 5 von 5 Sternen5/5 (1)
- Adrenocorticoids2- ادوية نظري - د.احسانDokument4 SeitenAdrenocorticoids2- ادوية نظري - د.احسانGhadeer M HassanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Quinoline SynthesisDokument6 SeitenQuinoline SynthesisFrancesco TutinoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Acs سريرية نظري- د.حيدرDokument56 SeitenAcs سريرية نظري- د.حيدرGhadeer M HassanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Compartment ModelsDokument67 SeitenCompartment ModelsGhadeer M HassanNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2004 OrgSeminarTestAnswerDokument2 Seiten2004 OrgSeminarTestAnswerGhadeer M HassanNoch keine Bewertungen
- ThiopheneDokument398 SeitenThiopheneAshwin MandaleNoch keine Bewertungen
- Year 2 Seminars, 06524, Semester 2, 2007 Bifunctional and Heterocyclic Chemistry TestDokument5 SeitenYear 2 Seminars, 06524, Semester 2, 2007 Bifunctional and Heterocyclic Chemistry TestGhadeer M HassanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Write Your Answers On This Sheet: N O O O O O PHDokument2 SeitenWrite Your Answers On This Sheet: N O O O O O PHGhadeer M HassanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cyclisations Problems 2013Dokument6 SeitenCyclisations Problems 2013Ghadeer M Hassan100% (1)
- Chapter 2Dokument39 SeitenChapter 2Ghadeer M HassanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 12 - Heterocyclic CompoundsDokument15 SeitenChapter 12 - Heterocyclic CompoundsGhadeer M HassanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Indole and Benzimidiazole NucleusDokument32 SeitenIndole and Benzimidiazole NucleusSrikanth MalipatelNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cycloadditions Problems 2013Dokument8 SeitenCycloadditions Problems 2013Ghadeer M HassanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cyclisations Solutions 2013Dokument7 SeitenCyclisations Solutions 2013Ghadeer M HassanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Heterocycles - PART 3 - PyridazinesDokument3 SeitenHeterocycles - PART 3 - PyridazinesGhadeer M HassanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Heterocycles - PART 3 - PyridazinesDokument3 SeitenHeterocycles - PART 3 - PyridazinesGhadeer M HassanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Heterocyclic Chemistry: There Are 9 Parts To These "Animated" Notes: 2. There Are Guidance Notes and ProblemsDokument4 SeitenHeterocyclic Chemistry: There Are 9 Parts To These "Animated" Notes: 2. There Are Guidance Notes and ProblemsGhadeer M HassanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cycloadditions Solutions 2013 2Dokument9 SeitenCycloadditions Solutions 2013 2Ghadeer M HassanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Reactivity QuinolineDokument107 SeitenReactivity QuinolineIan Otto100% (1)
- Heterocycles - PART 2 - Pall Knorr PyrroleDokument4 SeitenHeterocycles - PART 2 - Pall Knorr PyrroleGhadeer M HassanNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2012 Hetero Model AnswerDokument3 Seiten2012 Hetero Model AnswerGhadeer M HassanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Heterocycles - PART 5 - Isoxazoles and PyrazolesDokument4 SeitenHeterocycles - PART 5 - Isoxazoles and PyrazolesGhadeer M HassanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Heterocycles - PART 5 - Isoxazoles and PyrazolesDokument4 SeitenHeterocycles - PART 5 - Isoxazoles and PyrazolesGhadeer M HassanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Heterocycles - PART 6 - PyrimidinesDokument3 SeitenHeterocycles - PART 6 - PyrimidinesGhadeer M HassanNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2013 Hetero Model AnswerDokument2 Seiten2013 Hetero Model AnswerGhadeer M HassanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Heterocycles - PART 3 - PyridazinesDokument3 SeitenHeterocycles - PART 3 - PyridazinesGhadeer M HassanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Heterocycles - PART 6 - PyrimidinesDokument3 SeitenHeterocycles - PART 6 - PyrimidinesGhadeer M HassanNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2012 Hetero Model AnswerDokument3 Seiten2012 Hetero Model AnswerGhadeer M HassanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Year 2 Seminars, 06524, Semester 2, 2009 Heterocyclic Chemistry TestDokument4 SeitenYear 2 Seminars, 06524, Semester 2, 2009 Heterocyclic Chemistry TestGhadeer M HassanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bresenham N Circle AlgorithmDokument21 SeitenBresenham N Circle AlgorithmSOWMYANoch keine Bewertungen
- Lesson 2 The Cartesian PlaneDokument2 SeitenLesson 2 The Cartesian Planeapi-491086227Noch keine Bewertungen
- DrufelCNC STB5100 ManualDokument59 SeitenDrufelCNC STB5100 ManualvalentinNoch keine Bewertungen
- Micro 01 EconomicThinking-3Dokument33 SeitenMicro 01 EconomicThinking-3SamNoch keine Bewertungen
- V Unit Intersections of SolidsDokument13 SeitenV Unit Intersections of SolidsJohn K Kikwai100% (1)
- 2.0 Graphs of Functions 2Dokument123 Seiten2.0 Graphs of Functions 2juriah binti ibrahimNoch keine Bewertungen
- Space MatrixDokument3 SeitenSpace MatrixChris0% (1)
- Umang - CBSE 9 - 2020 - Co-Ordinate Geometry - 2 - Doubt MentiDokument30 SeitenUmang - CBSE 9 - 2020 - Co-Ordinate Geometry - 2 - Doubt MentiMariyam AfreenNoch keine Bewertungen
- CJC H2 MATH P1 Question PDFDokument5 SeitenCJC H2 MATH P1 Question PDFLeonard TngNoch keine Bewertungen
- Computer Graphics Lab Manual For IV CSEDokument67 SeitenComputer Graphics Lab Manual For IV CSEGopal RamNoch keine Bewertungen
- Math 8 Midetrm Exam First QuarterDokument10 SeitenMath 8 Midetrm Exam First QuarterJOHN MARK ORQUITANoch keine Bewertungen
- 12th ApplicationsDokument2 Seiten12th ApplicationsSenthil Kumar GanesanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Year 6 Mathematics Judging Standards Assessment-PointersDokument5 SeitenYear 6 Mathematics Judging Standards Assessment-Pointersapi-658503315Noch keine Bewertungen
- Mold Wizard, UnigraphicsDokument55 SeitenMold Wizard, Unigraphicsrankx00175% (4)
- Mortenson, Michael E. - Mathematics For Computer Graphics Applications PDFDokument368 SeitenMortenson, Michael E. - Mathematics For Computer Graphics Applications PDFAftab Alam100% (1)
- CS1407003E-008 YSM20 2beam Inst 20180314 Tablet PDFDokument8 SeitenCS1407003E-008 YSM20 2beam Inst 20180314 Tablet PDFGanapathy SakthiNoch keine Bewertungen
- External BallisticsDokument59 SeitenExternal Ballisticsblowmeasshole1911Noch keine Bewertungen
- Engineering Mechanics: Statics: ForceDokument16 SeitenEngineering Mechanics: Statics: ForceChristogratia Immanuel SimbolonNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2nd PUC Mathematics Jan 2016 PDFDokument2 Seiten2nd PUC Mathematics Jan 2016 PDFPrasad C M100% (3)
- Vehicle Dynamics NotesDokument116 SeitenVehicle Dynamics NotesJagadesh AbbuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Parametros Fanuc OmDokument19 SeitenParametros Fanuc OmJuan Fernando Salazar100% (2)
- CAM - Programming Guide - 840D - PGDokument504 SeitenCAM - Programming Guide - 840D - PGOleksQNoch keine Bewertungen