Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Cardiovascular Disease
Hochgeladen von
Dominique Excelsis J. DegamoCopyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Cardiovascular Disease
Hochgeladen von
Dominique Excelsis J. DegamoCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
TYPES
ASSESSMENT S/Sx
Subj: -Chest Pain -SOB -Dyspnea Obj: -Increased RR -Tachycardia -Palpitations -Diaphoresis
CARDIOVASCULAR DISEASE HEALTH HISTORY RISK FACTOR CONTRIBUTORY ASSOCIATED MODIF NON MODIF
-Smoking -Hypertension -DM -Obesity -Lack of exercise -Stress -High fat diet -Elevated serum cholesterol level -Alcohol consumption Age Sex (Male) Race (Black) Family history -MI -Atherosclerosis -Angina
PRESENTING PROBLEM SPECIFIC NON SPECIFIC -Hypercholesterolemia
(specifically,serum LDL concentrations) -Smoking -Hypertension (high systolic pressure seems to be most significant in this regard) -Hyperglycemia (due to DM) -Type A Behavioral Patterns, twice as likely to exhibit CAD as any other personality type. -Hemostatic factors: High levels of fibrinogen and coagulation factor VII are associated with an increased risk of CAD. Factor VII levels are higher in individuals with a high intake of dietary fat. Decreased fibrinolytic activity has been reported in patients with coronary atherosclerosis. -Genetics -High levels of Lipoprotein a compound formed when LDL cholesterol combines with a substance known as Apoliprotein -Lack of exercise -Alcohol -Stress -Diet low in -Antioxidants -Obesity -Men over 60 -Women over 65 -Low Hemoglobin
NURSING DX.
Coronary Artery Disease (aka Coronary heart disease, Ischemic heart disease, Atherosclerotic heart disease)
- Pain -Activity Intolerance -Anxiety -Risk for Dec. Card. Output -Ineffective Tissue Perfusion -Risk for Excess Fluid Volume -Knowledge Deficit
Cardiomyopathy
Subj: -Fatigue -Weakness -Dyspnea -Orthopnea Obj: -Jugular Vein Distention -Edema -Rales -Hepatomegaly
-Lifestyle
-Age -Gender -Race/ Culture -Family Hx
-CHF -Arrhythmias
-Decreased cardiac output -Activity intolerance -Ineffective role performance -Pain
Hypertensive Heart Disease
Subj: Fatigue Nausea Shortness of breath Difficulty sleeping flat in bed (orthopnea) Bloating and abdominal pain Obj: Irregular pulse or palpitations Swelling of feet and ankles Weight gain Greater need to urinate at night Altered mentation (in severe cases) An enlarged heart (cardiomegaly)
-Lifestyle (Alcohol, Smoking, Obesity) -Stress -Socio Economic Status
-Age -Gender -Race/ Culture -Family Hx
-Hormonal Changes
-Contraceptive -Menopause
-Acute Pain, headache -Risk for Dec. Card. Output -Activity Intolerance -Nutrition More than Body Req., Imbalanced -Ineffective Coping -Knowledge Deficit
Heart Failure
Easy fatigability, weakness, restlessness (earliest sign of tissue hypoxia), mental confusion, renal retention of Na and H20. Left Sided: -Pulmonary Congestion Dyspnea (exertional, orthopnea, paroxysmal nocturnal dyspnea) -Cardiac murmurs, -Cough -Pulmonary crackles. Right Sided: -Edema (peripheral dependent) -Jugular vein distension -Ascites -Hepatomegaly -Weight gain -Increase CVP -Jaundice Biventricular: -Pleura
-Smoking -Hypertension -DM -Obesity -Lack of exercise -Stress -High fat diet -Alcohol consumption
Age Sex Race Family history
-Decreased cardiac output -Excess fluid volume -Impaired gas exchange -Activity intolerance -Risk for impaired skin integrity -Deficient knowledge
Cor pulmonale
Subj: -Shortness of breath which occurs on exertion but when severe can occur at rest. Obj: -Wheezing -Chronic wet cough -Swelling of the abdomen
-Lifestyle -Diet
-Age -Sex(Male) -Heredity
with fluid (ascites) -Swelling of the ankles and feet (pedal edema) -Enlargement or prominent neck and facial veins -Raised Jugular Venous Pressure (JVP) -Enlargement of the liver -Bluish discoloration of the skin (cyanosis) -Presence of abnormal heart sounds possible bi-phasic atrial response shown on an EKG due to hypertrophy Cardiac Dysrhythmias Subj: - Anxiety - Weakness, dizziness, and light-headedness - Shortness of breath -Chest pain Obj: -Palpitations -Irregular heartbeat -Feeling pauses between heartbeats -Fainting or nearly fainting -Sweating Inflammatory Heart Disease -Endocarditis - CAD, other heart problems & previous heart surgery - High blood pressure. - Congenital heart disease. - Thyroid problems. - Drugs and supplements. - Diabetes. - Electrolyte imb. -Alcohol -Caffeine -Age -Gender -Heredity -Race -HPN -Atherosclerosis -MI -Sinus Node Dysrhythmias -Atrial Dysrhythmias -Junctional Dysrhythmias -Ventricular Dysrhythmias -AV Blocks -Risk for decreased cardiac output -Deficient knowledge -Risk for poisoning(digitalis toxicity)
-Flu-like symptoms, such as fever, chills, fatigue -aching muscles and joints, night sweats, and headaches. -Shortness of breath or a cough -Heart murmur. -Overall paleness. -Small, painful, red or purplish bumps under the skin on the fingers or toes. -Small, dark, painless flat spots on the palms of the hands or the soles of the feet. -Tiny spots under the fingernails, on the whites of the eyes, on the roof of the mouth and inside of the cheeks, or on the chest. These spots are from broken blood vessels. -Nausea (feeling sick to your stomach), vomiting
-Infection
-Age -Gender -Heredity -Race
-Viral Infection -Bacterial Infection
-Risk for decreased cardiac output -Anxiety -Acute pain -Activity intolerance -Ineffective tissue perfusion
-Blood in the urine. -Swelling in the feet, legs, or abdomen. -Myocarditis -Shortness of breath at night while lying down -Light-headedness -Chest pain or pressure, which may spread to neck and shoulders -Fatigue -Fever, muscle aches, sore throat, headache, or diarrhea -Painful joints, Swollen joints, legs, or neck veins -Small amounts of urine Palpitations SOB Chest Pain -Infection -Age -Gender -Heredity -Race -Viral Infection -Bacterial Infection -Activity intolerance -Decreased cardiac output -Deficient knowledge
-Cardiomegaly
-Lifestyle
-Age -Gender -Heredity -Race
-Diseases of the heart muscle or heart valves -High blood pressure -Arrhythmias -Pulmonary hpn -Rheumatic fever -HF -Aortic-Mitral Valve disorders -Pulmonary & tricuspid valve disorders -Tetralogy of Fallot
Valvular Heart Disease
Subj: -Fatigue -SOB -Chest Pain Obj: -Heart Murmur -Swelling of ankles, feet legs, abdomen, & veins of the neck. Subj: -Headache -Dizziness -Tinnitus -Visual and speech disturbances -Paresis to plegia -anorexia -N/V -dysphagia Obj: -increased ICP -cheyne-stokes resp. -neurological deficits -+kernigs & brudzinki
-Lifestyle -Infections and untreated strep throat, which can lead to rheumatic fever.
-Age -Gender -Heredity -Race
Cerebrovascular Disease (Stroke)
-HPN -DM -Atherosclerosis -Valvular heart disease -Lifestyle( Type A personality, smoking, hyperlipidemia, oral contraceptives)
-Age -Gender -Heredity -Race
-Transient ischemic attack -Stroke evolution -Complete stroke
Peripheral Arterial Disease
Subj: -Intermittent claudication-leg pain upon walking.
-Lifestyle
-Male -Age (30) -Female -Age (40)
-Atherosclerosis
-Thromboangitis obliterans -Raynauds disease -TIA
-Ineffective cerebral tissue perfusion -Impaired physical mobility -Impaired verbal and or written communication -Self-care deficit -Impaired swallowing -Risk for unilateral neglect -Impaired home maintenance -Complicated grieving -Situational lowesteem/ disturbed body image/ ineffective role performance -Ineffective tissue perfusion -Impaired walking or activity intolerance
Obj: -Cold sensitivity and skin color changes (pallor, bluish cyanosis) -Decrease peripheral pulse -Ulceration -Gangrene formation Congenital Heart Disease Subj: -High pitch voice Obj: -SOB -Cyanosis -Syncope -Heart Murmur -Under-developed limbs and muscles -Poor feeding & Growth -Resp. Infection -Lifestyle (Alcohol, Smoking, Drugs especially when youre pregnant) -DM -Rubella vaccine -Age -Gender -Heredity -Race
-Heart Attack -Stroke -Buergers disease
-Impaired skin/ tissue integrity
A cyanotic Diseases: -Patent Ductus Arteriosus -Atrial Septal Defect -Ventricular Septal Defect Coarctation of the Aorta -Pulmonic Valve Stenosis -Aortic Valve Stenosis Cyanotic Diseases: -Tetralogy of Fallot -Tricuspid Atresia -Total Anomalous Venous Return -Truncus arteriosus -Cardiovascular Defects -Cardiac surgery -CHF -Rheumatic Fever -Kawasaki Disease
-Ineffective tissue perfusion -Activity intolerance -Decreased cardiac output
Rheumatic Heart Disease
Subj: -Chest pain -Fatigue Obj: -Rapid breathing
-Smoking -Lifestyle -Sore throat (cause by untreated Group A streptococcus bacterial infection) -Uncompliance to medication
-Age(5-15) -Genetic(father w/ RHD) -Sex (Male)
-Ineffective tissue perfusion -Activity intolerance -Decreased cardiac output -Ineffective airway clearance
Objectives: To identify the Cardiovascular Diseases, Assessment, Health History and Presenting Problem. To identify the possible Nursing Diagnosis.
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Ventricular Septal Defect, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Treatment And Related ConditionsVon EverandVentricular Septal Defect, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Treatment And Related ConditionsNoch keine Bewertungen
- A Simple Guide to Stroke, (Cerebrovascular Infarction) Diagnosis, Treatment and Related ConditionsVon EverandA Simple Guide to Stroke, (Cerebrovascular Infarction) Diagnosis, Treatment and Related ConditionsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Arrhythmias Teacher GuideDokument12 SeitenArrhythmias Teacher GuideMayer Rosenberg100% (3)
- Cardiac OutputDokument61 SeitenCardiac OutputSyed Ali MoosaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Heart TransplantationDokument10 SeitenHeart TransplantationNajmi Leila SepyanisaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Congestive Heart FailureDokument14 SeitenCongestive Heart FailureBella Trix PagdangananNoch keine Bewertungen
- Myocardial InfarctionDokument23 SeitenMyocardial InfarctionAnelle Umali50% (2)
- CVDDokument22 SeitenCVDvijaymusic88100% (1)
- Distributive Shock PDFDokument8 SeitenDistributive Shock PDFAdreiTheTripleANoch keine Bewertungen
- Acute Arterial OcclusionDokument39 SeitenAcute Arterial Occlusionmaria teresa casili100% (1)
- CellulitisDokument18 SeitenCellulitismuthia saniNoch keine Bewertungen
- Coronary Heart Disease: Angina Pectoris Myocardial InfarctionDokument44 SeitenCoronary Heart Disease: Angina Pectoris Myocardial Infarctionalejandrino_leoaugustoNoch keine Bewertungen
- ECG Skill LabDokument37 SeitenECG Skill LabNayyer Khan100% (1)
- Emergency Department Evaluation Back PainDokument29 SeitenEmergency Department Evaluation Back PainRodolfo GorveñaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pathophysiology of ArrhythmiasDokument15 SeitenPathophysiology of ArrhythmiasJonathan MontecilloNoch keine Bewertungen
- Valvular Heart Disease. KulDokument60 SeitenValvular Heart Disease. KulIntan Kumalasari RambeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Peripheral Artery DiseaseDokument8 SeitenPeripheral Artery DiseasemainehoonaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cardiogenic Shock PDFDokument14 SeitenCardiogenic Shock PDFAdreiTheTripleANoch keine Bewertungen
- BurnsDokument58 SeitenBurnsMarie MayNoch keine Bewertungen
- Urinary IncontinenceDokument7 SeitenUrinary IncontinenceasuratosNoch keine Bewertungen
- Congestive Heart FailureDokument6 SeitenCongestive Heart Failureseigelystic100% (1)
- Coronary Artery Disease Cad2Dokument182 SeitenCoronary Artery Disease Cad2Mamot MotNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD) : Sultan Chaudhry Benny Dua Eric WongDokument7 SeitenChronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD) : Sultan Chaudhry Benny Dua Eric Wongjamil aldasriNoch keine Bewertungen
- Musculoskeletal ExamDokument14 SeitenMusculoskeletal ExamS.R.G100% (1)
- Pathophysiology of StrokeDokument22 SeitenPathophysiology of StrokeKingman844100% (3)
- Congenital Heart DiseasesDokument14 SeitenCongenital Heart DiseasesEulane Ferrer100% (1)
- Gullaine-Barré SyndromeDokument13 SeitenGullaine-Barré SyndromeOnieBoy CurayagNoch keine Bewertungen
- CVPDokument25 SeitenCVPNikhil YadavNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cardiovascular 9. Acute Myocardial InfarctionDokument39 SeitenCardiovascular 9. Acute Myocardial Infarctionapi-19641337100% (2)
- 19 Cardiac DisordersDokument51 Seiten19 Cardiac DisordersChessie Garcia100% (1)
- Cerebrovascular Accident (CVA)Dokument71 SeitenCerebrovascular Accident (CVA)nur muizzah afifah hussinNoch keine Bewertungen
- Myocardial Infarction. BPTDokument62 SeitenMyocardial Infarction. BPTAanchal GuptaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Congestive Heart Failure LectureDokument102 SeitenCongestive Heart Failure Lectureluke100% (1)
- Nephritic/nephrotic Syndrome.Dokument37 SeitenNephritic/nephrotic Syndrome.Kelechi OtamiriNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cardiac TumorsDokument37 SeitenCardiac TumorsdadupipaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Rheumatoid ArthritisDokument19 SeitenRheumatoid ArthritisLiya AnjelinaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 03 Cardiopulmonary PhysiologyDokument17 Seiten03 Cardiopulmonary Physiologyice cream1000791100% (1)
- CardiomyopathyDokument2 SeitenCardiomyopathyBianca SarmientoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Jugular Venous Pulse: Madras Medical MissionDokument53 SeitenJugular Venous Pulse: Madras Medical MissionJoshua JayakaranNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1st, 2nd, 3rd Degree AV BLockDokument8 Seiten1st, 2nd, 3rd Degree AV BLockladydreamer_92Noch keine Bewertungen
- Case Study: MYXEDEMATOUS COMADokument5 SeitenCase Study: MYXEDEMATOUS COMAjisooNoch keine Bewertungen
- Aortic Valve StenosisDokument4 SeitenAortic Valve StenosisYrag NoznipNoch keine Bewertungen
- Abdominal Aortic AneurysmDokument2 SeitenAbdominal Aortic AneurysmAria MontgomeryNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pathophysiology 2Dokument92 SeitenPathophysiology 2Princess AgarwalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Surgical Management of Coronary Artery DiseaseDokument41 SeitenSurgical Management of Coronary Artery Diseaseapi-19916399Noch keine Bewertungen
- Clinical Case Scenarios Slide Set Powerpoint 247326013Dokument51 SeitenClinical Case Scenarios Slide Set Powerpoint 247326013rwev3Noch keine Bewertungen
- Ischemic StrokeDokument49 SeitenIschemic StrokeMirna Ayu Permata SariNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hypertension Guidelines 2014: Jason A. Smith, DO Associated Cardiovascular Consultants at Lourdes Cardiology ServicesDokument33 SeitenHypertension Guidelines 2014: Jason A. Smith, DO Associated Cardiovascular Consultants at Lourdes Cardiology ServicesRido MaulanaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cardiomyopathy: M Taufik I, MDDokument28 SeitenCardiomyopathy: M Taufik I, MDChi RahmawatiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pulmonary EmbolismDokument5 SeitenPulmonary EmbolismNica Duco100% (2)
- Diabetic Ketoacidosis: Presented by The Students From Roll Numbers 31 - 40Dokument20 SeitenDiabetic Ketoacidosis: Presented by The Students From Roll Numbers 31 - 40HUSSAIN NAZEESHANoch keine Bewertungen
- CopdDokument35 SeitenCopdNurhidayahNoch keine Bewertungen
- Myocardial InfarctionDokument47 SeitenMyocardial Infarctionsanjesh1100% (2)
- Head To Toe ExaminationDokument6 SeitenHead To Toe ExaminationFadillah Raisyah MNoch keine Bewertungen
- Blood Transfusion: Etiology of Blood CellDokument4 SeitenBlood Transfusion: Etiology of Blood Cellbunso padillaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Diagnosis of Cardiovascular Disease - TranscriptionDokument11 SeitenDiagnosis of Cardiovascular Disease - TranscriptionPauline Del MundoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cardiovascular and CerebrovascularDokument6 SeitenCardiovascular and CerebrovascularJoshelle B. Bancilo0% (1)
- Types Heart Failure PDFDokument10 SeitenTypes Heart Failure PDFHannaNoch keine Bewertungen
- A Simple Guide to Abdominal Aortic Aneurysm, Diagnosis, Treatment and Related ConditionsVon EverandA Simple Guide to Abdominal Aortic Aneurysm, Diagnosis, Treatment and Related ConditionsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Synovial Chondromatosis, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsVon EverandSynovial Chondromatosis, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsNoch keine Bewertungen
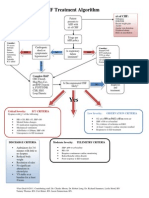
- CHFalgorithm Univ of MSDokument1 SeiteCHFalgorithm Univ of MSDominique Excelsis J. DegamoNoch keine Bewertungen
- The School As A Social SystemDokument19 SeitenThe School As A Social SystemDominique Excelsis J. Degamo100% (4)
- NCP - Hypovolemic ShockDokument7 SeitenNCP - Hypovolemic ShockDominique Excelsis J. Degamo71% (7)
- MS 2 - NCP Deep Vein ThrombosisDokument4 SeitenMS 2 - NCP Deep Vein ThrombosisDominique Excelsis J. Degamo67% (3)
- Nursing Theories Madeliene LieningerDokument3 SeitenNursing Theories Madeliene LieningerDominique Excelsis J. DegamoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Icp Member Handbook Il PDFDokument36 SeitenIcp Member Handbook Il PDFjohnNoch keine Bewertungen
- UntitledDokument17 SeitenUntitledInggrid Aprilia ChristyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Campylobacter Jejuni-Mediated Guillain-Barre Syndrome, An Overview of The Molecular Mimicry and Vaccine Development ApproachesDokument9 SeitenCampylobacter Jejuni-Mediated Guillain-Barre Syndrome, An Overview of The Molecular Mimicry and Vaccine Development ApproachesInternational Medical Publisher0% (1)
- A Silent KillerDokument3 SeitenA Silent KillerLinhNguyeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Is Doa 10 Cup TestDokument1 SeiteIs Doa 10 Cup TestUqi.Noch keine Bewertungen
- Case Report Acute Idiopathic Scrotal Edema MILMED-D-13-00103Dokument3 SeitenCase Report Acute Idiopathic Scrotal Edema MILMED-D-13-00103YJanitorNoch keine Bewertungen
- ARES Protocol Os UseDokument5 SeitenARES Protocol Os UseLeia AlbaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lesson Plan On Post Natal ExercisesDokument11 SeitenLesson Plan On Post Natal Exercisesvarshasharma0593% (15)
- Guide PDFDokument84 SeitenGuide PDFbiomeditechNoch keine Bewertungen
- Castor OilDokument1 SeiteCastor OilRohan EarnestNoch keine Bewertungen
- He2011 TMJ ANKYLOSIS CLASSIFICATIONDokument8 SeitenHe2011 TMJ ANKYLOSIS CLASSIFICATIONPorcupine TreeNoch keine Bewertungen
- PediatricsDokument312 SeitenPediatricsمحمد ابو مناضل الافينش100% (1)
- Acute Gastritis CiciDokument43 SeitenAcute Gastritis CiciDwi Rezky AmaliaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hepatoprotective Activity of Berberisaristata Root Extract Against Chemical Induced Acute Hepatotoxicity in RatsDokument4 SeitenHepatoprotective Activity of Berberisaristata Root Extract Against Chemical Induced Acute Hepatotoxicity in RatsAmit patelNoch keine Bewertungen
- Subinvolution Breast Complications: Prepared by Ms. Annu Panchal Assistant ProfessorDokument19 SeitenSubinvolution Breast Complications: Prepared by Ms. Annu Panchal Assistant Professorannu panchalNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Aao "At-A-Glance" Guide To CDT 2021 Orthodontic Codes: DentitionDokument2 SeitenThe Aao "At-A-Glance" Guide To CDT 2021 Orthodontic Codes: DentitionSweet ToothNoch keine Bewertungen
- ApendikDokument4 SeitenApendikSepti AyaNoch keine Bewertungen
- BLOOD DONATION (Autosaved)Dokument11 SeitenBLOOD DONATION (Autosaved)Anisa Fitri RachmaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Catalog EME PHYSIO 2016 - ENGDokument88 SeitenCatalog EME PHYSIO 2016 - ENGaudrey pahleviNoch keine Bewertungen
- Probiotic Supplementation For Prevention of Atopic Dermatitis in Infants and Children: A Systematic Review and Meta AnalysisDokument11 SeitenProbiotic Supplementation For Prevention of Atopic Dermatitis in Infants and Children: A Systematic Review and Meta AnalysisGrace Malinda LimopranotoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Assessment of Vital Signs&GCSDokument3 SeitenAssessment of Vital Signs&GCSNicole Jackson100% (3)
- Meningococcal Infection in ChildrenDokument6 SeitenMeningococcal Infection in ChildrenAdrian KhomanNoch keine Bewertungen
- F Buski 111003095909 Phpapp01Dokument15 SeitenF Buski 111003095909 Phpapp01Ashik MajumdarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Concept Map PTBDokument1 SeiteConcept Map PTBJoan Abardo100% (2)
- Defense Medical Epidemiology Database Report - Jan 26, 2022Dokument41 SeitenDefense Medical Epidemiology Database Report - Jan 26, 2022adan_infowars100% (2)
- Ncma215 - Nutrition and Diet Therapy: Week - 9Dokument4 SeitenNcma215 - Nutrition and Diet Therapy: Week - 9ABEGAIL BALLORANNoch keine Bewertungen
- Grand Case Presentation InformationDokument7 SeitenGrand Case Presentation InformationCristina L. JaysonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Reflection Paper Pediatric Community-Acquired Pneumonia in The United StatesDokument2 SeitenReflection Paper Pediatric Community-Acquired Pneumonia in The United StatesLecery Sophia WongNoch keine Bewertungen
- Dr. Ugi Sugiri, SpEm - PPT OBMED PDFDokument56 SeitenDr. Ugi Sugiri, SpEm - PPT OBMED PDFDaniel Aprianto SihotangNoch keine Bewertungen