Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Mis
Hochgeladen von
Nilanchal Sahu100%(1)100% fanden dieses Dokument nützlich (1 Abstimmung)
2K Ansichten13 SeitenMIS is an information system which helps in providing the management of an organization with information which is used by management for decision making. MIS is a subset of the overall internal controls of a business covering the application of people, documents, technologies, and procedures by management accountants.
Originalbeschreibung:
Originaltitel
mis
Copyright
© Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Verfügbare Formate
DOC, PDF, TXT oder online auf Scribd lesen
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenMIS is an information system which helps in providing the management of an organization with information which is used by management for decision making. MIS is a subset of the overall internal controls of a business covering the application of people, documents, technologies, and procedures by management accountants.
Copyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Verfügbare Formate
Als DOC, PDF, TXT herunterladen oder online auf Scribd lesen
100%(1)100% fanden dieses Dokument nützlich (1 Abstimmung)
2K Ansichten13 SeitenMis
Hochgeladen von
Nilanchal SahuMIS is an information system which helps in providing the management of an organization with information which is used by management for decision making. MIS is a subset of the overall internal controls of a business covering the application of people, documents, technologies, and procedures by management accountants.
Copyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Verfügbare Formate
Als DOC, PDF, TXT herunterladen oder online auf Scribd lesen
Sie sind auf Seite 1von 13
SET – 1
SOLVED ASSIGNMENT
Q 1: Define MIS ? What are the characteristics of MIS?
Answer:
MIS is an Information system which helps in providing the management
of anorganization with information which is used by management for
decision making.A management information system (MIS) is a subset of
the overall internal controls of a business covering the application of
people, documents, technologies, and procedures by management
accountants to solving business problems such as costing
a product, service or a business-wide strategy. Management information
systems are distinct from regular information systems in that they are
used to analyze other information systems applied in operational
activities in the organization. Academically, the term is commonly used
to refer to the group of information management methods
tied to the automation or support of human decision making, e.g.
Decision Support
Systems, Expert systems, and Executive information systems.
An 'MIS' is a planned system of the collecting, processing, storing and
disseminatingdata in the form of information needed to carry out the
functions of management.According to Philip Kotler "A marketing
information system consists of people,
equipment, and procedures to gather, sort, analyze, evaluate, and
distribute needed,timely, and accurate information to marketing decision
makers."The terms MIS and information system are often confused.
Information systems include systems that are not intended for decision
making. The area of study called MIS is sometimes referred to, in a
restrictive sense, as information technology
management. That area of study should not be confused with computer
science. IT service management is a practitioner-focused discipline. MIS
has also some differences with Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) as
ERP incorporates elements that are not necessarily focused on decision
support.
MIS has a major impact on the functions of any organization. The
organization derivesbenefits from the systems in the following form:
a) Speedy access to information,
b) Interpretation of data,
c) Quick decisions,
d) Speedy actions,
e) increased productivity and thereby increase in the profit
f) Reduced transaction cost.
MIS characteristics
In any organization managers will have varieties of tasks to manage. MIS
is mainlydesigned to take care of the needs of the managers in the
organization.
Organizations will have different departments like marketing, production,
sales,inventory, maintenance etc. Each of these departments function
individually and also in relationship with other departments. Information
is available in abundance. MIS aids in integrating the information
generated by variousdepartments of the organization.
MIS helps in identifying a proper mechanism of storage of data. The data
is maintained in such a way that the unnecessary duplication of data is
avoided.
MIS also helps in establishing mechanism to eliminate redundancies in
data.
MIS as a system can be broken down into sub systems. Each such sub
system may be programmed. This results in easy access of data,
accuracy of data and information. It helps in maintaining the consistency
of data.
Function of MIS
The main function of MIS is to help the managers and the executives in
theorganization in decision-making.
Large quantities of data like customers information, competitors
information,personnel records, sales data, accounting data etc is
collected from internal sources like the
Company records and external sources like annual reports and
publications.
The collected data is organized in the form of a database.
The data from the database is processed and analyzed by using
different toolsand techniques.
The results of the analysis are properly presented to the managers to
helpthem in decision-making.
Q 2: Explain strategic MIS categories in detail. Give relevant
examples.
Answer:
Strategic Information System
A Strategic Information System (SIS) is a system to manage information
and assist in strategic decision making. A strategic information system
has been defined as, "The information system to support or change
enterprise's strategy."A SIS is a type of Information System that is
aligned with business strategy and structure. The
alignment increases the capability to respond faster to environmental
changes and thus creates a competitive advantage. An early example was
the favorable position afforded American and
United Airlines by their reservation systems, Sabre and Apollo. For many
years these two systems ensured that the two carriers' flights appeared
on the first screens observed by travel
agents, thus increasing their bookings relative to competitors. A major
source of controversy surrounding SIS is their sustainability.
SISs are different from other comparable systems as:
1) they change the way the firm competes.
2) they have an external (outward looking) focus.
3) they are associated with higher project risk.
4) they are innovative (and not easily copied).
It is mainly concerned with providing and organization and its members
an assistance to perform the routine tasks efficiently and effectively. One
of the major issue before
any organization is the challenge of meeting its goals and objectives.
Strategic IS enable such organization in realizing their goals. Strategic
Information System (SIS) is
a support to the existing system and helps in achieving a competitive
advantage over the organizations competitors in terms of its objectives.
This unit deals with the critical
aspects of the strategic information system. This units indicates the
theoretical concepts and the way in which the same are realized in
practice. The flow of the unit is
in such a way that it starts with the development of contemporary theory
about strategic uses of corporations' internal information systems
leading to systems which transcend the boundaries of particular
organizations. The process whereby strategic
information systems are created or identified is then examined. A
number of weaknesses in the existing body of theory are identified, and
suggestions made as to directions in which knowledge is or may be
progressing. A strategic information system
is concerned with systems which contribute significantly to the
achievement of an organization's overall objectives. The body of
knowledge is of recent origin and highly dynamic, and the area has an
aura of excitement about it. The emergence of the key
ideas, the process whereby strategic information systems come into being
is assessed, areas of weakness are identified, and directions of current
and future development suggested.
Information system is regarded as a tool to provide various services to
different management functions. The tools have been developing year by
year and the application of the tool has become more and more diverse.
In management it is now a
very power means to manage and control various activities and decision
making process. The original idea of automating mechanical processes
got quickly succeeded
by the rationalization and integration of systems. In both of these forms,
IS was regarded primarily as an operational support tool, and
secondarily as a service to management. Subsequent to the development,
it was during the last few years that an
additional potential was discovered. It was found that, in some cases,
information technology (IT) had been critical to the implementation of an
organization's strategy.
An organization’s strategy supported by information system fulfilling its
business objectives came to be known as Strategic Information System.
The strategic information system consists of functions that involved
gathering, maintenance and
analysis of data concerning internal resources, and intelligence about
competitors, suppliers, customers, government and other relevant
organizations.
===========================================================
=============
Q 3: Write a detailed note on the planning and development of MIS?
Answer:
Information is a corporate resource, as important as the capital, labour,
know-how etc.and is being used for decision-making. Its quality,
therefore, is required to be very high.A low quality information would
adversely affect the organizational performance as it
affects decision-making. The quality of information is the result of the
quality of the input data, processing design, system design, system and
procedures which generate such a data, and the management of the data
processing function. Quality, unlike any other product, is not an
absolute concept. Its level is determined with reference to the
context and its use, and the user. Perfect quality just as perfect
information is nonachievable and has cost-benefit implications.
However, it is possible to measure the quality of information on certain
parameters. All these parameters need not have a very high value. Some
parameters may have lesser importance in the total value on account of
their relevance in the information and its use.
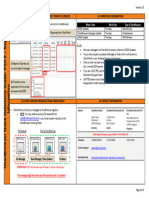
The quality parameters which are generally considered are shown in the
table
Individual Explanation Effect on Examples
differences information
processing
Locus of control The degree of More information The production
internal or perception Gathering and decisions, selection
external in assessing the
control
to the situation which is internal or external of tools and materials
to the etc.
organization or
external
to the
organization.
Personal The degree of faith Low dogmatism, The pricing,
dogmatism. in then advertising in a
beliefs, opinions more information Competitive
and past collection and environment.
experience. processing.
Risk propensity. The ability to take Higher, then more The top management
the information decision-making in a
risk. gathering strategic planning.
and analysis.
Tolerance for Level of clarity Tight tolerance Manager Constantly
ambiguity. required in then asking for more
the information. more information information.
The collection and
ability to read analysis
through the
information.
Manipulative The ability to High ability, then Experienced and
intelligence. manipulate less skillful
the data and information and managers rely on the
information more manipulative
vis-à-vis the self analysis.
intelligence.
stored
information and
knowledge
Experience in Extent of High, then correct The managers with a
decision-making. experience at filtering of data wide experience in
particular level of and the different fields
decision appropriate choice of management call
making. of for precise and less
decision
but pertinent
makingprocess.
information.
Knowledge of the The extent of Higher, then less The Technocrat
task, tools and knowledge information scientists, and
technology. in the application relevant managers of
of the to and tools technology have
tools and correct definite information.
technology. analysis.
The quality of these important parameters is ensured by conducting a
proper systems
analysis, designing a suitable information system and ensuring its
maintenance from
time to time, and also subjecting it to audit checks to ensure the system
integrity.
The quality of the parameters is assured if the following steps are taken.
1. All the input is processed and controlled, as input and process design.
2. All updating and corrections are completed before the data processing
begins.
3. Inputs (transactions, documents, fields and records) are subject to
validitychecks.
4. The access to the data files is protected and secured through an
authorizationscheme.
5. Intermediate processing checks are introduced to ensure that the
complete
data is processed right through, i.e. run to run controls.
6. Due attention is given to the proper file selection in terms of data,
periods and so on.
7. Backup of the data and files are taken to safeguard corruption or loss
of data.
8. The system audit is conducted from time to time to ensure that the
informationsystem specifications are not violated.
9. The system modifications are approved by following a set procedure
which
begins with authorization of a change to its implementation followed by
anaudit.
10. Systems are developed with a standard specification of design and
development.
11. Information system processing is controlled through programme
control,process control and access control.
12. Ensure MIS model confirms consistency to business plan satisfying
informationneeds to achieve business goals.
The assurance of quality is a continuing function and needs to be evolved
over a eriod and requires to be monitored properly. It cannot be assessed
in physical units of
measure. The user of the information is the best judge of the quality.
===========================================================
========
Q 5: Explain the challenges before an E-business management.
Answer:
Managing an E-business & Challenges before an E-business - Due to
Internetcapabilities and web technology, traditional business
organization definition has
undergone a change where scope of the enterprise now includes other
company ocations, business partners, customers and vendors. It has no
geographic boundaries s it can extend its operations where Internet
works. All this is possible due to Internet
and web moving traditional paper driven organization to information
driven Internet
enabled E-business enterprise. E-business enterprise is open twenty-four
hours, and eing independent, managers, vendors, customers transact
business any time from
anywhere. Internet capabilities have given E-business enterprise a
cutting edge apability advantage to increase the business value. It has
opened new channels of
business as buying and selling can be done on Internet. It enables to
reach new arkets across the world anywhere due to communication
capabilities. It has mpowered customers and vendors / suppliers
through secured access to information
to act, wherever necessary. The cost of business operations has come
down ignificantly due to the elimination of paper-driven processes, faster
communication nd effective collaborative working. The effect of these
radical changes is the reduction administrative and management
overheads, reduction in inventory, faster delivery of
goods and services to the customers.In E-business enterprise traditional
people organization based on 'Command Control'
principle is absent. It is replaced by people organization that is
empowered byinformation and knowledge to perform their role. They are
supported by informationsystems, application packages, and decision-
support systems. It is no longer
functional, product, and project or matrix organization of people but E-
organization where people work in network environment as a team or
work group in virtual mode. Ebusiness
enterprise is more process-driven, Technology-enabled and uses its own
information and knowledge to perform. It is lean in number, flat in
structure, broad in
scope and a learning organization. In E-business enterprise, most of the
things are electronic, use digital technologies and work on databases,
knowledge bases,
directories and document repositories. The business processes are
conducted through enterprise software like ERP, SCM, and CRM
supported by data warehouse, decision
support, and knowledge management systems. Today most of the
business organizations are using Internet technology, network, and
wireless technology for improving the business performance measured in
terms of cost, efficiency, competitiveness and profitability. They are using
E-business, Ecommerce solutions to
reach faraway locations to deliver product and services. The enterprise
solutions like ERP, SCM, and CRM run on Internet (Internet / Extranet)
& Wide Area Network (WAN). The business processes across the
organization and outside run on Etechnology
platform using digital technology. Hence today's business firm is also
called E-enterprise or Digital firm.
The paradigm shift to E-enterprise has brought four transformations,
namely:
Domestic business to global business.
Industrial manufacturing economy to knowledge-based service economy.
Enterprise Resource Management to Enterprise Network Management.
Manual document driven business process to paperless, automated,
electronically transacted business process.
These transformations have made conventional organization design
obsolete.
In E-enterprise, business is conducted electronically. Buyers and sellers
through Internet drive the market and Internet-based web systems.
Buying and selling is possible on Internet. Books, CDs, computer, white
goods and many such goods are bought and sold on Internet. The new
channel of business is well-known as
Ecommerce. On the same lines, banking, insurance, healthcare are being
managed
through Internet E-banking, E-billing, E-audit, & use of Credit cards,
Smart card, ATM,
E-money are the examples of the Ecommerce application. The digital
firm, which uses
Internet and web technology and uses E-business and Ecommerce
solutions, is a reality and is going to increase in number.
MIS for E-business is different compared to conventional MIS design of
an organization. The role of MIS in E-business organization is to deal
with changes in global market and enterprises. MIS produces more
knowledge-based products.
Knowledge management system is formally recognized as a part of MIS. It
is effectively used for strategic planning for survival and growth, increase
in profit and productivity and so on. To achieve the said benefits of E-
business organization, it is
necessary to redesign the organization to realize the benefits of digital
firm. The organization structure should be lean and flat. Get rid of rigid
established infrastructure
such as branch office or zonal office. Allow people to work from
anywhere. Automate processes after reengineering the process to cut
down process cycle time. Make use of groupware technology on Internet
platform for faster response processing. Another
challenge is to convert domestic process design to work for international
process,where integration of multinational information systems using
different communication standards, country-specific accounting
practices, and laws of security are to be adhered strictly.
Internet and networking technology has thrown another challenge to
enlarge the scope
of organization where customers and vendors become part of the
organization. This technology offers a solution to communicate,
coordinate, and collaborate with customers, vendors and business
partners. This is just not a technical change in business operations but a
cultural change in the mindset of managers and workers to look beyond
the conventional organization. It means changing the organization
behaviour to take competitive advantage of the E-business
technology.The last but not the least important is the challenge to
organize and implement information architecture and information
technology platforms, considering multiple
locations and multiple information needs arising due to global operations
of the business into a comprehensive MIS.
E-COMMERCE is a second big application next to ERP. It is essential
deals with buying and
selling of goods. With the advent of intent and web technology, E-
Commerce today covers an
entire commercial scope online including design and developing,
marketing, selling, delivering,
servicing, and paying for goods. Some E-Commerce application add order
tracking as a feature
for customer to know the delivery status of the order.
The entire model successfully works on web platform and uses internet
technology. ECommerce
process has two participants, namely
Buyer and
Seller, like in traditional business model.
And unique and typical to E-commerce there is one more participant to
seller by authorization
and authentication of commercial transaction.
E-Commerce process model can be viewed in four ways and categories:
B2C: Business Organisation to Customer
B2B: Business Organisation to Business
C2B: Customer to Business Organisation
C2C: Customer to Customer
In B2C Model, business organization uses websites or portals to offer
information about
product, through multimedia clippings, catalogues, product
configuration guidelines, customer
histories and so on. A new customer interacts with the site and uses
interactive order processing system for order placements. On placements
of order, secured payment systems comes into operation to authorize and
authenticate payment to seller. The delivery system then take over to
execute the delivery to customer.
In B2B Model, buyer and seller are business organizations. They
exchange technical & commercial through websites and portals. Then
model works on similar line like B2C. More advanced B2B model uses
Extranet and Conducts business transaction based on the information
status displayed on the buyer’s application server.In C2B Model,
customer initiates actions after logging on to seller’s website or to server.
On the
server of the selling organization, E-Commerce application are present
for the use of the customer. The entire Internet banking process work on
C2B model where account holders of the bank transact a number of
requirements such as seeking account balance, payment and soon.In
C2C model, Customer Participates in the process of selling and buying
through the auction
website. In this model, website is used for personal advertising of
products or services. ENewspaper
website is an Example of advertising and selling of goods to customer.
In B2B Model, the participants in E-business are two organisation with
relations as
buyer=seller, distributor-dealer and so on.
E-Collaboration every business has a number of work scenarios where
group of people work
together to complete the tasks and to achieve a common objective. The
group could be teams
or virtual teams with different member strength. They come together to
platform a task to
achieve some results. The process is called Collaboration. The Biggest
Advantage of ECollaboration
is that it taps the collective wisdom, knowledge and experience of the
members.
The collaboration team or group could be within the organization and
between the organisation as well.Since, E-Collaboration works on an
internet platform and uses web technology, work
group/team need not be at one physical location.
E-collaboration uses E-Communication capabilities to perform
collaborative tasks or project
assignment. Its effectiveness is increased by software ‘GroupWare’ that
enables the members of the group to share information, invoke an
application
E-Collaboration helps work effectively on applications like calendaring
and scheduling tasks,event, project management, workflow application,
work group application.
E-collaboration system components are internet, Intranet, Extranet and
LAN, WAN networks for communication through GroupWare tools,
browser.
Let us illustrate the model using an event in the business such as receipt
of material for a job to be processed on the shop floor. In this event there
is a transaction receipt of material, which needs to be processed, and
then a workgroup will use this information of material receipt. Each
member of this workgroup has a different goal.
===========================================================
===========
6 : What is an internet? Explain the differences between internet,
intranet and extranet.
Answer:
Internet is a global network of interconnected computers, enabling users
to share information along multiple channels. Typically, a computer that
connects to the Internet can access nformation from a vast array of
available servers and other computers by moving information from them
to the computer's local memory. The same connection allows that
computer to send information to servers on the network; that
information is in turn accessed and potentially modified by a variety of
other interconnected computers. A majority of widely accessible
information on the Internet consists of inter-linked hypertext documents
and other resources of the World Wide Web (WWW). Computer users
typically manage sent and received information with web browsers; other
software for users' interface with computer networks includes specialized
programs for electronic mail, online chat, file transfer and file sharing.
The movement of information in the Internet is achieved via a system of
interconnected computer networks that share data by packet switching
using the standardized Internet
Protocol Suite (TCP/IP). It is a "network of networks" that consists of
millions of private and public, academic, business, and government
networks of local to global scope that are linked by copper wires, fiber-
optic cables, wireless connections, and other technologies.
Difference between internet, intranet and extranet as follow:
Extranet :
An extranet is a private network that uses the Internet protocols and the
public telecommunication system to securely share part of a business's
information or operations with suppliers, vendors, partners, customers,
or other businesses. An extranet can be viewed as part of a company's
intranet that is extended to users outside the company.
An extranet
A new buzzword that refers to an intranet that is partially accessible to
authorized outsiders. Whereas an intranet resides behind a firewall and
is accessible only to people who are members of the same company or
organization, an extranet provides various levels of accessibility to
outsiders. You can access an extranet only if you have a valid username
and
password, and your identity determines which parts of the extranet you
can view.
An extranet is somewhat very similar to an intranet. Extranets are
designed specifically to give
external, limited access to certain files of your computer systems to:
Certain large or priviledged customers.
Selected industry partners.
Page 9
Suppliers and subcontractors... etc.
Therefore, a carefully designed extranet can bring additional business to
your company.
Intranets and extranets all have three things in common:
They both use secured Internet access to the outside world.
Both can drastically save your company or organization a lot of money.
Both need a user ID & password to control access to the whole system.
The professional development team at My Web Services has the expertise
and the right tools
to design the right intranet or extranet that will meet your exact needs,
both for today and the
future.
Intranet:
An internal use, private network inside an organisation that uses the
same kind of software which would also be found on the Internet.
Inter-connected network within one organization that uses Web
technologies for the sharing of
information internally, not world wide. Such information might include
organization policies and procedures, announcements, or information
about new products.
An intranet is a restricted-access network that works like the Web, but
isn't on it. Usually owned and managed by a company, an intranet
enables a company to share its resources with its employees without
confidential information being made available to everyone with Internet
access.
A network based on TCP/IP protocols (an internet) belonging to an
organization, usually a corporation, accessible only by the organization's
members, employees, or others with authorization. An intranet's Web
sites look and act just like any other Web sites, but the firewall
surrounding an intranet fends off unauthorized access. Like the Internet
itself, intranets are
used to share information.
An intranet is an information portal designed specifically for the internal
communications of
small, medium or large businesses, enterprises, governments, industries
or financial institutions
of any size or complexity. Intranets can be custom-designed to fit the
exact needs of
businesses no matter where they are situated. Users of intranets consists
mainly of:
Members of the executive team.
Accounting and order billing.
Managers and directors.
Sales people and support staff.
Customer service, help desk, etc.Internet:
An electronic network of computers that includes nearly every university,
government, and
research facility in the world. Also included are many commercial sites. It
started with four interconnected computers in 1969 and was known as
ARPAnet.
A network of computer networks which operates world-wide using a
common set of ommunications protocols.
The vast collection of inter-connected networks across the world that all
use the TCP/IP Protocols. A global network connecting millions of
computers. A worldwide network of computer networks.
It is an interconnection of large and small networks around the globe.
The Internet began in 1962 as a resilient computer network for the US
military and over time has grown into a global communication tool of
more than 12,000 computer networks that share a common addressing
scheme.
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeVon EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (537)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeVon EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (5794)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceVon EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (895)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Von EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Bewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (98)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceVon EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (588)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingVon EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (400)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerVon EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (271)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItVon EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (838)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyVon EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (2259)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealVon EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (74)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureVon EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (474)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryVon EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (231)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnVon EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (234)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaVon EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (266)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersVon EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (345)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaVon EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (45)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreVon EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Von EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Bewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (121)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesVon EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (821)
- Vending Machines Final PDFDokument20 SeitenVending Machines Final PDFRaina MalikNoch keine Bewertungen
- Raspberry Practical Manual SachinDokument49 SeitenRaspberry Practical Manual SachinVaibhav KarambeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Raspberry Pi Begginer Guide 2020 Part 4Dokument10 SeitenRaspberry Pi Begginer Guide 2020 Part 4New RegisterNoch keine Bewertungen
- Data Communication & Networking MCQs For IBPS IT Specialist OfficerDokument190 SeitenData Communication & Networking MCQs For IBPS IT Specialist Officersonavs75% (4)
- LabVIEW-Core-1-Exercises-Manual (Exercise 2 - 1) Jonathan Juan Manuel Fiscal MalagaDokument7 SeitenLabVIEW-Core-1-Exercises-Manual (Exercise 2 - 1) Jonathan Juan Manuel Fiscal MalagaJonathan FiiscalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mario Kart Tour Hack Generator Rubies No Human VerificationDokument3 SeitenMario Kart Tour Hack Generator Rubies No Human VerificationMark yoz100% (1)
- Excel Practical 2 - Peppis Pizza (2014) PDFDokument8 SeitenExcel Practical 2 - Peppis Pizza (2014) PDFrupende12Noch keine Bewertungen
- PDF Install WasDokument200 SeitenPDF Install Wasthiyagu_808Noch keine Bewertungen
- MRK1828-04-EN-00 Guide To Setting Up Access Permissions in The MACDokument16 SeitenMRK1828-04-EN-00 Guide To Setting Up Access Permissions in The MACMiguel Zuniga MarconiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Unit 1 PpsDokument132 SeitenUnit 1 PpsMadhav SinhaNoch keine Bewertungen
- ITIL V2 - Foundation EssentialsDokument5 SeitenITIL V2 - Foundation EssentialsRodrigo SilvaNoch keine Bewertungen
- CounterACT Console User Manual 7.0.0Dokument756 SeitenCounterACT Console User Manual 7.0.0bkshrestha69100% (2)
- Revive DX Computer User GuideDokument4 SeitenRevive DX Computer User GuideregreeNoch keine Bewertungen
- VI Editor Commands PDFDokument5 SeitenVI Editor Commands PDFfreidyfriendsNoch keine Bewertungen
- HP Compaq Presario All in One CQ 1503la Diagrama Tarjeta TcomDokument42 SeitenHP Compaq Presario All in One CQ 1503la Diagrama Tarjeta TcomJERARKIA LIRIKAL MCYASIRNoch keine Bewertungen
- Iiee TemplateDokument3 SeitenIiee TemplateLara Louise ConcepcionNoch keine Bewertungen
- TL1 Reference Guide - 323-1059-190.1.r16Dokument388 SeitenTL1 Reference Guide - 323-1059-190.1.r16akrh125Noch keine Bewertungen
- Operating System AssignmentDokument13 SeitenOperating System AssignmentMarc AndalloNoch keine Bewertungen
- Functions Added To Sample Project File For SP5000 Wide ModelDokument14 SeitenFunctions Added To Sample Project File For SP5000 Wide ModelJuan SilvaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Toy Claw For Brain Breaks SlidesManiaDokument30 SeitenToy Claw For Brain Breaks SlidesManiaFarih MansurNoch keine Bewertungen
- Static Variable and MethodDokument9 SeitenStatic Variable and Methodsiddhant kudesiaNoch keine Bewertungen
- CLI Management User GuideDokument25 SeitenCLI Management User GuideerickgugoNoch keine Bewertungen
- CPS109 C01 FerwornDokument33 SeitenCPS109 C01 Ferwornkejducuvq3Noch keine Bewertungen
- Unwired Learning: The Ultimate Python Developer BundleDokument19 SeitenUnwired Learning: The Ultimate Python Developer BundleNnnnngdggNoch keine Bewertungen
- C++ List of ExperimentDokument23 SeitenC++ List of ExperimentprateekevangelingNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ankon Gopal Banik: According To The Syllabus of Department of CSE, Gono BishwabidiyalayDokument36 SeitenAnkon Gopal Banik: According To The Syllabus of Department of CSE, Gono BishwabidiyalayAnkon Gopal BanikNoch keine Bewertungen
- 6 - ChartBrowser Quick Reference Guide - v2 0 - Support - InformationDokument1 Seite6 - ChartBrowser Quick Reference Guide - v2 0 - Support - Informationvodoley634Noch keine Bewertungen
- Unit 3: Name: Date: Score: / 50 PointsDokument2 SeitenUnit 3: Name: Date: Score: / 50 PointsMachtia Nemachtia100% (5)
- Digital Twin - RemovedDokument15 SeitenDigital Twin - RemovedAstha SinghNoch keine Bewertungen
- Allen Bradley Controllogix ManualDokument40 SeitenAllen Bradley Controllogix ManualkjfensNoch keine Bewertungen