Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
CH 02 GSM
Hochgeladen von
Michael PangkeregoOriginalbeschreibung:
Originaltitel
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
CH 02 GSM
Hochgeladen von
Michael PangkeregoCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
K1103 / K1205 GSM
Tektronix
2-1
2 GSM Network
2.1 GOAL................................................................................................................ 2-2
2.2 INTELLIGENT NETWORK (IN)......................................................................... 2-3
2.3 THE PUBLIC LAND MOBILE NETWORK (PLMN) AS EXAMPLE OF IN........ 2-5
2.3.1 NETWORK ELEMENTS..................................................................................... 2-7
2.3.1.1 Base Station Subsystem (BSS)............................................................ 2-7
2.3.1.2 Switching Subsystem (SSS)................................................................. 2-8
2.3.2 SYSTEM PROTOCOLS ................................................................................... 2-10
2.3.2.1 A-interface.......................................................................................... 2-11
2.3.2.2 A-bis interface .................................................................................... 2-12
2.3.2.3 B-interface.......................................................................................... 2-13
2.3.2.4 C-interface.......................................................................................... 2-14
2.3.2.5 E-interface.......................................................................................... 2-15
2.3.2.6 F-interface.......................................................................................... 2-16
2.3.2.7 External interface ............................................................................... 2-17
GSM K1103 / K1205
Tektronix 2-2
2.1 Goal
In this section the participants shall learn about;
the structure of a PLMN as example of IN
network elements
system interfaces and protocols
services and protocols of the Application Parts
K1103 / K1205 GSM
Tektronix
2-3
2.2 Intelligent network (IN)
Intelligent network (IN) is an architectural concept for the creation and
provision of telecommunications services. The implementation of the IN
architecture will facilitate the rapid introduction of new services. Its architecture
can be applied to various types of telecommunications networks, which
include: public switched telecommunications network (PSTN), public switched
packet data network (PSPDN), mobile, and integrated services digital
networks (N- and B-ISDN).
x
/
Structure and interfaces of IN
MTP / TUP+ (ISUP)
SS#7 with MTP / SCCP / TCAP / INAP
X.25 - data net
LAPD
SSP SSP
IP
USER
SMS
SCP
Controls (Signalling, NM-protocols)
Signalling and data links
GSM K1103 / K1205
Tektronix 2-4
SMS - Service Management System
The SMS performs service management control, service provision control, and
service deployment control. Examples of functions it can perform are data
base administration, network surveillance and testing, network traffic
management, and network data collection, also it is used to define, develop,
and test an IN service.
SCP - Service Control Point
The SCP contains the Service Logic Programs (SLPs) and data that are used
to provide IN-based services. The SCP is connected to SSPs by a signalling
network. The SCP can be connected to SSPs, and optionally to IPs, through
the signalling network. The SCP can also be connected to an IP via an SSP
relay function.
SSP - Service Switching Point
In addition to providing users with access to the network (if the SSP is a local
exchange) and performing any necessary switching functionality, the SSP
allows access to the set of IN capabilities. The SSP contains detection
capability to detect requests for IN-based services. The SSP may provide
IN-based services to users connected to subtending Network Access Points.
IP - Intelligent Peripheral
The IP provides resources such as customised and concatenated voice
announcements, voice recognition, and Dual Tone Multi-Frequencies (DTMF)
digit collection, and contains switching matrix to connect users to these
resources. The IP supports flexible information interactions between a user
and the network. The IP may directly connect to one or more SSPs, and/or
may connect to the signalling network.
K1103 / K1205 GSM
Tektronix
2-5
2.3 The Public Land Mobile Network (PLMN) as example of IN
The term PLMN further is used as abbreviation for a public communication
network with radio transmission to and from possibly roaming mobile
subscribers in accordance to the GSM-recommendations.
Features offered by a PLMN
high speech quality through digital transmission
interception proof by ciphering
protected against misuse
international roaming
access to all fixed and mobile networks
SS#7-signalling
The PLMN has the structure of an Intelligent Network (IN)
Decentralised intelligence is Iocated in the network nodes which are
distributed over the network
GSM K1103 / K1205
Tektronix 2-6
x
/
F
The PLMN as example of IN
Signalling (or control) links
Signalling and data links
VLR
HLR
AUC EIR
Other
networks
USER
LMT OMC-R
BTS BSC
BTS
(G) MSC MSC
OMC-S
MS
SMSC
IN-SMS-Level
IN-SCP-Level
IN-SSP-Level
IN-IP-Level
C
B
E
external
A
A-bis
AUC Authentication Centre
BSC Base Station Controller
BTS Base Transceiver Station
EIR Equipment ldentity Register
(G) MSC Gateway Mobile Switching Centre
HLR Home Location Register
LMT Local Maintenance Terminal
MS Mobile Station
MSC Mobile Switching Centre
OMC-R Operation and Maintenance Centre - Radio
OMC-S Operation and Maintenance Centre - Switch
SMS Short Message Service
VLR Visitor Location Register
A A-Interface
A-bis A-bis-Interface
B B-Interface
C C-Interface
E E-Interface
F F-Interface
external external interface
K1103 / K1205 GSM
Tektronix
2-7
2.3.1 Network elements
2.3.1.1 Base Station Subsystem (BSS)
The BSS offers all transmitting and control functions which are necessary to
provide radio communication for the service area.
x
/
Structure: Base Station Subsystem
MSC
OMC-R
BTS BTS BTS
BSC
Base Station Subsystem (BSS)
Signalling (or control) links
Signalling and data links
The Base Station Controller (BSC) performs radio processing functions such
as:
administration of the radio resources
radio frequency management
decentralised call processing functions
safeguarding functions.
The Base Transceiver Station (BTS) accommodates all radio transmission
equipment for one antenna site, along with the necessary monitoring
equipment. One BTS can support several radio terminals.
GSM K1103 / K1205
Tektronix 2-8
2.3.1.2 Switching Subsystem (SSS)
x
/
Structure: Switching Subsystem
OMC-S
VLR
HLR
AUC
EIR
Other
networks
MSC
BSC
S
w
i
t
c
h
i
n
g
S
u
b
s
y
s
t
e
m
(
S
S
S
)
Signalling (or control) links
Signalling and data links
Mobile Switching Centre (MSC)
covers the call control services within the PLMN
switches calls between
the PLMN and a fixed network
the PLMN and another radio network
one Mobile Station (MS) and another MS within the PLMN
K1103 / K1205 GSM
Tektronix
2-9
Authentication Centre (AUC)
contains several security boxes with mobile subscriber authentication keys
and algorithms required for the production of authentication parameters
generates a set of authentication parameters for each mobile subscriber
before the subscriber gets access to the network
the authentication parameters are used by the Visitor Location Register
(VLR) for authentication checks
for each authentication a new set of parameters is generated by the AC
Equipment ldentity Register (EIR)
database containing information about the device types and identity
numbers of all MS admitted in its area of responsibility
can be organised in relation to network areas i.e. to one or more MSCs
performs the equipment identification
deficient or illegal MS can be blocked
Home Location Register (HLR)
database containing the relevant data of its registered mobile subscribers
includes information about the VLR area in which the mobile subscriber is
temporarily roaming
logically related to the Authentication Centre (AUC)
Visitor Location Register (VLR)
contains information about all MS currently active in the area
supports one or more location areas
logically related to a MSC
GSM K1103 / K1205
Tektronix 2-10
2.3.2 System protocols
BSSAP Base Station System Application Part
BSSMAP Base Station System Management Application Part
DTAP Direct Transfer Application Part
ISUP ISDN User Part
LAPD Link Access Procedure on the D Channel
L2M Layer 2 Management
MAP Mobile Application Part
MTP Message transfer Part
O&M Operation and Maintenance
RSL Radio Signalling Link
SCCP Signalling Connection Control Part
TCAP Transaction Capability Part
The roaming capability of a Mobile Station (MS) requires an exchange of
control information between the different systems of a PLMN.
The exchange of control information between different networks is also
required.
K1103 / K1205 GSM
Tektronix
2-11
2.3.2.1 A-interface
x
/
Protocols used on A-Interface
BSC
Base Station Subsystem (BSS)
MSC
Switching Subsystem (SSS)
PCM30
BSSMAP
SCCP
MTP
DTAP
The A-interface supplies Traffic Channels (TCH) and signalling channels
Interworking is performed for the following functions:
speech/data traffic
signalling between MCS and BSC for e.g.:
BSS management
call control
mobility management
supplementary services
GSM K1103 / K1205
Tektronix 2-12
2.3.2.2 A-bis interface
x
/
Protocols used on A-bis-Interface
BTS
Base Station Subsystem (BSS)
BSC
PCM30
RSL
L
2
M
LAPD
DTAP
O
&
M
The A-bis interface supplies traffic channels and signalling channels
Interworking is performed for the following functions:
speech/data traffic
signalling between BSC and BIS for e.g.:
channel management
transport of synchronisation information to the BTS
radio equipment control by means of the BSC
O&M
K1103 / K1205 GSM
Tektronix
2-13
2.3.2.3 B-interface
x
/
Protocols used on B-Interface
MSC VLR
PCM30
TCAP
SCCP
MTP
MAP
The B-interface supplies signalling channels.
Interworking is performed for the following functions, e.g.:
attachment/detachment of International Mobile Station ldentity (IMSI) code,
when MS enter the active / inactive status
authentication for MSs
location registration of roaming MSs
retrieval of mobile subscriber parameters during a call set-up.
GSM K1103 / K1205
Tektronix 2-14
2.3.2.4 C-interface
x
/
Protocols used on C-Interface
MSC HLR
PCM30
TCAP
SCCP
MTP
MAP
The C-interface supplies signalling channels.
Interworking is performed for the following functions, e.g.:
interrogation of the HLR to obtain routing data for a mobile terminating call
transfer of charging data to the HLR
K1103 / K1205 GSM
Tektronix
2-15
2.3.2.5 E-interface
x
/
Protocols used on E-Interface
MSC MSC
PCM30
MAP
MTP
ISUP TCAP
SCCP
The E-interface supplies traffic channels and signalling channels.
Interworking is performed for the following functions:
speech/data traffic
signalling between MSC and MSC for e.g.:
request of measurements in another MSC
basic handover from a MSC to another MSC
subsequent handover from a MSC to another MSC
reception / provision of call control information from / to the MSC
on handover
GSM K1103 / K1205
Tektronix 2-16
2.3.2.6 F-interface
x
/
Protocols used on F-Interface
MSC EIR
PCM30
TCAP
SCCP
MTP
MAP
The F-interface supplies signalling channels.
Interworking is performed e.g. for:
interrogation of the EIR and check the International Mobile Equipment
ldentity (IMEI)
K1103 / K1205 GSM
Tektronix
2-17
2.3.2.7 External interface
E.g. PLMN towards ISDN
x
/
Protocols on external interfaces
MSC
PLMN
e.g. ISDN
PCM30
SCCP
MTP
ISUP
TCAP
INAP
specified as an MSC-ISDN interworking interface
SS#7 including ISUP is used
Interworking to the ISDN is performed by the MSC for:
speech/data traffic
signalling for e.g.:
call control
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Lazydog Epg 2012a-M 2013a-MDokument4 SeitenLazydog Epg 2012a-M 2013a-MMichael PangkeregoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nokia MOP - Troubleshoot For Alarm & Measurement Not Available On NetAct, No Ports 60000 or 60001 Listening On SGSNDokument5 SeitenNokia MOP - Troubleshoot For Alarm & Measurement Not Available On NetAct, No Ports 60000 or 60001 Listening On SGSNMichael PangkeregoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nokia MOP - Troubleshoot For Alarm & Measurement Not Available On NetAct, No Ports 60000 or 60001 Listening On SGSNDokument5 SeitenNokia MOP - Troubleshoot For Alarm & Measurement Not Available On NetAct, No Ports 60000 or 60001 Listening On SGSNMichael PangkeregoNoch keine Bewertungen
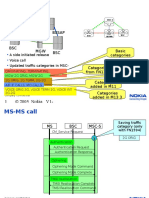
- MS-MS CallDokument8 SeitenMS-MS CallMichael PangkeregoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeVon EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (537)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Von EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Bewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (98)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeVon EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (5794)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingVon EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (400)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceVon EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (588)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureVon EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (474)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryVon EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (231)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceVon EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (895)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnVon EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (234)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItVon EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (838)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerVon EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (271)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaVon EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (266)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealVon EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (74)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaVon EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (45)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersVon EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (345)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyVon EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (2259)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreVon EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Von EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Bewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (121)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesVon EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (821)
- 06-901 Keyed Input SwitchesDokument4 Seiten06-901 Keyed Input Switchesmajed al.madhajiNoch keine Bewertungen
- MILL Series GB-1007 01Dokument20 SeitenMILL Series GB-1007 01Ady IonutNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hot Air Oven Or Dry Oven: نﺎﺸﻄﻋ ﻦﻴﺴﺣ ﻲﻠﻋ G @a - nv19Dokument2 SeitenHot Air Oven Or Dry Oven: نﺎﺸﻄﻋ ﻦﻴﺴﺣ ﻲﻠﻋ G @a - nv19حسين محمد مطرود كاظمNoch keine Bewertungen
- BM 81004 MuvDokument52 SeitenBM 81004 MuvHamza Abbasi AbbasiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Huawei ACU2 Wireless Access Controller DatasheetDokument12 SeitenHuawei ACU2 Wireless Access Controller Datasheetdexater007Noch keine Bewertungen
- ITP InstrumentationDokument9 SeitenITP InstrumentationzhangyiliNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Right Stuff PDFDokument4 SeitenThe Right Stuff PDFNeelank Tiwari100% (1)
- Curriculum Vitae: Augusto Javier Puican ZarpanDokument4 SeitenCurriculum Vitae: Augusto Javier Puican Zarpanfrank_d_1Noch keine Bewertungen
- Electro Magnetic Induction PDFDokument28 SeitenElectro Magnetic Induction PDFPuran BistaNoch keine Bewertungen
- BSR NH Circle Jaipur 2016Dokument103 SeitenBSR NH Circle Jaipur 2016vikash kumar50% (4)
- ElectronicsDokument3 SeitenElectronicsashishkumar218Noch keine Bewertungen
- Diesel Generator Set QSL9 Series Engine: Power GenerationDokument4 SeitenDiesel Generator Set QSL9 Series Engine: Power Generationsdasd100% (1)
- Optimasi Blending Pertalite Dengan Komponen Reformate Di PT. XYZ BalikpapanDokument7 SeitenOptimasi Blending Pertalite Dengan Komponen Reformate Di PT. XYZ BalikpapanFrizki AkbarNoch keine Bewertungen
- CovestroDokument2 SeitenCovestroRonaldo CamargoNoch keine Bewertungen
- EMOC 208 Installation of VITT For N2 Cylinder FillingDokument12 SeitenEMOC 208 Installation of VITT For N2 Cylinder Fillingtejcd1234Noch keine Bewertungen
- Computer Networking: A Top-Down Approach Featuring The InternetDokument27 SeitenComputer Networking: A Top-Down Approach Featuring The InternetmssacNoch keine Bewertungen
- Concept of Circulation in A Free Vortex FlowDokument55 SeitenConcept of Circulation in A Free Vortex FlowAnil KumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Aeroshell Fluid 41 PdsDokument2 SeitenAeroshell Fluid 41 Pdsja.moreno930Noch keine Bewertungen
- Ibr CalculationsDokument9 SeitenIbr Calculationsaroonchelikani67% (3)
- Delhi Public School Bangalore North ACADEMIC SESSION 2021-2022 Ut2 Revision Work Sheet TOPIC: Sorting Materials Into Group Answer KeyDokument6 SeitenDelhi Public School Bangalore North ACADEMIC SESSION 2021-2022 Ut2 Revision Work Sheet TOPIC: Sorting Materials Into Group Answer KeySumukh MullangiNoch keine Bewertungen
- AquaCal Tropical Brochure PDFDokument2 SeitenAquaCal Tropical Brochure PDFJC ParedesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sewerage & Sewage Treatment PlantDokument26 SeitenSewerage & Sewage Treatment PlantSyed ZamanNoch keine Bewertungen
- 4 Rec. ITU-R BS.775-3: Reference Loudspeaker Arrangement With Loudspeakers L/C/R and LS/RSDokument3 Seiten4 Rec. ITU-R BS.775-3: Reference Loudspeaker Arrangement With Loudspeakers L/C/R and LS/RSPaulo PiresNoch keine Bewertungen
- 4 and 6 Pole MotorDokument6 Seiten4 and 6 Pole Motorarajamani78100% (1)
- Experiment 5 DACDokument3 SeitenExperiment 5 DACABHISHEK SHARMANoch keine Bewertungen
- Huawei: Quidway Full Series Ethernet Routing SwitchesDokument90 SeitenHuawei: Quidway Full Series Ethernet Routing SwitchesWalter Aguiar0% (1)
- CoreJava Ratan CompleteMarerial PDFDokument398 SeitenCoreJava Ratan CompleteMarerial PDFSivaShankar100% (7)
- Wiring Color and Pin-Out Schematic Electronic Vessel Control EVC - C, D4/D6-DPH/DPRDokument2 SeitenWiring Color and Pin-Out Schematic Electronic Vessel Control EVC - C, D4/D6-DPH/DPRSivan Raj50% (2)
- 4.10) Arch Shaped Self Supporting Trussless Roof SpecificationsDokument11 Seiten4.10) Arch Shaped Self Supporting Trussless Roof Specificationshebh123100% (1)
- Folder Fiamm Neptune 2010 EngDokument4 SeitenFolder Fiamm Neptune 2010 EngchokribNoch keine Bewertungen