Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
03 - Differential Sticking
Hochgeladen von
Sam AbdulCopyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
03 - Differential Sticking
Hochgeladen von
Sam AbdulCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
12/12/2012
1
Differential Sticking
Filter Cake
Desired Filter Cake Properties:
Impermeable prevent further filtrate invasion
Thin minimum deposit of solids, effective cake building, min damage
Tough stays in place under dynamic conditions
Filter Cake usually does not form on impermeable formations like shale
Shale is very porous but the pore spaces are too small to allow filtrate invasion
Shale adsorbs water into the clay structure by osmotic pressure
12/12/2012
2
Filter Cake
Filter Cake usually does not form on impermeable formations like shale
Shale is very porous but the pore spaces are too small to allow filtrate invasion
Shale adsorbs water into the clay structure by osmotic pressure
5 Conditions Required for
Differential Sticking to Occur
1. Permeable formation in the open hole
2. Overbalanced to the formation
3. Thick filter cake
4. Pipe in contact with filter cake
5. Stationary pipe
12/12/2012
3
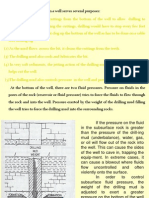
Impermeable Shale
1. Wellbore pressure >formation pressure (overbalanced).
2. Overbalance may cause fluid flow into formation. But since
shale is impermeable, fluid does not flow into the shale and
no filter cake forms.
3. Instead, overbalance generates a force which provides
mechanical support directly to the formation face.
4. Since no filter cake forms, when the drill string comes in
contact with the shale, the hydrostatic pressure very nearly
balances around the drill string because the contact area is
so small.
5. As a result, the differential sticking force is small and the
string usually will not get stuck.
12/12/2012
4
Permeable Sandstone
1. Filtrate enters permeable formation because of overbalance
and so filter cake accumulates.
2. An effective filter cake becomes impermeable with a thin
deposit of solids and stops further filtrate flowing into the
sandstone.
3. A poor filter cake remains permeable allowing filtrate to enter
the sandstone and a thick deposit of solids to build up on the
formation face.
4. When the drill string is adjacent to the sandstone, it may come
in contact with the filter cake deposited on the formation face.
5. While the drill string is moving, sufficient drilling fluid passes
between the drill string and the filter cake that the force from
hydrostatic pressure still very nearly balances around the drill
string.
6. As a result, the differential sticking force is small and the string
usually will not get stuck.
Permeable Sandstone
7. However, since the filter cake is still permeable, the filtrate
continues to flow into the sandstone. The mud that passes
between the drill string and the filter cake keeps it from
collapsing by keeping it wet.
8. When the drill string is in contact with the filter cake, the contact
area is much wider since the filter cake deforms around the drill
string.
9. Also, when the drill string becomes stationary while in contact
with the filter cake, there is no longer any fresh drilling fluid
passing between the drill string and the filter cake.
12/12/2012
5
Permeable Sandstone
10.Three events continue to happen:
1. There is no longer any fresh drilling fluid passing between the drill
string and the filter cake.
2. Filtrate continues to drain out of the filter cake between the drill string
and the sandstone.
3. Differential pressure is compressing the drill string against the filter
cake.
11.These events cause the filter cake between the drill string and
the sandstone to collapse which further increases the contact
area.
12.As a result, the differential sticking force is large and the string
is more likely to get stuck.
Permeable Sandstone
12/12/2012
6
Spotting Fluids and Filter Cake
Differential sticking does
not typically restrict
circulation in the annulus
This circulation capability
is used to free stuck pipe
Spotting fluids dehydrate
filter cake, causing it to
get thinner and sometimes
crack
This reduces sticking
force, allowing pipe to
come free more easily
1. Lower Filtration rate means thinner filter cake
2. Thinner filter cake means less contact area
3. Less contact area means less sticking force
Differential Sticking Warning Signs
Permeable formations in the open hole.
Mud weight creating high overbalance.
High or uncontrolled mud filtration rates.
Long unstabilized BHA segments
Increasing drag trend coming off the slips after
a connection.
Long stationary pipe times for connections,
surveys, etc.
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Wave Propagation in Drilling, Well Logging and Reservoir ApplicationsVon EverandWave Propagation in Drilling, Well Logging and Reservoir ApplicationsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fundamentals and Applications of Bionic Drilling FluidsVon EverandFundamentals and Applications of Bionic Drilling FluidsNoch keine Bewertungen
- ENM210 Cementing Operations Lecture 2 - Stage Cementing - 1 StageDokument8 SeitenENM210 Cementing Operations Lecture 2 - Stage Cementing - 1 StageHamid Reza BabaeiNoch keine Bewertungen
- CementingDokument27 SeitenCementingrezaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Drilling Engineering PresentationDokument49 SeitenDrilling Engineering PresentationFoxtyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hydraulic FracturingDokument31 SeitenHydraulic FracturingDeepesh KhandelwalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Spe - Iadc 79850 Kazakhstan PMCD Case StudyDokument21 SeitenSpe - Iadc 79850 Kazakhstan PMCD Case StudyThiban Chandra KeshavanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Guía para Tapones de CementoDokument15 SeitenGuía para Tapones de CementoJunnior López PintadoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Drilling With Casing Promises Major BenefitsDokument12 SeitenDrilling With Casing Promises Major BenefitsRaul Alberto Miranda LoayzaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Best Practice in Understanding and Managing Lost Circulation Challenges PDFDokument8 SeitenBest Practice in Understanding and Managing Lost Circulation Challenges PDFnguyenhuutruong100Noch keine Bewertungen
- Borehole: InstabilityDokument11 SeitenBorehole: InstabilitymeeeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Perf - Presentation AiymDokument32 SeitenPerf - Presentation AiymNaief Javaheri100% (1)
- Primary Cementing and Secondary CementingDokument25 SeitenPrimary Cementing and Secondary CementingAhmad RIfaiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Aerated DrillingDokument10 SeitenAerated DrillingDen YogaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 7 Hole ProblemsDokument23 SeitenChapter 7 Hole ProblemsAmine MimoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lesson 8b Introduction To UBDDokument57 SeitenLesson 8b Introduction To UBDbon1ngNoch keine Bewertungen
- Drilling Fluids For Drilling of Geothermal Wells - Hagen HoleDokument8 SeitenDrilling Fluids For Drilling of Geothermal Wells - Hagen HoleAdil AytekinNoch keine Bewertungen
- Well Engineering Guidlines For Hole CleaningDokument13 SeitenWell Engineering Guidlines For Hole CleaningWilliam100% (1)
- Solids Induced Pack-Off Packing Off - First ActionsDokument4 SeitenSolids Induced Pack-Off Packing Off - First ActionsBhagwal TravelsNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1.8 Casing Design1.9 Collapse, TensionDokument19 Seiten1.8 Casing Design1.9 Collapse, TensionRit Bangkruai100% (1)
- Drilling Practices For High Angle WellsDokument30 SeitenDrilling Practices For High Angle Wellseng20072007Noch keine Bewertungen
- Lost Circulation & Stuck Pipe Prevention QP Second CourseDokument47 SeitenLost Circulation & Stuck Pipe Prevention QP Second CourseMes JcNoch keine Bewertungen
- Drilling Engineering Ahmed-3Dokument83 SeitenDrilling Engineering Ahmed-3Loh Chun Liang100% (2)
- Stuck Pipe TOTALDokument41 SeitenStuck Pipe TOTALmosli_Noch keine Bewertungen
- CementingDokument27 SeitenCementingKrupal PatelNoch keine Bewertungen
- Group 4 - Expandable TubularDokument20 SeitenGroup 4 - Expandable TubularAzka Roby AntariNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sect-2 Diff StickDokument13 SeitenSect-2 Diff StickAbderrahim HaciniNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1 Drilling Fluids Overview & Principal Functions of Drilling Fluids-Lecture-1 PDFDokument37 Seiten1 Drilling Fluids Overview & Principal Functions of Drilling Fluids-Lecture-1 PDFأبراهيم كريم كاظمNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mr. Bentum CASINDokument19 SeitenMr. Bentum CASINSarkodie KwameNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cementing ActivityDokument42 SeitenCementing ActivityHiral jainNoch keine Bewertungen
- Completion and Workover FluidsDokument2 SeitenCompletion and Workover FluidsJit MukherheeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Shale Gas - Fracking: Presented byDokument20 SeitenShale Gas - Fracking: Presented byDiaz DavidNoch keine Bewertungen
- PE-12 Well Stimulation and Clean UpDokument14 SeitenPE-12 Well Stimulation and Clean Upeng20072007Noch keine Bewertungen
- Swab & Surge in DrillingDokument19 SeitenSwab & Surge in DrillingАбдуллах АNoch keine Bewertungen
- Centralizers & StopCollarsDokument19 SeitenCentralizers & StopCollarsSaurabh Parihar100% (1)
- L15 Cementing Lecture 1Dokument32 SeitenL15 Cementing Lecture 1advantage025Noch keine Bewertungen
- RT Bit Specific Energy SPE#00092194Dokument10 SeitenRT Bit Specific Energy SPE#00092194Asahel NuñezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Properties of Drilling FluidDokument3 SeitenProperties of Drilling FluidAnsell EwemeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pipe StickingDokument21 SeitenPipe StickingMarco100% (1)
- Remedial CementingDokument4 SeitenRemedial CementingColor RougeNoch keine Bewertungen
- 13 Remedial SqueezeDokument26 Seiten13 Remedial SqueezeLenin DiazNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cementing Operation - Part IDokument26 SeitenCementing Operation - Part IDoni KurniawanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Drilling Optimization PDFDokument22 SeitenDrilling Optimization PDFRoyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Dynamic Low Choke High Quality PDFDokument4 SeitenDynamic Low Choke High Quality PDFWCGNoch keine Bewertungen
- Drilling and Completion Egy Petroleum Engineer PDFDokument208 SeitenDrilling and Completion Egy Petroleum Engineer PDFRahma MejriNoch keine Bewertungen
- Leak Off Test: - Procedure - Maasp - Maximum Allowable Mud WeightDokument5 SeitenLeak Off Test: - Procedure - Maasp - Maximum Allowable Mud WeightSigit WiyonoNoch keine Bewertungen
- KL-22 Liner Integrity Test Procedures (Rev JJC)Dokument7 SeitenKL-22 Liner Integrity Test Procedures (Rev JJC)Hamza HamzaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hole Opening PracticesDokument13 SeitenHole Opening PracticesLuis HernándezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Drilling 16 Inch Section - Best PracticesDokument2 SeitenDrilling 16 Inch Section - Best PracticesYougchu Luan100% (1)
- Hydraulic Fracturing PDFDokument22 SeitenHydraulic Fracturing PDFpoojaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cementing BasicsDokument79 SeitenCementing BasicsAngel PadillaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Special Problems During DrillingDokument60 SeitenSpecial Problems During DrillingDanian PrimasatryaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Well Control FdreDokument27 SeitenWell Control FdreKhairi OmarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Drilling Application: Name of Company: Well Name & Number: DateDokument1 SeiteDrilling Application: Name of Company: Well Name & Number: DatescrbdgharaviNoch keine Bewertungen
- SPE-203872-MS - Multistage FracutringDokument24 SeitenSPE-203872-MS - Multistage Fracutringzach100% (1)
- 07 Well ProblemsDokument47 Seiten07 Well ProblemsMustafa0108910% (1)
- Section02 Drilling ApparatusDokument31 SeitenSection02 Drilling ApparatusMohamed ElshoraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Plugbak Sidetracks - Open HoleDokument5 SeitenPlugbak Sidetracks - Open HoleAdel Ahmed AlkhaligyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Measurement While Drilling: Signal Analysis, Optimization and DesignVon EverandMeasurement While Drilling: Signal Analysis, Optimization and DesignNoch keine Bewertungen
- Research On Sustainable Development of Textile Industrial Clusters in The Process of GlobalizationDokument5 SeitenResearch On Sustainable Development of Textile Industrial Clusters in The Process of GlobalizationSam AbdulNoch keine Bewertungen
- Gas BangladeshDokument34 SeitenGas BangladeshSam AbdulNoch keine Bewertungen
- Production Shari C T Ac S (PSC) : NG On R TDokument2 SeitenProduction Shari C T Ac S (PSC) : NG On R TSam AbdulNoch keine Bewertungen
- General Inquiries: Mphil / PHD Program OfficeDokument1 SeiteGeneral Inquiries: Mphil / PHD Program OfficeSam AbdulNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bapex FileDokument81 SeitenBapex FileSam AbdulNoch keine Bewertungen
- Approval Process Complaints and Appeals: Click To Edit Master Subtitle StyleDokument37 SeitenApproval Process Complaints and Appeals: Click To Edit Master Subtitle StyleSam AbdulNoch keine Bewertungen
- DdoDokument23 SeitenDdoSam AbdulNoch keine Bewertungen
- B.SC BOTANY Semester 5-6 Syllabus June 2013Dokument33 SeitenB.SC BOTANY Semester 5-6 Syllabus June 2013Barnali DuttaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Aleksandrov I Dis 1-50.ru - enDokument50 SeitenAleksandrov I Dis 1-50.ru - enNabeel AdilNoch keine Bewertungen
- Impact of Advertising On Consumers' Buying Behavior Through Persuasiveness, Brand Image, and Celebrity EndorsementDokument10 SeitenImpact of Advertising On Consumers' Buying Behavior Through Persuasiveness, Brand Image, and Celebrity Endorsementvikram singhNoch keine Bewertungen
- All You Need To Know About Egg YolkDokument7 SeitenAll You Need To Know About Egg YolkGolden Era BookwormNoch keine Bewertungen
- WebLMT HelpDokument12 SeitenWebLMT HelpJoão LopesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Monergism Vs SynsergismDokument11 SeitenMonergism Vs SynsergismPam AgtotoNoch keine Bewertungen
- AlpaGasus: How To Train LLMs With Less Data and More AccuracyDokument6 SeitenAlpaGasus: How To Train LLMs With Less Data and More AccuracyMy SocialNoch keine Bewertungen
- Study 107 - The Doctrine of Salvation - Part 8Dokument2 SeitenStudy 107 - The Doctrine of Salvation - Part 8Jason MyersNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fss Presentation Slide GoDokument13 SeitenFss Presentation Slide GoReinoso GreiskaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Richardson Heidegger PDFDokument18 SeitenRichardson Heidegger PDFweltfremdheitNoch keine Bewertungen
- Log Building News - Issue No. 76Dokument32 SeitenLog Building News - Issue No. 76ursindNoch keine Bewertungen
- Assignment#10 Global Strategy and The Multinational CorporationDokument1 SeiteAssignment#10 Global Strategy and The Multinational CorporationAnjaneth A. VillegasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Iec TR 61010-3-020-1999Dokument76 SeitenIec TR 61010-3-020-1999Vasko MandilNoch keine Bewertungen
- Digital MetersDokument47 SeitenDigital MetersherovhungNoch keine Bewertungen
- CX Programmer Operation ManualDokument536 SeitenCX Programmer Operation ManualVefik KaraegeNoch keine Bewertungen
- AnticyclonesDokument5 SeitenAnticyclonescicileanaNoch keine Bewertungen
- HirePro Video Proctored Online-Instruction Sheet - Bain IndiaDokument1 SeiteHirePro Video Proctored Online-Instruction Sheet - Bain Indiaapoorv sharmaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Crown WF-3000 1.2Dokument5 SeitenCrown WF-3000 1.2Qirat KhanNoch keine Bewertungen
- User S Manual AURORA 1.2K - 2.2KDokument288 SeitenUser S Manual AURORA 1.2K - 2.2KEprom ServisNoch keine Bewertungen
- Golf Croquet Refereeing Manual - Croquet AustraliaDokument78 SeitenGolf Croquet Refereeing Manual - Croquet AustraliaSenorSushi100% (1)
- SMC 2D CADLibrary English 1Dokument590 SeitenSMC 2D CADLibrary English 1Design IPGENoch keine Bewertungen
- Mcdonald 2016Dokument10 SeitenMcdonald 2016Andrika SaputraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mastertop 1230 Plus PDFDokument3 SeitenMastertop 1230 Plus PDFFrancois-Noch keine Bewertungen
- Lesson PlanDokument2 SeitenLesson Plannicole rigonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Making Effective Powerpoint Presentations: October 2014Dokument18 SeitenMaking Effective Powerpoint Presentations: October 2014Mariam TchkoidzeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Howard R700X - SPL - INTDokument44 SeitenHoward R700X - SPL - INTJozsefNoch keine Bewertungen
- Powerpoint Speaker NotesDokument4 SeitenPowerpoint Speaker Notesapi-273554555Noch keine Bewertungen
- The Indonesia National Clean Development Mechanism Strategy StudyDokument223 SeitenThe Indonesia National Clean Development Mechanism Strategy StudyGedeBudiSuprayogaNoch keine Bewertungen
- SHCDokument81 SeitenSHCEng Mostafa ElsayedNoch keine Bewertungen
- 3 ALCE Insulators 12R03.1Dokument12 Seiten3 ALCE Insulators 12R03.1Amílcar Duarte100% (1)