Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Computer System Components: Computing (Informatica)
Hochgeladen von
Lorena ArroyoOriginalbeschreibung:
Originaltitel
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Computer System Components: Computing (Informatica)
Hochgeladen von
Lorena ArroyoCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
COMPUTING (INFORMATICA)
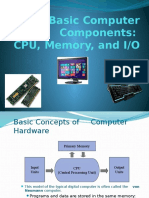
Computer: an electronic machine that can store, organize and find information, do calculations and control other machines:a personal computer Our sales information is processed by computer. a computer program computer software / hardware / graphics a computer error computer-aided designsee also desktop computer, microcomputer, personal computer, supercomputer. Computer System Components CPU or Central Processing Unit: This is the brain of the computer. It has a basic calculating unit called the Arithmetic Logic Unit (ALU), a Control Unit that manages what it does, and a very small amount of memory. The CPU and internal memory make up the computer proper. Internal Memory: This is where information is stored in the computer. It can be thought of as a long line of pigeonholes, each of which can hold one tem of information. Each pigeonhole has a unique address or location so that the CPU can find it. There are two basic varieties of memory: ROM (read only memory) which contains permanent machine instructions and RAM (random access memory) which is temporary memory where applications are stored. The contents of RAM are lost when the power is cut off. Peripherals: The generic term for anything that attaches to the computer proper. Included are things like the keyboard, monitor, printer,etc. These are tipically classified as input and output devices. Every peripheral has an interface (interface= a connection between two pieces of electronic equipment) or go-between that allows it to communicate with the computer. Input Devices: any devices that put information into the computer. Common examples are the keyboard, mouse,etc. Output Devices: any devices that allow the user to receive information from the computer. Common examples include the monitor (or CRT or LCD),printer, etc. External or Mass Storage: any device that allows for permanent storage and retrieval of information. This can be thought of as a special kind of input/output(I/O) device, or, alternatively, it can be viewed as a permanent extensin of RAM. Common example magnetic disk. In operation, a computer system involves a complex interplay between its components. The CPU rapidly performs calculations and moves information between external storage, internal memory, input devices, and output devices. Any computer system performs three basic funtions: input, processing, and output. At its most basic, the computer treats everything as numbers. Off can be represented with a 0 and on with a 1. So, digital computers work with binary numbers. (interplay= the effect that two or more things have on each other) Hardware and Software: The physical parts of a computer system are called hardware. Software is the programs or instructions that make the hardware work.
Keyboard: Input device, it is used to type the letters. Speaker: Output device, it helps you to listen. Screen: Output device, it helps you to see. Mouse: Input device, used to click things on the screen. Tower: It contains the CPU. Earphones: Used in your head, to hear. Webcam: Used to introduce images. Template: A model for producing others. Spreadsheets: A computer program. Basic Computer Operations Open: Abrir Close: Cerrar Save: Guardar Save as: Guardar como Select: seleccionar Print: imprimir Enter: entrar Cut: cortar Delete: borrar Press: apretar Copy: copiar Insert: insertar Load: cargar Paste: unir/pegar Merge: combinar
Log in/on: access pick up something: check Log off/out: stop Scroll across/down/up something: move Hack into something: get information from someone secretly Zoom in/out: to show the object closer/further Computing Verbs Insert.a floppy disk Make.a back up copy Run...a program Surf...the internet send.an e-mail click on.. an icon highlight..the part of the text back upa copy of important files. (respaldo)
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Basic Computer Course, For Beginners and Technology StudentsVon EverandBasic Computer Course, For Beginners and Technology StudentsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Computer EssentialsDokument2 SeitenComputer EssentialsRocio A RubecindoNoch keine Bewertungen
- What Is Computer Hardware (IT FUNDAMNETALS)Dokument6 SeitenWhat Is Computer Hardware (IT FUNDAMNETALS)JSON AMARGANoch keine Bewertungen
- Basic Fundamentals of ComputerDokument5 SeitenBasic Fundamentals of ComputerAyushi AgrawalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Workshop - I Lab ManualDokument36 SeitenWorkshop - I Lab Manualatulya singhNoch keine Bewertungen
- Course: Introduction To Computers: Basic Computer ConceptsDokument18 SeitenCourse: Introduction To Computers: Basic Computer ConceptsMaha AliNoch keine Bewertungen
- Module IT COM1 Unit 4Dokument15 SeitenModule IT COM1 Unit 4Joshua DalmacioNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1basic Computer OrganizationDokument13 Seiten1basic Computer OrganizationAdrija SinghNoch keine Bewertungen
- MS Office 2007 - NotesDokument89 SeitenMS Office 2007 - NotesmanuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Intorduction To Computer SystemDokument7 SeitenIntorduction To Computer SystemMohsin Ali AwanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Components of ComputerDokument9 SeitenComponents of ComputersanidhyaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Module 3Dokument9 SeitenModule 3bscomputersciencelsstiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Computer: Made by Surbhi JainDokument25 SeitenComputer: Made by Surbhi JainniveshjainNoch keine Bewertungen
- Class - XI - IT - About Computer FundamentalsDokument15 SeitenClass - XI - IT - About Computer Fundamentalsnakulshali1Noch keine Bewertungen
- Meeting 2 Inside ComputerDokument16 SeitenMeeting 2 Inside ComputerFelix Rizky LesmanaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Computer Has A Full FormDokument48 SeitenComputer Has A Full FormDeepak kr. patelNoch keine Bewertungen
- Computer OrganisationDokument25 SeitenComputer OrganisationJessy RajasundarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Computer Lecture # 1Dokument7 SeitenComputer Lecture # 1minha.bl987Noch keine Bewertungen
- Peripheral DevicesDokument2 SeitenPeripheral DevicesAngelus Mortis PrimeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Grade 9 Final ModuleDokument3 SeitenGrade 9 Final Moduletonton OlitaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Parts of Computer and Input and Output DevicesDokument27 SeitenParts of Computer and Input and Output Devicesdua tanveerNoch keine Bewertungen
- Intoduction It Hardware-1Dokument11 SeitenIntoduction It Hardware-1Nishitha PriyankaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Intoduction It Hardware-1Dokument11 SeitenIntoduction It Hardware-1Nishitha PriyankaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Unit 2. Hardware ComponentsDokument10 SeitenUnit 2. Hardware ComponentsRaju KumaarNoch keine Bewertungen
- 01 Notes Hardware ConceptsDokument11 Seiten01 Notes Hardware ConceptsAbhinav AnandNoch keine Bewertungen
- Casi CompletandoDokument13 SeitenCasi CompletandoAndy Josè ReyesNoch keine Bewertungen
- HMHDokument4 SeitenHMHCraqihnoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Introduction To ComputerDokument23 SeitenIntroduction To ComputerLourdes Idanan BancoroNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter Two:-: Computer SystemDokument134 SeitenChapter Two:-: Computer SystemTolera TamiruNoch keine Bewertungen
- 105-P02 (Compatibility Mode)Dokument15 Seiten105-P02 (Compatibility Mode)Ahmad Thariq RahmatullahNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lesyituuson 4 Looking Inside The CoDokument33 SeitenLesyituuson 4 Looking Inside The CoJohn Mark De JesusNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hardware DevicesDokument10 SeitenHardware DevicesToto AbdulazizNoch keine Bewertungen
- Computer AwernesDokument145 SeitenComputer AwernessekharNoch keine Bewertungen
- Overview of A Computer System.Dokument32 SeitenOverview of A Computer System.grenamoNoch keine Bewertungen
- C Program NoteDokument77 SeitenC Program NoteMityaprangya DasNoch keine Bewertungen
- IT Infrastuctural Management NotesDokument26 SeitenIT Infrastuctural Management NotesAayush JainNoch keine Bewertungen
- Unit - 1: 1. Functional UnitsDokument34 SeitenUnit - 1: 1. Functional UnitsManoj gollapelliNoch keine Bewertungen
- PDF Inggris GabunganDokument135 SeitenPDF Inggris GabunganRiadhi RaznanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ict Hand BookDokument25 SeitenIct Hand BookSamaeel UrielNoch keine Bewertungen
- Computer Education: Basic Concepts in Computer OperationDokument28 SeitenComputer Education: Basic Concepts in Computer OperationEINSTEIN - Stephen Troy C. AlgenteraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Comp Subj. k1Dokument6 SeitenComp Subj. k1Christian BaytanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Xi Ip 2013-14Dokument136 SeitenXi Ip 2013-14Ravi JhaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Introduction To Computers (Concepts) : ObjectivesDokument6 SeitenIntroduction To Computers (Concepts) : Objectivesshraddha malhotraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Basic Concepts of Computer (1.25 MB)Dokument32 SeitenBasic Concepts of Computer (1.25 MB)poo235Noch keine Bewertungen
- CTE I Computer PartsDokument30 SeitenCTE I Computer PartsYasir RajpootNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lecture 1 WhatiscomputerDokument30 SeitenLecture 1 WhatiscomputerMARIELLA TRACY BANDONG100% (1)
- Computer 1: (Introduction To Computer Concepts and Software)Dokument32 SeitenComputer 1: (Introduction To Computer Concepts and Software)Cristin Porcadilla AranteNoch keine Bewertungen
- Computer Application in HRMDokument10 SeitenComputer Application in HRMshazzymutukuNoch keine Bewertungen
- ICT 1101 - PC Hardware Assembly 02 Fall 2021Dokument24 SeitenICT 1101 - PC Hardware Assembly 02 Fall 2021yvan dollarsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Igcse Ict Notes CompressDokument25 SeitenIgcse Ict Notes CompressYara MohmoudNoch keine Bewertungen
- Computers: Inventor of ComputerDokument25 SeitenComputers: Inventor of ComputerJohn Philip VuelbaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ict AssignmentDokument13 SeitenIct AssignmentAnita LopokoiyitNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter OneDokument65 SeitenChapter Oneaddim6748Noch keine Bewertungen
- ENGLAISDokument15 SeitenENGLAISDan BurgNoch keine Bewertungen
- Unit 1 - Computer SystemDokument8 SeitenUnit 1 - Computer SystemAkashNoch keine Bewertungen
- Class Notes - Computer HardwareDokument6 SeitenClass Notes - Computer Hardwaregerrad cortezNoch keine Bewertungen
- ITC Week 1Dokument27 SeitenITC Week 1Fareeha MunawarNoch keine Bewertungen
- ComputerDokument8 SeitenComputerBeth AlcontinNoch keine Bewertungen
- Flash CardsDokument4 SeitenFlash CardsLorena ArroyoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Different Types of MusicDokument37 SeitenDifferent Types of MusicLorena Arroyo100% (1)
- Plans MusicDokument9 SeitenPlans MusicLorena ArroyoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Present To Past: Write The Sentences in The Past .Use TheDokument2 SeitenPresent To Past: Write The Sentences in The Past .Use TheLorena ArroyoNoch keine Bewertungen
- English PronunciationDokument7 SeitenEnglish PronunciationLorena Arroyo50% (2)
- Kinds of SentencesDokument11 SeitenKinds of SentencesLorena ArroyoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bowerman 1974 LearningStructureCausativeVerbsDokument37 SeitenBowerman 1974 LearningStructureCausativeVerbsLorena ArroyoNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Wheels On The Bus Learn ItDokument5 SeitenThe Wheels On The Bus Learn ItLorena ArroyoNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Role of The Teacher in Teaching and LearningDokument4 SeitenThe Role of The Teacher in Teaching and LearningLorena ArroyoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Collective NounsDokument2 SeitenCollective NounsLorena ArroyoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Rapacity: Henry VII (Dokument1 SeiteRapacity: Henry VII (Lorena ArroyoNoch keine Bewertungen
- When Your Teacher Tells You Time Is Up, Count Your Points. How Many Points Total Do You Have? - (DO NOT Repeat Names !)Dokument1 SeiteWhen Your Teacher Tells You Time Is Up, Count Your Points. How Many Points Total Do You Have? - (DO NOT Repeat Names !)Lorena ArroyoNoch keine Bewertungen
- BattleshipDokument0 SeitenBattleshipLorena ArroyoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Planning Lesson - Speaking Skill: Improving Speaking Confidence When Using Question FormsDokument2 SeitenPlanning Lesson - Speaking Skill: Improving Speaking Confidence When Using Question FormsLorena ArroyoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Listening and SpeakingDokument3 SeitenListening and SpeakingLorena ArroyoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Student Motivation Is A NecessityDokument5 SeitenStudent Motivation Is A NecessityLorena ArroyoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Planning Lesson - Listening Skill: Improving Listening Confidence When Using Question FormsDokument1 SeitePlanning Lesson - Listening Skill: Improving Listening Confidence When Using Question FormsLorena ArroyoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Suggestions To Break The Ice in The Classroom: Introduce MyselfDokument7 SeitenSuggestions To Break The Ice in The Classroom: Introduce MyselfLorena ArroyoNoch keine Bewertungen
- IxChariot Trade-Up Program FAQsDokument7 SeitenIxChariot Trade-Up Program FAQsSaiful Friday OsmanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Deploying Oracle SOA Suite 12c On AWS: April 2020Dokument24 SeitenDeploying Oracle SOA Suite 12c On AWS: April 2020dileep.sNoch keine Bewertungen
- User Manual: Wireless AC1200 Dual Band Access PointDokument99 SeitenUser Manual: Wireless AC1200 Dual Band Access PointNicolas MunozNoch keine Bewertungen
- Migration Guide Sentinel HASP To Sentinel LDKDokument30 SeitenMigration Guide Sentinel HASP To Sentinel LDKRazvan Marin CalugarasuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Business Data Communications and Networking: Jerry Fitzgerald and Alan DennisDokument48 SeitenBusiness Data Communications and Networking: Jerry Fitzgerald and Alan DennisTuan DoanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lab CCNA Security ACLDokument4 SeitenLab CCNA Security ACLAngel SczNoch keine Bewertungen
- HP Pavilion Dv6000 Dv6500 Dv6600 Dv6700 Dv9000 Dv9500 - DA0AT3MB8F0 - QUANTA AT3 - SC (Intel) - Rev 1ADokument48 SeitenHP Pavilion Dv6000 Dv6500 Dv6600 Dv6700 Dv9000 Dv9500 - DA0AT3MB8F0 - QUANTA AT3 - SC (Intel) - Rev 1Agbouret0% (1)
- Presentation On Shortcut Keys Byy Seerat AbbasDokument21 SeitenPresentation On Shortcut Keys Byy Seerat AbbasSalaar GhaznaviNoch keine Bewertungen
- CLEVO Notebook NH55 NH58RCQDokument5 SeitenCLEVO Notebook NH55 NH58RCQMsi InfotronicNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cek LengkapDokument4 SeitenCek LengkapYudha PrakosaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Portal Info StubDokument12 SeitenPortal Info StubEti NasilaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Git Commands Cheat Sheet by PhoenixNAPDokument1 SeiteGit Commands Cheat Sheet by PhoenixNAPsahuaditya2009Noch keine Bewertungen
- Vmware Vsan Licensing GuideDokument14 SeitenVmware Vsan Licensing Guideanhsang123Noch keine Bewertungen
- Siebel - Native - Gateway - Cluster - Overview - Videodoc ID 2768007 - 1Dokument37 SeitenSiebel - Native - Gateway - Cluster - Overview - Videodoc ID 2768007 - 1sasankgogineniNoch keine Bewertungen
- SP PuttyDokument97 SeitenSP PuttyAnonymous a6l0CQNoch keine Bewertungen
- Konfigurasi Routing CiscoDokument12 SeitenKonfigurasi Routing Ciscodiki alfariziNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lastexception 63723924347Dokument1 SeiteLastexception 63723924347Misty RivertuneNoch keine Bewertungen
- Oracle Parameters and Their DescriptionsDokument9 SeitenOracle Parameters and Their DescriptionsPILLINAGARAJUNoch keine Bewertungen
- 5.3.1.3 Packet Tracer - Identify MAC and IP AddressesDokument5 Seiten5.3.1.3 Packet Tracer - Identify MAC and IP AddressesParthPatel88% (8)
- 1.6 Next Generation Server Access Architecture With Cisco Nexus 6000 Eddie Tan1 2Dokument44 Seiten1.6 Next Generation Server Access Architecture With Cisco Nexus 6000 Eddie Tan1 2txNoch keine Bewertungen
- Keyscape 1.1Dokument281 SeitenKeyscape 1.1DoonooNoch keine Bewertungen
- Clasic ShellDokument18 SeitenClasic ShellIvan MarianNoch keine Bewertungen
- NSX-T Reference Design Guide 3-0 PDFDokument300 SeitenNSX-T Reference Design Guide 3-0 PDFkdjhNoch keine Bewertungen
- Unit 2 StudocuDokument42 SeitenUnit 2 StudocuAzhagu MeenuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Install AdopisoftDokument2 SeitenInstall AdopisoftphubwieNoch keine Bewertungen
- Plastic Memory ReportDokument31 SeitenPlastic Memory ReportAjit Padmarajan100% (2)
- How To Install Nonpdrm PluginDokument1 SeiteHow To Install Nonpdrm PluginanrihmNoch keine Bewertungen
- Firmware Change/Update SONY Xperia X Performance: Necessary Tools and DriversDokument19 SeitenFirmware Change/Update SONY Xperia X Performance: Necessary Tools and DriversPadloe BmjNoch keine Bewertungen
- NFT Tutorial PDFDokument33 SeitenNFT Tutorial PDFlist_courseNoch keine Bewertungen
- Virtualization TechniquesDokument22 SeitenVirtualization TechniquesrashmiNoch keine Bewertungen