Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Hormones Phyana
Hochgeladen von
Claire Anne CaringalOriginalbeschreibung:
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Hormones Phyana
Hochgeladen von
Claire Anne CaringalCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
#9 Caringal, Claire Anne E.
2BMT
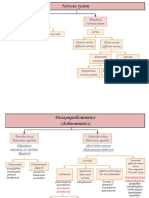
HORMONE
Insulin
Source
Pancreas Pancreas
Stimulus for release
Elevated blood glucose levels Low bs
Inhibitor
Glucagon Amilyn
Effects
Increases uptake and use of glucose and amino acids Increases breakdown of glycogen and release of glucose into the circulatory system Increased rate of breakdown of bone by osteoclasts; increased reabsorption of Calcium in kidneys; increased absorption of Calcium from the small intestine; increased vitamin D synthesis; increased blood Calcium levels Decreases the rate of bone breakdown; prevents large increases of blood calcium levels following a meal Avoid disease due to deficiency Conserves water; constricts blood vessels
Glucagon Parathyroid glands Low bl. Calcium stimulate, Produce and release of PTH Calcitonin
PTH
Thyroid Gland Calcitonin Bone Posterior Pituitary Gland ADH/AVP
High bl. Calcium levels (humoral)
Osteoblast
Vitamin D
PTH respectively dehydration (humoral control)
Caffeine Hydrated. Alcohol is an inhibitor.the hangover is a result of alcohol dehydration. Caffeine also inhibit ADH. Catecholamines
Oxytocin
Posterior Pituitary Gland
GH
Anterior Pituitary Gland
Positive Feedback, stretch receptors in the vagina and touch receptors around the nipple for milk ejection (lactation) Exercise, hypoglycaemia
Increase uterine contractions Increases milk letdown for mammary glands
Somatostatin
ACTH
Anterior Pituitary Gland
CRH (corticotropic releasing hormone) from hypothalamus
Somatostatin
Adrenal Cortex Cortisol
Inc. ACTH, intense prolong exercise
ACTH
Increases gene expression, breakdown of lipids, and release of fatty acids from cells; increases blood glucose levels Increases secretion of glucocorticoid hormones, such as cortisol; increases skin pigmentation at high concentrations Increase fat and protein breakdown, increase glucose synthesis from amino acids; increase blood nutrient levels; inhibit inflammation and immune response
Adrenal Cortex Aldosterone
ACTH at times of stress, Low Na; reninangiotensin System triggered by kidney
Glyccyrrhetinic Acid
Increase rate of sodium transport into body; increase rate of potassium excretion; secondarily favour water retention Insignificant in males; increase female sexual drive, growth of pubic and axillary hair Promotes ovulation and progesterone production in ovary; promotes testosterone synthesis and support for sperm cell production in testis Promotes follicle maturation and estrogen secretion in ovary; promotes sperm cell production in testis
Adrenal Androgen
Adrenal Cortex
ACTH
Abiratrone Acetate
LH
Anterior Pituitary Gland
GnRH from hypothalamus
Estrogen and androgens
Anterior Pituitary Gland FSH
beg. of puberty and all thru reprod. yrs., the hypothalamus will release GNrH (Gonadotropin Releasing Hormone)
Sex Steroids
Progesterone
Reproductive OrgansOvaries
LH
Estrogen
Estrogen
Reproductive OrgansOvaries
Inc. FSH Inc. LH
Gonadotroponin
Reproductive organs- Testes Testosterone
Inc. FSH Inc. LH , stress
Antiandrogens
Aid in uterine and mammary gland development and function, external genitalia structure, secondary sexual characteristics, sexual behaviour, menstrual cycle Aid in uterine and mammary gland development and function, external genitalia structure, secondary sexual characteristics, sexual behaviour, menstrual cycle Aid in sperm cell production, maintenance of functional reproductive organs, secondary sexual characteristics, sexual behaviour Milk production in lactating women; increased response of follicle in females to LH and FSH; unclear function in males
Anterior Pituitary Gland Prolactin
PRF from hypothalamus, also when already breastfeeding, the infant sucking on the nipple will cause her to make more milk TRH from hypothalamus when thyroid hormone levels in the bl. are low
Estrogen and progesterone
TSH
Anterior Pituitary Gland
Somatostatin
Increased thyroid hormone secretion
Thyroid Gland T3/T4
Low levels of T3 & T4 in the blood trigger hypothal. To release TRH
Somatostatin
Thymosin Erythropoietin MSH Renin Angiotensin ANP Leptin hCG
Thymus Kidneys
THS Oxygen, hypoxic stress
Sex hormones Monocyte conditioned medium Dopamine ANH
accelerates the rate of cellular metabolism (mitochondrial breakdown of carbohydrates, rate of protein syn, and lipid breakdown) in every cell Promotes immune system development and function RBC Production
Pituitary gland Livers
CRH Negative, Dec. Bp
Angiotensin I Angiotesin II Heart
Negatve, Dec. Bp Sympathetic stimulation of B-adrew receptosAntigen 1 Food intake Pregnancy Stimulated by daylight (circardian rythm)
ARB Elevated endogenous kinin levels Decreased number of adipocytes Child delivery Light
Stimulate production and release of melanin Mediates extracellular volume at arterial vasoconstriction Vasoconstriction Vasodilatation
Adipose Tissue Placenta Pineal Gland
Suppresses Appetite Maintenance of corpus uuteum Inhibits secretion of gonadotropin-releasing hormone, thereby inhibiting reproduction
Melatonin Seminal Vesicle
PG/LT
Pregnancy
Aspirin
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeVon EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (5794)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreVon EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (1090)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItVon EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (838)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceVon EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (895)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceVon EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (588)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeVon EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (537)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersVon EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (344)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureVon EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (474)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesVon EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (821)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Von EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Bewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (121)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerVon EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (271)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingVon EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (400)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyVon EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (2259)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Von EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Bewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (98)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaVon EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (266)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryVon EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (231)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnVon EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (234)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealVon EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (74)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaVon EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (45)
- Endocrine SystemDokument27 SeitenEndocrine SystemAlen Vukosavljevic100% (2)
- Renin Angiotensin Aldosterone SystemDokument3 SeitenRenin Angiotensin Aldosterone SystemDivya Ranasaria100% (1)
- Test Bank Endocrine PDFDokument29 SeitenTest Bank Endocrine PDFWenzy Cruz100% (3)
- Veterinary PeptidesDokument26 SeitenVeterinary PeptidesImran KhanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hormon Hipotalamus HipofisisDokument20 SeitenHormon Hipotalamus HipofisisSyam UnhasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 22 - Chemical Coordination and IntegrationDokument4 SeitenChapter 22 - Chemical Coordination and IntegrationanuminiatureNoch keine Bewertungen
- ROCHE-LIVA Ready Reagent BECHAMN SYSMEXDokument9 SeitenROCHE-LIVA Ready Reagent BECHAMN SYSMEXLimon Medikal Sistemleri Limon MedicalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Biorad Lyphocheck Immunoassay Plus Control (Ref) 370,: HumanDokument1 SeiteBiorad Lyphocheck Immunoassay Plus Control (Ref) 370,: HumanMaherNoch keine Bewertungen
- Luteinizing Hormone: Luteinizing Hormone (LH, Also Known As Lutropin andDokument9 SeitenLuteinizing Hormone: Luteinizing Hormone (LH, Also Known As Lutropin andFuzz FuzzNoch keine Bewertungen
- Brain Mapping KMB 1 + PenilaianDokument5 SeitenBrain Mapping KMB 1 + PenilaianAnisNoch keine Bewertungen
- Precociou S Puberty: BY Vishnupriya Ravimohandoss Year-6 Group-1Dokument31 SeitenPrecociou S Puberty: BY Vishnupriya Ravimohandoss Year-6 Group-1Priya RaviNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pharmacology of Sex HormonesDokument6 SeitenPharmacology of Sex Hormonesarnold23456100% (4)
- Hormone/Contraceptive Use in O&G: Provera Acute Maintena NceDokument2 SeitenHormone/Contraceptive Use in O&G: Provera Acute Maintena Ncekhangsiean89Noch keine Bewertungen
- Sampada Sanjay SotreDokument39 SeitenSampada Sanjay SotreAbdul AhadNoch keine Bewertungen
- молитва мальчик crosti.ru) - colorDokument14 Seitenмолитва мальчик crosti.ru) - colorAna PetrovNoch keine Bewertungen
- Grade 10 QuizDokument2 SeitenGrade 10 QuizSHEILA MAE CONCEPCIONNoch keine Bewertungen
- Endocrine Gland - Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaDokument5 SeitenEndocrine Gland - Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediakbhattacNoch keine Bewertungen
- مذكرة فارماكولوجي روعةDokument56 Seitenمذكرة فارماكولوجي روعةKomang Gede Suwija Negara100% (1)
- Pl-Tosoh-Maret 2020Dokument3 SeitenPl-Tosoh-Maret 2020Labkesda Kota BaubauNoch keine Bewertungen
- Puberty and The HPG AxisDokument36 SeitenPuberty and The HPG AxiskjhkaNoch keine Bewertungen
- CBSE Quick Revision Notes (Class-11 Biology) Chapter-22 Chemical Coordination and IntegrationDokument3 SeitenCBSE Quick Revision Notes (Class-11 Biology) Chapter-22 Chemical Coordination and IntegrationNANDAKUMAR BABUNoch keine Bewertungen
- Gonad in The BodyDokument10 SeitenGonad in The Bodyjuliana leonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tabela Grifo LaboratoryDokument11 SeitenTabela Grifo LaboratoryGRIFO DIVULGA100% (2)
- Up-To-Date Review About Minipuberty and Overview On Hypothalamic-Pituitary-Gonadal Axis Activation in Fetal and Neonatal LifeDokument9 SeitenUp-To-Date Review About Minipuberty and Overview On Hypothalamic-Pituitary-Gonadal Axis Activation in Fetal and Neonatal LifeBerry BancinNoch keine Bewertungen
- اسئلة فسلجة ثاني كورس ثانيDokument5 Seitenاسئلة فسلجة ثاني كورس ثانيRad RYNoch keine Bewertungen
- Adrenal GlandDokument22 SeitenAdrenal GlandSurvey IndiaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Aditiawati - No Signs of Puberty PDFDokument43 SeitenAditiawati - No Signs of Puberty PDFJayantiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Endocrine Glands Mini ProjectDokument7 SeitenEndocrine Glands Mini ProjectJoy-Ann NuptialNoch keine Bewertungen
- Introduction To EndocrinologyDokument22 SeitenIntroduction To EndocrinologyUrwah KhanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Central Precocius PubertyDokument29 SeitenCentral Precocius PubertyNurhidayat DayatNoch keine Bewertungen