Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Types of Banks
Hochgeladen von
kingvelCopyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Types of Banks
Hochgeladen von
kingvelCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Different Types of Banks & Banking Activities
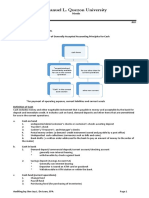
TYPES OF BANKS AND BANKING ACTIVITIES Schedul ed And Non-Schedul ed Banks In India t he cent r al banking au t hor it y is t he Reser v e Bank of India. It is also r efer r ed t o as t he Apex Bank. It fu nct ions u nder an act called The Reser v e Bank of India Act , 1 9 3 4 . All t he banks and ot her financial inst it u t ions oper at ing in India com e u nder t he m onit or ing and cont r ol of RBI. RBI cont r ols t he banking sect or in India t hr ou gh an Act called The Banking Regu lat ions Act 1 9 4 9 . In t he past , when t her e wer e v er y few banks, RBI u sed t o inclu de all t he schedu led banks in it s schedu le. Nowaday , when t he nu m ber of banks has gone u p su bst ant ially , RBI has t o change t he schedu le ev er y now and t hen, hence ir r espect iv e of whet her a bank finds it s nam e in t he schedu le t o t he RBI Act or not , it s schedu le st at u s can be fou nd ou t fr om it s banking licence. A Bank t hat is not a schedu led bank is r efer r ed t o as non-schedu led bank ev en in it is hav ing banking licence. The differ ence lies in t he t y pe of banking act iv it ies t hat a bank can car r y ou t in India. In t he case of a schedu led bank, it is licensed by t he RBI t o car r y on ext ensiv e banking oper at ions inclu ding for eign exchange oper at ions, wher eas, a non-schedu led bank can car r y ou t only lim it ed oper at ions. Ther e ar e a nu m ber of fact or s consider ed by RBI t o declar e a bank as a schedu led bank, like t he am ou nt of shar e capit al, t y pe of banking act iv it ies t hat t he bank is per m it t ed t o car r y ou t et c. An exam ple of differ ence bet ween a schedu led and non-schedu led bank is dealing in For eign Exchange. Commercial And Co-operat iv e Banks Com m er cial banks ar e by far t he m ost widespr ead banking inst it u t ions in India. They pr ov ide m ajor pr odu ct s and ser v ices in India. A com m er cial bank is r u n on com m er cial lines, for pr ofit s of t he or ganizat ion. A co-oper at iv e bank on t he ot her hand is r u n for t he benefit of a gr ou p of m em ber s of t he co-oper at iv e body . A co-oper at iv e bank dist r ibu t es only a v er y sm all por t ion of it s pr ofit as div idend, r et aining a m ajor por t ion of it in bu siness. All t he nat ionalized banks in India and alm ost all t he pr iv at e sect or banks ar e com m er cial schedu led banks. Ther e ar e a lar ge nu m ber of pr iv at e sect or cooper at iv e banks and m ost of t hem ar e non-schedu led banks. In t he pu blic sect or also, wit hin a st at e, st ar t ing fr om t he St at e capit al, t her e ar e St at e Co-oper at iv e Banks and Dist r ict Cent r al Co-oper at iv e Banks at t he Dist r ict lev el. Under t he Dist r ict Cent r al Co-oper at iv e Bank, t her e ar e Co-oper at iv e Societ ies. At pr esent , In India, t he banks can be bifu r cat ed int o following cat egor ies. Publ ic Sect or Banks or Nat ional ized Banks, which are commercial and scheduled Exam ples: St at e Bank of India, Bank of India et c. Publ ic Sect or Banks, which are co-operative and non-scheduled-These ar e st at e owned banks like t he Mahar asht r a St at e Co-oper at iv e Bank, Ju nnar Cooper at iv e Societ y et c. Priv at e Sect or Banks, which are commercial and scheduled-These cou ld be for eign banks, as well as Indian Banks. Exam ples: For eign Banks- CITI Bank, St andar d Char t er ed Bank et c. Indian Banks, Bank of Rajast han Lim it ed, VYSYA Bank Lim it ed et c. Priv at e Sect or Banks, which are co-operative and scheduled These ar e lar ge co-oper at iv e sect or banks bu t which ar e schedu led banks. Exam ples: Sar aswat Co-oper at iv e Bank Lim it ed, Cosm os Co-oper at iv e Bank Lim it ed et c. Priv at e Sect or Banks, which are co-operative and non-scheduled-These ar e sm all co-oper at iv e banks bu t which ar e non-schedu led. Exam ples: Local cooper at iv e banks which oper at e wit hin a t own or a cit y . Exam ple: Mahesh Sahakar i Bank Lim it ed. Regional Rural Banks. These ar e st at e owned. These banks hav e been est ablished wit h a v iew t o dev eloping t he r u r al econom y by pr ov iding, for t he pu r pose of dev elopm ent of agr icu lt u r e, t r ade, com m er ce, indu st r y and ot her pr odu ct iv e act iv it ies in t he r u r al ar eas, cr edit and ot her facilit ies, par t icu lar ly t o t he sm all
and marginal farmers, agricultural labourers and artisans and small entrepreneurs Gramin Banks, that are also state owned. They operate at still smaller level than RRBs and serve at villages level. Foreign banks, These banks have Head Office outside India and branch in India, Besides, the Reserve Bank of India (hereinafter referred to as RBI) acts as the central bank of the country . RBI is responsible for development and supervision of the constituents of the Indian financial sy stem (which comprises banks and non-banking financial institutions) as well as for determining, in conjunction with the central Government, the monetary and credit policies. They are also controlled by RBI. Retail Banking Vs Wholesale Banking Whole sale banking ty pically involves a small number of very large customers such as big corporations and governments, whereas retail banking consists of a large number of small customers who consume personal banking and small business services. Wholesale banking is largely inter-bank; banks use the inter-bank markets to borrow from or lend to other banks/ large customers, to participate in large bond issues and to engage in sy ndicated lending. Retail banking is largely intra-bank; the bank itself makes many small loans. Most of the Indian public sector banks practice retail banking; they are slowly practising the concept of wholesale banking. On the other hand, most of the wellestablished foreign banks in India and the recent private sector banks practice wholesale banking alongside retail banking. As a result of this difference, the composition of income for a public sector bank is different. While a major portion of the income for large public sector banks is from lending operations, in the case of any private sector bank in India, the amount of non-operating income (other than interest income) is substantially higher. The composition of other income is commission on bills/ guarantees/ letters of credit, counselling fees, sy ndication fees, credit report fees, loan processing fees, correspondent bank charges etc. Global Banking Global Banking activities are an extension of various activities listed above into the international market. Global banking primarily consists of trade in international banking services and establishment of branches and subsidiaries in foreign countries. Special Kinds Of Bank Branches
Most Banks in India have special kind of branches. This is done to reap benefits of specialisation as activities done by these branches are quite complex and require specialised knowledge and attention. Ty pes of some special branches are 1. Foreign exchange branches 2. NPA recovery branches 3. Service branches dealing in Clearing house operations/Corporate banking and Industrial finance branches 4. Personal banking branches 5. Housing finance branch 6. SSI branches 7. Agricultural finance branches
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Von EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Bewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (98)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceVon EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (895)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeVon EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (5794)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingVon EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (399)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaVon EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (266)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeVon EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (537)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureVon EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (474)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItVon EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (838)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceVon EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (588)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryVon EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (231)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerVon EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (271)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyVon EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (2259)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealVon EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (73)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersVon EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (344)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnVon EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (234)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaVon EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (45)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreVon EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Von EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Bewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (121)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesVon EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (821)
- Investments That Do Not Normally Change in Value Are Disclosed On The Balance Sheet As Cash and Cash EquivalentsDokument3 SeitenInvestments That Do Not Normally Change in Value Are Disclosed On The Balance Sheet As Cash and Cash EquivalentsHussainNoch keine Bewertungen
- "Financial Statement Analysis of Bank of Maharashtra": A Project Report OnDokument65 Seiten"Financial Statement Analysis of Bank of Maharashtra": A Project Report OnShashi RanjanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Audit of Cash and Cash EquivalentsDokument38 SeitenAudit of Cash and Cash Equivalentsxxxxxxxxx86% (81)
- Cbe Ac STMT RPDokument1 SeiteCbe Ac STMT RPBayechNoch keine Bewertungen
- Order of Payment: CNC Online Application SystemDokument1 SeiteOrder of Payment: CNC Online Application SystemEva MarquezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Vendor Payments F-53Dokument2 SeitenVendor Payments F-53Promoth JaidevNoch keine Bewertungen
- March 2020 Insight Part IDokument88 SeitenMarch 2020 Insight Part INifezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Experience & Relieving LetterDokument2 SeitenExperience & Relieving LetterAnandNoch keine Bewertungen
- ACC - ACF1200 Topic 3 SOLUTIONS To Questions For Self-StudyDokument3 SeitenACC - ACF1200 Topic 3 SOLUTIONS To Questions For Self-StudyChuangjia MaNoch keine Bewertungen
- CRED's Plan To Acquire Smallcase Falls ThroughDokument1 SeiteCRED's Plan To Acquire Smallcase Falls ThroughaxfNoch keine Bewertungen
- Answer No. 1Dokument5 SeitenAnswer No. 1Anurag GuptaNoch keine Bewertungen
- TaxInvoice 01012016Dokument4 SeitenTaxInvoice 01012016Chiong Yew TiongNoch keine Bewertungen
- Acc 109 Quiz 1 P3Dokument2 SeitenAcc 109 Quiz 1 P3GargaritanoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bank Mandiri (Persero) TBK.: Company Report: July 2014 As of 25 July 2014Dokument3 SeitenBank Mandiri (Persero) TBK.: Company Report: July 2014 As of 25 July 2014davidwijaya1986Noch keine Bewertungen
- Ebay Order Baterias 9V - Edenorte-FusionadoDokument4 SeitenEbay Order Baterias 9V - Edenorte-FusionadoYamilka MedranoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tds ChallanDokument2 SeitenTds Challannilesh vithalaniNoch keine Bewertungen
- Liability of PartiesDokument16 SeitenLiability of PartiesSGTNoch keine Bewertungen
- MTH 154-Preview - Final ExamDokument5 SeitenMTH 154-Preview - Final Exampro mansaNoch keine Bewertungen
- LCF Mum 0007001053Dokument4 SeitenLCF Mum 0007001053The Shah'sNoch keine Bewertungen
- HLB Faq en PDFDokument26 SeitenHLB Faq en PDFMohd AzhariNoch keine Bewertungen
- Money LendingDokument20 SeitenMoney LendingAnkit KumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Analisis Kasus Rogue Trader Societe GeneraleDokument2 SeitenAnalisis Kasus Rogue Trader Societe GeneraleWulan NurjannahNoch keine Bewertungen
- Audit - Cash and Cash Equivalents PDFDokument15 SeitenAudit - Cash and Cash Equivalents PDFSiena Farne100% (1)
- Income Taxes: Sri Lanka Accounting Standard - LKAS 12Dokument46 SeitenIncome Taxes: Sri Lanka Accounting Standard - LKAS 12Sineth NeththasingheNoch keine Bewertungen
- XXXXXXXXXX6781 - 20230615160830874376 (1) - UnlockedDokument16 SeitenXXXXXXXXXX6781 - 20230615160830874376 (1) - UnlockedRajendra SharmaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Wise Transaction BookletDokument3 SeitenWise Transaction BookletBGangadharReddyNoch keine Bewertungen
- On BOBDokument37 SeitenOn BOBVishakha SaxenaNoch keine Bewertungen
- BikashDokument2 SeitenBikashBikash Kumar NayakNoch keine Bewertungen
- Job Order CostingDokument4 SeitenJob Order CostingTrina Mae BarrogaNoch keine Bewertungen
- PHD "A COMPARATIVE STUDY OF NON-FUND BASED INCOME OF SELECTED PUBLIC SECTOR BANKS & SELECTED PRIVATE SECTOR BANKS IN INDIA"Dokument262 SeitenPHD "A COMPARATIVE STUDY OF NON-FUND BASED INCOME OF SELECTED PUBLIC SECTOR BANKS & SELECTED PRIVATE SECTOR BANKS IN INDIA"Pooja Patel100% (3)