Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Military Plating Spec-1
Hochgeladen von
Durbha RaviCopyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Military Plating Spec-1
Hochgeladen von
Durbha RaviCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Document Title
Mil Spec Plating Standards used in defining plating and coating requirements. Several process have been changed, deleted and new ones added since the printing of this document.
Military Plating Specifications Process Black Chrome
A hard, non-reflective, abrasion resistant, heat and corrosion resistant coating. Black Chromium has poor throwing power, and conforming anodes are necessary for intricate shapes. Apply after heat treating and all mechanical operations are performed. The Black Chrome surface may be waxed or oiled to darken the surface.
MIL. Spec. Thickness
MIL-C-14538A As specified on drawing.
Comments
Color is a dull dark gray, approaching black. It shall approximate color plate 37038 of Fed. Std. No. 595.
Black Oxide Coating
A uniform black coating for ferrous metals. Mostly a decorative coating. Only very limited corrosion protection under mild corrosion conditions. Black oxide coatings should normally be given a supplementary treatment (i.e., oil displacement per Mil-C16173 Grade 3 or protective treatments of mil-C-16173).
MIL-C-13924B No dimensional change. For moving parts which cannot tolerate the dimensional change of a more corrosion resistant finish. For decorative applications and can be used to decrease light reflection. Alkaline oxidizing. For wrought iron, plain carbon, and low alloy steels. Alkaline chromate. For corrosion resistant steels. Fused salt oxidizing. For steels having draw temp. above 900 deg. Alkaline oxidizing. For corrosion resistant steels.
Class 1 Class 2 Class 3 Class 4
Cadmium
Bright silvery white. Supplementary treatments for Type II can be golden, iridescent, amber, black, olive drab. Corrosion resistance is very good, especially with Type II finish. Type II shall show no surface corrosion products after 96 hours (20%) salt spray exposure. Parts with hardness greater than Rc-40 shall be stressrelieved before cleaning and plating. Parts subject to flexure (springs, etc.) over Rc-40 hardness shall be given a 375 deg. +/- 25 deg. post bake. Salt Spray Test Type I Class I Test Period for White Corrosion Products (Hours)
QQ-P-416C Type I Type II Type III No supplementary treatment. Supplementary chromate treatment. Supplementary phosphate treatment.
Class 1 Class 2 Class 3
.0005 min. .0003 min. .0002 min.
Type II best for corrosion resistance. Type III is used as a paint base. Excellent for plating stainless steels that are to be used in conjunction with aluminum to prevent galvanic corrosion.
Reference Military Plating Specifications - Continued Process Chemical Films
Coatings for aluminum. Color can vary from colorless to goldeniridescent-brown, or can be dyed in specific colors. Materials should conform to Mil-C-81706. Coatings shall be continuous, free from powdery areas, breaks, scratches, etc.
MIL. Spec. Thickness
MIL-C-5541B No dimensional change.
Comments
Class 1A is used as corrosion preventative film (unpainted) or to improve adhesion of paint finish systems. Class 3 is used as a corrosion preventative film for electrical and electronic applications, where lowresistance contacts are required.
Class 1A
For maximum protection against corrosion, painted or unpainted. For protection against corrosion where low electrical resistance is required.
Class 3
Chemical Finish; Black
A uniform black corrosion retardant for copper. Coating has no abrasion resistance.
MIL-F-495C No dimensional change. QQ-C-320A Type I Type II Class 1 Class 2 Class 2a .00001-.00002 As specified on drawing. Used as base for lacquer, light oil, or wax. For decorative, optical, and corrosion retardant applications.
Chrome
Excellent hardness (Rc68-74), wear resistance, and erosion resistance. Has low coeffecient of friction, and is resistant to heat. In addition to above properties, can be rendered porous for lubrication purposes. Post bake at 375 deg. +/- 25 deg.F for 3 hours or as specified. Shot peening and post baking not required. Shot peen per Mil-S-13165. Post bake at 375 deg. +/- 25 deg.F for 3 hours. Shot peen before plating. Post bake at 375 deg. +/- 25 deg.F for 3 hours.
Bright. Satin. Decorative plating. (Usually over copper and nickel undercoats.) Engineering plating. Plated to Specified dimensions or processed to Specified dimensions after plating. Parts below Rockwell C40 and subject to static loads or designed for limited life under dynamic loads. Parts below Rockwell C40 and designed for unlimited life under dynamic loads. Parts have hardness of Rockwell C40 or above and subject to static loads or designed for limited life under dynamic loads. Parts have hardness of Rockwell C40 or above and are designed for unlimited life under dynamic loads.
Class 2b
Class 2c
Class 2d
Class 2e
Reference Military Plating Specifications - Continued Process Chromic Anodize
Color will vary from light gray to dark gray depending on alloy. New salt spray requirement is 336 hours (5% solution per method 811 of FED-STD-No. 151). Minimum weight for Type I coatings: Class 1 200 Milligrams/sq. ft. Class 2 500 Milligrams/sq. ft. Because of thinness, will scratch easily. Can be used for inspection of aluminum forgings or castings by noting evidence of chromic acid bleed out from laps, cracks, seams, etc.
MIL. Spec. Thickness
MIL-A-8625C Type I .00005-.0003
Comments
Unless otherwise specified, coating will be sealed. Metal salt sealants should not be used on items that will be painted. Non-dyed (Natural, including dichromate sealing). Dyed. Shall not be applied to aluminum alloys with over 5.0% copper, 7.0% silicon, or total alloying constituents over 7.5%. When copper content is less than 4.6% and for all suitable casting alloys, be sure aluminum is tempered (such as T-4 or T-6).
Class 1
Class 2
Copper
Copper to color and matte to a very shiny finish. Good corrosion resistance when used as undercoat. A number of copper processes are available, each designed for a specific purpose. Brightness (to eliminate the need for buffing); High speed (for electroforming); Fine grain (to prevent casehardening); etc.
MIL-C-14550A Unless otherwise specified. Class 0 Class 1 .001-.005 .001 For heat treatment stop-off. For carburizing and decarburizing shield, also plated through printed circuit boards. As an undercoat for nickel and other platings. To prevent basis metal migration into tin (prevents poisoning solderability).
Class 2
.0005
Class 3 Class 4
.0002 .0001
Dow #1
A chrome pickle treatment for magnesium. Color varies from matte gray to yellow-red. Only fair corrosion resistance (less than 24 hours 20% salt spray resistance).
MIL-M-3171C Removes metal Type I (Approximately .0006 for wrought-less for die castings.) Used mainly for protecting magnesium during shipment, storage, and machining. Can be used as a paint base. Note: Must remove Type 1 coating before applying Type III and Type IV treatments.
Reference Military Plating Specifications - Continued Process Dow #7
A dichromate treatment for magnesium. Color varies from light brown to gray depending on alloy. Only fair corrosion resistance (less than 24 hours 20% salt spray resistance).
MIL. Spec. Thickness
MIL-M-3171C No dimensional change. Type III
Comments
Good paint base and protective qualities for all magnesium alloys except EK30A, EK41A, EZ33A, HK31A, and M1A. Note: Pre-cleaning and pickling may result in dimensional changes due to metal loss.
Dow #9
A galvanic anodize treatment for magnesium. Produces a dark brown to black coating. Designed to give a protective film on alloys which do not react to Dow No. 7 treatment. Only fair corrosion resistance (less than 24 hours 20% salt spray resistance).
MIL-M-3171C Type IV No dimensional change. Can be used as a paint base, and is applicable to all magnesium alloys. Used where optical properties (black) are required on close tolerance parts (camera parts, etc.). Note: Pre-cleaning and pickling may result in dimensional changes due to metal loss. MIL-M-45202B Typical thickness Type I Class C Type II Class D Class E MIL-C-26074B Unless otherwise specified. Class 1 Class 2 As coated. Steel; copper, nickel, and cobalt base alloys. Heat treated after plating. Aluminum alloys other than alloy 7075. Heat treated after plating. Minimum thickness. For iron and aluminum based alloys. Minimum thickness. For copper, nickel, and cobalt based alloys. .002 .00030 Light coating. Light green coating. Heavy coating. Dark green coating. High density dark green.
Dow #17
Light green coating is recommended for sheet magnesium. The heavier dark green coatings have greater corrosion and abrasion resistance and are applied to castings and extrusions. Coating is brittle and tends to spall from a surface that is flexed. Vinyl and epoxy coatings are applied over coating to reduce spalling.
Electroless Nickel
Similar to stainless steel in color. Plates uniformly in recesses and cavities (does not build up on edges). Corrosion resistance is good for coatings over .001 thickness. electroless nickel is used extensively in salvage of mismachined parts. Also, for inside dimensions and irregular shapes (where assembly tolerances need uniformity provided by electroless process).
Class 3 Grade A Grade B 0.001 0.0005
Reference Military Plating Specifications - Continued Process Electropolishing
Process electrolytically removes or diminishes scratches, burrs and unwanted sharp edges from most metals. Finishes from satin to mirrorbright are produced by controlling time, temperature, or both.
MIL. Spec. Thickness
(No MIL-SPEC) Typical thickness. 0.0002
Comments
Typical dimensional change Process is not recommended for close tolerance surfaces.
Gold
Yellow to orange color depending on proprietary process used. Will range from matte to bright finish depending on basis metal. Good corrosion resistance, and has high tarnish resistance. Provides a low contact resistance, and is a good conductor. Has excellent solderability.
MIL-G-45204B Unless otherwise specified. Type I Type II Type III Class 00 Class 0 Class 1 Class 2 Class 3 Class 4 Class 5 Class 6 MIL-M-45202B Type I Class A Grade 1 Grade 2 Class B Type II Class A Grade 1 Grade 2 Grade 3 Grade 4 Grade 5 99.7% gold min. 95.5% gold min. 99.9% gold min. Grade A 90 Knoop max. Grade B 91-129 Knoop Grade C 130-200 Knoop Grade D 201 Knoop and over. Type I (Grades A, B, or C). Type II (Grades B, C, or D). Type III (Grade A only).
0.00002 min. 0.00003 min. 0.00005 min. 0.00010 min. 0.00020 min. 0.00030 min. 0.00050 min. 0.00150 min.
HAE
A corrosion, heat, and abrasionresistant coating for magnesium. Suitable for use on all forms and alloys of magnesium. the color of HAE shall be lustreless brown and within range form number 3010 to 3035 of Specification TT-C-595. The coating shall be able to withstand a 20% salt spray exposure of 196 hours.
.0001-.0003
.0003-.0005
.0006-.0011
Light coating. Tan coating. without post treatment. With chromate seal. Low voltage coating with dichromate seal. Heavy coating. Hard brown coating. Without post treatment. with chromate seal. With bifluoride-dichromate seal. With bifluoride-dichromate seal and moist heat aging. Double application of Grade 4 post treatment.
Reference Military Plating Specifications - Continued Process Hard Anodize
Color will vary form light tan to black depending on alloy and thickness. Can be dyed in darker colors depending on thickness. Coating PENETRATES base metal as much as builds up on the surface. The term THICKNESS includes both the buildup and penetration. Provides very hard ceramic type coating. Abrasion resistance will vary with alloy and thickness of coating. Good dielectric properties. Corrosion resistance is good, but recommend seal hard anodize in 5% dichromate solution where increased corrosion resistance is required. Where extreme abrasion resistance is required, do not seal as some softening is encountered.
MIL. Spec. Thickness
MIL-A-8625C Type III As specified on drawing.
Comments
Most aluminum alloys depending on process used. Where maximum serviceability or special properties are required, consult metal finisher for best alloy choice. Thick coatings (over .004) will tend to break down sharp edges. Typical applications: hydraulic cylinders, wear surfaces, actuating cams, etc. Can be used as an electrical insulation coating. Flash hard anodize may be used instead of conventional anodize for corrosion resistance and may be more economical in conjunction with other hard anodized areas. Non-dyed. Dyed.
Class 1 Class 2
Lubricant; Solid Film
Used to prevent galling and seizure of metals. Lubricant covered by this specification is intended for use on steel, titanium, aluminum, aluminum alloys and on other metals for which its use proves satisfactory. Useful where conventional lubricants are difficult to apply or retain or where other lubricants may be easily contaminared.
MIL-L-8937A Unless otherwise specified. 0.0002-0.0005 Solid Film Lubricants are generally suitable for sliding motion applications such as in plain spherical bearings, flap tracks, hinges, and cam surfaces. Do not use on materials adversely affected by exposure to temperatures of 300 deg.F for 1 hour. It should no be used with oils or greases unless field use indicates otherwise.
Reference Military Plating Specifications - Continued Process Nickel
There is a nickel finish for almost any need. Nickel can be deposited soft or hard dull or bright, depending on process used and conditions employed in plating. This, hardness can range from 150-500 Vickers. Can be similar to stainless stell in color, or can be a dull gray or light gray (almost white) color. Corrosion resistance is a function of thickness. Has a low coefficient of thermal expansion is magnetic. all steel parts having a hardness of Rc-40 or greater require a post bake at 375 deg.F for 3 hours.
MIL. Spec. Thickness
QQ-N-290A Total thickness of copper and nickel. Class 1 Type I Type II Type III Type IV Type V Type VI Type VII Type VIII Type IX Type X Class 2
Comments
Note: All steel parts having a tensile strength of 220,000 or greater shall not be nickel plated without specific approval of procuring agency. For decorative applications on: Steel base; Steel base; Steel base; Steel base; Copper base; Copper base; Copper base; Zinc base; Zinc base; Zinc base; For engineering applications. Type of nickel (process) should be called out. For salvage and where good hardness and corrosion req.
.002 min. .00125 min. .00075 min. .00040 min. .00050 min. .00030 min. .00010 min. .00125 min. .00075 min. .00050 min. Nickel plated to specified thickness or after plating dim.
Passivate
A process designed to remove foreign metals from the surface of stainless and corrosion resistant steels and to promote natural tendency of surface to oxidize. Does not change the appearance of the base metal. Process purifies surface which improves corrosion resistance.
QQ-P-35B MILS-5002C Type I Type II Type III Type IV Type V Type VI Cleaning Methods Method I Method II Method III Method IV Method V Method VI Pretreatment Coatings Type I Type II Type III
No dimensional change.
Low temperature. Medium temperature. High temperature. For steels containing large amounts (.015%) of sulfur or selenium. Anodic For high carbon martensitic (440) steels. Low temperature (optional). Light coating for use as paint base. Mechanical or abrasive cleaning. Solvent cleaning. Hot alkaline. Emulsion. Alkaline de-rusting. Phosphoric acid.
Phosphate Coating, Light
Specification covers cleaning methods and pretreatment processes. Type I Intended as a general allpurpose pretreatment prior to painting. Type II Intended primarily for use where metal parts are to be formed after painting. Type III Intended for use where size and shape preclude using Type I and Type II, metal components are assembled prior to treatment.
Zinc phosphate. Iron phosphate. Organic pre-treatment coating (wash primer). Non-aqueous iron phosphate.
Reference Military Plating Specifications - Continued Process Phosphate Coating;Heavy
A coating for medium and low alloy steel. Gray to black in color. Type M is more resistant than Type Z to alkaline environments. Type M can be used up to 250 deg.F. Provides moderate corrosion resistance and prevents wear.
MIL. Spec. Thickness
Comments
Heavy coating for corrosion and wear resistance.
Type M
.0002-.0004
Manganese phosphate base coating (1500 milli-gms/ft-2). Supplementary preservative oil treatment as specified. Treated with lubricating oil conforming to MIL-L-3150. No supplementary treatment. Chemically converted, no supplementary treatment. Chemically converted and treated with lubricating oil conforming to MILL-3150. Chemically converted and dyed to a color, as specified. Chemically converted, dyed to a color as specified and treated with lubricating oil conforming to MIL-L3150. Chemically converted and supplementary treatment.
Class 1
Class 2
Class 3 Class 4A
Class 4B
Class 4C
Class 4D
Class 4E
Type Z can be used up to 200 deg.F, to prevent galling in extrusion and deep drawing. Class 2 is good for corrosion resistance.
Type Z
.0002-.0006
Zinc phosphate base coating (1000 milli-gms/ft-2). Supplementary preservative oil treatment, as specified. Treated with non-drying type preservative conforming to MIL-C16173, Grade I. No supplementary treatment. Chemically converted, no supplementary treatment.
Class 1
Class 2
Class 3 Class 4A
Reference Military Plating Specifications - Continued Process Phosphate Coating;Heavy Continued MIL. Spec. Thickness Comments
Class 4B
Chemically converted and treated with a preservative oil or high melting wax. Chemically converted and dyed to a color, as specified. Chemically converted, dyed to a color as specified and treated with a preservative oil or high melting wax. Chemically converted and supplementary treatment, as specified.
Class 4C
Class 4D
Class 4E
Rhodium
Metallic and similar to stainless steel in color. Excellent corrosion resistance. Almost as hard as chromium. Very good abrasion resistance. Good solderability. Low contact resistance. Thicker coatings are very brittle. Has high reflectivity.
MIL-R-46085 Type I Type II Class 1 Class 2 Class 3 Class 4 Class 5 QQ-S-365A .0005 min. unless otherwise specified. Type I Type II Type III Grade A .000001-.00001 .00001-.00002 .00002-.0001 .0001-.00025 .00025-.0005
Over nickel, silver, gold, or platinum. Over other metals. Used on silver for tarnish resistance. Applications range from electronic to nose cones wherever wear, corrosion resistance, solderability, and reflectivity are important.
Silver
White matte to very bright in appearance. Good corrosion resistance, depending on base metal. Will tarnish easily. Hardness varies from about 90 Brinnell to about 135 Brinnell depending on process and plating conditions. Solderability is excellent, but decreases with age. Best electrical conductor. Has excellent lubricity and smear characteristics for anti-galling uses on static seals, bushings, etc.
Increasing use in both decorative and engineering fields, including electrical and electronic fields. Matte. Semi-bright Bright. Chromate post-treatment to improve tarnish resistance. No chromate treatment
Grade B
Sulfamate Nickel
The plating conforming to this specification is intended to facilitate the formation of a seal between two metallic surfaces. Plating Hardness. Not to exceed 150 Knoop hardness (500 gm. load) after annealing.
MIL-P-27418 Unless otherwise specified. 0.0020 +/-.0003 The nickel plating shall have a columnar crystalline structure before annealing.
Reference Military Plating Specifications - Continued Process Sulfuric Anodize
Color will vary with alloy. Aluminum with low alloying elements will show practically no color change. Best coating on aluminum for dyeing. Can be dyed practically any color or shade (black, blue, red, etc.). Salt spray requirement is 336 hours (5% solution per method 811 of FEDSTD- No. 151). Minimum weight for Type II coatings: Class 1 600 Milligrams/sq. ft. Class 2 2500 Milligrams/sq. ft.
MIL. Spec. Thickness
MIL-A-8625C Type II .00005-.0010
Comments
All aluminum alloys, but do not use where solution will entrap. FED-STD. No. 595 may be used as a Guide for specifying color (approximate comparison only).
Class 1 Class 2
Non-dyed. Dyed.
Tin
Color is gray-white in a plated condition. Had very high luster in fused condition. Soft, but is very ductile. Corrosion resistance is good. (Coated items should meet 24 hours 20% salt spray requirement.) Solderability is excellent. tin is not good for low temperature applications (changes structure and loses adhesion when exposed to temperatures below 40 deg.F). If a bright finish is desired to be used in lieu of fused tin, specify Bright Tin plate. Thickness can exceed that of fused tin and deposit shows excellent corrosion resistance and solderability.
MIL-T-10727A As specified on drawing. Thickness Guide (not part of Spec.): Type I Type II .0001-.00025 .0002-.0004 .0003 min. .0002-.0006 Electro-deposited. Hot dipped. Flash for soldering. To prevent galling and seizing. Where corrosion resistance is important. To prevent formation of case during nitriding.
Vacuum Aluminum
Used to provide corrosion resistance to ferrous parts free from hydrogen contamination and possible embrittlement. Does not protect from hydrogen embrittlement in use. Alternate wetting and drying can induce hydrogen into susceptible high strength stell parts. Also used to provide stress corrosion cracking and pitting corrosion to high strength aluminum alloys.
MIL-C-23217B Class 1 0.0010 thick + .0005 - .0001 0.0005 thick + .0002 - .0002 Serviceability up to 925 deg.F. No bake is required after plating. Salt-Spray Test Test Period (hours) 336 192
Class 2
Class 1 2
Reference Military Plating Specifications - Continued Process Vacuum Cadmium
Used primarily to provide corrosion resistance to ferrous parts free from hydrogen contamination and possible embrittlement. Recommended on steels 220,000 psi or above. Coating is applied after all machining, brazing, welding and forming has been completed. Steel parts over Rc-33 shall be cleaned using materials which will have no damaging effects, including intergranular attack, etching and hydrogen embrittlement. Salt spray test for Type II is 96 hours.
MIL. Spec. Thickness
MIL-C-8837A Type I Type II Type III Class 1 Class 2 Class 3 0.00050 min. 0.00030 min. 0.00020 min.
Comments
Without supplementary chromate or phosphate treatment. With supplementary chromate. With supplementary phosphate.
No bake is required after plating.
Zinc
Either a bright or dull finish is acceptable. Bright Zinc plating closely resembles bright chromium. However, bright zinc does not have the permanence of surface appearance. Zinc coated steel will not rust even when exposed by scratches because of the galvanic protection of the zinc. On weathering, zinc turns to a drab gray color. Zinc should be deposited directly on the base metal (Nickel is permissible undercoat if base metal is a corrosion resisting steel). Parts having a hardness greater than Rc40 must be given a heat treatment prior to plating. Springs having a hardness over Rc-40 must be given an after plating baking at 375 deg.F +/- 25 deg.F for 3 hours.
QQ-Z-325B Class 1 Class 2 Class 3 .0010 .00050 .00020 The primary purpose of phosphate coating on zinc is to provide a paint base. Type I Type II Type III Without supplementary treatments. With supplementary chromate treatment. With supplementary phosphate treatment. The primary use of chromate finishes on zinc is to retard or prevent formation of white corrosion products on zinc surfaces.
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- API Spec 6a MaterialDokument28 SeitenAPI Spec 6a MaterialFathur Deka Aprianda100% (2)
- ANODIZING: ELECTROLYTIC PROCESS INCREASES ALUMINUM OXIDE LAYERDokument4 SeitenANODIZING: ELECTROLYTIC PROCESS INCREASES ALUMINUM OXIDE LAYERShubham JainNoch keine Bewertungen
- MIL-PRF-46010G (Molycote) PDFDokument17 SeitenMIL-PRF-46010G (Molycote) PDFalfie_nNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sae Ams 2759-3H-2019Dokument20 SeitenSae Ams 2759-3H-2019Reza NooriNoch keine Bewertungen
- ASTM B733 Electroless Nickel PlatingDokument13 SeitenASTM B733 Electroless Nickel PlatingManan Vadher100% (1)
- E 1751 - e 1751M - 15Dokument95 SeitenE 1751 - e 1751M - 15Eric GozzerNoch keine Bewertungen
- AnodizingDokument9 SeitenAnodizingalphadingNoch keine Bewertungen
- Steel Framed House - EedosteelDokument36 SeitenSteel Framed House - Eedosteelwoongrae100% (1)
- Electrodeposited Coatings On Mechanical Fasteners, Inch and MetricDokument14 SeitenElectrodeposited Coatings On Mechanical Fasteners, Inch and MetricKamal El ShawadfyNoch keine Bewertungen
- ISO 17781 2017 EditionDokument26 SeitenISO 17781 2017 EditionNirmal100% (6)
- Evaluating Coatings For High Temperature Service: Standard Test Methods ForDokument3 SeitenEvaluating Coatings For High Temperature Service: Standard Test Methods ForFernando Berrospi Garay100% (1)
- Zinc Flake Vs Zinc-Nickel ComparisonDokument7 SeitenZinc Flake Vs Zinc-Nickel ComparisonSon NguyenNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mechanical Hydrogen Embrittlement Evaluation of Plating/ Coating Processes and Service EnvironmentsDokument19 SeitenMechanical Hydrogen Embrittlement Evaluation of Plating/ Coating Processes and Service EnvironmentsLeo Costa100% (1)
- Black Oxide MIL DTL 13924DDokument11 SeitenBlack Oxide MIL DTL 13924DadamhomeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mar-M-247 1984Dokument22 SeitenMar-M-247 1984sunsirNoch keine Bewertungen
- Automotive Gray Iron Castings: Standard Specification ForDokument5 SeitenAutomotive Gray Iron Castings: Standard Specification ForJosé Ramón GutierrezNoch keine Bewertungen
- ASTM A-967-13 Pasivado Inoxidable PDFDokument7 SeitenASTM A-967-13 Pasivado Inoxidable PDFmagierezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ams 2451 Rev. DDokument9 SeitenAms 2451 Rev. DJorge Luis Gonzalez Gonzalez100% (1)
- Safecoat Hard AnodizingDokument47 SeitenSafecoat Hard AnodizingyahsooyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mil I 24768Dokument35 SeitenMil I 24768Rahul Goud100% (1)
- Astm G152 - 13Dokument10 SeitenAstm G152 - 13morteza nourooziNoch keine Bewertungen
- NASA Plating PaperDokument142 SeitenNASA Plating PaperRussell ShacklefordNoch keine Bewertungen
- TALAT Lecture 5201: Aluminium Surface PretreatmentDokument12 SeitenTALAT Lecture 5201: Aluminium Surface PretreatmentCORE Materials100% (1)
- ASTM B912 02 Passivation of Stainless Steels Using Electropolishing PDFDokument4 SeitenASTM B912 02 Passivation of Stainless Steels Using Electropolishing PDFankit7588Noch keine Bewertungen
- Brochure - Rev 15 PDFDokument9 SeitenBrochure - Rev 15 PDFCicero Gomes de SouzaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Astm b650 Proceso de PlatingDokument5 SeitenAstm b650 Proceso de PlatingALEXANDRA TALAMANTESNoch keine Bewertungen
- Dstan 03-25Dokument26 SeitenDstan 03-25jmills7560Noch keine Bewertungen
- MIL-STD-645B Dip Brazing of Aluminum AlloysDokument16 SeitenMIL-STD-645B Dip Brazing of Aluminum AlloysRichard BennardoNoch keine Bewertungen
- A357 PDFDokument60 SeitenA357 PDF孙俊磊Noch keine Bewertungen
- Anodising - Def Stan 03-25Dokument22 SeitenAnodising - Def Stan 03-25Jai BhandariNoch keine Bewertungen
- Jed-257 008 en LDokument4 SeitenJed-257 008 en LcroplaninecNoch keine Bewertungen
- Plating and MetPLATING & METAL FINISHING SPECIFICATIONS ISO 9001:2008, Nadcap, ITAR, Federal Fire Arms Licenseal Finishing SPECDokument1 SeitePlating and MetPLATING & METAL FINISHING SPECIFICATIONS ISO 9001:2008, Nadcap, ITAR, Federal Fire Arms Licenseal Finishing SPECStas Zabarsky0% (1)
- Mil DTL 81706Dokument20 SeitenMil DTL 81706plemsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Inconel 600 PDFDokument16 SeitenInconel 600 PDF孙俊磊100% (1)
- ATOTECH - EcoTri - Bright Zinc Plating - Hexavalent Chrome FreeDokument4 SeitenATOTECH - EcoTri - Bright Zinc Plating - Hexavalent Chrome FreeWK Sinn100% (1)
- Chemical Deterioration of ConcreteDokument17 SeitenChemical Deterioration of Concretemanu_696Noch keine Bewertungen
- Ams4943l 2020Dokument8 SeitenAms4943l 2020BauyrzhanNoch keine Bewertungen
- ECISGROUP - Cooling Tower Water Treatment - Rev1Dokument31 SeitenECISGROUP - Cooling Tower Water Treatment - Rev1Ecisgroup100% (2)
- Adiabatic Shear Localization: Frontiers and AdvancesVon EverandAdiabatic Shear Localization: Frontiers and AdvancesBradley DoddNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chromate Conversion Coating and Alternatives As Corrosion-Resistant Treatments For Metal Parts v1Dokument17 SeitenChromate Conversion Coating and Alternatives As Corrosion-Resistant Treatments For Metal Parts v1Ivy LiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Annex2 Who GMP Water For PharmaceuticalDokument23 SeitenAnnex2 Who GMP Water For Pharmaceuticalpamy26250Noch keine Bewertungen
- Carefully To Carry: Sulphur CargoesDokument3 SeitenCarefully To Carry: Sulphur Cargoesdoan80100% (1)
- Anodizing Info PDFDokument48 SeitenAnodizing Info PDFantzz alljc100% (1)
- Steel Purlins ManualDokument48 SeitenSteel Purlins ManualKenshin HimuraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sulfuric Acid Dew Point Corrosion in Waste Heat Boiler Tube For Coppe PDFDokument8 SeitenSulfuric Acid Dew Point Corrosion in Waste Heat Boiler Tube For Coppe PDFFaiz AgungNoch keine Bewertungen
- Alkali Corrosion of Refractories in Cement KilnsDokument69 SeitenAlkali Corrosion of Refractories in Cement KilnsplazanaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Buc Will: Document Identifier NND Heading Has Lncn-Poijndi !iIL-PRF-16173EDokument40 SeitenBuc Will: Document Identifier NND Heading Has Lncn-Poijndi !iIL-PRF-16173EJustformedia JustformediaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Heavy Phosphate Coatings SpecificationDokument17 SeitenHeavy Phosphate Coatings Specificationrobert_in_ar100% (1)
- SAE - AMS 5759lv003Dokument6 SeitenSAE - AMS 5759lv003Nilesh PatilNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chrome Plating and Anodizing Operations GuideDokument6 SeitenChrome Plating and Anodizing Operations GuidePuguh Cahpordjo BaeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mil DTF 5541fDokument12 SeitenMil DTF 5541fMarcos PerezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Qualanod SpecDokument62 SeitenQualanod SpecwilliamNoch keine Bewertungen
- Standard Specification For: Designation: B6 13Dokument3 SeitenStandard Specification For: Designation: B6 13Ahmed BilalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ionic Technologies Aerospace Heat Treatment and Nitriding ServicesDokument3 SeitenIonic Technologies Aerospace Heat Treatment and Nitriding ServicesSinan YıldızNoch keine Bewertungen
- ISO9000:2000 Certified Chem Film Coating ServicesDokument1 SeiteISO9000:2000 Certified Chem Film Coating ServicesShahid Ahmed.cNoch keine Bewertungen
- Zinc Plating InformationDokument4 SeitenZinc Plating Informationankur panwarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Astm 2016 A247 - 859Dokument13 SeitenAstm 2016 A247 - 859luis_f1l1Noch keine Bewertungen
- F 31 - 94 R99 - RJMXDokument5 SeitenF 31 - 94 R99 - RJMXAnilNoch keine Bewertungen
- MIL-PRF-46010H Solid Film Lubricant SpecificationDokument17 SeitenMIL-PRF-46010H Solid Film Lubricant SpecificationGoogle UserNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chromic Acid Lanxess-MSDS PDFDokument10 SeitenChromic Acid Lanxess-MSDS PDFyuk ming wongNoch keine Bewertungen
- Astm B 480 - 88 R01Dokument3 SeitenAstm B 480 - 88 R01SamuelNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ti 6al 4v Grade 5Dokument1 SeiteTi 6al 4v Grade 5Angga Kurniawan DharmaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Astm B571-97 PDFDokument3 SeitenAstm B571-97 PDFDillonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Modern Electroplating Fourth Edition Edited by M SDokument2 SeitenModern Electroplating Fourth Edition Edited by M Smiguelin91690% (1)
- Shallow Crack Fracture Mechanics Toughness Tests and Applications: First International ConferenceVon EverandShallow Crack Fracture Mechanics Toughness Tests and Applications: First International ConferenceNoch keine Bewertungen
- Material Finish GuideDokument3 SeitenMaterial Finish GuideAng Tiong WeeNoch keine Bewertungen
- 3ap 0862Dokument4 Seiten3ap 0862Durbha RaviNoch keine Bewertungen
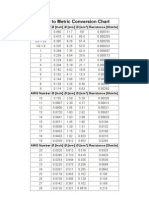
- AWG Wire Gauge Conversion Chart with Diameters and ResistanceDokument2 SeitenAWG Wire Gauge Conversion Chart with Diameters and ResistanceAdesina OladayoNoch keine Bewertungen
- A Wideband Printed Monopole Antenna For Wireless ApplicationsDokument4 SeitenA Wideband Printed Monopole Antenna For Wireless ApplicationsDurbha RaviNoch keine Bewertungen
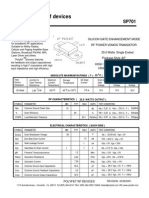
- SP 701Dokument2 SeitenSP 701Durbha RaviNoch keine Bewertungen
- Microstrip Patch Antenna: Analysis of Surface Area For Bandwidth ImprovementDokument4 SeitenMicrostrip Patch Antenna: Analysis of Surface Area For Bandwidth ImprovementDurbha RaviNoch keine Bewertungen
- 750W RF Power MOSFET DatasheetDokument4 Seiten750W RF Power MOSFET DatasheetDurbha RaviNoch keine Bewertungen
- AWG Wire Gauge Conversion Chart with Diameters and ResistanceDokument2 SeitenAWG Wire Gauge Conversion Chart with Diameters and ResistanceAdesina OladayoNoch keine Bewertungen
- GSM / UMTS freqency ranges and antenna guideDokument29 SeitenGSM / UMTS freqency ranges and antenna guideDurbha RaviNoch keine Bewertungen
- Vertically Polarized Cavity Backed Hexagonal Patch AntennaDokument6 SeitenVertically Polarized Cavity Backed Hexagonal Patch AntennaDurbha RaviNoch keine Bewertungen
- Screen Out PutDokument1 SeiteScreen Out PutDurbha RaviNoch keine Bewertungen
- HF Antennas: Active Rod Antenna HE 010Dokument2 SeitenHF Antennas: Active Rod Antenna HE 010Durbha RaviNoch keine Bewertungen
- [Doi 10.1109%2Fapcap.2012.6333141] Wongsakulphasatch, P.; Phongcharoenpanich, C.; Kawdungta, S. -- [IEEE 2012 IEEE Asia-Pacific Conference on Antennas and Propagation (APCAP) - Singapore, Singapore (2012.08.27-2012.08.29)]Dokument2 Seiten[Doi 10.1109%2Fapcap.2012.6333141] Wongsakulphasatch, P.; Phongcharoenpanich, C.; Kawdungta, S. -- [IEEE 2012 IEEE Asia-Pacific Conference on Antennas and Propagation (APCAP) - Singapore, Singapore (2012.08.27-2012.08.29)]Durbha RaviNoch keine Bewertungen
- CN 0100Dokument3 SeitenCN 0100Durbha RaviNoch keine Bewertungen
- Point Nine D1010 Tetrafet Point Nine: DafetDokument5 SeitenPoint Nine D1010 Tetrafet Point Nine: DafetDurbha RaviNoch keine Bewertungen
- A Wideband Printed Monopole Antenna For Wireless ApplicationsDokument4 SeitenA Wideband Printed Monopole Antenna For Wireless ApplicationsDurbha RaviNoch keine Bewertungen
- Planar Monopole AntennaDokument18 SeitenPlanar Monopole AntennaDurbha RaviNoch keine Bewertungen
- Aiaa 2010 8720Dokument8 SeitenAiaa 2010 8720Durbha RaviNoch keine Bewertungen
- CN 0240Dokument5 SeitenCN 0240Durbha RaviNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sem03 Paper 03307421Dokument24 SeitenSem03 Paper 03307421Durbha RaviNoch keine Bewertungen
- Planar Monopole AntennaDokument18 SeitenPlanar Monopole AntennaDurbha RaviNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hmc783lp6c Eval PCB SchematicDokument1 SeiteHmc783lp6c Eval PCB SchematicDurbha RaviNoch keine Bewertungen
- Determining The FM Bandwidth of A Wideband Varactor Tuned VCODokument13 SeitenDetermining The FM Bandwidth of A Wideband Varactor Tuned VCODurbha RaviNoch keine Bewertungen
- CGHV96100F2Dokument12 SeitenCGHV96100F2Durbha RaviNoch keine Bewertungen
- Broadband Biasing of Amplifiers v00p1112Dokument2 SeitenBroadband Biasing of Amplifiers v00p1112Fer CurtinoNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1P1 0030Dokument4 Seiten1P1 0030Durbha RaviNoch keine Bewertungen
- Basic PifaDokument6 SeitenBasic PifaDurbha RaviNoch keine Bewertungen
- A Wideband Printed Monopole Antenna For Wireless ApplicationsDokument4 SeitenA Wideband Printed Monopole Antenna For Wireless ApplicationsDurbha RaviNoch keine Bewertungen
- Base CatalogueDokument2 SeitenBase CatalogueDurbha RaviNoch keine Bewertungen
- HFSS RCSDokument42 SeitenHFSS RCSStanley Ochieng' OumaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Vco15 19Dokument3 SeitenVco15 19Durbha RaviNoch keine Bewertungen
- CMP CopperDokument2 SeitenCMP CopperPablo PachecoNoch keine Bewertungen
- MS51844 - SLEEVE, SWAGING-WIRE ROPE - With Amendment 1 - 3 December 2012Dokument5 SeitenMS51844 - SLEEVE, SWAGING-WIRE ROPE - With Amendment 1 - 3 December 2012JMNoch keine Bewertungen
- La Grange Issues With 30 S. La Grange RoadDokument61 SeitenLa Grange Issues With 30 S. La Grange RoadDavid GiulianiNoch keine Bewertungen
- En CR12471-1996 Screening Tests For Nickel Release From Alloys and Coatings in Items That Come Into Direct and Prolonged Contact With The SkinDokument10 SeitenEn CR12471-1996 Screening Tests For Nickel Release From Alloys and Coatings in Items That Come Into Direct and Prolonged Contact With The SkinHi HelloNoch keine Bewertungen
- Oilfield, Tubulars & ValvesDokument24 SeitenOilfield, Tubulars & ValvesAsser AymanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Interzinc - 52 (Primer)Dokument4 SeitenInterzinc - 52 (Primer)Marko AnticNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lack of Mechanical Integrity Blamed For Leak at Exxon Mobil RefineryDokument4 SeitenLack of Mechanical Integrity Blamed For Leak at Exxon Mobil RefineryKalaivani ArunachalamNoch keine Bewertungen
- Checklist For Inspection of Bridges by Bridge Line UnitsDokument3 SeitenChecklist For Inspection of Bridges by Bridge Line UnitsSSE Bridge SSBNoch keine Bewertungen
- Factory Finished Sliding Pass Windows SpecificationDokument5 SeitenFactory Finished Sliding Pass Windows SpecificationJuanPaoloYbañezNoch keine Bewertungen
- 17 4ph PDFDokument1 Seite17 4ph PDFMalavikaVarmaNoch keine Bewertungen
- W2P Membrane DiffuserDokument1 SeiteW2P Membrane DiffuserAngirishNoch keine Bewertungen
- StoragetechDokument24 SeitenStoragetechKaustav PatnaikNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fosroc Solutions For: General BuildingsDokument11 SeitenFosroc Solutions For: General BuildingsramatchatNoch keine Bewertungen
- Identifying Metal Can DefectsDokument19 SeitenIdentifying Metal Can DefectsAdeesha DeshanNoch keine Bewertungen
- NESCO utility tender for transformer repairing materialsDokument26 SeitenNESCO utility tender for transformer repairing materialsfddfNoch keine Bewertungen
- Frantz & Breen 1980Dokument262 SeitenFrantz & Breen 1980groger23Noch keine Bewertungen
- Ijias 002 01Dokument101 SeitenIjias 002 01jats_zNoch keine Bewertungen
- Conant Brochure OriginalDokument15 SeitenConant Brochure OriginalEduardo E HernandezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Corrosion Prevention For Metal Boats: Paint SystemsDokument4 SeitenCorrosion Prevention For Metal Boats: Paint SystemsdichauvinNoch keine Bewertungen
- Triple7 Enviroscale BrochureDokument2 SeitenTriple7 Enviroscale BrochureAsadNoch keine Bewertungen














































































![[Doi 10.1109%2Fapcap.2012.6333141] Wongsakulphasatch, P.; Phongcharoenpanich, C.; Kawdungta, S. -- [IEEE 2012 IEEE Asia-Pacific Conference on Antennas and Propagation (APCAP) - Singapore, Singapore (2012.08.27-2012.08.29)]](https://imgv2-2-f.scribdassets.com/img/document/245691689/149x198/717918330d/1415253880?v=1)


































