Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
GHJGH
Hochgeladen von
albertpktuOriginaltitel
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
GHJGH
Hochgeladen von
albertpktuCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
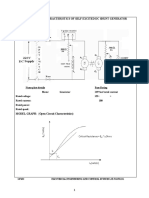
O.C.C OF DC SHUNT GENERATOR 1. What is the need for starter in a d.c motor? 2. How does a 3-point starter function?
3. Why is Rh1 kept in minimum position at starting? 4. Why is Rh2 kept in maximum position at start up? 5. What is residual voltage? How is it measured? 6. What is critical resistance? How can it be determined? 7. What are the conditions necessary for voltage build up in a d.c shunt generator? 8. What is critical speed? 9. Explain the shape of the O.C.C. LOAD TEST ON DC SERIES MOTOR 1. What is the precaution to be taken when working with a d.c series motor? 2. What is the need for starter with a d.c motor? 3. How does a 2-point starter function? 4. Explain the shape of the electrical and mechanical characteristics. 5. What is the condition for maximum efficiency in a d.c motor? 6. What are the different losses occurring in a d.c machine? 7. How are the meter ratings selected for this experiment? 8. Give some applications of d.c series motor. O.C AND S.C TESTS ON SINGLE PHASE TRANSFORMER 1. How are the meter ratings selected for O.C and S.C tests? 2. Why is the O.C test conducted on the l.v side of the transformer and S.C test on h.v side? 3. What are the losses measured in an O.C test? 4. What are the losses measured in an S.C test? 5. What is the condition for maximum efficiency in a transformer? 6. What is meant by regulation of a transformer? 7. Is a high or low value of regulation preferred? Why? 8. How can the parameters on one side of the transformer be transferred to the other side? Ex. No. 1 Open circuit and load characteristics of separately and self excited DC shunt generators. What is the principle of DC generator? Mention the application of separately excited DC generator. Give the advantages and disadvantages of separately excited DC generators. What will be the value of current in open circuit condition? What is the purpose of starter? On what occasions DC generators may not have residual flux? Define the term critical resistance referred to DC shunt generator. Define the term critical speed in DC shunt generator. The efficiency of generator rises to a maximum value and then decreases. Why?
What do you mean by residual magnetism in DC shunt generators? Ex. No. 3 Load characteristics of DC shunt and compound motor. State the principle of DC motor. How may the direction of DC motor be able to be reversed? Why the field rheostat of DC motor is kept at minimum position while starting? What will happen if the field of the DC motor is opened? What will happen if both the field current and armature current are reversed? What will happen if the shunt motor is directly connected across the supply line? Mention the applications of DC compound motor. Ex. No. 4 Load characteristics of DC series motor. What are the applications of DC series motors? What are the special features of a DC series motors? Which type of starter is used for DC series motors? How will you control the speed of DC series motor? What will happen to the speed of series motor when the supply voltage is reduced? What is the importance of no-load current of the motor? Why we use starters to start DC motors? DC series motors should never be started on no-load. Why? Why the DC series motors have high starting torque? What is meant by speed losses in DC machines? Ex. No. 5 Swinburnes test DC shunt motor. State the advantage of Swinburnes test. Is it possible to conduct Swinburnes test on DC series motor? Justify. State the Torque equation of DC motor. Which one of the speed will be higher either no-load speed or full load speed? What will be the efficiency of the motor at no-load? What will be the approximate value of armature and field resistance of DC motors? Why the armature control method is employed only below the rated speed in DC shunt motors? Why the field control method is employed only above the rated speed in DC shunt motors? Where we use shunt motor? Why is field control method superior to armature control method for DC shunt motors? Ex. No. 6 Hopkinsons test on DC motor generator set. What are the advantages of Hopkinsons test over Swinburnes test and what are its limitations? What is the function of no-voltage release (NVR) coil provided in a DC motor starter? How does a 4-point starter differ from 3-point starter? What are the other names of Hopkinsons test? What are the advantages of Hopkinsons test? A DC motor fails to start when switched on. What could be the reasons and remedies?
When does the armature of dc motor likely to get over-heated? What is the function of interpoles? How the interpoles are connected? Name different methods of electrical braking of DC motors. Ex. No. 7 Load test on single phase transformer . What is the function of a transformer? What is a load? Why do we perform load test when the efficiency can be determined by O.C. and S.C. tests? Mention the types of transformer. Explain the operating principle of a transformer. List out general applications of transformer. Define voltage regulation of a transformer. Ex. No. 8 Open circuit and short circuit tests on single phase transformer. Why the S.C. test is performed on HV side? Why the O.C. test is performed on LV side? What is the need of stepped core in transformers? At what power factor the voltage regulation of transformer is maximum? Under what value of power factor a transformer gives zero voltage regulation? What transformers are rated in kVA? How the eddy current loss can be reduced? What test is to be conducted on a transformer to estimate its voltage regulation? Define power factor. Is copper loss affected by power factor? Exp.No.1 LOAD TEST ON D.C. SHUNT MOTOR 1.Why should the field rheostat be kept in the position of minimum resistance? 2.What is the loading arrangement used in a dc motor? 3.How can the direction of rotation of a DC shunt motor be reversed? 4.What are the mechanical and electrical characteristics of a DC shunt motor? 5.What are the applications of a DC shunt motor? Exp.No.2 LOAD TEST ON D.C. SERIES MOTOR 1.Why a DC series motor should never be stared without load? 2. Why a DC series motor has a high starting torque? 3.Compare the resistances of the field windings of DC shunt and series motor? 4.What are the applications of DC series motor? 5. Comment on the Speed Torque characteristics of a DC series motor. 6. How does the torque vary with the armature current in a DC series motor? EXP.NO. 4 OCC ON SEPERATELY EXCITED DC GENERATOR What is the principle of generator? What is meant by residual magnetism? What is critical field resistance?
What is meant by saturation? What are the reasons for the drooping load characteristics? What is the difference between external and internal characteristics? Write the voltage equation of a separately excited DC generator. State the difference between generated emf and terminal voltage. Exp. No. 5 OCC AND LOAD TEST ON DC SHUNT GENERATOR What is the difference between a separately excited dc generator and dc shunt generator? If a DC shunt generator fails to build up voltage, what may be the probable reasons? What is SPST? What is its use in this experiment? What is the reason the presence of residual magnetism in the field poles? Why does the terminal voltage decrease as the load current increases? Write the voltage equation of a DC shunt generator. State the difference between generated emf and terminal voltage. Exp.No. 7 LOAD TEST ON SINGLE PHASE TRANSFORMER What is the principle of a transformer? What are the types of transformer? What are the applications of transformer? Why is the capacity of a transformer specified as KVA and not as KW? What is the condition for maximum efficiency of a transformer From the graph, find the load at which it occurs. Why is the efficiency of a transformer higher than that of motors? EXP.NO. 8 OC AND SC TESTS ON SINGLE PHASE TRANSFORMER 1. What is the purpose of OC and SC tests? 2. Why is the core of a transformer laminated? 3. What is meant by regulation? 4. Define the term transformation ratio? 5. What are the components of no load current? 6. What are the parameters of the equivalent circuit? 7. How are the parameters referred to the HV or LV side? Explain with an example. EXP.NO. 9 SWINBURNES TEST What is the purpose of Swinburnes test? What are the constant losses in a DC machine? What are the assumptions made in Swinburnes test? Why is the indirect method preferred to the direct loading test? The efficiency of DC machine is generally higher when it works as a generator than when it works as a motor. Is this statement true or false? Justify your answer with proper reasons.
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceVon EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (895)
- HGVHJHJFDokument1 SeiteHGVHJHJFalbertpktuNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeVon EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (5794)
- HjssDokument1 SeiteHjssalbertpktuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeVon EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (537)
- DSJJDokument1 SeiteDSJJalbertpktuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceVon EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (588)
- Kldsjalfkksdalfm L Sdflkds LDSLF LSDFLK LSDFKL LDokument1 SeiteKldsjalfkksdalfm L Sdflkds LDSLF LSDFLK LSDFKL LalbertpktuNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Von EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Bewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (98)
- DGDS, DFP GDK Kpodg Dfko GFDDokument1 SeiteDGDS, DFP GDK Kpodg Dfko GFDalbertpktuNoch keine Bewertungen
- GCNGFBM LKML MFDLGML, MLLH, FGH LDokument1 SeiteGCNGFBM LKML MFDLGML, MLLH, FGH LalbertpktuNoch keine Bewertungen
- GHGFH GFH GFHGH FDHFDHFHFG GFHD GFHDokument1 SeiteGHGFH GFH GFHGH FDHFDHFHFG GFHD GFHalbertpktuNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingVon EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (400)
- RHFGTHGFHGH GF Hgfhjigfj FG HHGF Ghu Ggfoihj GFH Hgo Ijghokg Ghiojohh GohogohDokument1 SeiteRHFGTHGFHGH GF Hgfhjigfj FG HHGF Ghu Ggfoihj GFH Hgo Ijghokg Ghiojohh GohogohalbertpktuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItVon EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (838)
- CABLEDokument48 SeitenCABLEElectrical RadicalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureVon EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (474)
- High-Voltage Direct Current (HVDC) Installations - Systems TestDokument77 SeitenHigh-Voltage Direct Current (HVDC) Installations - Systems TestChristian MarquezNoch keine Bewertungen
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryVon EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (231)
- Shunt Capacitor BanksS Best Pracitices For Protection and SwitchingDokument95 SeitenShunt Capacitor BanksS Best Pracitices For Protection and Switchingheriberhuerta100% (1)
- E06-017 Rev 1 EIV Manual PDFDokument29 SeitenE06-017 Rev 1 EIV Manual PDFPalomino VergaraNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerVon EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (271)
- Circuit Diagram:: Open Circuit Characteristics of Self Excited DC Shunt GeneratorDokument121 SeitenCircuit Diagram:: Open Circuit Characteristics of Self Excited DC Shunt GeneratorAbdul RahumanNoch keine Bewertungen
- OCCDokument4 SeitenOCCkudupudinageshNoch keine Bewertungen
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaVon EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (266)
- Ina 169Dokument15 SeitenIna 169Christian Jay MendozaNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersVon EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (345)
- Imp Objective For Assistant Engineer Electrical by UppclDokument15 SeitenImp Objective For Assistant Engineer Electrical by UppclRishi Kant Sharma100% (4)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealVon EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (74)
- SUPPLIER SIGNAL CONDITIONNER CTA125 DF 5665007 01 PDFDokument5 SeitenSUPPLIER SIGNAL CONDITIONNER CTA125 DF 5665007 01 PDFDaniel Rolando Gutierrez FuentesNoch keine Bewertungen
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyVon EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (2259)
- Ohms LawDokument15 SeitenOhms LawM Kumar MarimuthuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnVon EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (234)
- s2c-s h6r AccDokument5 Seitens2c-s h6r AccWellington SilvaNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaVon EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (45)
- Superconducting Fault Current EPRIDokument68 SeitenSuperconducting Fault Current EPRIhozan_soranNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreVon EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (1090)
- Electrical Engineering Lab Manual For II Mech Part IDokument54 SeitenElectrical Engineering Lab Manual For II Mech Part IArivumani80% (5)
- Problem Set 1Dokument1 SeiteProblem Set 1Chaeyoung YooNoch keine Bewertungen
- Protection, Monitoring and Control of Shunt ReactorsDokument198 SeitenProtection, Monitoring and Control of Shunt Reactorsrodrigocmam100% (3)
- Komatsu ErrorCodeDokument28 SeitenKomatsu ErrorCodeHuấn Đặng100% (1)
- Hitungan KapasitorDokument4 SeitenHitungan Kapasitorbella vertikaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Generator Protection 7UM62Dokument39 SeitenGenerator Protection 7UM62Reji Kurian100% (1)
- Electronic Measurements & InstrumentationDokument20 SeitenElectronic Measurements & Instrumentation06121a040160% (5)
- Electrical Measurement Lab by SK FinalDokument40 SeitenElectrical Measurement Lab by SK FinalAjit PatraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Practical Manual: Electrical Machine LabDokument4 SeitenPractical Manual: Electrical Machine LabSurajMauryaNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Von EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Bewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (121)
- Metasol MCCB EDokument140 SeitenMetasol MCCB EJose AntonioNoch keine Bewertungen
- S.Y. Resistance of A Galvanometer G by Shunting GR - IIDokument2 SeitenS.Y. Resistance of A Galvanometer G by Shunting GR - IINeelam KapoorNoch keine Bewertungen
- ObservationsDokument2 SeitenObservationsRalph SeminianoNoch keine Bewertungen
- EV-1W Motor ControllerDokument43 SeitenEV-1W Motor ControllerMarioNoch keine Bewertungen
- Parallel GeneratorsDokument4 SeitenParallel GeneratorsMariam FatimaNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Direct Current MotorGeneratorDokument8 SeitenThe Direct Current MotorGeneratorLaurent VitugNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mycbseguide: Class 12 - Physics Sample Paper 08Dokument17 SeitenMycbseguide: Class 12 - Physics Sample Paper 08Divydarshan MishraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Specification of Lightening ArrestersDokument12 SeitenSpecification of Lightening ArrestersS BalasubramaniamNoch keine Bewertungen
- Trasfor User Manual-EnglishDokument28 SeitenTrasfor User Manual-EnglishElectrifying GuyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesVon EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (821)