Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Boef
Hochgeladen von
metroroadOriginalbeschreibung:
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Boef
Hochgeladen von
metroroadCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
"BOEF" --- BEAM ON ELASTIC FOUNDATION ANALYSIS
Program Description:
"BOEF" is a spreadsheet program written in MS-Excel for the purpose of analysis a finite length beam with free ends supported continuously on an elastic foundation. This program is ideally suited for analyzing a soil supported beam, a combined footing, or a strip of a slab or a mat. Specifically, the beam shear, moment, deflection, and soil bearing pressure are calculated for 100 equal beam segments, as well as the maximum values. Plots of both the shear, moment, and soil bearing pressure diagrams are produced, as well as a tabulation of the shear, moment, deflection, and bearing pressure for the beam. This program is a workbook consisting of two (2) worksheets, described as follows:
Worksheet Name
Doc Beam on Elastic Foundation
Description
This documentation sheet Beam on elastic foundation analysis
Program Assumptions and Limitations:
1. The following reference was used in the development of this program (see below): "Formulas for Stress and Strain" - Fifth Edition by Raymond R. Roark and Warren C. Young, McGraw-Hill Book Company (1975), pages 128 to 146. 2. This program uses the equations for a "finite-length" beam in the analysis. This usually gives very similar to exact results for a "semi-infinite" beam which has had end-corrections applied to "force" the moment and shear values to be equal to zero at the ends. (Note: a "semi-infinite" beam is defined as one that has a b *L value > 6.) 3. This program uses the five (5) additional following assumptions as a basis for analysis: a. Beam must be of constant cross section (E and I are constant for entire length, L). b. Beam must have both ends "free". ("Pinned" or "fixed" ends are not permitted.) c. Elastic support medium (soil) has a constant modulus of subgrade, K, along entire length of beam. d. Applied loads are located in the center of the width, W, of the beam and act along a centroidal line of the beam-soil contact area. e. Bearing pressure is linearly proportional to the deflection, and varies as a function of subgrade modulus, K. 4. This program can handle up to twelve (12) concentrated (point) loads, a full uniformly distributed load with up to six (6) additional full or partial uniformly distributed loads, and up to four (4) externally applied moments. 5. Beam self-weight is NOT automatically included in the program analysis, but may be accounted for as a full uniformly distributed applied load. Beam self-weight will only affect the deflection and bearing pressure, and not the moment or shear. 6. This program will calculate the maximum positive and negative shears, the maximum positive and negative moments, the maximum negative deflection, and the maximum soil bearing pressure. The calculated values for the maximum shears, maximum moments, deflection, and bearing pressure are determined from dividing the beam into 100 equal segments with 101 points, and including all of the point load and applied moment locations as well. 7. The user is given the ability to input four (4) specific locations from the left end of the beam to calculate the shear, moment, deflection, and bearing pressure. 8. The plots of the shear, moment, and bearing pressure diagrams as well as the displayed tabulation of shear, moment, deflection, and bearing pressure are based on the beam being divided up into 100 equal segments with 101 points. 9. This program contains numerous comment boxes which contain a wide variety of information including explanations of input or output items, equations used, data tables, etc. (Note: presence of a comment box is denoted by a red triangle in the upper right-hand corner of a cell. Merely move the mouse pointer to the desired cell to view the contents of that particular "comment box".)
Formulas Used to Determine Shear, Moment, Slope, Deflection, and Pressure in Beam on Elastic Foundation General Constants and Functions: I = W*T^3/12
b = ((K*W)/(4*E*144*I))^(1/4) F1 = COSH(b *x)*COS(b *x) F2 = COSH(b *x)*SIN(b *x) + SINH(b *x)*COS(b *x) F3 = SINH(b *x)*SIN(b *x) F4 = COSH(b *x)*SIN(b *x) - SINH(b *x)*COS(b *x) C1 = COSH(b *L)*COS(b *L) C2 = COSH(b *L)*SIN(b *L) + SINH(b *L)*COS(b *L) C3 = SINH(b *L)*SIN(b *L) C4 = COSH(b *L)*SIN(b *L) - SINH(b *L)*COS(b *L) C11 = SINH(b *L)^2 - SIN(b *L)^2
For Full Uniform or Distributed Loads:
(Note: units of 'K' are "kcf".)
Specific Constants and Functions: Ca2 = COSH(b *(L-b))*SIN(b *(L-b)) + SINH(b *(L-b))*COS(b *(L-b)) Ca3 = SINH(b *(L-b))*SIN(b *(L-b)) Cb2 = COSH(b *(L-e))*SIN(b *(L-e)) + SINH(b *(L-e))*COS(b *(L-e)) Cb3 = SINH(b *(L-e))*SIN(b *(L-e)) If x > b: Fa1 = COSH(b *(x-b))*COS(b *(x-b)) Fa2 = COSH(b *(x-b))*SIN(b *(x-b)) + SINH(b *(x-b))*COS(b *(x-b)) Fa3 = SINH(b *(x-b))*SIN(b *(x-b)) Fa4 = COSH(b *(x-b))*SIN(b *(x-b)) - SINH(b *(x-b))*COS(b *(x-b)) Fa5 = 1- Fa1 If x > e: Fb1 = COSH(b *(x-e))*COS(b *(x-e)) Fb2 = COSH(b *(x-e))*SIN(b *(x-e)) + SINH(b *(x-e))*COS(b *(x-e)) Fb3 = SINH(b *(x-e))*SIN(b *(x-e)) Fb4 = COSH(b *(x-e))*SIN(b *(x-e)) - SINH(b *(x-e))*COS(b *(x-e)) Fb5 = 1- Fb1
else: else: else: else: else: else: else: else: else: else:
Fa1 = Fa2 = Fa3 = Fa4 = Fa5 = Fb1 = Fb2 = Fb3 = Fb4 = Fb5 =
0 0 0 0 -Fa1 0 0 0 0 -Fb1
Loading functions for each uniform or distributed load evaluated at distance x = L from left end of beam: Va = 0 Ma = 0 qa = w/(2*E*144*I*b^3)*(C2*Ca3-C3*Ca2)/C11 Da = w/(4*E*144*I*b^4)*(C4*Ca2-2*C3*Ca3)/C11 Loading functions for each uniform or distributed load evaluated at distance = x from left end of beam: Fvx = Va*F1 - Da*2*(E*144)*I*b ^3*F2 - qa*2*(E*144)*I*b ^2*F3 - Ma*b *F4 - w/(2*b )*Fa2 Fmx = Ma*F1 + Va/(2*b )*F2 - Da*2*(E*144)*I*b ^2*F3 - qa*(E*144)*I*b *F4 - w/(2*b ^2)*Fa3 Fqx = qa*F1 + Ma/(2*E*144*I*b )*F2 + Va/(2*E*144*I*b ^2)*F3 - Da*b *F4 - w/(4*E*144*I*b ^3)*Fa4 FDx = Da*F1 + qa/(2*b )*F2 + Ma/(2*E*144*I*b ^2)*F3 + Va/(4*E*144*I*b ^3)*F4 - w/(4*E*144*I*b ^4)*Fa5
For Point Loads: Specific Constants and Functions: Ca1 = COSH(b *(L-a))*COS(b *(L-a)) Ca2 = COSH(b *(L-a))*SIN(b *(L-a)) + SINH(b *(L-a))*COS(b *(L-a)) If x > a: Fa1 = COSH(b *(x-a))*COS(b *(x-a)) Fa2 = COSH(b *(x-a))*SIN(b *(x-a)) + SINH(b *(x-a))*COS(b *(x-a)) Fa3 = SINH(b *(x-a))*SIN(b *(x-a)) Fa4 = COSH(b *(x-a))*SIN(b *(x-a)) - SINH(b *(x-a))*COS(b *(x-a)) Loading functions for each point load evaluated at distance x = L from left end of beam: Va = 0 Ma = 0 qa = P/(2*E*144*I*b^2)*(C2*Ca2-2*C3*Ca1)/C11 Da = P/(2*E*144*I*b^3)*(C4*Ca1-C3*Ca2)/C11 Loading functions for each point load evaluated at distance = x from left end of beam: Fvx = Va*F1 - Da*2*(E*144)*I*b ^3*F2 - qa*2*(E*144)*I*b ^2*F3 - Ma*b *F4 - P*Fa1 Fmx = Ma*F1 + Va/(2*b )*F2 - Da*2*(E*144)*I*b ^2*F3 - qa*(E*144)*I*b *F4 - P/(2*b )*Fa2 Fqx = qa*F1 + Ma/(2*E*144*I*b )*F2 + Va/(2*E*144*I*b ^2)*F3 - Da*b *F4 - P/(2*E*144*I*b ^2)*Fa3 FDx = Da*F1 + qa/(2*b )*F2 + Ma/(2*E*144*I*b ^2)*F3 + Va/(4*E*144*I*b ^3)*F4 - P/(4*E*144*I*b ^3)*Fa4 For Applied Moments: Specific Constants and Functions: Ca1 = COSH(b *(L-c))*COS(b *(L-c)) Ca4 = COSH(b *(L-c))*SIN(b *(L-c)) - SINH(b *(L-c))*COS(b *(L-c)) If x > c: Fa1 = COSH(b *(x-c))*COS(b *(x-c)) Fa2 = COSH(b *(x-c))*SIN(b *(x-c)) + SINH(b *(x-c))*COS(b *(x-c)) Fa3 = SINH(b *(x-c))*SIN(b *(x-c)) Fa4 = COSH(b *(x-c))*SIN(b *(x-c)) - SINH(b *(x-c))*COS(b *(x-c)) Loading functions for each applied moment evaluated at distance x = L from left end of beam: Va = 0 Ma = 0 qa = -M/(E*144*I*b)*(C3*Ca4+C2*Ca1)/C11 Da = M/(2*E*144*I*b^2)*(2*C3*Ca1+C4*Ca4)/C11 Loading functions for each applied moment evaluated at distance = x from left end of beam: Fvx = Va*F1 - Da*2*(E*144)*I*b ^3*F2 - qa*2*(E*144)*I*b ^2*F3 - Ma*b *F4 - M/(2*b )*Fa2 Fmx = Ma*F1 + Va/(2*b )*F2 - Da*2*(E*144)*I*b ^2*F3 - qa*(E*144)*I*b *F4 - M*Fa1 Fqx = qa*F1 + Ma/(2*E*144*I*b )*F2 + Va/(2*E*144*I*b ^2)*F3 - Da*b *F4 - M/(2*E*144*I*b )*Fa2 FDx = Da*F1 + qa/(2*b )*F2 + Ma/(2*E*144*I*b ^2)*F3 + Va/(4*E*144*I*b ^3)*F4 - M/(2*E*144*I*b ^2)*Fa3 Summations of shear, moment, slope, and deflection at distance = x from left end of beam: Shear: Moment: Slope: Deflection: Pressure: Vx = Mx = qx = Dx = Qx =
else: else: else: else:
Fa1 = Fa2 = Fa3 = Fa4 =
0 0 0 0
else: else: else: else:
Fa1 = Fa2 = Fa3 = Fa4 =
0 0 0 0
S(Fvx) S(Fmx) S(Fqx) S(FDx) Dx*K
"BOEF.xls" Program Version 1.2
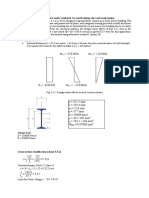
BEAM ON ELASTIC FOUNDATION ANALYSIS
For Soil Supported Beam, Combined Footing, Slab Strip or Mat Strip of Assumed Finite Length with Both Ends Free Job Name: Koenders MFG - Pipe Sleeper Subject: Sleeper on Grade Job Number: 401EN12 Originator: JMT Checker: Input Data:
c
Beam Data:
b
e
ft. ft. ft. ksi pci ft.^4
Length, L = 20.6690 Width, W = 0.7500 Thickness, T = 0.5000 Modulus, E = 130 Subgrade, K = 55 Inertia, I = 0.003 Beam Loadings: Full Uniform: w=
a +P +wb +we +M +w T E,I x L
Subgrade
Nomenclature 0.0000
kips/ft.
Results:
End
Start
Distributed:
#1: #2: #3: #4: #5: #6:
b (ft.) 4.1725 9.7500 15.3270
wb (kips/ft.) 8.0920 8.0920 8.0920
e (ft.) 5.4225 11.0000 16.5773
we (kips/ft.) 8.0920 8.0920 8.0920
Beam Flexiblity Criteria: for b*L <= p/4 beam is rigid for p/4 < b*L < p beam is semi-rigid for b*L >= p beam is flexible for b*L >= 6 beam is semi-infinite long b= b*L = 0.760 15.70 b = ((K*W)/(4*E*144*I))^(1/4) b*L = Flexibility Factor
Point Loads:
#1: #2: #3: #4: #5: #6: #7: #8: #9: #10: #11: #12:
a (ft.)
P (kips)
Beam is flexible
Max. Shears and Locations: +V(max) = k @x= 2.91 -V(max) = -2.77 k @x= Max. Moments and Locations: +M(max) = ft-k @x= 2.02 -M(max) = -1.07 ft-k @x= Max. Deflection and Location: D(max) = -0.597 in. @x= c (ft.) M (ft-kips) Max. Soil Pressure and Location: Q(max) = 4.726 ksf @x=
15.30 10.95
ft. ft.
10.33 13.23
ft. ft.
4.75
ft.
Moments:
#1: #2: #3: #4:
4.75
ft.
4 of 6
1/21/2014 5:15 PM
Bearing Pressure (ksf)
Moment (ft-kips) Shear (kips)
2.0 2.5 -0.5
-1.5
0.0 0.5 1.0 1.5
-1.0
-1.000
5.000 0.0 1.0 2.0 3.0 4.0 -4.0 -3.0 -2.0 -1.0 0.00 0.00 0.83 1.65 2.48 3.31 4.13 4.96 5.79 6.61 7.44 8.27 9.09 9.92 10.75 11.57 12.40 13.23 14.05 14.88
15.71 16.54 0.00 0.83 1.65
4.000 0.83 1.65 2.48 3.31 4.13 4.96 5.79 6.61 7.44 8.27 9.09 9.92 10.75 11.57 12.40 13.23 14.05
14.05
14.88 12.40 11.57 9.09 8.27 7.44 4.96 4.13
3.000
2.48 3.31 5.79 6.61
2.000
1.000
0.000
Moment Diagram
Bearing Pressure Diagram
5 of 6
9.92 10.75
x (ft.)
Shear Diagram
x (ft.) x (ft.)
13.23
14.88 15.71 16.54 17.36 18.19 19.02 19.84 20.67
15.71 16.54
17.36 18.19
19.02 19.84
17.36 18.19 19.02 19.84
20.67
"BOEF.xls" Program Version 1.2
1/21/2014 5:15 PM
20.67
Compatibility Report for BOEF Full Beam Length.xls Run on 9/18/2012 10:53 The following features in this workbook are not supported by earlier versions of Excel. These features may be lost or degraded when opening this workbook in an earlier version of Excel or if you save this workbook in an earlier file format.
Significant loss of functionality
# of occurrences 25
Version
One or more cells in this workbook contain data validation rules which refer to values on other worksheets. These data validation rules will not be saved.
Beam on Excel 97-2003 Elastic Foundation'!E 25:E30 Beam on Elastic Foundation'!L 21:L22 Beam on Elastic Foundation'!B 47:B50 Beam on Elastic Foundation'!B 25:B30 Beam on Elastic Foundation'!B 33:B44 Beam on Elastic Foundation'!D 29:D30 Beam on Elastic Foundation'!D 25:D28 Beam on Elastic Foundation'!L 23:L24
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Welding Procedure PreparationDokument122 SeitenWelding Procedure Preparationthe_badass1234100% (21)
- Timber Ridge Beam Calculation Report 2Dokument5 SeitenTimber Ridge Beam Calculation Report 2CartecSyriaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fluid Power Graphic SymbolsDokument24 SeitenFluid Power Graphic SymbolsJShearer94% (16)
- Single Box Culvert Structural Design 1 5m X 1 5mDokument24 SeitenSingle Box Culvert Structural Design 1 5m X 1 5mdanilo m.sampagaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Screw Thread CalculationsDokument4 SeitenScrew Thread Calculationsyauction50% (2)
- Project Budget Worksheet v2 7Dokument4 SeitenProject Budget Worksheet v2 7metroroadNoch keine Bewertungen
- Load CombinationsDokument3 SeitenLoad CombinationsKutty MansoorNoch keine Bewertungen
- Instantaneous Center of Rotation MethodDokument3 SeitenInstantaneous Center of Rotation MethodrammohanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Scientific Research and Experimental Development (SR&ED) Expenditures ClaimDokument40 SeitenScientific Research and Experimental Development (SR&ED) Expenditures ClaimmetroroadNoch keine Bewertungen
- FSA Gasket Handbook - June 2017Dokument138 SeitenFSA Gasket Handbook - June 2017Dijin MaroliNoch keine Bewertungen
- Beam Cantiliever CalculationDokument16 SeitenBeam Cantiliever CalculationAnonymous sfkedkymNoch keine Bewertungen
- Beam On Elastic Foundation AnalysisDokument5 SeitenBeam On Elastic Foundation Analysisbuffyto5377100% (1)
- Earthquake Load Calculation (Base Shear Method) : Rigid FrameDokument4 SeitenEarthquake Load Calculation (Base Shear Method) : Rigid FrameJohn Rheynor MayoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Merritt H.E. Hydraulic Control SystemsDokument366 SeitenMerritt H.E. Hydraulic Control Systemsrwcooldude100% (2)
- Elastic Lateral Torsional BucklingDokument3 SeitenElastic Lateral Torsional BucklingRuchit ParmarNoch keine Bewertungen
- One Way Slab DesignDokument19 SeitenOne Way Slab DesignWinston Advincula100% (1)
- Mat FoundationsDokument10 SeitenMat FoundationsKamran KhurshidNoch keine Bewertungen
- US Stair oDokument3 SeitenUS Stair oRenvil PedernalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Norma CMAA 70Dokument90 SeitenNorma CMAA 70Marcelo Navarro100% (7)
- Brookfield Viscosimetro PDFDokument59 SeitenBrookfield Viscosimetro PDFKike BayonaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Example TorsionDokument5 SeitenExample Torsiontemestruc71Noch keine Bewertungen
- Traffic Characterization PDFDokument11 SeitenTraffic Characterization PDFAlejandro GonzalezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cruciform Sections + NSCApril06 - TechDokument3 SeitenCruciform Sections + NSCApril06 - TechIho1Noch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 2 Design For Serviceability PDFDokument14 SeitenChapter 2 Design For Serviceability PDFChee Fong MakeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Soil Dynamics Using FlacDokument57 SeitenSoil Dynamics Using FlacVivian Kallou100% (3)
- Deep BeamDokument31 SeitenDeep BeamEngr Mohammed Ubaid QureshiNoch keine Bewertungen
- One Way SlabDokument5 SeitenOne Way SlabShoaib Mohammad Quraishi100% (2)
- Resistance of Members To Flexural Buckling According To Eurocode 3Dokument95 SeitenResistance of Members To Flexural Buckling According To Eurocode 3venkatasrikanthNoch keine Bewertungen
- Design of Beam LedgeDokument7 SeitenDesign of Beam LedgeAnonymous 0JQGC2Noch keine Bewertungen
- How To Scale-Up Mixing Processes in Non-Newtonian FluidsDokument9 SeitenHow To Scale-Up Mixing Processes in Non-Newtonian FluidsMarek PawelNoch keine Bewertungen
- Beam On Elastic FoundationDokument7 SeitenBeam On Elastic FoundationsdewssNoch keine Bewertungen
- Stair Case DesignDokument4 SeitenStair Case DesignTefera TemesgenNoch keine Bewertungen
- Elastic Foundation of Beams AnalysisDokument5 SeitenElastic Foundation of Beams AnalysisEFECANNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sspc-Pa 14Dokument6 SeitenSspc-Pa 14Anonymous rYZyQQot5580% (5)
- Elastic Stresses in Single Mitred BendsDokument22 SeitenElastic Stresses in Single Mitred BendsWang Kin HuiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Strength of MaterialsDokument121 SeitenStrength of MaterialsHenry Hong91% (32)
- Beam On Elastic Foundation AnalysisDokument5 SeitenBeam On Elastic Foundation AnalysisMagdy BakryNoch keine Bewertungen
- SAP2000 Section PropertiesDokument3 SeitenSAP2000 Section PropertiesCon Can100% (1)
- Accounting Accidental Torsion STAADDokument3 SeitenAccounting Accidental Torsion STAADmogustNoch keine Bewertungen
- CPP Tank DesignDokument118 SeitenCPP Tank Designchristian reyesNoch keine Bewertungen
- TR 334 Tutorial-1Dokument5 SeitenTR 334 Tutorial-1Adaminovic MrishoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Influence LineDokument7 SeitenInfluence Linemr_sam91Noch keine Bewertungen
- British Problem 5 PDFDokument5 SeitenBritish Problem 5 PDFelixnzNoch keine Bewertungen
- 10 FT Restrained Wall Design of CMU Wall: See Analysis BelowDokument1 Seite10 FT Restrained Wall Design of CMU Wall: See Analysis Belowmeetvinayak2007Noch keine Bewertungen
- Wind Load On Cable TraysDokument10 SeitenWind Load On Cable TraysAaron EasleyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Huong Dan MegafloorDokument11 SeitenHuong Dan Megafloortrung1983Noch keine Bewertungen
- Working Draft of Combined Piled-Raft Foundation, Doc - CED 43 (196) WDDokument19 SeitenWorking Draft of Combined Piled-Raft Foundation, Doc - CED 43 (196) WDKedarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Foundation Design of Lamp PostDokument1 SeiteFoundation Design of Lamp PostMayank AgrawalNoch keine Bewertungen
- SikaTack Panel System - Sheet 1 Cert 05 - 4218Dokument10 SeitenSikaTack Panel System - Sheet 1 Cert 05 - 4218Peter DudasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Prestressing FlexuralDokument22 SeitenPrestressing FlexuralGhulamRanger100% (1)
- Flexural-Torsional Buckling of Compression Members PDFDokument33 SeitenFlexural-Torsional Buckling of Compression Members PDFYirga Bezabeh100% (1)
- Ekspan EA-EQF-EKR Series Bearing BrochureDokument12 SeitenEkspan EA-EQF-EKR Series Bearing Brochurechithirai10Noch keine Bewertungen
- Lecture 4 - House DesignDokument18 SeitenLecture 4 - House Designkkhan_451062Noch keine Bewertungen
- Design of Doubly Reinforced BeamDokument7 SeitenDesign of Doubly Reinforced BeamAmrutha SivaramanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lec9 Strength Design Methoddoubly Reinforced Beams 160214192041 PDFDokument8 SeitenLec9 Strength Design Methoddoubly Reinforced Beams 160214192041 PDFဒုကၡ သစၥာNoch keine Bewertungen
- Two Way SlabDokument17 SeitenTwo Way SlabGetachew MekuriawNoch keine Bewertungen
- Examples in Column's ChapterDokument12 SeitenExamples in Column's Chapterrd radenNoch keine Bewertungen
- Concrete Slab Analysis by Coefficient Method PDFDokument7 SeitenConcrete Slab Analysis by Coefficient Method PDFJones EdombingoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tall Buildings Chap 3 ADokument7 SeitenTall Buildings Chap 3 ATharangi MunaweeraNoch keine Bewertungen
- ProkonDokument7 SeitenProkonmark7301158Noch keine Bewertungen
- Pier Design Example - US Units - Design Step 8Dokument50 SeitenPier Design Example - US Units - Design Step 8amitdas19830131Noch keine Bewertungen
- Introduction To Beams: Part ADokument49 SeitenIntroduction To Beams: Part AMorad AJNoch keine Bewertungen
- W12x30 Beam To BeamDokument6 SeitenW12x30 Beam To BeamWin ThanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Shallow Foundation Design 2: SettlementDokument32 SeitenShallow Foundation Design 2: SettlementPhanna MongNoch keine Bewertungen
- Amendment No. 1 November 2014 TO Is 4326: 2013 Earthquake Resistant Design and Construction of Buildings - Code of PracticeDokument9 SeitenAmendment No. 1 November 2014 TO Is 4326: 2013 Earthquake Resistant Design and Construction of Buildings - Code of PracticeAKSNoch keine Bewertungen
- AISC LRFD Column DesignDokument4 SeitenAISC LRFD Column Designwinlugue3059Noch keine Bewertungen
- Calculation of Long-Term Cracked Deflection and Deflection Due To Live LoadDokument1 SeiteCalculation of Long-Term Cracked Deflection and Deflection Due To Live LoadJohn STC0% (1)
- Design Drawing of Steel StructuresDokument4 SeitenDesign Drawing of Steel StructuresDEVINoch keine Bewertungen
- BS8110 Span-Depth Ratios PDFDokument1 SeiteBS8110 Span-Depth Ratios PDFA KNoch keine Bewertungen
- GrillageDokument6 SeitenGrillagevasanthk81Noch keine Bewertungen
- Reinforced Concrete Design - One-Way SlabDokument2 SeitenReinforced Concrete Design - One-Way SlabRal GLNoch keine Bewertungen
- Structural Design Calculations: Spread Footing For Temporary BridgeDokument3 SeitenStructural Design Calculations: Spread Footing For Temporary BridgeFeras TemimiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Singly Reinforced Concrete Beams AS3600Dokument6 SeitenSingly Reinforced Concrete Beams AS3600Preston WilliamNoch keine Bewertungen
- Steel 2022 BeamDokument26 SeitenSteel 2022 BeamRaven Von DizonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Rectangular Beam AnalysisDokument5 SeitenRectangular Beam AnalysisheshamNoch keine Bewertungen
- "Boef" - Beam On Elastic Foundation Analysis: Program DescriptionDokument7 Seiten"Boef" - Beam On Elastic Foundation Analysis: Program DescriptionAJR365Noch keine Bewertungen
- Wind Load Calculation For Roof Covering and Add-Ons - National Research Council CanadaDokument1 SeiteWind Load Calculation For Roof Covering and Add-Ons - National Research Council CanadametroroadNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tanya's Comprehensive Guide To Feline Chronic Kidney DiseaseDokument11 SeitenTanya's Comprehensive Guide To Feline Chronic Kidney Diseasemetroroad100% (1)
- Hoist Monorail Pre Commissioning ITPDokument7 SeitenHoist Monorail Pre Commissioning ITPmetroroadNoch keine Bewertungen
- CDH1 MP5Dokument44 SeitenCDH1 MP5DTNoch keine Bewertungen
- Edusat Presentation On Pneumatics5Dokument147 SeitenEdusat Presentation On Pneumatics5metroroadNoch keine Bewertungen
- B5 1R1Dokument74 SeitenB5 1R1Mohamed Osman AbdallaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Wire Rope Engineering HandBookDokument139 SeitenWire Rope Engineering HandBookhari1008108Noch keine Bewertungen
- A955305 PDFDokument177 SeitenA955305 PDFAnonymous EOy00uV7Z100% (1)
- Astm A786 PDFDokument11 SeitenAstm A786 PDFLuis Esteban Armijos MacasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Welding Line Analsys SampleDokument9 SeitenWelding Line Analsys SamplemetroroadNoch keine Bewertungen
- EN - 08 SAF and SAW - TCM - 12-107699 PDFDokument66 SeitenEN - 08 SAF and SAW - TCM - 12-107699 PDFPetter PeñaNoch keine Bewertungen
- FUNdaMENTALs Topic 10Dokument85 SeitenFUNdaMENTALs Topic 10metroroadNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sample Qs Manual PDFDokument59 SeitenSample Qs Manual PDFDairon GutierrezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Expansion Joints TutorialDokument17 SeitenExpansion Joints TutorialGeetanjali YallaNoch keine Bewertungen
- CRA Software Webinar 23-Jan-17 EowSpcsd Wo2-EDokument60 SeitenCRA Software Webinar 23-Jan-17 EowSpcsd Wo2-EmetroroadNoch keine Bewertungen
- SP SP VP V PR) : Velocity Pressure Method Calculation SheetDokument6 SeitenSP SP VP V PR) : Velocity Pressure Method Calculation SheetAnkit LonareNoch keine Bewertungen
- SCC Requirements and Guidance For The Accreditation of Testing LaboratoriesDokument22 SeitenSCC Requirements and Guidance For The Accreditation of Testing LaboratoriesmetroroadNoch keine Bewertungen
- SR&ED Template 2014Dokument4 SeitenSR&ED Template 2014metroroadNoch keine Bewertungen
- Guidelines For Resolving Claimants' SR&ED ConcernsDokument4 SeitenGuidelines For Resolving Claimants' SR&ED ConcernsmetroroadNoch keine Bewertungen
- Report Guidelines Consolidated - July 2005Dokument1 SeiteReport Guidelines Consolidated - July 2005metroroadNoch keine Bewertungen
- Project Costing Guide - Client 20050606Dokument7 SeitenProject Costing Guide - Client 20050606metroroadNoch keine Bewertungen
- Guide To Claiming The Alberta Scientific Research and Experimental Development (Sr&Ed) Tax CreditDokument7 SeitenGuide To Claiming The Alberta Scientific Research and Experimental Development (Sr&Ed) Tax CreditmetroroadNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fluid Mechanics - Gupta & Gupta.Dokument673 SeitenFluid Mechanics - Gupta & Gupta.Rajat RathoreNoch keine Bewertungen
- PHD Thesis - Sandra Nunes - Reduced SizeDokument357 SeitenPHD Thesis - Sandra Nunes - Reduced Sizesandra_nunitas100% (1)
- Section 7 - Structural SteelDokument31 SeitenSection 7 - Structural SteeltunlajiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Introduction To TPDokument47 SeitenIntroduction To TPRaja SelvarajNoch keine Bewertungen
- PCI Design Example (Unlocked by WWW - Freemypdf.com)Dokument49 SeitenPCI Design Example (Unlocked by WWW - Freemypdf.com)chuchocivil100% (1)
- Comparision of The Flow in Co-Rotating and Counter-Rotating Twin-Screw ExtrudersDokument5 SeitenComparision of The Flow in Co-Rotating and Counter-Rotating Twin-Screw ExtrudersHaresh BhanushaliNoch keine Bewertungen
- HydraulicsDokument18 SeitenHydraulicsJeff MagliaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Module 1Dokument31 SeitenModule 1Carms GameNoch keine Bewertungen
- U-2-Turbulent Flow in Pipes and Channels PDFDokument23 SeitenU-2-Turbulent Flow in Pipes and Channels PDFLaxmi PrasannaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Introduction To Fluid Statics and Manometers OutlineDokument8 SeitenIntroduction To Fluid Statics and Manometers OutlineVerin VericuetoNoch keine Bewertungen
- A +Gyr,+H - W +bewersdorff+auth +Drag+Reduction+of+Turbulent+Flows+by+Additives PDFDokument242 SeitenA +Gyr,+H - W +bewersdorff+auth +Drag+Reduction+of+Turbulent+Flows+by+Additives PDFSara RodriguezNoch keine Bewertungen
- CIA 2 Part ADokument9 SeitenCIA 2 Part Aradhakrishnan100% (1)
- Bingham Model For Pumpable ConcreteDokument11 SeitenBingham Model For Pumpable ConcreteYogendra SINGH PATELNoch keine Bewertungen
- Correlations To Predict Frictional Pressure Loss of Hydraulic-Fracturing Slurry in Coiled TubingDokument15 SeitenCorrelations To Predict Frictional Pressure Loss of Hydraulic-Fracturing Slurry in Coiled TubingErdal AYDINNoch keine Bewertungen
- Transport Phenomena NotebookDokument13 SeitenTransport Phenomena NotebookTemple MaduomaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Part B - Viscous FlowDokument68 SeitenPart B - Viscous FlowSamNoch keine Bewertungen
- Seismic Design of Reinforced Concrete StructuresDokument44 SeitenSeismic Design of Reinforced Concrete Structuresruspra100% (1)
- Assignment PDFDokument6 SeitenAssignment PDFRehan HakroNoch keine Bewertungen
- Engineering Structures: Gaetano Russo, Margherita Pauletta, Andrea CortesiaDokument12 SeitenEngineering Structures: Gaetano Russo, Margherita Pauletta, Andrea CortesiaMario ROSSINoch keine Bewertungen
- CE2202 Mechanics of FluidsDokument17 SeitenCE2202 Mechanics of FluidsSiva ReddyNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Effect of Fluid Rheology and Medium On The Performance of A Helical Ribbon Mixer For Concentrated Manganese Nodule SlurryDokument32 SeitenThe Effect of Fluid Rheology and Medium On The Performance of A Helical Ribbon Mixer For Concentrated Manganese Nodule SlurrypankhadingtidingNoch keine Bewertungen
- Film Coextrusion Troubleshooting 7832Dokument29 SeitenFilm Coextrusion Troubleshooting 7832OscarLucianoNoch keine Bewertungen