Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Animals Fossil
Hochgeladen von
amrikesaCopyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Animals Fossil
Hochgeladen von
amrikesaCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
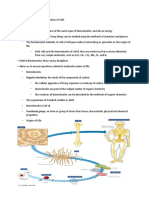
Origin and fossil recordFurther information: Urmetazoan Dunkleosteus was a 10-metre-long (33 ft) prehistoric fish.
[38]Animals are genera lly considered to have evolved from a flagellated eukaryote.[39] Their closest k nown living relatives are the choanoflagellates, collared flagellates that have a morphology similar to the choanocytes of certain sponges.[40] Molecular studie s place animals in a supergroup called the opisthokonts, which also include the choanoflagellates, fungi and a few small parasitic protists.[41] The name comes from the posterior location of the flagellum in motile cells, such as most anima l spermatozoa, whereas other eukaryotes tend to have anterior flagella.[42] The first fossils that might represent animals appear in the Trezona Formation a t Trezona Bore, West Central Flinders, South Australia.[43] These fossils are in terpreted as being early sponges. They were found in 665-million-year-old rock.[ 43] The next oldest possible animal fossils are found towards the end of the Precamb rian, around 610 million years ago, and are known as the Ediacaran or Vendian bi ota.[44] These are difficult to relate to later fossils, however. Some may repre sent precursors of modern phyla, but they may be separate groups, and it is poss ible they are not really animals at all.[45] Aside from them, most known animal phyla make a more or less simultaneous appear ance during the Cambrian period, about 542 million years ago.[46] It is still di sputed whether this event, called the Cambrian explosion, represents a rapid div ergence between different groups or a change in conditions that made fossilizati on possible. Some paleontologists suggest that animals appeared much earlier than the Cambria n explosion, possibly as early as 1 billion years ago.[47] Trace fossils such as tracks and burrows found in the Tonian era indicate the presence of triploblast ic worms, like metazoans, roughly as large (about 5 mm wide) and complex as eart hworms.[48] During the beginning of the Tonian period around 1 billion years ago , there was a decrease in Stromatolite diversity, which may indicate the appeara nce of grazing animals, since stromatolite diversity increased when grazing anim als went extinct at the End Permian and End Ordovician extinction events, and de creased shortly after the grazer populations recovered. However the discovery th at tracks very similar to these early trace fossils are produced today by the gi ant single-celled protist Gromia sphaerica casts doubt on their interpretation a s evidence of early animal evolution.[49
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryVon EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (231)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Von EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Bewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (121)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceVon EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (588)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaVon EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (266)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingVon EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (399)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItVon EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (838)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeVon EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (537)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerVon EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (271)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeVon EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (5794)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyVon EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (2259)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersVon EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (344)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnVon EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (234)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreVon EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (1090)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceVon EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (895)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesVon EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (821)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureVon EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (474)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaVon EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (45)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Von EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Bewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (98)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealVon EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (73)
- Class 8 Science: Chapter 1 Living World and Classification of MicrobesDokument149 SeitenClass 8 Science: Chapter 1 Living World and Classification of MicrobesKure RukminiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Biology Cells NotesDokument21 SeitenBiology Cells NotesashwanthraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Student Exploration: Cell StructureDokument3 SeitenStudent Exploration: Cell StructurejnfidnjNoch keine Bewertungen
- Gen Bio 1 Module 3Dokument20 SeitenGen Bio 1 Module 3Ante,Glainry Rose Basan100% (2)
- Parmesan Potato CasseroleDokument1 SeiteParmesan Potato CasseroleamrikesaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Jaya 1Dokument2 SeitenJaya 1amrikesaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Quotient of 9 and ZDokument3 SeitenQuotient of 9 and ZamrikesaNoch keine Bewertungen
- AddSubtract Fractions With Different DenominatorsDokument4 SeitenAddSubtract Fractions With Different DenominatorsamrikesaNoch keine Bewertungen
- AddSubtract Fractions With The Same DenominatorsDokument4 SeitenAddSubtract Fractions With The Same DenominatorsamrikesaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Prehistory of TNDokument3 SeitenPrehistory of TNamrikesaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lease AdminDokument2 SeitenLease AdminamrikesaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ayurvedha - Principles and TechnologyDokument3 SeitenAyurvedha - Principles and TechnologyamrikesaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Marathi IntroDokument1 SeiteMarathi IntroamrikesaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Malayalam NovelsDokument1 SeiteMalayalam NovelsamrikesaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ayurvedha - Intro and 8 ComponentDokument2 SeitenAyurvedha - Intro and 8 ComponentamrikesaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Malayalam NovelsDokument1 SeiteMalayalam NovelsamrikesaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Marathi HistoryDokument1 SeiteMarathi HistoryamrikesaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Malayalam HistoryyDokument3 SeitenMalayalam HistoryyamrikesaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Dry Fruit IntroDokument2 SeitenDry Fruit IntroamrikesaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Malayalam History2Dokument2 SeitenMalayalam History2amrikesaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Malayalam IntroDokument2 SeitenMalayalam IntroamrikesaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ramayana Textual HistDokument1 SeiteRamayana Textual HistamrikesaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Raisin ItroDokument1 SeiteRaisin ItroamrikesaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Malayalam EtymologyDokument4 SeitenMalayalam EtymologyamrikesaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ramayana IntroDokument1 SeiteRamayana IntroamrikesaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Raisin ProductionDokument1 SeiteRaisin ProductionamrikesaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Plants and ProductsDokument2 SeitenPlants and ProductsamrikesaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Raisin NutrientDokument2 SeitenRaisin NutrientamrikesaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Spices MaDokument1 SeiteSpices MaamrikesaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nutmeg UseDokument2 SeitenNutmeg UseamrikesaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Spices ClassaDokument1 SeiteSpices ClassaamrikesaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Spices HandlingDokument1 SeiteSpices HandlingamrikesaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Spices IntroDokument2 SeitenSpices IntroamrikesaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nutmeg ProductDokument1 SeiteNutmeg ProductamrikesaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cellular Structure and Function WorksheetsDokument24 SeitenCellular Structure and Function WorksheetsLouiseNoch keine Bewertungen
- AutophagyDokument7 SeitenAutophagymikikiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Six Kingdoms Chart T 2Dokument2 SeitenSix Kingdoms Chart T 2Angelo D PeraltaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Institute of Technology Tralee: Semester 1 Examinations A/Y 2009/2010 Biology 1 BIOL 61000 (CRN 45419) (CRN 43186)Dokument4 SeitenInstitute of Technology Tralee: Semester 1 Examinations A/Y 2009/2010 Biology 1 BIOL 61000 (CRN 45419) (CRN 43186)Mohmmad Alhazmi AliNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cell TypesDokument16 SeitenCell TypesyvetteNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sas #3Dokument6 SeitenSas #3Joana Elizabeth A. CastroNoch keine Bewertungen
- GB1 LS2Dokument3 SeitenGB1 LS2Luz AguineaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Biology SyllabusDokument18 SeitenBiology SyllabusragibNoch keine Bewertungen
- Anatony and Human PhysiologyDokument66 SeitenAnatony and Human PhysiologyMurali RajagopalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Activity 2 - Making Venn DiagramDokument3 SeitenActivity 2 - Making Venn DiagramVea Ann CantollasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Biology Lecture 1Dokument14 SeitenBiology Lecture 1Subham PaulNoch keine Bewertungen
- Plant Cell and Animal CellDokument8 SeitenPlant Cell and Animal CellDURANO, ROSELLE Z.SCINoch keine Bewertungen
- 01 Exploring+Biology+TextDokument43 Seiten01 Exploring+Biology+TextKatrina FermocilloNoch keine Bewertungen
- HistoriaDokument7 SeitenHistoriaКарлас ПортильоNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lecture 1 Cell and Molecular Biology IntroDokument21 SeitenLecture 1 Cell and Molecular Biology IntroElleNoch keine Bewertungen
- Module in Micro & paraDokument6 SeitenModule in Micro & paraAlpha-z PrinNoch keine Bewertungen
- A16 Bio 101-Nya-05 BiologyDokument10 SeitenA16 Bio 101-Nya-05 BiologyUmehabibah RehmanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Eukaryotic - Prokaryotic Cell Structure - Function 1 QPDokument13 SeitenEukaryotic - Prokaryotic Cell Structure - Function 1 QPramloghun veerNoch keine Bewertungen
- 7 Prokaryote and Eukaryote Cells-SDokument6 Seiten7 Prokaryote and Eukaryote Cells-SeNoch keine Bewertungen
- LESSON - 2 and 3Dokument26 SeitenLESSON - 2 and 3Kerberos DelabosNoch keine Bewertungen
- Earth & Life Science-Q2-M2Dokument14 SeitenEarth & Life Science-Q2-M2Yen SantosNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lecture 2Dokument32 SeitenLecture 2alizeh amanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Biology - Cell Structure OrganizationDokument42 SeitenBiology - Cell Structure OrganizationzubairNoch keine Bewertungen
- Prokaryotes vs. EukaryotesDokument6 SeitenProkaryotes vs. EukaryotesChennille Ann Bleu GundayaoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Biochemistry and The Organization of CellsDokument5 SeitenBiochemistry and The Organization of CellsEdgar DumagpiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Biotechnology 8 TestDokument5 SeitenBiotechnology 8 TestKristine A. LopezNoch keine Bewertungen