Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Magnetic Domains: Home - Education Resources - NDT Course Material - MPI
Hochgeladen von
heartbreakkid132Originalbeschreibung:
Originaltitel
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Magnetic Domains: Home - Education Resources - NDT Course Material - MPI
Hochgeladen von
heartbreakkid132Copyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Magnetic Domains
Page 1 of 2
Home - Education Resources - NDT Course Material - MPI
Magnetic Domains
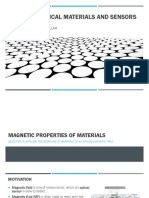
Ferromagnetic materials get their magnetic properties not only because their atoms carry a magnetic moment but also because the material is made up of small regions known as magnetic domains. In each domain, all of the atomic dipoles are coupled together in a preferential direction. This alignment develops as the material develops its crystalline structure during solidification from the molten state. Magnetic domains can be detected using Magnetic Force Microscopy (MFM) and images of the domains like the one shown below can be constructed. Magnetic Force Microscopy (MFM) image showing the magnetic domains in a piece of heat treated carbon steel. During solidification a trillion or more atom moments are aligned parallel so that the magnetic force within the domain is strong in one direction. Ferromagnetic materials are said to be characterized by "spontaneous magnetization" since they obtain saturation magnetization in each of the domains without an external magnetic field being applied. Even though the domains are magnetically saturated, the bulk material may not show any signs of magnetism because the domains develop themselves are randomly oriented relative to each other. Ferromagnetic materials become magnetized when the magnetic domains within the material are aligned. This can be done by placing the material in a strong external magnetic field or by passing electrical current through the material. Some or all of the domains can become aligned. The more domains that are aligned, the stronger the magnetic field in the material. When all of the domains are aligned, the material is said to be magnetically saturated. When a material is magnetically saturated, no additional amount of external magnetization force will cause an increase in its internal level of magnetization.
Introductio Magnetic Pa Inspection
Introduction Introduction Basic Principles History of MPI Physics Magnetism Magnetic Mat'ls Magnetic Domain Magnetic Fields Electromag. Field Field From a Coil Mag Properties Hysteresis Loop Permeability Field Orientation Magnetization of Magnetizing Curr Longitudinal Mag Circular Mag Field Demagnetization Measuring Mag F Equipment & M Portable Equipme Stationary Equipm Multidirectional E Lights Field Strength Ind Magnetic Particle Suspension Liquid Testing Practice Dry Particles Wet Suspension Magnetic Rubber Continuous & Res Field Direction & Process Control Particle Concentr Suspension Conta Electrical System Lighting Eye Consideration Example Indica Visible Dry Powde Fluorescent Wet
http://www.ndt-ed.org/EducationResources/CommunityCollege/MagParticle/Physics/Magn...
4/7/2006
Magnetic Domains
Page 2 of 2
Unmagnetized Material
Magnetized Material
http://www.ndt-ed.org/EducationResources/CommunityCollege/MagParticle/Physics/Magn...
4/7/2006
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Diamagnetic, Paramagnetic, and Ferromagnetic Materials: Home - Education Resources - NDT Course Material - MPIDokument2 SeitenDiamagnetic, Paramagnetic, and Ferromagnetic Materials: Home - Education Resources - NDT Course Material - MPIheartbreakkid132Noch keine Bewertungen
- Basic Principles of MPI TestingDokument48 SeitenBasic Principles of MPI TestingManivannanMudhaliarNoch keine Bewertungen
- NDT Module 3Dokument22 SeitenNDT Module 3Sajeesh SajiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Magnetic Particle Inspection Page6Dokument1 SeiteMagnetic Particle Inspection Page6Balram JiNoch keine Bewertungen
- MPI - Magnetic Particle Inspection PresentationDokument64 SeitenMPI - Magnetic Particle Inspection Presentationmahesh070100% (1)
- Lab Report OnDokument10 SeitenLab Report Onbhaski88Noch keine Bewertungen
- Magnetic Field Characteristics: Magnetic Field in and Around A Bar MagnetDokument2 SeitenMagnetic Field Characteristics: Magnetic Field in and Around A Bar Magnetheartbreakkid132Noch keine Bewertungen
- Magnetic Field: Magnetic Susceptibility, Quantitative Measure of The Extent To Which A Material May BeDokument8 SeitenMagnetic Field: Magnetic Susceptibility, Quantitative Measure of The Extent To Which A Material May BethisispasswordNoch keine Bewertungen
- Definition of Magnetic Particle TestingDokument44 SeitenDefinition of Magnetic Particle Testingகோகுல் இராNoch keine Bewertungen
- Module 3 PDF Magnetic Particle TestingDokument50 SeitenModule 3 PDF Magnetic Particle Testingjesna mohammedNoch keine Bewertungen
- Clasification of Magnetic MaterialsDokument16 SeitenClasification of Magnetic MaterialsdirtycutfreakNoch keine Bewertungen
- Magnetic MaterialsDokument45 SeitenMagnetic MaterialsPhil John FernandezNoch keine Bewertungen
- MT Self-Study NoteDokument153 SeitenMT Self-Study Notenewdao100% (5)
- Unit-4 Magnetic Particle Testing: Course Outline .Dokument32 SeitenUnit-4 Magnetic Particle Testing: Course Outline .Selvam ChidambaramNoch keine Bewertungen
- That QDokument5 SeitenThat QNavin Kumar (B21MT022)Noch keine Bewertungen
- Advanced Morden Solid State Physics 4Dokument9 SeitenAdvanced Morden Solid State Physics 4Edge of ScenesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ferromagnetism: Relative Permeability IndexDokument6 SeitenFerromagnetism: Relative Permeability Indexparallax1957Noch keine Bewertungen
- Magnetic Fields and SourcesDokument21 SeitenMagnetic Fields and SourcesGhost GhostNoch keine Bewertungen
- 6.1 NDT Magnetic TestingDokument30 Seiten6.1 NDT Magnetic TestingJose Gamaliel Legaspi Ibalarrosa IIINoch keine Bewertungen
- Magnetic Particle TestingDokument35 SeitenMagnetic Particle TestingWALIDNoch keine Bewertungen
- Magnetic Particle InspectionDokument6 SeitenMagnetic Particle Inspectionsuparna ShreeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Magnetic Particle TestingDokument34 SeitenMagnetic Particle TestingYusuf BagewadiNoch keine Bewertungen
- An Overview of The Structure and Magnetism of Spinel FerriteDokument15 SeitenAn Overview of The Structure and Magnetism of Spinel FerriteCosty VirlanNoch keine Bewertungen
- MagnetismDokument39 SeitenMagnetismBuse Temirr100% (1)
- Physics Project MagnetismDokument27 SeitenPhysics Project MagnetismDheekshith KumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Physics ProjectDokument10 SeitenPhysics ProjectMandeep TanwarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Presentation3 MM ASSIGNMENTDokument12 SeitenPresentation3 MM ASSIGNMENTabhilash gowdaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Magnetic Particle Testing, OrigDokument34 SeitenMagnetic Particle Testing, OrigTinaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ead - L-2Dokument9 SeitenEad - L-2Sreejith KailasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Material ScienceDokument20 SeitenMaterial ScienceVarsha PraburamNoch keine Bewertungen
- Magnetism in Engg.Dokument4 SeitenMagnetism in Engg.Naima SadiqNoch keine Bewertungen
- Thermal Magnetic Characteristics and Crystal Field Interactions Are Present in CompositesDokument13 SeitenThermal Magnetic Characteristics and Crystal Field Interactions Are Present in CompositesShravan_redNoch keine Bewertungen
- Magnetic Properties & CharacteristicsDokument9 SeitenMagnetic Properties & CharacteristicsRogelyn JosolNoch keine Bewertungen
- University of Information Technology and Sciences Uits: Assignment No.: 01Dokument22 SeitenUniversity of Information Technology and Sciences Uits: Assignment No.: 01Shri KumaranNoch keine Bewertungen
- Page 1Dokument2 SeitenPage 1Muhammad NozarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Basic MagnetismDokument13 SeitenBasic Magnetismnadjat_21100% (1)
- Magnetic Particle TestingDokument34 SeitenMagnetic Particle Testingmnaseemiqbal4200Noch keine Bewertungen
- DiamagnetismDokument6 SeitenDiamagnetismMis ter StudenttNoch keine Bewertungen
- MagnetikDokument31 SeitenMagnetikMuhammad Ilham FathoniNoch keine Bewertungen
- Module in Magnetic Properties of MaterialsDokument14 SeitenModule in Magnetic Properties of MaterialsFrendick LegaspiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Magnetism NotesDokument5 SeitenMagnetism Noteskalalund2562006Noch keine Bewertungen
- Magnetic Particle TestingDokument87 SeitenMagnetic Particle TestingMidhun SukumaranNoch keine Bewertungen
- Properties of Ferromagnetic Materials PDFDokument9 SeitenProperties of Ferromagnetic Materials PDFSäjidëë KisÅnNoch keine Bewertungen
- Presenter: S.M.K. HosseiniDokument62 SeitenPresenter: S.M.K. HosseiningtchungNoch keine Bewertungen
- Physical Principles of MagnetismDokument3 SeitenPhysical Principles of MagnetismJUVY GRACE ARANASNoch keine Bewertungen
- Optical Material and SensorsDokument23 SeitenOptical Material and SensorsdinasharanaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Introduction To Magnetic Particle TestingDokument58 SeitenIntroduction To Magnetic Particle TestingjerryceppyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Magnetic Properties of Solids: TotalDokument3 SeitenMagnetic Properties of Solids: Totalparallax1957Noch keine Bewertungen
- Lab Manual 2 (Magnetism Phase Transition)Dokument14 SeitenLab Manual 2 (Magnetism Phase Transition)Furqan Ali CheemaNoch keine Bewertungen
- MPT Ndt-EdDokument53 SeitenMPT Ndt-EdSaiKumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Magnetic Particle InspectionDokument58 SeitenMagnetic Particle InspectionnikafiqNoch keine Bewertungen
- Magnetic Properties of MaterialsDokument31 SeitenMagnetic Properties of MaterialssoumyajyotideyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Magnatic Particle Inspection 2023-2024Dokument61 SeitenMagnatic Particle Inspection 2023-2024طيف ابراهيم سعيد صدامNoch keine Bewertungen
- Introduction To Magnetic Particle InspectionDokument60 SeitenIntroduction To Magnetic Particle InspectionFasil ParuvanathNoch keine Bewertungen
- MPT NDTDokument60 SeitenMPT NDTpraveentienNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nano MagnetismDokument19 SeitenNano MagnetismVijey KumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- MPTDokument27 SeitenMPTPratik SalveNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 1. Introduction To Magnetic TestingDokument12 SeitenChapter 1. Introduction To Magnetic TestingGaurav ChopraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Advanced Functional Materials: A Perspective from Theory and ExperimentVon EverandAdvanced Functional Materials: A Perspective from Theory and ExperimentNoch keine Bewertungen
- 201057162941468Dokument116 Seiten201057162941468ambition1340cn100% (1)
- Saes H 201Dokument9 SeitenSaes H 201heartbreakkid132Noch keine Bewertungen
- Saes H 204Dokument34 SeitenSaes H 204heartbreakkid132Noch keine Bewertungen
- Cswip 2Dokument8 SeitenCswip 2heartbreakkid132Noch keine Bewertungen
- Electromagnetic Fields: A Word of Caution About The Right-Hand RuleDokument2 SeitenElectromagnetic Fields: A Word of Caution About The Right-Hand Ruleheartbreakkid132Noch keine Bewertungen
- Magnetic Field Characteristics: Magnetic Field in and Around A Bar MagnetDokument2 SeitenMagnetic Field Characteristics: Magnetic Field in and Around A Bar Magnetheartbreakkid132Noch keine Bewertungen
- Last DayDokument68 SeitenLast Dayheartbreakkid132Noch keine Bewertungen
- VAV Fundamentals ASHRAEDokument24 SeitenVAV Fundamentals ASHRAEheartbreakkid132Noch keine Bewertungen
- VAV Fundamentals ASHRAEDokument24 SeitenVAV Fundamentals ASHRAEheartbreakkid132Noch keine Bewertungen
- Surah MulkDokument2 SeitenSurah Mulkheartbreakkid132100% (1)
- Riba HadithDokument28 SeitenRiba Hadithheartbreakkid132Noch keine Bewertungen
- Magnetic Effect of Electric Current Notes Chpt2Dokument11 SeitenMagnetic Effect of Electric Current Notes Chpt2Sarathrv Rv100% (2)
- Ad 01202010214Dokument14 SeitenAd 01202010214theijesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Physics Investigatory Project: Self Inductance of A CoilDokument10 SeitenPhysics Investigatory Project: Self Inductance of A CoildevuNoch keine Bewertungen
- ch29 PDFDokument29 Seitench29 PDFRodrigo S QuirinoNoch keine Bewertungen
- PTG Chapter 14 Asal PhysicsDokument11 SeitenPTG Chapter 14 Asal Physicszzrnwdzpsmhs951003Noch keine Bewertungen
- Magnetic Effect of Electric CurrentDokument13 SeitenMagnetic Effect of Electric Currentanjupal100% (4)
- Module 6.2 Magnetism and CompassDokument4 SeitenModule 6.2 Magnetism and CompassVenus VelascoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chap10no1 PDFDokument2 SeitenChap10no1 PDFTajiriMollel0% (9)
- Chapter 11. Griffiths-Radiation-Dipole Radiation PDFDokument13 SeitenChapter 11. Griffiths-Radiation-Dipole Radiation PDFPranveer Singh Parihar100% (1)
- The Hall Effect in GermaniumDokument12 SeitenThe Hall Effect in GermaniumSanele ZiqubuNoch keine Bewertungen
- "Introduction": AV-222 Electromechanical SystemsDokument14 Seiten"Introduction": AV-222 Electromechanical SystemsSyed HaiderNoch keine Bewertungen
- Grade 10 Physics L1 FeedbackDokument3 SeitenGrade 10 Physics L1 FeedbackYonasNoch keine Bewertungen
- R17 Ug PDFDokument55 SeitenR17 Ug PDFAlapati RajasekharNoch keine Bewertungen
- Electromagnetic MethodDokument29 SeitenElectromagnetic Method'ara' 'fara'Noch keine Bewertungen
- Electric Charges and FieldsDokument8 SeitenElectric Charges and Fieldsdheeraj831Noch keine Bewertungen
- Faradays LawDokument6 SeitenFaradays LawtlabNoch keine Bewertungen
- Test On Electromagnetic Induction and ACDokument3 SeitenTest On Electromagnetic Induction and ACUttam PathakNoch keine Bewertungen
- Why Is The Following Situation Impossible? The Magnitude: NM IR X XDokument3 SeitenWhy Is The Following Situation Impossible? The Magnitude: NM IR X XCALON TARUNANoch keine Bewertungen
- Development of An Edge-Element Model For AC Loss Computation of High-Temperature SuperconductorsDokument10 SeitenDevelopment of An Edge-Element Model For AC Loss Computation of High-Temperature SuperconductorsAndrea MussoNoch keine Bewertungen
- PHYSICS 08&09 ChapterDokument76 SeitenPHYSICS 08&09 ChapterPAVAN KUMARNoch keine Bewertungen
- Physics Worksheet For Grade - 10 (Part - 2) Ebenezer School (From K-G Up To Preparatory)Dokument6 SeitenPhysics Worksheet For Grade - 10 (Part - 2) Ebenezer School (From K-G Up To Preparatory)YishakNoch keine Bewertungen
- Crop Circles. The Question Resolved Newly. Puzzled OutDokument9 SeitenCrop Circles. The Question Resolved Newly. Puzzled OutTHERESA JNoch keine Bewertungen
- Capitulo 26 TiplerDokument22 SeitenCapitulo 26 TiplerHamzaAouidatNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 6 - Magnetic Compass AdjustmentDokument32 SeitenChapter 6 - Magnetic Compass Adjustmentapi-109026167100% (4)
- Electro Magnetic FieldsDokument6 SeitenElectro Magnetic FieldshelenarajNoch keine Bewertungen
- How To Properly Use The Zapper and Magnetic PulserDokument7 SeitenHow To Properly Use The Zapper and Magnetic PulserJiggaWhaaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Physics For IIT JEE Vol 2 How To Read The BookDokument24 SeitenPhysics For IIT JEE Vol 2 How To Read The BookNaveen Kumar SinghNoch keine Bewertungen
- Double Acting Hacksaw Using Scotch Yoke MechanismDokument38 SeitenDouble Acting Hacksaw Using Scotch Yoke MechanismDevendra Thakur78% (37)
- Lecture Notes On ElectrodynamicsDokument3 SeitenLecture Notes On Electrodynamicsahmeday22manNoch keine Bewertungen
- Btech Civil SyllabusDokument44 SeitenBtech Civil SyllabusValmik PatelNoch keine Bewertungen