Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
The Modern View of Atomic Structure: An Introduction 2.5-2.8
Hochgeladen von
Anita LopesOriginaltitel
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
The Modern View of Atomic Structure: An Introduction 2.5-2.8
Hochgeladen von
Anita LopesCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
The modern view of atomic structure: An Introduction 2.5-2.
8
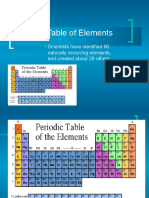
Isotopes Atoms with the same number of protons but different numbers of neutrons Atoms with the same chemical properties, can have different mass, due to its electrons Mass number is the upper number over the elements is the sum of protons and neutrons If the is a upper number on the right size is the charge of the element The number of the masses on the table is the average of all isotopes The redundancy is to the say the bottom left (element number) When a isotope is positive X+ contains 54 e- it has one more p+ Chemical Bonds Covalent o Formed when two atoms come close together and they share the electrons have to be between the nuclei o A molecule is formed Ionic Bonds o The attraction in only due charge, attracted between opposite charged ions o Ion- atom or group of atoms that has a net positive or negative charge o Cation-positive ion o Anion-negative ion. o Ionic bonds usually crystal, positive surrounded by negative it is stable not for one (+ or -) but by a collection. Periodic table o 80% are metals o Groups or families (elements in the same vertical columns: have similar chemical properties) o Main group (1,2,13-18) or (1-8) o Periods- horizontal rows of elements wide range of properties n each row. Groups or families Group 1 or 1A Alkali1+ charge Group 2 or 2A Alkali earth2+ charge Group 7 or 7A Halogens1- charge Group 8 or 8A Noble gases0 charge
Naming compounds o Binary Compounds 2 elements ionic or covalent compounds included o Binary ionic compound Metal and non-metal o Binary covalent compound Non-metal and metal Binary ionic compounds (type I) 1. The cation always named first and the anion second 2. A monoatomic cation takes its name from the name of the element 3. A monatomic anion is named by taking the root and adding ide to the end Binary ionic compounds (type II) o Metals in these compounds form more than one type of positive charge o Charge on the metal ion must be specified o Using roman numeral to know which transition metal we are using because the can form more than one compounds with the same 2 elements Polyatomic Ions o Must memorize page 65 o NaOH Sodium hydroxide o Mg(NO3)2 magnesium nitrate o (NH4)2SO4 ammonium sulfate o IUM ending meaning is metallic even though they are not metal they behave like metal Binary Covalent compounds (type III) o Formed between two nonmetals 1. The first element in the formula is named first, using the full element name 2. The second element is name of the element ide 3. Use prefixes 4. Never use mono prefix on the first element
Acids
o Can be recognized by a hydrogen (H) that appears first in the formula HCl o Hydrogen is written first o If the anion does not contain oxygen, the acid is name with the prefix hydro- and the suffix ic o HCl Hydrochloric o HCN Hydrocyanic acid CN1- and H1+
If the anion does contain oxygen The suffix- ic is added to the root name if the anion ends in ate The suffix ous is added to the root name if the anion ends in -ite
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- An Introduction to the Periodic Table of Elements : Chemistry Textbook Grade 8 | Children's Chemistry BooksVon EverandAn Introduction to the Periodic Table of Elements : Chemistry Textbook Grade 8 | Children's Chemistry BooksBewertung: 5 von 5 Sternen5/5 (1)
- Ions and MoleculesDokument69 SeitenIons and MoleculeslanceskyagredaNoch keine Bewertungen
- GCSE Chemistry Revision: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsVon EverandGCSE Chemistry Revision: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (3)
- Chapter 2-Atoms and MatterDokument44 SeitenChapter 2-Atoms and MatterNajma AqilahNoch keine Bewertungen
- Atoms Molecules and IonsDokument3 SeitenAtoms Molecules and Ionsapi-304350501Noch keine Bewertungen
- Jhoan Rhea L. Pizon, PHDDokument59 SeitenJhoan Rhea L. Pizon, PHDRancell Vincent Gablines MorenoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ch2 Atoms, Molecules, and Ions 1Dokument18 SeitenCh2 Atoms, Molecules, and Ions 1Ariyandi PurnamaNoch keine Bewertungen
- General Chemistry Lesson 3Dokument31 SeitenGeneral Chemistry Lesson 3Michaela BorjaNoch keine Bewertungen
- ScienceDokument10 SeitenScienceMazze Ashley SenaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Science 10 FINAL ReviewDokument27 SeitenScience 10 FINAL ReviewL.MorrisNoch keine Bewertungen
- SCIENCEDokument10 SeitenSCIENCEMazze Ashley SenaNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Chemical Earth-Ahmad ShahDokument46 SeitenThe Chemical Earth-Ahmad ShahYouseffNoch keine Bewertungen
- ATOMSDokument6 SeitenATOMSSarah HantonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Atoms, Molecules, & IonsDokument13 SeitenAtoms, Molecules, & IonsyeunbiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Naming For SchrodingerDokument38 SeitenNaming For SchrodingercttrangiaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Classification of Elements and Periodicity in Properties Class 11 Notes Chemistry Chapter 3Dokument12 SeitenClassification of Elements and Periodicity in Properties Class 11 Notes Chemistry Chapter 3Bijay SchoolNoch keine Bewertungen
- Atoms and Elements: ObjectivesDokument5 SeitenAtoms and Elements: ObjectivesAngel RingorNoch keine Bewertungen
- Che101 Chap 2Dokument60 SeitenChe101 Chap 2Ruhi AfsaraNoch keine Bewertungen
- General Chemistry - DocsDokument17 SeitenGeneral Chemistry - DocsJohn leeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 2 PDFDokument29 SeitenChapter 2 PDFghs26w5s2tNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter TwoDokument47 SeitenChapter Twoeliasferhan1992Noch keine Bewertungen
- كتابDokument187 Seitenكتابdalyrazan60Noch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 5 - Ionic BondingDokument12 SeitenChapter 5 - Ionic BondingAbrienne CaprichoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Reviewer in ChemistryDokument16 SeitenReviewer in Chemistryxian tanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chemical FormulaDokument35 SeitenChemical FormulaKim Clauwie AnchetaNoch keine Bewertungen
- G8 Science Q3 - Week 7-8 - Periodic TableDokument66 SeitenG8 Science Q3 - Week 7-8 - Periodic TableIemmee Jane DinglasanNoch keine Bewertungen
- General Chemistry CHE 101: Atoms, Molecules and IonsDokument60 SeitenGeneral Chemistry CHE 101: Atoms, Molecules and IonsDavid MaranzhyanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Formulas of CompoundsDokument2 SeitenFormulas of CompoundsMarcus MatanguihanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chemistry Exam Review Grade 11Dokument28 SeitenChemistry Exam Review Grade 11Michael Chiu100% (2)
- Modern Periodic TableDokument8 SeitenModern Periodic TableSabbir HossainNoch keine Bewertungen
- UMs Topic List For End of Year Examination 2023Dokument4 SeitenUMs Topic List For End of Year Examination 2023sevebv2Noch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 2Dokument7 SeitenChapter 2asianpanda14Noch keine Bewertungen
- Lecture 5Dokument23 SeitenLecture 5boledi angelaNoch keine Bewertungen
- ES III Midterm Module 6 WK 6Dokument5 SeitenES III Midterm Module 6 WK 6Oct Toberey MendozaNoch keine Bewertungen
- GC1 Lesson 3 Atoms Molecules and Ions 3 The Periodic TableDokument31 SeitenGC1 Lesson 3 Atoms Molecules and Ions 3 The Periodic TableYeri KimNoch keine Bewertungen
- Science 8 Take Notes Assesment Answer RefelctionDokument6 SeitenScience 8 Take Notes Assesment Answer RefelctionMary Ellain Sorima DaelNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nomenclature of Inorganic CompoudsDokument3 SeitenNomenclature of Inorganic CompoudsMazon, Dinah Melisse P.Noch keine Bewertungen
- Science Notes 2010Dokument15 SeitenScience Notes 2010Allen PanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Module 5 Chemical Symbols NotesDokument10 SeitenModule 5 Chemical Symbols NotesaerinNoch keine Bewertungen
- Periodic Table of Elements: Scientists Have Identified 90 Naturally Occurring Elements, and Created About 28 OthersDokument54 SeitenPeriodic Table of Elements: Scientists Have Identified 90 Naturally Occurring Elements, and Created About 28 OthersTrixieCamposanoNoch keine Bewertungen
- 20 Page GCSE To AS Transition BookletDokument20 Seiten20 Page GCSE To AS Transition BookletHanaNoch keine Bewertungen
- CHEMDokument31 SeitenCHEMSheena Ann L. LLarenasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Periodic Table of ElementsDokument58 SeitenPeriodic Table of ElementsMichelle Casayuran - RegalaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chemical Bonding Reading MaterialDokument6 SeitenChemical Bonding Reading MaterialJohann Carlo C. AldecoaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Naming Compounds Ions and Ionic CompoundsDokument3 SeitenNaming Compounds Ions and Ionic CompoundsAlexa AbulNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Periodic Table of Elements: Chemistry Lec 3Dokument11 SeitenThe Periodic Table of Elements: Chemistry Lec 3المونتاج الاخيرNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ions Cnhs Grade 9Dokument6 SeitenIons Cnhs Grade 9Jammianne 919Noch keine Bewertungen
- LQ 2 NotesDokument42 SeitenLQ 2 NotesThe BluemanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Calculations Involving Balanced Chemical EquationsDokument107 SeitenCalculations Involving Balanced Chemical Equationsmain.20002245Noch keine Bewertungen
- Ions and Bonds PowerpointDokument26 SeitenIons and Bonds Powerpointapi-2622192730% (1)
- Chemical Symbols and Ions: Tel/Fax No.: (047) 811-1683Dokument9 SeitenChemical Symbols and Ions: Tel/Fax No.: (047) 811-1683Carl PaduaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Modern Periodic TableDokument8 SeitenModern Periodic Tablemixing hubNoch keine Bewertungen
- 3.2 Names and Formulas of Ionic CompoundsDokument5 Seiten3.2 Names and Formulas of Ionic CompoundsKen WuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chemistry Quiz One NotesDokument7 SeitenChemistry Quiz One NotesCourseCentralNoch keine Bewertungen
- Modern Periodic TableDokument4 SeitenModern Periodic TableNabil Abdullah0% (1)
- Chemistry in Our Everyday LifeDokument36 SeitenChemistry in Our Everyday LifeArnob TanjimNoch keine Bewertungen
- What Is The Atomic NumberDokument31 SeitenWhat Is The Atomic NumberMennatallah Mohamed HamedNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 2 Notes - Atoms, Molecules and IonsDokument4 SeitenChapter 2 Notes - Atoms, Molecules and Ionsmzhao8Noch keine Bewertungen
- Matter and Stoichiometry Chm092 June 2014Dokument223 SeitenMatter and Stoichiometry Chm092 June 2014ida hadiNoch keine Bewertungen
- High School Chemistry PDFDokument12 SeitenHigh School Chemistry PDFAleph ContinuumNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chemistry Lesson Notes For Form TwoDokument35 SeitenChemistry Lesson Notes For Form TwoMBOTAKE Lawson100% (3)
- 2018 Basic Sci 22102 Common Ut1 Sem1Dokument9 Seiten2018 Basic Sci 22102 Common Ut1 Sem1Swati NavaniNoch keine Bewertungen
- 8F AssessmentDokument14 Seiten8F AssessmentAbdallah Elmenawy100% (3)
- Lesson - Basic Chemistry and Physics Lyst1463Dokument61 SeitenLesson - Basic Chemistry and Physics Lyst1463anilNoch keine Bewertungen
- Electronic Structure and PeriodicityDokument58 SeitenElectronic Structure and PeriodicityAlekhoy Pakz100% (1)
- Peer TutoringDokument37 SeitenPeer TutoringAndrea Celina DinglasanNoch keine Bewertungen
- CH 4 Carbon and Its Compound DPP - 01Dokument1 SeiteCH 4 Carbon and Its Compound DPP - 01HemantBhardwajNoch keine Bewertungen
- KISS Notes - Chemical EarthDokument44 SeitenKISS Notes - Chemical EarthMaheesha Perera67% (6)
- Periodic Table and Periodic Properties: 1 Key PointsDokument5 SeitenPeriodic Table and Periodic Properties: 1 Key PointsMichelle GillNoch keine Bewertungen
- Jeep 105Dokument10 SeitenJeep 105Ishan LakhwaniNoch keine Bewertungen
- NCERT Book Class 11 Chemistry Chemistry II Chapter 11 The P Block Elements PDFDokument19 SeitenNCERT Book Class 11 Chemistry Chemistry II Chapter 11 The P Block Elements PDFSubham RajputNoch keine Bewertungen
- Grade 8 PeriodicTableDokument11 SeitenGrade 8 PeriodicTablesaintEmNoch keine Bewertungen
- Activity in Periodic TableDokument10 SeitenActivity in Periodic TableKristann BautistaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 9th Chemistry Guess 2023Dokument2 Seiten9th Chemistry Guess 2023ashfaq4985Noch keine Bewertungen
- 0 Reviewer MeasurementsDokument17 Seiten0 Reviewer MeasurementsCylle Jerone BuenviajeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chemistry and Chemistry For Engineers Midterm ExamDokument6 SeitenChemistry and Chemistry For Engineers Midterm ExamChristian Paul A. AsicoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Science and Technology 7 2ndDokument3 SeitenScience and Technology 7 2ndANDJELYN M. ABALOSNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ch6 Periodic Table HW PKT KEY 12-13Dokument12 SeitenCh6 Periodic Table HW PKT KEY 12-13翁林駿Noch keine Bewertungen
- Grade 7 Curriculum MapDokument10 SeitenGrade 7 Curriculum MapLolit MarasiganNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chemistry Grade 9 Review AssignmentDokument12 SeitenChemistry Grade 9 Review AssignmentaniedorfNoch keine Bewertungen
- Question Bank Periodic Table and Periodic PropertiesDokument21 SeitenQuestion Bank Periodic Table and Periodic Propertieshetal zalaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Metals and Non-MetalsDokument10 SeitenMetals and Non-MetalsPavandakoreNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1 of 44 © Boardworks LTD 2007Dokument58 Seiten1 of 44 © Boardworks LTD 2007CaribelatinaNoch keine Bewertungen
- EL10C029 Compressed PDFDokument600 SeitenEL10C029 Compressed PDFDeepak Banoth100% (1)
- Metallic BondingDokument10 SeitenMetallic BondingArmando Alberto MassingueNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2.5 The Periodic TableDokument33 Seiten2.5 The Periodic TableJohn Michael DitchonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Periodic Table Online Scavenger HuntDokument6 SeitenPeriodic Table Online Scavenger HuntAaya Alowaiyesh0% (1)
- Aupagan National High SchoolDokument2 SeitenAupagan National High SchoolLouie Jane EleccionNoch keine Bewertungen
- 8th Grade Science Eog PacketDokument177 Seiten8th Grade Science Eog Packetapi-284282126Noch keine Bewertungen
- Atoms and Elements: Chemistry: A Molecular Approach, 2nd EdDokument61 SeitenAtoms and Elements: Chemistry: A Molecular Approach, 2nd EdKai YangNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Nature of Drugs Vol. 1: History, Pharmacology, and Social ImpactVon EverandThe Nature of Drugs Vol. 1: History, Pharmacology, and Social ImpactBewertung: 5 von 5 Sternen5/5 (5)
- Periodic Tales: A Cultural History of the Elements, from Arsenic to ZincVon EverandPeriodic Tales: A Cultural History of the Elements, from Arsenic to ZincBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (137)
- AP® Chemistry Crash Course, For the 2020 Exam, Book + Online: Get a Higher Score in Less TimeVon EverandAP® Chemistry Crash Course, For the 2020 Exam, Book + Online: Get a Higher Score in Less TimeBewertung: 5 von 5 Sternen5/5 (1)
- It's Elemental: The Hidden Chemistry in EverythingVon EverandIt's Elemental: The Hidden Chemistry in EverythingBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (10)
- Is That a Fact?: Frauds, Quacks, and the Real Science of Everyday LifeVon EverandIs That a Fact?: Frauds, Quacks, and the Real Science of Everyday LifeBewertung: 5 von 5 Sternen5/5 (4)
- Taste: Surprising Stories and Science About Why Food Tastes GoodVon EverandTaste: Surprising Stories and Science About Why Food Tastes GoodBewertung: 3 von 5 Sternen3/5 (20)
- Guidelines for Defining Process Safety Competency RequirementsVon EverandGuidelines for Defining Process Safety Competency RequirementsBewertung: 3 von 5 Sternen3/5 (1)
- Monkeys, Myths, and Molecules: Separating Fact from Fiction, and the Science of Everyday LifeVon EverandMonkeys, Myths, and Molecules: Separating Fact from Fiction, and the Science of Everyday LifeBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (1)
- Chemistry for Breakfast: The Amazing Science of Everyday LifeVon EverandChemistry for Breakfast: The Amazing Science of Everyday LifeBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (14)
- Formulating, Packaging, and Marketing of Natural Cosmetic ProductsVon EverandFormulating, Packaging, and Marketing of Natural Cosmetic ProductsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Handbook of Formulating Dermal Applications: A Definitive Practical GuideVon EverandHandbook of Formulating Dermal Applications: A Definitive Practical GuideNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Periodic Table: A Very Short IntroductionVon EverandThe Periodic Table: A Very Short IntroductionBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (3)
- AP Chemistry Flashcards, Fourth Edition: Up-to-Date Review and PracticeVon EverandAP Chemistry Flashcards, Fourth Edition: Up-to-Date Review and PracticeNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Billion-Dollar Molecule: The Quest for the Perfect DrugVon EverandThe Billion-Dollar Molecule: The Quest for the Perfect DrugBewertung: 5 von 5 Sternen5/5 (2)
- Guidelines for Integrating Process Safety into Engineering ProjectsVon EverandGuidelines for Integrating Process Safety into Engineering ProjectsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fundamentals of Chemistry: A Modern IntroductionVon EverandFundamentals of Chemistry: A Modern IntroductionBewertung: 5 von 5 Sternen5/5 (1)
- Chemistry for Breakfast: The Amazing Science of Everyday LifeVon EverandChemistry for Breakfast: The Amazing Science of Everyday LifeBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (90)
- The Nature of Drugs Vol. 1: History, Pharmacology, and Social ImpactVon EverandThe Nature of Drugs Vol. 1: History, Pharmacology, and Social ImpactBewertung: 5 von 5 Sternen5/5 (1)
- Organic Chemistry for Schools: Advanced Level and Senior High SchoolVon EverandOrganic Chemistry for Schools: Advanced Level and Senior High SchoolNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tribology: Friction and Wear of Engineering MaterialsVon EverandTribology: Friction and Wear of Engineering MaterialsBewertung: 5 von 5 Sternen5/5 (1)
- The Disappearing Spoon: And Other True Tales of Madness, Love, and the History of the World from the Periodic Table of the ElementsVon EverandThe Disappearing Spoon: And Other True Tales of Madness, Love, and the History of the World from the Periodic Table of the ElementsBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (146)