Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Computation
Hochgeladen von
April Rose PlacerCopyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Computation
Hochgeladen von
April Rose PlacerCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
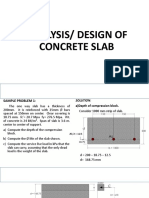
DEAD LOADS (per unit area): 4- CHANNEL BARS FOR RAFTERS1 5- CHANNEL BARS FOR PURLINS2 7 ANGLE BARS
FOR TRUSSES BEAM SELF WEIGHT 3272.616 N 2251.395 N 995.715 N 38160 N 44.679727 kN/roof area =1.148 kN/m2 THICK PLYWOOD FOR CEILING LIVE LOAD (per unit area): LR2 (Roof live load)3 750 N 0.399 kN /m2
LOAD COMBINATIONS (Force per area): 1.4D =2.166094193 kN/m2 1.2D + 1.6L = 3.0566521664 kN/m2
TRIBUTARY AREA A1 = 12.3594 m2 A2 = 12.7719 m2 A3 = 6.8906 m2 A4 = 6.8906 m2
L S A4 A2 A1 A3
1 2
Weight per 6m length (6mm x 75mm x 150mm) = 83.4 kg Weight per 6m length (5mm x 50mm x 100mm) = 45.9 kg 3 2 Uniform live load for Tributary Area of 0-20 m taken from NSCP 2010 Table 205-3 4 Governing Ultimate Load
DESIGN OF BEAMS
Assume simply supported beam (FOR CONSERVATIVE DESIGN): BEAMS ALONG SHORT SPAN:
( ) ( )
Design for flexure Assume: 16 mm bars and 10 mm stirrups 200 mm x 300 mm beam fc = 21 Mpa fy = 275 Mpa
( (
)(
)( (
) ) ( )
Use
( We used 4- 16 mm bars.
Analysis: Find the moment capacity of the beam as designed,
Check for beam shear, ( )
BEAMS ALONG LONG SPAN:
( )
Design for flexure Assume: 16 mm bars and 10 mm stirrups 200 mm x 300 mm beam fc = 21 Mpa fy = 275 Mpa
( (
)(
)( (
) ) ( )
( We used 4- 16 mm bars.
Analysis: Find the moment capacity of the beam as designed,
Check for beam shear, ( )
DESIGN OF COLUMNS COLUMNS Reactions from beam along short span:
Reactions from beam along short span:
Load carried by column:
Dead load from weight of column:
Total Ultimate Load:
For economical design, use ( )( )
( )( We used 4- 16 mm bars. ( )( ( Since )[ (
) ) )]
DESIGN OF FOOTINGS
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- армирование колонаDokument25 Seitenармирование колонаtangerineNoch keine Bewertungen
- Three Dimensional Analysis and Design of Al-Arab Hospital ProjectDokument52 SeitenThree Dimensional Analysis and Design of Al-Arab Hospital ProjectkusumchitikaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Design of Pile FoundationDokument16 SeitenDesign of Pile FoundationJagal Udaya100% (3)
- Flexural Strength-Column Base PlateDokument9 SeitenFlexural Strength-Column Base PlateAl-fin KaytingNoch keine Bewertungen
- 3D Dynamic Soil Structure Interaction Design For Al-Manar BuildingDokument55 Seiten3D Dynamic Soil Structure Interaction Design For Al-Manar BuildingHimanshu SauravNoch keine Bewertungen
- One Way Solid SlabDokument26 SeitenOne Way Solid SlabalaajabbarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Final QuesDokument5 SeitenFinal QuesMani KumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Design of Pile FoundationDokument16 SeitenDesign of Pile FoundationHani AboobackerNoch keine Bewertungen
- Prepared By: Ayman Naalweh Mustafa Mayyaleh Nidal TurkomanDokument55 SeitenPrepared By: Ayman Naalweh Mustafa Mayyaleh Nidal TurkomanHugo RodriguezNoch keine Bewertungen
- ONE-WAY SLABS DESIGNDokument26 SeitenONE-WAY SLABS DESIGNJohn Mejia50% (4)
- MOM Mod4@AzDOCUMENTS - inDokument15 SeitenMOM Mod4@AzDOCUMENTS - inMahadev MetriNoch keine Bewertungen
- Design A Deck Type Plate Girder Railway Bridge For Single TractDokument5 SeitenDesign A Deck Type Plate Girder Railway Bridge For Single Tractjs kalyana rama57% (7)
- Slabs Problem PDFDokument23 SeitenSlabs Problem PDFChesley MoralesNoch keine Bewertungen
- STEEL ROOF TRUSS DESIGN FOR PETROL STATIONDokument22 SeitenSTEEL ROOF TRUSS DESIGN FOR PETROL STATIONemuan vanessaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Superstructure Analysis DesignDokument25 SeitenSuperstructure Analysis DesignskumaraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Be Mechanical Engineering Semester 3 2018 May Strength of Materials CbcgsDokument19 SeitenBe Mechanical Engineering Semester 3 2018 May Strength of Materials CbcgsRehansh JadhavNoch keine Bewertungen
- Design of Steel Exhibition Building: B.Q.Rahman Computer Aided Structural Engineering FINAL YEAR 2007-08, Iiit-HyderabadDokument23 SeitenDesign of Steel Exhibition Building: B.Q.Rahman Computer Aided Structural Engineering FINAL YEAR 2007-08, Iiit-HyderabadRoni EnjelaniNoch keine Bewertungen
- DESIGN FLOOR JOISTS SPECIFICATIONSDokument7 SeitenDESIGN FLOOR JOISTS SPECIFICATIONSTalen Marzan-LelisNoch keine Bewertungen
- Two Way Slab BestDokument25 SeitenTwo Way Slab BestErnest Christian Nanola100% (1)
- Analysis/ Design of Concrete SlabDokument23 SeitenAnalysis/ Design of Concrete SlabMark Kevin C. PingolNoch keine Bewertungen
- Timber DesignDokument26 SeitenTimber DesignRichmon Pangilinan100% (6)
- Design and Comparison of Flat Slab Using Is 456 - 2000Dokument26 SeitenDesign and Comparison of Flat Slab Using Is 456 - 2000Mukesh Mande100% (6)
- Design SectionDokument19 SeitenDesign SectionKrishna KumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Assignment of SteelDokument25 SeitenAssignment of SteelSamih S. BarzaniNoch keine Bewertungen
- Concrete Slabs Design ExampleDokument31 SeitenConcrete Slabs Design ExampleandinumailNoch keine Bewertungen
- Design of Deck Girder BridgesDokument65 SeitenDesign of Deck Girder BridgesEna Mie CambaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Design of Small BuildingDokument28 SeitenDesign of Small BuildingJaime CoronellNoch keine Bewertungen
- EG7005 STEEL DESIGN-BATCH 21-22: Lijose Jacob 2235791Dokument83 SeitenEG7005 STEEL DESIGN-BATCH 21-22: Lijose Jacob 2235791lijosejacobNoch keine Bewertungen
- Design of Box CulvertDokument21 SeitenDesign of Box CulvertAnirbanBhattacharjeeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Simple Stress StrainDokument141 SeitenSimple Stress StrainvelavansuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Design of Beam Ledge Reinforcement as per ACI 318M95Dokument2 SeitenDesign of Beam Ledge Reinforcement as per ACI 318M95auatipu100% (1)
- Faculty of Applied Engineering and Urban PlanningDokument22 SeitenFaculty of Applied Engineering and Urban PlanningHazem Almasry100% (1)
- Combined Footing Vtu DocumentDokument22 SeitenCombined Footing Vtu DocumentSyed IsmailNoch keine Bewertungen
- Full Beam Design Example: GivenDokument17 SeitenFull Beam Design Example: Giventap ramosNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pile CapDokument8 SeitenPile CapMdShahbazAhmedNoch keine Bewertungen
- Steps in Designing A Rectangular BeamDokument8 SeitenSteps in Designing A Rectangular BeamIvan GonzalesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Truss Design NS NegiDokument23 SeitenTruss Design NS NegiSushmit Sharma100% (1)
- Tee Beam ProbDokument14 SeitenTee Beam ProbSai GowthamNoch keine Bewertungen
- Design of Composite Steel Girder BridgeDokument10 SeitenDesign of Composite Steel Girder BridgesorowareNoch keine Bewertungen
- Steel Bracket DesignDokument3 SeitenSteel Bracket Designrandy_pabilona50% (4)
- Topic 6 - Pile FootingDokument27 SeitenTopic 6 - Pile FootingDhanmer Lopez0% (2)
- Isolated Footing Design ProblemDokument5 SeitenIsolated Footing Design ProblemthabisNoch keine Bewertungen
- Design and detailing of a combined footing with central beam supporting two columnsDokument34 SeitenDesign and detailing of a combined footing with central beam supporting two columnsgundulpNoch keine Bewertungen
- Undergraduate Project on Design of Prestressed Concrete BridgeDokument29 SeitenUndergraduate Project on Design of Prestressed Concrete BridgeimamtaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Isolated Footing Design Example and Excel SheetDokument6 SeitenIsolated Footing Design Example and Excel SheetshakeelNoch keine Bewertungen
- RCC DESIGN CASE STUDYDokument25 SeitenRCC DESIGN CASE STUDYWHATS APP STATUSNoch keine Bewertungen
- 15epme011 Strength of MaterialsDokument50 Seiten15epme011 Strength of MaterialsgsanthoshskNoch keine Bewertungen
- RC2009 University of HongKong Reinforced Concrete DesignDokument29 SeitenRC2009 University of HongKong Reinforced Concrete DesignApril IngramNoch keine Bewertungen
- O level Physics Questions And Answer Practice Papers 2Von EverandO level Physics Questions And Answer Practice Papers 2Bewertung: 5 von 5 Sternen5/5 (1)
- Strength of Materials and Structures: An Introduction to the Mechanics of Solids and StructuresVon EverandStrength of Materials and Structures: An Introduction to the Mechanics of Solids and StructuresBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (1)
- Cylindrical Compression Helix Springs For Suspension SystemsVon EverandCylindrical Compression Helix Springs For Suspension SystemsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mechanical Science for Technicians: Volume 1Von EverandMechanical Science for Technicians: Volume 1Bewertung: 5 von 5 Sternen5/5 (1)
- The Fatigue Strength of Transverse Fillet Welded Joints: A Study of the Influence of Joint GeometryVon EverandThe Fatigue Strength of Transverse Fillet Welded Joints: A Study of the Influence of Joint GeometryNoch keine Bewertungen
- Strength of Materials: Theory and ExamplesVon EverandStrength of Materials: Theory and ExamplesBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (13)
- Ship Magnetism and the Magnetic Compass: The Commonwealth and International Library of Science, Technology, Engineering and Liberal Studies: Navigation and Nautical CoursesVon EverandShip Magnetism and the Magnetic Compass: The Commonwealth and International Library of Science, Technology, Engineering and Liberal Studies: Navigation and Nautical CoursesBewertung: 5 von 5 Sternen5/5 (3)
- Padre Garcia PDFDokument184 SeitenPadre Garcia PDFApril Rose PlacerNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Vegetation of Mt. Maculot, Cuenca, Batangas, PhilippinesDokument5 SeitenThe Vegetation of Mt. Maculot, Cuenca, Batangas, PhilippinesApril Rose PlacerNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cavite-Laguna Expressway Project EISDokument250 SeitenCavite-Laguna Expressway Project EISmangengueyNoch keine Bewertungen
- DPWH IV-A Presentation For Engineering CongressDokument45 SeitenDPWH IV-A Presentation For Engineering CongressApril Rose PlacerNoch keine Bewertungen
- Stat Cy2003 PDFDokument234 SeitenStat Cy2003 PDFjenizacallejaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Field - Management - Plan - 2 - SEMP - Province of BatangasDokument128 SeitenField - Management - Plan - 2 - SEMP - Province of BatangasApril Rose PlacerNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Essence of Ecotourism An Environmental Study To The Application of Carrying Capacity in Mt. Gulugud Baboy in BatangasDokument13 SeitenThe Essence of Ecotourism An Environmental Study To The Application of Carrying Capacity in Mt. Gulugud Baboy in BatangasApril Rose PlacerNoch keine Bewertungen
- Road Construction EstimateDokument306 SeitenRoad Construction EstimateRJ SisonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Plenary Paper 2. Environmental Impact Assessment of Development Projects in The Philippines - Some Experiences Q.L., KintanarDokument38 SeitenPlenary Paper 2. Environmental Impact Assessment of Development Projects in The Philippines - Some Experiences Q.L., KintanarGraciaVelitarioNoch keine Bewertungen
- Final ReportDokument81 SeitenFinal ReportApril Rose PlacerNoch keine Bewertungen
- Department of Agricluture BAS PDFDokument57 SeitenDepartment of Agricluture BAS PDFApril Rose PlacerNoch keine Bewertungen
- Anilao Case Study PDFDokument22 SeitenAnilao Case Study PDFVictor Gregor LimonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ce 199Dokument25 SeitenCe 199April Rose PlacerNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Essence of Ecotourism An Environmental Study To The Application of Carrying Capacity in Mt. Gulugud Baboy in BatangasDokument13 SeitenThe Essence of Ecotourism An Environmental Study To The Application of Carrying Capacity in Mt. Gulugud Baboy in BatangasApril Rose PlacerNoch keine Bewertungen
- Final ReportDokument81 SeitenFinal ReportApril Rose PlacerNoch keine Bewertungen
- March A. Observed Climatologic Data & Relevant Parameters: If Solar Radiation Rs Is Not AvailableDokument18 SeitenMarch A. Observed Climatologic Data & Relevant Parameters: If Solar Radiation Rs Is Not AvailableApril Rose PlacerNoch keine Bewertungen
- 7Kh, Psdfwri7Rxulvw$Uulydov3K/Vlfdo, Qiudvwuxfwxuhvdqg (Psor/Phqwrq5Hjlrqdo2Xwsxw UrzwkDokument10 Seiten7Kh, Psdfwri7Rxulvw$Uulydov3K/Vlfdo, Qiudvwuxfwxuhvdqg (Psor/Phqwrq5Hjlrqdo2Xwsxw UrzwkApril Rose PlacerNoch keine Bewertungen
- Biaxial Bending in ColumnsDokument14 SeitenBiaxial Bending in Columnsnvnrev100% (1)
- Evaluating Roads As Investments: The Center ForDokument16 SeitenEvaluating Roads As Investments: The Center ForApril Rose PlacerNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nonlinear Pushover Analysis of Reinforced Concrete StructuresDokument117 SeitenNonlinear Pushover Analysis of Reinforced Concrete StructuresEdwin Marino Betancur Díaz100% (6)
- Group assignment 1: Water quality standardsDokument1 SeiteGroup assignment 1: Water quality standardsApril Rose PlacerNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pili Drive Road DevelopmentDokument45 SeitenPili Drive Road DevelopmentApril Rose PlacerNoch keine Bewertungen