Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
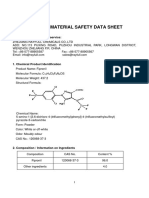
Material Safety Data Sheet: Bayer Corporation Agriculture Division P.O. Box 4913 Hawthorn Road Kansas City, MO 64120-001
Hochgeladen von
Marlon Mallillin IIIOriginaltitel
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Material Safety Data Sheet: Bayer Corporation Agriculture Division P.O. Box 4913 Hawthorn Road Kansas City, MO 64120-001
Hochgeladen von
Marlon Mallillin IIICopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
MATERIAL SAFETY DATA SHEET
BAYER CORPORATION
AGRICULTURE DIVISION
P.O. Box 4913 Hawthorn Road
Kansas City, MO 64120-001
TRANSPORTATION EMERGENCY:
CALL CHEMTREC: (800) 424-9300
DISTRICT OF COLUMBIA: (202) 483-7616
NON-TRANSPORTATION:
BAYER EMERGENCY PHONE: (800) 414-0244
BAYER INFORMATION PHONE: (800) 842-8020
I. PRODUCT IDENTIFICATION:
PRODUCT NAME BAYGON 2% Bait
PRODUCT CODE: 21134
EPA REGISTRATION NO.: 3125-121
CHEMICAL FAMILY: Carbamate Insecticide
CHEMICAL NAME: 2-(1-Methylethoxy)phenol methylcarbamate
SYNONYMS: Aprocarb, SENDRAN, Unden, Propoxur, Suncide
FORMULA: C11 H15 N O3
2. HAZARDOUS INGREDIENTS:
INGREDIENT NAME
/CAS NUMBER EXPOSURE LIMITS CONCENTRATION (%)
BAYGON (propoxur) 2 %
114-26-1 OSHA: .500 mg/m3 TWA
ACGIH: .500 mg/m3 TWA
3. PHYSICAL PROPERTIES:
PHYSICAL FORM: Granules
COLOR: Tan
ODOR: Slight phenol
MOLECULAR WEIGHT: 209.2 (for propoxur)
BOILING POINT: Not applicable
MELTING/FREEZING POINT: Not applicable
SOLUBILITY IN WATER: 0.18% (for propoxur)
SPECIFIC GRAVITY: Not established
BULK DENSITY: Approx. 30 lb./cu ft
% VOLATILE BY VOLUME: Not applicable
VAPOR PRESSURE: 9.7 x 10 -6 mm Hg @ 20
o
C (for propoxur)
VAPOR DENSITY: Not applicable (Air = 1)
4. FIRE AND EXPLOSION DATA:
FLASH POINT: Not Applicable
FLAMMABLE LIMITS:
UPPER EXPLOSIVE LIMIT (UEL)(%): Not applicable
LOWER EXPLOSIVE LIMIT (LEL)(%): Not applicable
EXTINGUISHING MEDIA: Water; Dry Chemical
SPECIAL FIRE FIGHTING PROCEDURES: Keep out of smoke, cool
exposed containers with water spray. Fight fire from upwind position.
Use self-contained breathing equipment. Contain runoff to prevent entry
into sewers or waterways. Equipment or materials involved in pesticide
fires may become contaminated.
5. HUMAN HEALTH DATA:
ROUTE(S) OF ENTRY: Inhalation; Skin Contact; Skin Absorption
HUMAN EFFECTS AND SYMPTOMS OF OVEREXPOSURE:
ACUTE EFFECTS OF EXPOSURE: Inhalation, dermal absorption or
ingestion of this material may result in systemic intoxication due to
inhibition of the enzyme cholinesterase. The sequence of development
of systemic effects varies with the route of entry, and the onset of
symptoms may be delayed an hour or more. First symptoms of
poisoning may be nausea, increased salivation, lacrimation, blurred
vision and constricted pupils. Other symptoms of systemic poisoning
include vomiting, diarrhea, abdominal cramping, dizziness and
sweating. After inhalation, respiratory symptoms like tightness of chest,
wheezing, and laryngeal spasms, may be pronounced at first. If the
poisoning is severe, then symptoms of convulsions, low blood pressure,
cardiac irregularities, loss of reflexes and coma may occur. In extreme
cases, death may occur due to a combination of factors such as
respiratory arrest, paralysis of respiratory muscles or intense
bronchoconstrictions. Complete symptomatic recovery from sublethal
poisoning usually occurs within 24 hours once the source of exposure is
completely removed. Animal studies have shown that this product is
mildly toxic by the oral and dermal routes. It can cause mild irritation to
the conjunctiva with all irritation resolving within 7 days.
CHRONIC EFFECTS OF EXPOSURE: Repeated exposure to small
amounts of this material may result in unexpected cholinesterase
depression causing symptoms such as malaise, weakness, and
anorexia that resemble other illnesses such as influenza. Exposure to
the concentration that would not have produced symptoms in a person
that was not previously exposed may produce severe symptoms of
cholinesterase inhibition in a previously exposed person. High doses of
propoxur induced bladder cancers when fed to rats in one study.
Cancer was not induced in several other feeding studies on rats and
other mammals. The implications of these studies for humans are not
known.
CARCINOGENICITY: This product is not listed by NTP, IARC or regulated
as a carcinogen by OSHA.
MEDICAL CONDITIONS AGGRAVATED BY EXPOSURE: No specific
medical conditions are known which may be aggravated by exposure to
the active ingredient in this product; however, any disease, medication
or prior exposure which reduces normal cholinesterase activity may
increase susceptibility to the toxic effects of the active ingredient.
MATERIAL SAFETY DATA SHEET
Baygon 2% Bait Page 2
6. EMERGENCY AND FIRST AID PROCEDURES:
FIRST AID FOR EYES: Hold eyelids open and flush with copious amounts
of water for 15 minutes. Call a physician if irritation develops or persists
after flushing.
FIRST AID FOR SKIN: Remove contaminated clothing. Wash skin with
soap and water. Get medical attention if irritation develops or persists. If
signs of intoxication (poisoning) occur, get medical attention
immediately.
FIRST AID FOR INHALATION: If a person is overcome by excessive
exposure to this material, remove to fresh air or uncontaminated area. If
not breathing, give artificial respiration, preferably mouth-to-mouth. Get
medical attention as soon as possible.
FIRST AID FOR INGESTION: If ingestion is suspected, call a physician or
poison control center. Drink one or two glasses of water and induce
vomiting by touching back of throat with finger, or, if available, by
administering syrup of ipecac. If syrup of ipecac is available, administer
1 tablespoonful (15 mL) of syrup of ipecac followed by 1 to 2 glasses of
water. If vomiting does not occur within 20 minutes, repeat the dose
once. Do not induce vomiting or give anything by mouth to an
unconscious person.
NOTE TO PHYSICIAN: This product contains the carbamate insecticide,
propoxur, a cholinesterase inhibitor. Cholinesterase inhibition results in
stimulation of the central nervous system, the parasympathetic nervous
system and the somatic motor nerves. If symptoms of carbamate
poisoning are present, the administration of atropine sulfate is indicated.
Administer atropine sulfate in large, therapeutic doses. In mild cases,
start treatment by giving 1-2 mg of atropine intravenously every 15
minutes until signs of atropinization appear (dry mouth, flushing and
dilated pupils if pupils were originally pinpoint). In severe cases, start
treatment by giving 2-4 mg intravenously every 5-10 minutes until fully
atropinized. Dosages for children should be appropriately reduced. Do
not use oximes such as 2-PAM unless organophosphate intoxication is
also suspected. Do not give morphine. Watch for pulmonary edema
which may develop in serious cases of poisoning even after 24 hours.
At first sign of pulmonary edema, place patient in oxygen tent and treat
symptomatically. In case of poisoning, it is also requested that Bayer
Corporation, Agriculture Division, Kansas City, MO, be notified.
Telephone: 816/242-2582
7. EMPLOYEE PROTECTION RECOMMENDATIONS:
EYE PROTECTION REQUIREMENTS: Goggles should be used when
needed to prevent dust from getting into eyes.
SKIN PROTECTION REQUIREMENTS: Avoid skin contact. Wear long
sleeves and trousers. Wear chemical-resistant gloves, boots or shoe
covers when needed to prevent dermal exposure.
RESPIRATOR REQUIREMENTS: If necessary under the conditions of use,
wear a NIOSH-approved dust/mist respirator or a NIOSH-approved
pesticide respirator.
VENTILATION REQUIREMENTS: Maintain exposure levels below the
exposure limit through the use of general and local exhaust ventilation.
ADDITIONAL PROTECTIVE MEASURES: Clean water should be available
for washing in case of eye or skin contamination. Educate and train
employees in safe use of the product. Follow all label instructions.
Launder clothing separately after use. Wash thoroughly after handling.
8. REACTIVITY DATA:
STABILITY: This is a stable material.
HAZARDOUS POLYMERIZATION: Will not occur.
INCOMPATIBILITIES: Alkaline materials, strong oxidants
INSTABILITY CONDITIONS: Sustained temperatures above 100
o
F
DECOMPOSITION PRODUCTS: Proposed compounds include: CO,
CO2, CH3NCO, CH3NH2
9. SPILL AND LEAK PROCEDURES:
SPILL OR LEAK PROCEDURES: Isolate area and keep unauthorized
people away. Do not walk through spilled material. Avoid breathing
dusts and skin contact. Wear proper protective equipment. Carefully
sweep up spilled material. Place in covered container for reuse or
disposal. Scrub contaminated area with detergent and bleach solution.
Repeat. Rinse with water. Contaminated soil may have to be removed
and disposed. Do not allow material to enter streams, sewers, or other
waterways or contact vegetation.
WASTE DISPOSAL METHOD: Follow container label instructions for
disposal of wastes generated during use in compliance with the FIFRA
product label. In other situations, dispose in a RCRA hazardous waste
landfill or incinerate in a RCRA hazardous waste incinerator. An empty
container that previously contained this product is regulated as a RCRA
hazardous waste and must be disposed as a hazardous waste. The
container may be triple rinsed in accordance with 40 CFR 261.7 and
then disposed in an EPA approved landfill. The rinsate must be
managed as a RCRA hazardous waste or used in accordance with the
FIFRA product label. Do not reuse the container.
10. SPECIAL PRECAUTIONS & STORAGE DATA:
STORAGE TEMPERATURE(MIN/MAX): None/30-day average not to
exceed 100
o
F
SHELF LIFE: Not Noted
SPECIAL SENSITIVITY: Heat, moisture
HANDLING/STORAGE PRECAUTIONS: Store in a cool dry area
designated specifically for pesticides. Do not store near any material
intended for use or consumption by humans or animals.
11. SHIPPING INFORMATION:
TECHNICAL SHIPPING NAME: Propoxur
FREIGHT CLASS BULK: Insecticide, O/T Agricultural, N.O.I.
FREIGHT CLASS PACKAGE: Insecticide, O/T Agricultural, N.O.I.
PRODUCT LABEL: Not Noted
DOT (DOMESTIC SURFACE)
HAZARD CLASS OR DIVISION: Non-Regulated
IMO / IMDG CODE (OCEAN)
HAZARD CLASS DIVISION NUMBER: Non-Regulated
ICAO / IATA (AIR)
HAZARD CLASS DIVISION NUMBER: Non-Regulated
12. ANIMAL TOXICITY DATA:
Only acute studies have been performed on this product as formulated. The
non-acute information pertains to the active ingredient, propoxur.
ACUTE TOXICITY:
ORAL LD50: Male Rat: >2012 mg/kg (feeding study); Female Rat: >1795
mg/kg (feeding study)
DERMAL LD50: Rabbit: >2000 mg/kg
INHALATION LC50: 4-hr exposure to dust: Rat: >0.850 mg/l (analytical) --
1-hr exposure to dust (extrapolated from 4-hr LC50): Rat: >3.4 mg/l
(analytical)
EYE EFFECTS: Rabbit: Mild irritation to the conjunctiva was observed with
all irritation resolving within 7 days.
SKIN EFFECTS: Rabbit: Not a dermal irritant.
SENSITIZATION: Guinea pig: Not a dermal sensitizer.
MATERIAL SAFETY DATA SHEET
Baygon 2% Bait Page 3
ANIMAL TOXICITY DATA continued:
SUBCHRONIC TOXICITY:
In a 3 month dermal toxicity study, rabbits were treated with propoxur at
levels up to and including the limit dose (1000 mg/kg) for 6 hours/day, 5
days week. There were no local or systemic effects observed at any of the
levels tested. The no-observed-effect-level (NOEL) was 1000 mg/kg. In a
13 week oral gavage study using Rhesus monkeys, a dose of 40 mg/kg/day
resulted in cholinergic symptoms lasting 5-15 minutes after administration.
These symptoms included salivation, chewing, twitching and rapid
respiration. A 50% depression in plasma cholinesterase occurred by 1 hour.
This returned to normal by 24 hours after administration. In an inhalation
study, in which rats were exposed to propoxur at aerosol concentrations of
15.3, 45.3 or 139.6 mg/cubic meter for 6 hours/day, 5 days/week for a
period of either 4 or 8 weeks, cholinesterase inhibition occurred.
CHRONIC TOXICITY:
In a 1 year study, dogs were administered propoxur at dietary
concentrations of 200, 600 or 1800 ppm. The high dose was increased to
3600 ppm during the 41st week and subsequently to 5400 ppm from the 45
th
week until the end of the study. Effects at the high dose included reduced
body weight gain, cholinesterase inhibition, elevated plasma cholesterol
levels, increased liver weights and thymus atrophy. An additional study was
conducted in which the NOEL was determined to be 70 ppm on the basis of
plasma cholesterol. In a 2 year study, propoxur was administered to rats at
dietary concentrations of 200, 1000 or 5000 ppm. Treatment with 5000 ppm
resulted in decreased food consumption, decreased body weight gain,
cholinesterase inhibition, neuropathy and muscular atrophy. The NOEL was
200 ppm. Rats were exposed to propoxur at liquid aerosol concentrations of
2.2, 10.4 or 50.5 mg/m3 for 6.3 hours/day, 5 days/week for 2 years.
Cholinesterase inhibition occurred at concentrations of 10.4 mg/m3 and
above. The NOEL was determined to be 2.2 mg/m3.
CARCINOGENICITY:
Propoxur was investigated for carcinogenic effects in a 2 year feeding study
on mice. Dietary concentrations of 500, 2000 or 8000 ppm were employed
in the study. An increased incidence of benign liver adenomas occurred in
male mice at 2000 ppm and greater. When rats were fed propoxur for 2
years in a single type of diet, urinary bladder neoplasias were observed at
concentrations of 1000 ppm and above. Propoxur was not carcinogenic in
other types of diets administered to rats at high doses up to and including
the maximum tested concentration of 8000 ppm. In a 2 year inhalation study
on rats, propoxur was determined to be nononcogenic at liquid aerosol
concentrations up to and including the maximum tested concentration of
50.5 mg/m3.
MUTAGENICITY:
A large mutagenicity database supports the conclusion that propoxur is not
genotoxic. This database includes s special study to evaluate genotoxic
potential using urinary bladder cells from propoxur-treated rats. This study
clearly demonstrated that propoxur and its metabolites are nongenotoxic to
urinary bladder cells.
DEVELOPMENTAL TOXICITY:
In a developmental toxicity study using rats, propoxur was administered
during gestation by oral gavage at doses of 3, 9 or 27 mg/kg. The NOEL for
maternal toxicity was 3 mg/kg. No developmental effects were observed at
any of the levels tested. In a developmental toxicity study using rabbits,
propoxur was administered during gestation at oral doses of 3, 10 or 30
mg/kg. Developmental toxicity occurred at the maternally toxic level of 30
mg/kg. The NOEL for maternal and developmental toxicity was 10 mg/kg.
REPRODUCTION:
In reproduction studies using rats, propoxur was administered at dietary
concentrations ranging from 30 to 6000 ppm. Reproductive effects
observed at parentally toxic levels included reductions in the following
parameters: gestation rates, mean number of implantation sites, litter size,
pup body weights, and survival rate of young. The parental and reproductive
NOELs were 30 and 80 ppm, respectively.
ANIMAL TOXICITY DATA continued:
NEUROTOXICITY:
Propoxur has been investigated for delayed neurotoxicity in acute and
subacute studies using hens. Maximum levels tested in the acute studies
were 100 and 1000 mg/kg via intraperitoneal injection and oral gavage,
respectively. Dietary concentrations up to and including 4500 ppm were
tested in a 30 day subacute feeding study. There was no indication of
propoxur causing delayed neurotoxicty in any of these studies. In an acute
neurotoxicity study using rats, propoxur was administered as a single oral
dose at levels of 2, 10 or 25 mg/kg. The NOEL for motor and locomotor
activity was 2 mg/kg for males and 10 mg/kg for females based on
decreased activity in the figure-eight maze. All clinical signs and
neurobehavioral effects were ascribed to acute cholinergic toxicity. The
NOEL for neurotoxicity was 25 mg/kg for both sexes. In a 13 week
neurotoxicity study, propoxur was administered to rats at dietary
concentrations of 500, 2000 or 8000 ppm. Evidence of toxicity at the mid-
and high-dose included reduced body weight and feed consumption, body
weight-related effects on grip strength, foot splay and organ weights, and
clinical chemical findings (cholinesterase inhibition and liver enzyme
induction). Primary neurobehavioral changes were not evident at any dose
level. There were no micropathological findings in neural or muscle tissues.
Excluding cholinergic responses, the NOEL for neurotoxicity is 8000 ppm.
13. FEDERAL REGULATORY INFORMATION:
OSHA STATUS: This product is hazardous under the criteria of the Federal
OSHA Hazard Communication Standard 29 CFR 1910.1200.
TSCA STATUS: This product is exempt from TSCA Regulation under
FIFRA Section 3 (2)(B)(ii) when used as a pesticide.
CERCLA REPORTABLE QUANTITY: 5000 pounds of formulation which
contains 100 pounds of technical.
SARA TITLE III:
SECTION 302 EXTREMELY HAZARDOUS SUBSTANCES: No
components listed
SECTION 311/312 HAZARD CATEGORIES: Immediate Health Hazard;
Delayed Health Hazard
SECTION 313 TOXIC CHEMICALS: Propoxur (CAS #114-26-1) 2.0%
RCRA STATUS: When discarded in its purchased form, this product is a
listed RCRA hazardous waste and should be managed as a hazardous
waste. (40 CFR 261.20-24) Propoxur is listed as U411.
14. OTHER REGULATORY INFORMATION:
NFPA 704M RATINGS:
Health: 1 Flammability: 1 Reactivity: 1 Other:
0=Insignificant 1=Slight 2=Moderate 3=High 4=Extreme
Bayers method of hazard communication is comprised of Product Labels
and Material Safety Data Sheets. NFPA ratings are provided by Bayer
Corporation as a customer service.
15. APPROVALS:
REASON FOR ISSUE: Revise Section IX (waste disposal); Section XII
(additional neurotoxicity data); Section XIII (CERCLA RQ; RCRA status)
PREPARED BY: V. C. Standart
APPROVED BY: D. C. Eberhart
TITLE: Product Safety Manager
APPROVAL DATE: 12/19/95
SUPERSEDES DATE: 11/18/94
MSDS NUMBER: 08133
This information is furnished without warranty, expressed or implied,
except that it is accurate to the best knowledge of Bayer Corporation.
The data on this sheet relates only to the specific material designated
herein. Bayer Corporation assumes no legal responsibility for use or
reliance upon these data.
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Material Safety Data Sheet Malathion 57 EcDokument3 SeitenMaterial Safety Data Sheet Malathion 57 EcSafira RamadhaniNoch keine Bewertungen
- HC DSN Descaler Neutralizer SolidDokument9 SeitenHC DSN Descaler Neutralizer SolidCNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fibrohas 5 1 MSDSDokument9 SeitenFibrohas 5 1 MSDSSAIGOKUL SETHUMADHAVANNoch keine Bewertungen
- MSDS Blockade 100 EC PDFDokument5 SeitenMSDS Blockade 100 EC PDFDean Hadi WardanaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Diazinon Ag600 WBC InsecticideDokument3 SeitenDiazinon Ag600 WBC InsecticideCaesar DQNoch keine Bewertungen
- 10 Tenths Race Coolant Inhibitor Rev 7.02 0515Dokument9 Seiten10 Tenths Race Coolant Inhibitor Rev 7.02 0515ᮛᮥᮞ᮪ᮓᮤ ᮎᮦᮎᮦᮕ᮪Noch keine Bewertungen
- 11 2017 IngDokument5 Seiten11 2017 IngPetro DoroshNoch keine Bewertungen
- Material Safety Data Sheet Fipronil 5% SC: 1. Identification of Company & ProductDokument7 SeitenMaterial Safety Data Sheet Fipronil 5% SC: 1. Identification of Company & Productusman khalid100% (1)
- Gulmaron - DiuronDokument4 SeitenGulmaron - Diuronnataliaek812Noch keine Bewertungen
- Lambda Cyhal Matador 120ecDokument7 SeitenLambda Cyhal Matador 120ecJonatan SiraitNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cambistat MSDSDokument5 SeitenCambistat MSDSkyu9999Noch keine Bewertungen
- 250 Propoxur-MSDSDokument2 Seiten250 Propoxur-MSDSWuri Handayani EldiNoch keine Bewertungen
- MSDS PPDokument4 SeitenMSDS PPdiantikaNoch keine Bewertungen
- MSDS TemplateDokument4 SeitenMSDS TemplateSanjay KapoorNoch keine Bewertungen
- Msds - A A 2904 1 1Dokument6 SeitenMsds - A A 2904 1 1PT. SURYAGITA NUSARAYANoch keine Bewertungen
- N Spec 120 Cleaner Data SheetDokument11 SeitenN Spec 120 Cleaner Data SheetSergio Alejandro Loza EscobarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Material Safety Data SheetDokument31 SeitenMaterial Safety Data SheetDito Anggriawan PrasetyoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Alphanol Super11.07.10Dokument6 SeitenAlphanol Super11.07.10serge.pungweNoch keine Bewertungen
- Material Safety Data Sheet Malathion Ulv® Concentrate InsecticideDokument3 SeitenMaterial Safety Data Sheet Malathion Ulv® Concentrate InsecticideLaura GreenNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fipronil SdsDokument5 SeitenFipronil Sdsapi-387946507Noch keine Bewertungen
- MSDS Mustang 25ECDokument10 SeitenMSDS Mustang 25ECSadhana Sentosa100% (2)
- MSDS Bistar 25 ECDokument7 SeitenMSDS Bistar 25 ECSadhana SentosaNoch keine Bewertungen
- ALTIMA Ar PDFDokument6 SeitenALTIMA Ar PDFmohamed atefNoch keine Bewertungen
- USA DEF - Safety Data SheetDokument4 SeitenUSA DEF - Safety Data SheetRafael FerreiraNoch keine Bewertungen
- SDS-Purple-Primer-722 and PVC Cleaner 733Dokument9 SeitenSDS-Purple-Primer-722 and PVC Cleaner 733Macuto JunieNoch keine Bewertungen
- PC 56 Biocide (Old)Dokument13 SeitenPC 56 Biocide (Old)Hyun Jin YooNoch keine Bewertungen
- Safety Data Sheet FuseDokument7 SeitenSafety Data Sheet Fuse. .Noch keine Bewertungen
- Actellic 50 EcDokument9 SeitenActellic 50 Ecnadi1onlyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Section 1 Product and Company Information: Propionic AcidDokument4 SeitenSection 1 Product and Company Information: Propionic AcidBeatrix DhoneNoch keine Bewertungen
- MX 416 MSDSDokument9 SeitenMX 416 MSDSMunirah Hani HarunNoch keine Bewertungen
- Oleum EnglishDokument10 SeitenOleum Englishhyde2520015754Noch keine Bewertungen
- Atrazine 97-98 % TechDokument5 SeitenAtrazine 97-98 % TechHimawan FirdausNoch keine Bewertungen
- 4015-Flocculant SDSDokument5 Seiten4015-Flocculant SDSAquasoul CoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Acetone CPDokument6 SeitenAcetone CPJonesHutaurukNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cyperpro SDSDokument5 SeitenCyperpro SDSADMIN IIINoch keine Bewertungen
- Safety Data Sheet: Section 1: Identification of The Material and SupplierDokument7 SeitenSafety Data Sheet: Section 1: Identification of The Material and SupplierNama TanpaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Glycerol MSDSDokument5 SeitenGlycerol MSDSJohn BearNoch keine Bewertungen
- Material Safety Data Sheet: #360F Liquid Flux 1. Product and Company IdentificationDokument5 SeitenMaterial Safety Data Sheet: #360F Liquid Flux 1. Product and Company IdentificationteknoartistNoch keine Bewertungen
- Material Safety Data Sheet: I - Product IdentificationDokument8 SeitenMaterial Safety Data Sheet: I - Product IdentificationHaris OktaviantoNoch keine Bewertungen
- MSDS - Furadan-4fDokument11 SeitenMSDS - Furadan-4fDuda64Noch keine Bewertungen
- MSDS Delstar Plus (Profenofos) Qingdao PDFDokument6 SeitenMSDS Delstar Plus (Profenofos) Qingdao PDFAgung Septama AndrifazaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Material Safety Data Sheet Glyphosate 5.4Dokument5 SeitenMaterial Safety Data Sheet Glyphosate 5.4Ahfi Rizqi FajrinNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chemical Product and Company Identification: Substance: Sulfuric Acid - SpentDokument8 SeitenChemical Product and Company Identification: Substance: Sulfuric Acid - SpentJason DuranNoch keine Bewertungen
- Material Safety Data Sheet Diazinon Ag600 WBC Insecticide: 1. Chemical Product and Company IdentificationDokument3 SeitenMaterial Safety Data Sheet Diazinon Ag600 WBC Insecticide: 1. Chemical Product and Company Identificationgraha hermineNoch keine Bewertungen
- Larvin375 MSDS 0907Dokument7 SeitenLarvin375 MSDS 0907Nugroho HartonoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chalcone MSDS: Section 1: Chemical Product and Company IdentificationDokument5 SeitenChalcone MSDS: Section 1: Chemical Product and Company IdentificationNaveed SajidNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ficha de Seguridad Neolone PH 100 MsdsDokument11 SeitenFicha de Seguridad Neolone PH 100 MsdsDora Nelcy Rincón DazaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Aquatower 100Dokument7 SeitenAquatower 100Diego y MagelaNoch keine Bewertungen
- AkzoNobel SMCA MSDS 0909 Tcm18-10237Dokument0 SeitenAkzoNobel SMCA MSDS 0909 Tcm18-10237David HoffmanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Msds GoalDokument19 SeitenMsds GoalAhmad AndiNoch keine Bewertungen
- MSDS Rum 60%Dokument3 SeitenMSDS Rum 60%Hugo MarticorenaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 4.amine 4 2,4-D Weed Killer (Vulgar)Dokument3 Seiten4.amine 4 2,4-D Weed Killer (Vulgar)efrinov1174Noch keine Bewertungen
- Stihl BioPlus Chain and Bar Oil Rev 0-0-0713Dokument10 SeitenStihl BioPlus Chain and Bar Oil Rev 0-0-0713MolokoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pyridine PDFDokument6 SeitenPyridine PDFanon_342721354Noch keine Bewertungen
- Grotan - MSDSDokument3 SeitenGrotan - MSDSjmquinonesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Filter Aid MSDSDokument11 SeitenFilter Aid MSDSfructoraNoch keine Bewertungen
- NALCO® EC9149A: Section 1. Identification of The Substance/Mixture and of The Company/UndertakingDokument14 SeitenNALCO® EC9149A: Section 1. Identification of The Substance/Mixture and of The Company/UndertakingDonatas BertasiusNoch keine Bewertungen
- Georgia Pest Management Handbook: 2021 Home and Garden EditionVon EverandGeorgia Pest Management Handbook: 2021 Home and Garden EditionEmily CabreraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pharmaceutical Microbiology: A Laboratory ManualVon EverandPharmaceutical Microbiology: A Laboratory ManualBewertung: 3 von 5 Sternen3/5 (2)
- Edsa HijackedDokument5 SeitenEdsa HijackedRoss Wahlen Mojica RolloNoch keine Bewertungen
- What Is ShigellosisDokument8 SeitenWhat Is ShigellosisMarlon Mallillin IIINoch keine Bewertungen
- What Is ShigellosisDokument8 SeitenWhat Is ShigellosisMarlon Mallillin IIINoch keine Bewertungen
- Meta-Analysis: 4CLPH - Group 9Dokument36 SeitenMeta-Analysis: 4CLPH - Group 9Marlon Mallillin IIINoch keine Bewertungen
- SCL PrayerDokument1 SeiteSCL PrayerMarlon Mallillin IIINoch keine Bewertungen
- Literature Review of Food DyeDokument7 SeitenLiterature Review of Food Dyedpsjefsif100% (1)
- Oral Cancer WordDokument18 SeitenOral Cancer WordAdeesh saraf100% (1)
- ABC Fire Extinguisher - Ansul Incorporated PDFDokument10 SeitenABC Fire Extinguisher - Ansul Incorporated PDFPubcrawlNoch keine Bewertungen
- Health Tips PDFDokument11 SeitenHealth Tips PDFcarte_blueNoch keine Bewertungen
- Natural Dyes - Alternative For Synthetic DyesDokument7 SeitenNatural Dyes - Alternative For Synthetic DyesviswaNoch keine Bewertungen
- SDS Alodine 600Dokument9 SeitenSDS Alodine 600adboni1612Noch keine Bewertungen
- Material Safety Data Sheet West System Inc.: MSDS #105-11b Last Revised: 22JUN11Dokument4 SeitenMaterial Safety Data Sheet West System Inc.: MSDS #105-11b Last Revised: 22JUN11Thanhnam PhanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sigma-Aldrich: Material Safety Data SheetDokument7 SeitenSigma-Aldrich: Material Safety Data Sheethollymc86Noch keine Bewertungen
- CancerDokument24 SeitenCancerPavitam ChucksNoch keine Bewertungen
- Electronic Cigarettes and Head and Neck Cancer RiskDokument16 SeitenElectronic Cigarettes and Head and Neck Cancer RiskMafourNoch keine Bewertungen
- KFC Grilled Chicken Phip Report-FinalDokument2 SeitenKFC Grilled Chicken Phip Report-FinaljiskaninawazNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cancer BiologyDokument138 SeitenCancer BiologyLenken Loccoc100% (3)
- Rapid Analysis of Genotoxic Nitrosamines by HPLC MS MSDokument3 SeitenRapid Analysis of Genotoxic Nitrosamines by HPLC MS MSMarcio SchiavelliNoch keine Bewertungen
- Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons (PAHs) and Heterocyclic Amines (HCAs)Dokument6 SeitenPolycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons (PAHs) and Heterocyclic Amines (HCAs)shawnleegabrielNoch keine Bewertungen
- Rule: Pesticide Tolerance: FlonicamidDokument7 SeitenRule: Pesticide Tolerance: FlonicamidJustia.comNoch keine Bewertungen
- Recommendations: (Text With EEA Relevance)Dokument2 SeitenRecommendations: (Text With EEA Relevance)Jose Filipe Bacalhau RodriguesNoch keine Bewertungen
- The CEllular AberrationsDokument17 SeitenThe CEllular AberrationsShara Sampang100% (1)
- OSPAR List of Substances / Preparations Used and Discharged Offshore Which Are Considered To Pose Little or No Risk To The Environment (PLONOR)Dokument5 SeitenOSPAR List of Substances / Preparations Used and Discharged Offshore Which Are Considered To Pose Little or No Risk To The Environment (PLONOR)MaychelBetaWNoch keine Bewertungen
- Material Safety Data Sheet - MSDS: Section 1. Chemical Product and Company IdentificationDokument5 SeitenMaterial Safety Data Sheet - MSDS: Section 1. Chemical Product and Company IdentificationPubcrawlNoch keine Bewertungen
- Material Safety Data Sheet: 1. Product and Company IdentificationDokument9 SeitenMaterial Safety Data Sheet: 1. Product and Company IdentificationRizkiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Safety Data Sheet: Delo Gold Ultra SAE 15W-40Dokument6 SeitenSafety Data Sheet: Delo Gold Ultra SAE 15W-40Nasta Ina RobayasaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Biology Project 2015Dokument40 SeitenBiology Project 2015vivaan50% (12)
- Oxo AQAGCSE B7 ws01 XxaannDokument2 SeitenOxo AQAGCSE B7 ws01 XxaannParam BhimaniNoch keine Bewertungen
- Neoplasia 1Dokument14 SeitenNeoplasia 1Omar MaanNoch keine Bewertungen
- D-Limonene: Safety and Clinical ApplicationsDokument6 SeitenD-Limonene: Safety and Clinical ApplicationsbreakingthesilenceNoch keine Bewertungen
- Safety Data Sheet: Butyrylcholinesterase Inhibitor Screening Kit (Colorimetric)Dokument6 SeitenSafety Data Sheet: Butyrylcholinesterase Inhibitor Screening Kit (Colorimetric)Verliyanti BastariNoch keine Bewertungen
- Oncology Nursing: Detection and Prevention of CancerDokument14 SeitenOncology Nursing: Detection and Prevention of CancerEdwin Delos Reyes AbuNoch keine Bewertungen
- CL439/CL954 Contaminated LandDokument21 SeitenCL439/CL954 Contaminated LandSanti PoNoch keine Bewertungen
- SDS Westpac Ready Mix CompoundsDokument8 SeitenSDS Westpac Ready Mix CompoundsSherif ShahinNoch keine Bewertungen
- Oncology Nursing Oncology What Is Cancer?Dokument10 SeitenOncology Nursing Oncology What Is Cancer?NeweeJoonYow100% (1)