Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Reviewer Indus
Hochgeladen von
Bajogs RamosCopyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Reviewer Indus
Hochgeladen von
Bajogs RamosCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
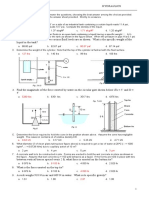
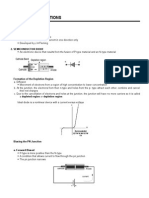
1. A thyristor can be used as a. A resistor b. An amplifier c. A switch d. A power source 2.
Positive feedback means that the returning signal a. Opposes the original change b. Aids the original change c. Is equivalent to negative feedback d. Is amplified 3. A latch always uses a. Transistors b. Negative feedback c. Current d. Positive feedback 4. To turn on a four-layer diode, you need a. A positive trigger b. Low-current drop-out c. Breakover d. Reverse-bias triggering 5. The minimum input currents that can turn on a thyristor is called the a. Holding current b. Trigger current c. Breakover current d. Low-current drop-out 6. The only way to stop a four-layer diode that is conducting is by a. A positive trigger b. Low-current drop-out c. Breakover d. Reverse-bias triggering 7. The minimum anode current that keeps a thyristor turned on is called the a. Holding current b. Trigger current c. Breakover current d. Low-current drop-out
8. A SCR has a. Two external leads b. Three external leads c. Four external leads d. Three doped regions 9. An SCR is usually turned on by a. Breakover b. A gate trigger c. Breakdown d. Holding current 10. SCRs are a. Low-power devices b. Four-layer diodes c. High-current devices d. Bidirectional 11. The usual way to protect a load from excessive supply voltage is with a a. Crowbar b. Zener diode c. Four-layer diode d. Thyristor 12. An RC snubber protects an SCR against a. Supply overvoltages b. False triggering c. Breakover d. Crowbarring 13. When a crowbar is used with a power supply, the supply needs to have a fuse or a. Adequate trigger current b. Holding current c. Filtering d. Current limiting 14. The photo-SCR responds to a. Current b. Voltage c. Humidity d. Light
15. The diac is a a. Transistor b. Unidirectional device c. Three-layer diode d. Bidirectional device 16. The triac is equivalent to a. A four-layer diode b. Two diacs in parallel c. A thyristor with a gate lead d. Two SCRs in parallel 17. The unijunction transistor acts as a a. Four-layer diode b. Diac c. Triac d. Latch 18. Any thyristor can be turned on with a. Breakover b. Forward-bias triggering c. Low-current drop-out d. Reverse-bias triggering 19. A Schockley diode is the same as a. A four-layer diode b. An SCR c. A diac d. A triac 20. The trigger voltage of an SCR is closest to a. 0 b. 0.7V c. 4V d. Breakover voltage 21. Any thyristor can be turned off with a. Breakover b. Forward-bias triggering c. Low-current drop-out d. Reverse-bias triggering
22. Exceeding the critical rate of rise produces a. Excessive power dissipation b. False triggering c. Low-current drop-out d. Reverse-bias triggering 23. A four-layer diode is sometimes called a a. Unijunction transistor b. Diac c. Pnpn diode d. Switch 24. A latch is based on a. Negative feedback b. Positive feedback c. The four-layer diode d. SCR action 25. An SCR can switch to the on state if a. Its forward breakover voltage is exceeded b. IGT is applied c. The critical rate of voltage rise is exceeded d. All of the above 26. To properly test an SCR using an ohmmeter a. The ohmmeter must supply the SCRs breakover voltage b. The ohmmeter cannot supply more than 0.7V c. The ohmmeter must supply the SCRs reverse breakover voltage d. The ohmmeter must supply the SCRs holding current
27. The maximum firing angle with a single RC phase control circuit is a. 45 b. 90 c. 180 d. 360 28. A triac is generally considered most sensitive in a. Quadrant I b. Quadrant II c. Quadrant III d. Quadrant IV 29. An IGBT is essentially a a. BJT on the input and MOSFET on the output b. MOSFET on the input and MOSFET on the output c. MOSFET on the input and BJT on the output d. BJT on the input and BJT on the output 30. The maximum on-state output voltage of an IGBT is a. VGS(ON) b. VCE(SAT) c. RDS(ON) d. VCES 31. A PUT is considered programmable by using a. External gate resistors b. Applying preset cathode voltage levels c. An external capacitor d. Doped pn junctions
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Reversi (Othello) - Game StrategyDokument11 SeitenReversi (Othello) - Game StrategysuperyoopyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Termpaper-Strength Analysis of Screw Jack-Mechanics of SolidsDokument21 SeitenTermpaper-Strength Analysis of Screw Jack-Mechanics of SolidsOmkar Kumar JhaNoch keine Bewertungen
- AnalyticDokument8 SeitenAnalyticMark Neil Delgaco GastiloNoch keine Bewertungen
- General Systems Theory A Mathematical ApproachDokument385 SeitenGeneral Systems Theory A Mathematical Approachselotejp7100% (4)
- Problems 2Dokument2 SeitenProblems 2ThomasAdiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Inputs Process Output: Conceptual FrameworkDokument2 SeitenInputs Process Output: Conceptual FrameworkBajogs RamosNoch keine Bewertungen
- Advanced PHP ManualDokument246 SeitenAdvanced PHP Manualkennedy onuzulikeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Guide-Tone Space - Navigating Voice-Leading Syntax in Tonal JazzDokument23 SeitenGuide-Tone Space - Navigating Voice-Leading Syntax in Tonal JazzCacau Ricardo FerrariNoch keine Bewertungen
- EE20L Exp1Dokument5 SeitenEE20L Exp1Patrick HernandezNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Silicon-Controlled Switch (SCS)Dokument7 SeitenThe Silicon-Controlled Switch (SCS)Joshua Roberto GrutaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Statics SPDokument67 SeitenStatics SPDianne VillanuevaNoch keine Bewertungen
- RinkiDokument4 SeitenRinkiRinki SoniNoch keine Bewertungen
- Assignment - IDokument4 SeitenAssignment - IchritNoch keine Bewertungen
- PS 1 - Unit 3 - PDFDokument20 SeitenPS 1 - Unit 3 - PDFariel mentawanNoch keine Bewertungen
- IE005 Lab Exercise 1 and 2mnDokument7 SeitenIE005 Lab Exercise 1 and 2mnApril Dawates100% (1)
- C1 - Introduction To Engineering Economy-1Dokument23 SeitenC1 - Introduction To Engineering Economy-1Jon Welba100% (1)
- Experiment 102 Friction OnlineDokument6 SeitenExperiment 102 Friction OnlineCyruz LapinasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Problems: 1. A Residential Urban Area Has The Following Proportions of Different Land Use: Roofs, 25Dokument1 SeiteProblems: 1. A Residential Urban Area Has The Following Proportions of Different Land Use: Roofs, 25TWICE TEUDOONGIENoch keine Bewertungen
- Fluid Mach. Nos. 1 8 Part 1Dokument10 SeitenFluid Mach. Nos. 1 8 Part 1Kim Howard CastilloNoch keine Bewertungen
- Thermodynamics Handout Chapter 1Dokument18 SeitenThermodynamics Handout Chapter 1Stephen Zydric A. SalibioNoch keine Bewertungen
- Experiment # 1-Falling Sphere Viscometer (1-6)Dokument6 SeitenExperiment # 1-Falling Sphere Viscometer (1-6)hgfhfghfghgNoch keine Bewertungen
- BorderDokument11 SeitenBorderasdsadsadsadas100% (1)
- Electronics Module 2Dokument13 SeitenElectronics Module 2tirsollantadaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 6 DC Machimes - DC GeneratorsDokument30 Seiten6 DC Machimes - DC GeneratorsJohn Rennier MandanasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Engg Management - Chapter - 10Dokument9 SeitenEngg Management - Chapter - 10John Rexel CaroNoch keine Bewertungen
- Simulation of Power Supply Circuit (Paloma)Dokument16 SeitenSimulation of Power Supply Circuit (Paloma)Emmanuel PalomaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Instrumentation (Finale)Dokument20 SeitenInstrumentation (Finale)Jonathan BacusNoch keine Bewertungen
- Kuddus Sir PDFDokument443 SeitenKuddus Sir PDFTapu mojumderNoch keine Bewertungen
- Transformer T1Dokument1 SeiteTransformer T1Vikash TiwariNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bus 6Dokument3 SeitenBus 6kittleboyNoch keine Bewertungen
- 11 WattmeterDokument14 Seiten11 WattmeterislahidNoch keine Bewertungen
- Capitalized Cost Eng Econo As1Dokument8 SeitenCapitalized Cost Eng Econo As1Francis Valdez LopezNoch keine Bewertungen
- First Benchmark PublishingDokument17 SeitenFirst Benchmark PublishingChan Mark AyapanaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Power Elex Finals PDFDokument5 SeitenPower Elex Finals PDFDanilo PerezNoch keine Bewertungen
- ACE 10L - AC/DC Machinery 1LDokument6 SeitenACE 10L - AC/DC Machinery 1LSky FallNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lista 5Dokument22 SeitenLista 5vsabioniNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 5 Eneergy Con 2Dokument4 SeitenChapter 5 Eneergy Con 2LuelsonCordovaDeclaradorNoch keine Bewertungen
- Experiment 6: Power in AC CircuitsDokument13 SeitenExperiment 6: Power in AC Circuitshiruma aizenNoch keine Bewertungen
- CH-2-DC MachineDokument83 SeitenCH-2-DC MachineÙm ØrthøbøyNoch keine Bewertungen
- D.C. Machin BaidaDokument53 SeitenD.C. Machin BaidaLeonard ValdezNoch keine Bewertungen
- NU DB and NOISE CALCULATION PDFDokument49 SeitenNU DB and NOISE CALCULATION PDFChristelle Cha LotaNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Equations of The Currents in Two Parallel Connected Electric Devices Are I1Dokument3 SeitenThe Equations of The Currents in Two Parallel Connected Electric Devices Are I1Tim Picar100% (1)
- Module 4Dokument18 SeitenModule 4streetranpuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Section 7: Thyristors and SwitchesDokument18 SeitenSection 7: Thyristors and Switcheschrist9088Noch keine Bewertungen
- CE Review Advanced MathematicsDokument2 SeitenCE Review Advanced MathematicsRAYNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 2 PDFDokument83 SeitenChapter 2 PDFzarrinNoch keine Bewertungen
- Transmission Lines and E.M. Waves Lec 04Dokument34 SeitenTransmission Lines and E.M. Waves Lec 04Vishnu ShashankNoch keine Bewertungen
- 7 Osborne Reynold'S Demonstration: Mapúa UniversityDokument11 Seiten7 Osborne Reynold'S Demonstration: Mapúa UniversityJemuel FloresNoch keine Bewertungen
- Strength of Materials - MCQ2Dokument30 SeitenStrength of Materials - MCQ2jenny0% (1)
- Plates in EnerconDokument38 SeitenPlates in EnerconJevan Calaque100% (1)
- 10dc GeneratorDokument6 Seiten10dc GeneratorJj JumawanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Engineering Economy Course Student 4Dokument27 SeitenEngineering Economy Course Student 4Baesl 2000Noch keine Bewertungen
- Auto TransformerDokument5 SeitenAuto TransformerAugy HaerudyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Day 2 Board ReviewDokument8 SeitenDay 2 Board ReviewAkiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Orca Share Media1535596930012Dokument64 SeitenOrca Share Media1535596930012Julia Latawan LasilasNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1352 Muhamadfadlibinsamsudin2011Dokument109 Seiten1352 Muhamadfadlibinsamsudin2011Bogdan VicolNoch keine Bewertungen
- CE141-2 M3 Exam Part 1Dokument1 SeiteCE141-2 M3 Exam Part 1Jemuel FloresNoch keine Bewertungen
- Zener Diode and Diode ApplicationDokument62 SeitenZener Diode and Diode Applicationnibar dyllanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Control System Chapter 1 19-20Dokument36 SeitenControl System Chapter 1 19-20Venkat Gopinaath PolamuriNoch keine Bewertungen
- D. Can Be Triggered by Either A Positive or A Negative Gate VoltageDokument6 SeitenD. Can Be Triggered by Either A Positive or A Negative Gate VoltagePritamjit RoutNoch keine Bewertungen
- MEPCO Assistant Engineer Operations Test QuestionsDokument6 SeitenMEPCO Assistant Engineer Operations Test QuestionszahidwaqarktkNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mas Awan Titip 2Dokument8 SeitenMas Awan Titip 2Wahyu Muhamad RomadoniNoch keine Bewertungen
- Power Electronics BasicsDokument23 SeitenPower Electronics BasicsSrivatsa MadhaliNoch keine Bewertungen
- EST Sample Problems 10Dokument9 SeitenEST Sample Problems 10Genesis PinedaNoch keine Bewertungen
- UserForm RamosDokument8 SeitenUserForm RamosBajogs RamosNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lesson 1 - Introduction To Power ElectronicsDokument20 SeitenLesson 1 - Introduction To Power ElectronicsBajogs RamosNoch keine Bewertungen
- Switching Regulator BasicsDokument33 SeitenSwitching Regulator BasicsUtpal100% (11)
- TEA1721ATDokument14 SeitenTEA1721ATBajogs RamosNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lugar Grand CanyonDokument5 SeitenLugar Grand CanyonBajogs RamosNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lesson 5 - Buck Converter 2011-07-30Dokument16 SeitenLesson 5 - Buck Converter 2011-07-30Bajogs RamosNoch keine Bewertungen
- TRONIXDokument11 SeitenTRONIXBajogs RamosNoch keine Bewertungen
- Gauss JordanDokument32.767 SeitenGauss JordanBajogs RamosNoch keine Bewertungen
- AsdasdasDokument4 SeitenAsdasdasBajogs RamosNoch keine Bewertungen
- ELECDokument4 SeitenELECMiradel LasquiteNoch keine Bewertungen
- Indus Chapter 2Dokument5 SeitenIndus Chapter 2Bajogs RamosNoch keine Bewertungen
- Electronic Devices Byas L Floyd 7th Solution Manual 106Dokument1 SeiteElectronic Devices Byas L Floyd 7th Solution Manual 106Bajogs RamosNoch keine Bewertungen
- DDDokument2 SeitenDDBajogs RamosNoch keine Bewertungen
- Slide FrogDokument3 SeitenSlide FrogBajogs RamosNoch keine Bewertungen
- Electronic Devices Byas L Floyd 7th Solution Manual 103Dokument1 SeiteElectronic Devices Byas L Floyd 7th Solution Manual 103Bajogs RamosNoch keine Bewertungen
- HahaDokument8 SeitenHahaBajogs RamosNoch keine Bewertungen
- BajogsDokument1 SeiteBajogsBajogs RamosNoch keine Bewertungen
- CH06Dokument37 SeitenCH06Bajogs RamosNoch keine Bewertungen
- I2c To LCD InterfaceDokument1 SeiteI2c To LCD InterfaceTTM_SOBINoch keine Bewertungen
- Steel Design (Moment and Shear Check) (For Simply Supported)Dokument8 SeitenSteel Design (Moment and Shear Check) (For Simply Supported)aikalessNoch keine Bewertungen
- Calculation and Adjustment of Silica (Sio) Scaling For Reverse OsmosisDokument3 SeitenCalculation and Adjustment of Silica (Sio) Scaling For Reverse OsmosismerksssNoch keine Bewertungen
- 24/10/2017. ",, IssnDokument2 Seiten24/10/2017. ",, IssnMikhailNoch keine Bewertungen
- Reviewer For Art AppreciationDokument10 SeitenReviewer For Art AppreciationSharmaine FernandezNoch keine Bewertungen
- What Is Generator Efficiency Calculation Formula GuideDokument6 SeitenWhat Is Generator Efficiency Calculation Formula Guidejitender.singh29Noch keine Bewertungen
- Reasoning Calendar Questions Finding Day or Date, Concepts, Shortcuts ExplainedDokument8 SeitenReasoning Calendar Questions Finding Day or Date, Concepts, Shortcuts ExplainedManish KumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Atellica IM Analyzers: Technical SpecificationsDokument4 SeitenAtellica IM Analyzers: Technical SpecificationsNazarii KordupelNoch keine Bewertungen
- SolverTable HelpDokument13 SeitenSolverTable HelpM Ibnu Aji DwiyantoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Linear Partial Differential Equations of High Order With Constant CoefficientsDokument58 SeitenLinear Partial Differential Equations of High Order With Constant CoefficientsShahin Kauser ZiaudeenNoch keine Bewertungen
- Anatomy of GallbladderDokument14 SeitenAnatomy of GallbladderSamridhi DawadiNoch keine Bewertungen
- External Interface (XINTF)Dokument38 SeitenExternal Interface (XINTF)AlonsoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sorting in ALV Using CL - SALV - TABLE - SAP Fiori, SAP HANA, SAPUI5, SAP Netweaver Gateway Tutorials, Interview Questions - SAP LearnersDokument4 SeitenSorting in ALV Using CL - SALV - TABLE - SAP Fiori, SAP HANA, SAPUI5, SAP Netweaver Gateway Tutorials, Interview Questions - SAP LearnerssudhNoch keine Bewertungen
- 3tnv82a Bdsa2Dokument2 Seiten3tnv82a Bdsa2BaggerkingNoch keine Bewertungen
- Summa Roll Cutters: S One - S Class 2 Series World Renowned Vinyl and Contour CuttersDokument32 SeitenSumma Roll Cutters: S One - S Class 2 Series World Renowned Vinyl and Contour CuttersPU PUNoch keine Bewertungen
- Determination of Hydrocarbons in Liquefied Petroleum (LP) Gases and Propane/Propene Mixtures by Gas ChromatographyDokument11 SeitenDetermination of Hydrocarbons in Liquefied Petroleum (LP) Gases and Propane/Propene Mixtures by Gas ChromatographyКарат центрNoch keine Bewertungen
- AN78M20FDokument10 SeitenAN78M20FFrantsiskoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Difference Between DWA and TEB Local PlannersDokument2 SeitenDifference Between DWA and TEB Local PlannersChandrajit GangulyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Delta ASDA B User ManualDokument321 SeitenDelta ASDA B User ManualRichard ThainkhaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Current Calculator For Barrel Plating - Chlorize Zinc PlatingDokument4 SeitenCurrent Calculator For Barrel Plating - Chlorize Zinc PlatingARVINDA KUMARNoch keine Bewertungen
- Adverse WeatherDokument13 SeitenAdverse WeathermurugeshunivNoch keine Bewertungen
- Systemmeldungen GBDokument28 SeitenSystemmeldungen GBAhmet0% (1)
- Precision 10 40 Operating InstructionsDokument27 SeitenPrecision 10 40 Operating InstructionsDaniel PeluffoNoch keine Bewertungen
- g484 Physics Newtonian World Notes Ocr Robbie PeckDokument10 Seiteng484 Physics Newtonian World Notes Ocr Robbie Peckapi-236179294Noch keine Bewertungen
- Alkali MetalsDokument12 SeitenAlkali MetalsSaki Sultana LizaNoch keine Bewertungen
- A New Approach For Sizing Finger-Type (Multiple-Pipe) Slug CatchersDokument9 SeitenA New Approach For Sizing Finger-Type (Multiple-Pipe) Slug CatchersnicolasNoch keine Bewertungen