Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
My Draft Partial Pressures
Hochgeladen von
lovelyc95Originalbeschreibung:
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
My Draft Partial Pressures
Hochgeladen von
lovelyc95Copyright:
Verfügbare Formate
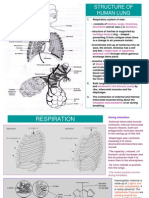
Partial pressure of gases in Aveoli: 1) PO2 in alveoli is 100 mm hg and thats because a) the fresh air entering the
alveoli that has PO2 160 mm hg will mix with the air in alveoli already present from previous expiration which has low PO2, and b) when air enter to lungs through air ways it will be humidified by adding water vapor to it and by this reducing O2 percentage in the inspired air and resulting reduced PO2 2) We can consider that PO2 in the inspired air is constant 100 mm hg with little variation between inspiration and expiration (thats because there is always some volume of air remain in alveoli even after forceful expiration called residual volume) 3) Air entering alveoli has very little PCO2 and when mixes with air present in alveoli from previous expiration, which has high PCO2, the resultant PCO2 is 40 mm hg constantly Partial pressures of gases in pulmonary capillaries: 1) Blood coming through venous system from body tissues will be pumped to lungs and pass through pulmonary capillaries. 2) This venous blood has low PO2 because the tissues used the O2 for energy production. So the PO2 in pulmonary blood is low (40 mm hg), and PCO2 is high (46 mm hg) 3) The capillaries come surrounding alveoli, gas exchange will occur from high to low partial pressure and trying to equilibrate 4) Blood leaving pulmonary capillaries has the same PO2 values for alveoli like PO2 is 100 mm hg and PCO 2 is 40 mm hg and this blood will return to heart to be pumped to body tissues 5) Blood coming to capillaries at tissue level will equilibrate with tissue gases which have PO2 40 mm hg and PCO2 46 mm hg, and thus it will deliver O2 to tissues and take CO2 from them and the blood leaving tissues will have PO2 40 mm hg and PCO2 46 mm hg
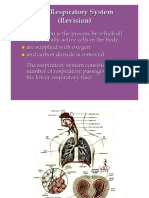
Mixed venous blood
By the time the blood reaches the pulmonary artery in the right side of the heart, all venous blood has "mixed" with venous systemic system and venous blood of the heart from coronary sinus drainage into the right atrium. Mixed venous oxygen saturation (SvO2) is the percentage of oxygen bound to hemoglobin in blood returning to the right side of the heart. It is the amount of oxygen "left over" after the tissues extracted oxygen. It is used to help us to recognize when a patient's body is extracting more oxygen than normally. An increase in extraction is the bodies way to meet tissue oxygen needs when the amount of oxygen reaching the tissues is less than needed. Caution :There is often little to no correlation between SvO2 and SaO2, PaO2, CO or Hgb, esp. in critically ill patients. The only consistent clinical correlation is the one between SvO2 and O2 ER. Therefore, SvO2 reflects the amount of O2 consumed (demand) by the body tissues
Normal SvO2 ranges from 60-80%. Low SvO2 is an indication of increased oxygen consumption or extraction by tissues. It can also indicate impaired oxygen delivery such as cardiogenic shock. In septic states, the SvO2 may actually be elevated, because tissues cannot effectively extract oxygen from hemoglobin.
What does it tell us? Mixed venous oxygen saturation (SvO2) can help to determine whether the cardiac output and oxygen delivery is high enough to meet a patient's needs.
There are 4 fundamental causes for a drop in SvO2: 1. The cardiac output is not high enough to meet tissue oxygen needs 2. The Hb is too low 3. The SaO2 is too low 4. The oxygen consumption has increased without an increase in oxgyen delivery
Compensation :
ATP (energy) is needed for all cell function and survival. Tissues require oxygen in order to make ATP ( amount of oxygen being received by the tissues falls below the amount of oxygen required (because of need, or decreased supply), the body attempts to compensate as follows: First Compensation: Cardiac Output increases
The cardiac output is increased in an effort to increase the amount of oxygen being delivered to the tissu below.
Oxygen Delivery is the amount of oxygen being sent to the tissues, and is determined by the foll
ATP (energy) is needed for all cell function and survival. Tissues require oxygen in order to make ATP (energy). If the amount of oxygen being received by the tissues falls below the amount of oxygen required (because of an increased need, or decreased supply), the body attempts to compensate as follows: First Compensation: Cardiac Output increases The cardiac output is increased in an effort to increase the amount of oxygen being delivered to the tissues as shown below. Oxygen Delivery is the amount of oxygen being sent to the tissues, and is determined by the following: Oxygen Delivery (DO2) = Cardiac Output (HR X Stroke Volume) X Oxygen Content (Hb X SaO2) If this is not sufficient to meet tissue energy needs, we move to our second compensation. Second Compensation: Tissue oxygen extraction increases. Tissues begin to remove or extract a higher percentage of oxygen from the arterial blood. This results in a reduced amount of oxygen remaining in the blood as it returns to the right side of the heart (decreased SvO2).
If this is not sufficient to meet tissue energy needs, we move to our second compensation.
Third Compensation: Anaerobic Metabolism iIncreases If the tissues fail to receive an adequate supply of oxygen, anaerobic metabolism becomes the only mechanism to produce tissue ATP. Anaerobic metabolism is inefficient, producing a large amount of metabolic waste (e.g. lactic acid) that is difficult for the body to eliminate quickly. It also produces a relatively poor supply of ATP. Prolonged anaerobic metabolism leads to energy depletion and metabolic acidosis. In hypovolemic shock, cardiac output will decrease, and become unable to keep up with the rate of oxygen uptake by the tissue, which further increase the "oxygen consumption/cariac output" figure, increaseing venous oxygen content. While in septic shock oxygen cosumption (tissue extraction) is impaired, and cardiac output is initially high, making the venous oxygen content high, much like the Artervenous shunts you have talked about.. that's why I saw it frequently in questions about septic shock.
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- The Physiology of Oxygen Delivery: DR Rob Law, DR H BukwirwaDokument4 SeitenThe Physiology of Oxygen Delivery: DR Rob Law, DR H BukwirwaPrabhakar KumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Layout DR KUN 2 RevDokument6 SeitenLayout DR KUN 2 RevM.Firwan KhalidNoch keine Bewertungen
- General Physiology II - Transport of Oxygen & Carbon - SIUST, College of DentistryDokument7 SeitenGeneral Physiology II - Transport of Oxygen & Carbon - SIUST, College of DentistryNoor Al-Deen MaherNoch keine Bewertungen
- Edubriefs in CCTC: Svo (Mixed Venous Oxygen Saturation) or Scvo Central Venous Oxygen Saturation)Dokument3 SeitenEdubriefs in CCTC: Svo (Mixed Venous Oxygen Saturation) or Scvo Central Venous Oxygen Saturation)l1o2stNoch keine Bewertungen
- Oxygen and Carbon Dioxide Transport - PPTX JONELTADokument32 SeitenOxygen and Carbon Dioxide Transport - PPTX JONELTArithikaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Respira SiDokument47 SeitenRespira SiIkbal NurNoch keine Bewertungen
- Respiratory System/4: Ventilation Perfusion RateDokument28 SeitenRespiratory System/4: Ventilation Perfusion RateMohammad AlomariNoch keine Bewertungen
- About Pulse OximetryDokument16 SeitenAbout Pulse OximetrySrdjan DimitrijevicNoch keine Bewertungen
- Oxygen Delivery UpdateDokument6 SeitenOxygen Delivery UpdateRahman Mukti AjiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Biology Chapter 7Dokument18 SeitenBiology Chapter 7edain84Noch keine Bewertungen
- 11.17 Breathing and Exchanges of GasesDokument7 Seiten11.17 Breathing and Exchanges of GasesMoonesh MKNoch keine Bewertungen
- Answer Discussion Share: (A) Inspiratory Reserve Volume (IRV) Expiratory Reserve Volume (ERV)Dokument8 SeitenAnswer Discussion Share: (A) Inspiratory Reserve Volume (IRV) Expiratory Reserve Volume (ERV)gopeabhijit85Noch keine Bewertungen
- Respiratory System Physiology PDFDokument121 SeitenRespiratory System Physiology PDFVizhiNoch keine Bewertungen
- CH 17Dokument20 SeitenCH 17Maria BoccaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ncert Solution Breathing and Exchange of GasesDokument10 SeitenNcert Solution Breathing and Exchange of GasesAyush DuttaNoch keine Bewertungen
- O2 CascadeDokument6 SeitenO2 CascadeBharath NarasimhaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Introduction To Blood: PlasmaDokument7 SeitenIntroduction To Blood: Plasmaعبدالحكيم النهديNoch keine Bewertungen
- Breathing and Exchange of GasesDokument5 SeitenBreathing and Exchange of Gasessonu kumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Part 1: Critical Thinking: A. Arterial Blood Gas Analysis Is Commonly Used Diagnostic Tool To Evaluate The PartialDokument4 SeitenPart 1: Critical Thinking: A. Arterial Blood Gas Analysis Is Commonly Used Diagnostic Tool To Evaluate The PartialJewel BerbanoNoch keine Bewertungen
- List Major Muscles Involved in Respiration (Inspiration and Expiration) at Rest and During ExerciseDokument5 SeitenList Major Muscles Involved in Respiration (Inspiration and Expiration) at Rest and During ExerciseEmMa DHieyahNoch keine Bewertungen
- Altitude Physiology: PRESENTED BY Dick WilliamsDokument52 SeitenAltitude Physiology: PRESENTED BY Dick WilliamsDeepak ArkalgudNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ards and RF FileDokument12 SeitenArds and RF FileEdwin Delos Reyes Abu100% (1)
- 9572 (21) 00068-X/fulltext: GuidelinesDokument53 Seiten9572 (21) 00068-X/fulltext: GuidelinesRehoboth BandaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Transport of Respiratory GasesDokument27 SeitenTransport of Respiratory GasesSyahmi Ieskandar100% (1)
- Goljan - Audio TranscriptsDokument296 SeitenGoljan - Audio TranscriptsGurbir Singh Gill90% (30)
- Oxygen TherapyDokument34 SeitenOxygen Therapysarahsheikh28100% (5)
- FON oxygenationPPTDokument58 SeitenFON oxygenationPPTSaeed khanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Internal RespirationDokument9 SeitenInternal RespirationRhose ReyesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Post Lab Question Experiment 6, 7, 8 (Farah)Dokument3 SeitenPost Lab Question Experiment 6, 7, 8 (Farah)Skefadiuto100% (2)
- Gas Exchange L2Dokument21 SeitenGas Exchange L2delicata.benNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lecture 7 (Gasses & Pressure)Dokument9 SeitenLecture 7 (Gasses & Pressure)Άγγελος ΧαβέλαςNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mechanism of Respiration, Fermentation and ChemoheterothropDokument59 SeitenMechanism of Respiration, Fermentation and Chemoheterothropd25Noch keine Bewertungen
- Rispiratory System & Circulatory SystemDokument23 SeitenRispiratory System & Circulatory Systemapi-19753215Noch keine Bewertungen
- Exercise Physiology NotesDokument41 SeitenExercise Physiology Notesstarlight9394100% (1)
- What Is The Oxygen CascadeDokument27 SeitenWhat Is The Oxygen CascadeRandhir Singh90% (10)
- Ventilation: Describe Alveolar and Pulmonary VentilationDokument6 SeitenVentilation: Describe Alveolar and Pulmonary VentilationNorrifhan Akmal IsmailNoch keine Bewertungen
- Respiration: Human Respiratory SystemDokument4 SeitenRespiration: Human Respiratory SystemSheehan MathurNoch keine Bewertungen
- Oxygen CascadeDokument2 SeitenOxygen CascadelovefifteenNoch keine Bewertungen
- Abstrak: 1 - Fakultas Kedokteran UKRIDA - Blok 7: Respiratory 1Dokument9 SeitenAbstrak: 1 - Fakultas Kedokteran UKRIDA - Blok 7: Respiratory 1TreitzNoch keine Bewertungen
- Educational ProgramsDokument28 SeitenEducational ProgramsEsha KuttiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Breathing and Exchange of GasesDokument8 SeitenBreathing and Exchange of GasesArnav DeshpandeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Respiration Physiology SEQs With KeyDokument12 SeitenRespiration Physiology SEQs With KeyMudassar Roomi100% (1)
- 224392278 BMAT Biology Revision Notesรรร PDFDokument9 Seiten224392278 BMAT Biology Revision Notesรรร PDFB. ChillNoch keine Bewertungen
- SPM Notes On Chapter RespirationDokument18 SeitenSPM Notes On Chapter RespirationSyamila YusofNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pulmonary Presentation MERGEDDokument20 SeitenPulmonary Presentation MERGEDShubha DiwakarNoch keine Bewertungen
- How Much Energy Is in Our Food ?: RespirationDokument4 SeitenHow Much Energy Is in Our Food ?: RespirationnestinarkaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 05 RespiratoryDokument38 Seiten05 Respiratoryglenn johnstonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Respiratory System Structure and FunctionDokument6 SeitenRespiratory System Structure and FunctionRavi BhollahNoch keine Bewertungen
- Basic Respiratory Mechanics (DR Arif)Dokument36 SeitenBasic Respiratory Mechanics (DR Arif)Rizqi Luqmanul HakimNoch keine Bewertungen
- Oxygen CascadeDokument12 SeitenOxygen Cascadehy3pjb1984Noch keine Bewertungen
- Reflection Respiratory SystemDokument4 SeitenReflection Respiratory SystemAin Sufiza0% (1)
- BMAT Biology Revision NotesDokument9 SeitenBMAT Biology Revision Notesmissymar123100% (5)
- Bio 3 InternalsDokument16 SeitenBio 3 InternalsROHAN T ANoch keine Bewertungen
- CapnografiaDokument19 SeitenCapnografiaJunior BarbozaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 11 Respiratory SystemDokument19 Seiten11 Respiratory SystemSenthereng MoaisiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Respi PhysiologyDokument55 SeitenRespi Physiologymutthineni.sushma28Noch keine Bewertungen
- 2.-Oxygen Therapy and Toxicity - Paper L. MuñozDokument16 Seiten2.-Oxygen Therapy and Toxicity - Paper L. MuñozchascokillNoch keine Bewertungen
- BIOMEDIC SCIENCES (Kardiovaskular)Dokument2 SeitenBIOMEDIC SCIENCES (Kardiovaskular)Yusuf Rifaldi lawiraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Respiratory Monitoring in Mechanical Ventilation: Techniques and ApplicationsVon EverandRespiratory Monitoring in Mechanical Ventilation: Techniques and ApplicationsJian-Xin ZhouNoch keine Bewertungen
- Menstrual Cycle and Fertility by Neville Mvo NgumDokument7 SeitenMenstrual Cycle and Fertility by Neville Mvo Ngumlovelyc95Noch keine Bewertungen
- Embryo For Real CycleDokument31 SeitenEmbryo For Real Cyclelovelyc95Noch keine Bewertungen
- Hobden Antibiotics II 09Dokument12 SeitenHobden Antibiotics II 09lovelyc95Noch keine Bewertungen
- Anatomy of The Intercostal SpaceDokument17 SeitenAnatomy of The Intercostal Spacelovelyc95Noch keine Bewertungen
- Make Your Self ClearDokument5 SeitenMake Your Self Clearlovelyc95Noch keine Bewertungen
- CHAPT 05 Intestinal AbsorptionDokument14 SeitenCHAPT 05 Intestinal Absorptionlovelyc95Noch keine Bewertungen
- Anatomy of The Intercostal SpaceDokument17 SeitenAnatomy of The Intercostal Spacelovelyc95Noch keine Bewertungen
- Anatomy Midterm Study GuideDokument53 SeitenAnatomy Midterm Study Guidelovelyc95Noch keine Bewertungen
- Your Fearless Leaders:: SSN Anatomy #2Dokument10 SeitenYour Fearless Leaders:: SSN Anatomy #2lovelyc95Noch keine Bewertungen
- Review Quiz - Chapter 16: Head & Neck: C. Laryngeal CarcinomaDokument4 SeitenReview Quiz - Chapter 16: Head & Neck: C. Laryngeal Carcinomalovelyc95Noch keine Bewertungen
- Anatomy: Important Vessels and Source of BleedingDokument87 SeitenAnatomy: Important Vessels and Source of Bleedinglovelyc95Noch keine Bewertungen
- Anatomy of The Intercostal SpaceDokument17 SeitenAnatomy of The Intercostal Spacelovelyc95Noch keine Bewertungen
- Cell Signaling Objectives - SanchezDokument14 SeitenCell Signaling Objectives - Sanchezlovelyc95Noch keine Bewertungen
- ObgynDokument1 SeiteObgynlovelyc95Noch keine Bewertungen
- Amino AcidDokument33 SeitenAmino Acidlovelyc95100% (1)
- Fayat Activity Report 2020 - en - Page by Page - Low Resolution - 0Dokument44 SeitenFayat Activity Report 2020 - en - Page by Page - Low Resolution - 0arlyNoch keine Bewertungen
- TM 9 4935 601 14 3&PDokument137 SeitenTM 9 4935 601 14 3&Pkhaerul jannahNoch keine Bewertungen
- Magnetic Float Level Switch - KleevDokument2 SeitenMagnetic Float Level Switch - KleevRAMZI ALJILANYNoch keine Bewertungen
- CAT 323 DL 2013 LeafletDokument20 SeitenCAT 323 DL 2013 LeafletLuka BornaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Differential Gear MechanismDokument32 SeitenDifferential Gear MechanismMohammad Amir100% (2)
- Expt 8.7 Finding The Formula of Copper OxideDokument2 SeitenExpt 8.7 Finding The Formula of Copper OxideIra Munirah0% (2)
- 1.diesel Engine AssemblyDokument22 Seiten1.diesel Engine Assemblypepenapao1217Noch keine Bewertungen
- UL Cyber ParkDokument9 SeitenUL Cyber ParkGeet RangNoch keine Bewertungen
- IEEE Power and Energy Magazine Volume 9 Issue 3 2011 (Doi 10.1109/mpe.2011.940579) Katiraei, K.F. Agüero, J.R. - Solar PV Integration ChallengesDokument10 SeitenIEEE Power and Energy Magazine Volume 9 Issue 3 2011 (Doi 10.1109/mpe.2011.940579) Katiraei, K.F. Agüero, J.R. - Solar PV Integration Challengesjagadeeshkumar116100% (1)
- Ponchon Savarit MethodDokument34 SeitenPonchon Savarit Methodppga410100% (7)
- Ist 50 Smartletloose One 1x00 EngDokument2 SeitenIst 50 Smartletloose One 1x00 EngMihai MecaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Electrical All Sizing CalculationDokument123 SeitenElectrical All Sizing Calculationvijaydev7594% (18)
- mayada5977 مهمDokument7 Seitenmayada5977 مهمAmmar Al-KindyNoch keine Bewertungen
- 22661-Sample-Question-Paper (Msbte Study Resources) PDFDokument4 Seiten22661-Sample-Question-Paper (Msbte Study Resources) PDFAmit Ghade100% (2)
- ELL-332 Electric Drives Lecture 3: Different Types of Load TorquesDokument25 SeitenELL-332 Electric Drives Lecture 3: Different Types of Load TorquesNikhil KumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Detailed CalculationsDokument14 SeitenDetailed CalculationsrozNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1 Home Base Work March 19-MRCH 31Dokument3 Seiten1 Home Base Work March 19-MRCH 31Celso AmotoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Xmt350cccvauto Line (Le073174)Dokument150 SeitenXmt350cccvauto Line (Le073174)Jose Arcesio Betancourt Trujillo100% (1)
- Matbal 001H Flowsheet CycloHexaneDokument29 SeitenMatbal 001H Flowsheet CycloHexaneRizky AnugrahNoch keine Bewertungen
- Large Field Refrigeration System-USMC Technical ManualDokument228 SeitenLarge Field Refrigeration System-USMC Technical ManualbusybusybusyNoch keine Bewertungen
- HO2 Sensor InfoDokument24 SeitenHO2 Sensor InfoÇağrı SivrikayaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Esm-48100u2 v100r022c91 User ManualDokument49 SeitenEsm-48100u2 v100r022c91 User ManualBiniVincentNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lincoln Vantage 300 CaracterísticasDokument8 SeitenLincoln Vantage 300 CaracterísticasJean MunozNoch keine Bewertungen
- Essay Synoptic e Book PDFDokument64 SeitenEssay Synoptic e Book PDFChandrasekaran SubramaniamNoch keine Bewertungen
- Insulation CoordinationDokument75 SeitenInsulation CoordinationDundi Kumar BevaraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Asme Ea-3-2009 (R2019)Dokument23 SeitenAsme Ea-3-2009 (R2019)Jesus Rodriguez100% (1)
- What Is A Gripper? Why Use One?: GrippersDokument4 SeitenWhat Is A Gripper? Why Use One?: Gripperssagarsinghal26Noch keine Bewertungen
- TALAT Lecture 1253: CreepDokument26 SeitenTALAT Lecture 1253: CreepCORE Materials100% (1)
- Sunlight Battery 12V 12ahDokument1 SeiteSunlight Battery 12V 12ahCarolyn MunozNoch keine Bewertungen
- Miller 652 and 812 Owners Manualo278aj - MilDokument44 SeitenMiller 652 and 812 Owners Manualo278aj - MilrobertoarellanocastiNoch keine Bewertungen