Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
East West University: Department of Electrical and Electronic Engineering
Hochgeladen von
Md Asif HossainOriginaltitel
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
East West University: Department of Electrical and Electronic Engineering
Hochgeladen von
Md Asif HossainCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
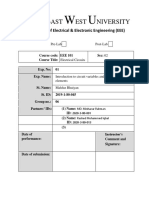
EAST WEST UNIVERSITY
DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRICAL AND ELECTRONIC ENGINEERING
Course No Section No Group No
: EEE 101 : 04 : 03
Experiment No
: 01
Experiment Name : Introduction to circuit variables and elements
Date of Performance : 26.01.2011 Date of Submission : 02.02.2011
Students Name : MD.ASIF HOSSAIN Students ID : 2011-1-80-081
Introduction to circuit variables and elements
OBJECTIVE :
Current and voltage are the two basic variables in an electric circuit, they are not sufficient by themselves. Power is defined as the rate of energy dissipation. An element is the basic building block of a circuit. An electric circuit is simply an interconnection of the elements. Circuit analysis is the process of determining voltage across the elements of the circuit.
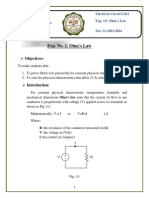
CIRCUIT DIAGRAMS :
(a)
(b)
Figure : Diagrams for a series circuit (a) and a parallel circuit (b). Experimental Data :
Table 1 : Measured values of resistors.
R1 (Ohm) 46
R2 (Ohm) 98
R3 (Ohm) 98
R4 (Ohm) 219
Table 2 : Measured voltages and currents for the circuit of figure(a).
Vs (V) 2.5
VR1 (V) 0.782
VR2 (V) 1.66
I (mA) 17
Table 3 : Measured voltages and currents for the circuit of figure(b).
Vs (V) 2.5
V (V) 2.5
I1 (mA) 25.5
I2 (mA) 11.4
Answer to Report Questions : 1 . Submitted the experimental datasheet. 2 . RS=R1+R2
=46+98 =144 VS=IRS I = VS/RS = 2.5/144 = 0.017 V1 = IR1 = 0.017 X 46 = 0.782 V2 = IR2 = 0.017 X 98 = 1.66
For circuit (b) We know, 1/RP = 1/R3 + 1/R4 = 1/98 + 1/219 RP = 67.72 I1 = VS/R3 = 2.5/98 = 25.5 mA I2 = VS/R4 = 2.5/219 = 11.4 mA
3 . Compare the calculated values with the measured values : Calculated Values V1 = 0.799 V V2 = 1.70 V V = 2.5 V I = 17 mA I1 = 25 mA I2 = 11.4 mA Measured Values V1 = 0.782 V2 = 1.66 V = 2.5 I = 17 mA I1 = 25.5 mA I1 = 11.4 mA
There are no differences with the measured and calculated values. So the measured and the calculated values are equal.
4 . R1 = V1/I = 0.798/0.017 = 46.94 (Ohm)
R2 = V2/I = 1.66/0.017 = 97.64 (Ohm) R3 = Vs/I1 = 2.5/0.025 = 98 (Ohm) R4 = VS/I2 = 2.5/0.0114 = 219 (Ohm) Comments : The measured and the calculated value R1 and R2 are equal. Also R3 and R4 are equal.
5 . The ammeter in the circuit with series and the voltmeter in the circuit with parallel. The
ammeter and voltmeter has two scales, one is 100 to 1000 and another is 30 to 300. If we take reading 100 scale then we divided 1000/100 = 10 and if we take reading 30 scale then we divided 300/30 = 3.
Conclusion :
We see that there are two circuits. One circuit is connected in series and other is connected in parallel. We can learn how to flow current and voltage in the circuit and we also learn to take reading with ammeter and voltmeter. We are able to take value with resistance. We apply in the experiment ohms law to calculate.
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- A Guide to Electronic Maintenance and RepairsVon EverandA Guide to Electronic Maintenance and RepairsBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (7)
- EEE 101 Lab Explores Circuit VariablesDokument6 SeitenEEE 101 Lab Explores Circuit VariablesMANS Packaging EnterpriseNoch keine Bewertungen
- Experimental report LC1 THÂN NGỌC SƠN 20195813Dokument24 SeitenExperimental report LC1 THÂN NGỌC SƠN 20195813Hoàng SơnNoch keine Bewertungen
- Abing Jesbel EE-387 Final Report E1Dokument9 SeitenAbing Jesbel EE-387 Final Report E1Jesbel AbingNoch keine Bewertungen
- Circuits ReportDokument6 SeitenCircuits ReportsarahpotpotNoch keine Bewertungen
- EE Lab Analyzes Linear and Non-Linear ComponentsDokument15 SeitenEE Lab Analyzes Linear and Non-Linear ComponentsMagdalena SimicNoch keine Bewertungen
- EE131.1 LabDokument40 SeitenEE131.1 LabMarc MontillaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Experiment 3 Duran ZanderDokument8 SeitenExperiment 3 Duran ZanderFreos VinciNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lab 2Dokument6 SeitenLab 2HAMM3TNoch keine Bewertungen
- Verify Kirchhoff's Laws Using DC CircuitsDokument30 SeitenVerify Kirchhoff's Laws Using DC CircuitsJigar SoniNoch keine Bewertungen
- EE204 LabDokument37 SeitenEE204 LabKrishnaveni Subramani SNoch keine Bewertungen
- PHY CourseworkDokument8 SeitenPHY CourseworkLIANG HUI YI MoeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Example of Lab ReportDokument6 SeitenExample of Lab ReportRomi Necq S. AbuelNoch keine Bewertungen
- BE.01.08 Series Resistive Circuits SHDokument12 SeitenBE.01.08 Series Resistive Circuits SHleslynjdNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lab1 - Manuel AbadieDokument6 SeitenLab1 - Manuel AbadieManuel AbadieNoch keine Bewertungen
- Electrical Circuits and Kirchhoff's RulesDokument6 SeitenElectrical Circuits and Kirchhoff's RulesKaye RamosNoch keine Bewertungen
- Physics Investigatory ProjectDokument15 SeitenPhysics Investigatory ProjectPranav JagtianiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Experiment 1Dokument3 SeitenExperiment 1rastgonikoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Activity 5 SimulinkDokument19 SeitenActivity 5 Simulinkjanana marieNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ohm's Law Lab: Current Varies Linearly with VoltageDokument4 SeitenOhm's Law Lab: Current Varies Linearly with Voltageeve zzNoch keine Bewertungen
- Verify Ohm's Law ExperimentDokument5 SeitenVerify Ohm's Law ExperimentHajer JejeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Experiment 2Dokument5 SeitenExperiment 2Benedict DiwaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Electrical Circuit Lab Report 1Dokument12 SeitenElectrical Circuit Lab Report 1IzaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Kota Damansara Lab Report on Kirchhoff's LawDokument9 SeitenKota Damansara Lab Report on Kirchhoff's LawmajedNoch keine Bewertungen
- Applied Physics LabDokument59 SeitenApplied Physics LabEngr Waqas MalikNoch keine Bewertungen
- Engineering Practice Lab ElectricalDokument23 SeitenEngineering Practice Lab ElectricalKrishna Moorthy50% (2)
- WWW Universityquestions inDokument63 SeitenWWW Universityquestions inRajgir Raj100% (1)
- MAXWELL'S MESH EQUATIONS EXPERIMENTDokument5 SeitenMAXWELL'S MESH EQUATIONS EXPERIMENTairaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2 - OhmsLawDokument8 Seiten2 - OhmsLawawab.hassan.eng23Noch keine Bewertungen
- Superposition Theorem Lab ReportDokument7 SeitenSuperposition Theorem Lab ReportElbashir ElaminNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lab #1 (ELE)Dokument14 SeitenLab #1 (ELE)RoyceNoch keine Bewertungen
- CKT LabManual 21-22Dokument11 SeitenCKT LabManual 21-22Anirban MandalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Laboratory Work No 7 - MananganDokument10 SeitenLaboratory Work No 7 - MananganJaypee PascualNoch keine Bewertungen
- A Simplified LigDokument6 SeitenA Simplified Ligqais652002Noch keine Bewertungen
- Electrical Circuits Lab EE 213Dokument10 SeitenElectrical Circuits Lab EE 213Ahmed QanahNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lab Report 1Dokument9 SeitenLab Report 1Hajer JejeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Electrical EngineeringDokument190 SeitenElectrical EngineeringAmol ShrivastavaNoch keine Bewertungen
- ENGR2200 Lab Manual Lab2Dokument12 SeitenENGR2200 Lab Manual Lab2Sure TipsNoch keine Bewertungen
- DC-Lab Report 02Dokument10 SeitenDC-Lab Report 02Shahriar Ahsan JohaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Eee1001-Electric Circuits and Systems Lab AssesmentDokument19 SeitenEee1001-Electric Circuits and Systems Lab AssesmentÀnuràg Sîngh.Noch keine Bewertungen
- Lab Report 1Dokument9 SeitenLab Report 1Moad AbusninaNoch keine Bewertungen
- ACT-1 Answer EM-1Dokument8 SeitenACT-1 Answer EM-1Aegee Cedrick ManicaoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Phy150 Lab 3 DC Circuit (Sabah)Dokument28 SeitenPhy150 Lab 3 DC Circuit (Sabah)Izz002Noch keine Bewertungen
- Equivalent Resistance Delta - Wye Transformation: Experiment # 4Dokument12 SeitenEquivalent Resistance Delta - Wye Transformation: Experiment # 4John Phillip Lopez MasagcaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lab Report For CSE 109: East West UniversityDokument6 SeitenLab Report For CSE 109: East West UniversityDaudKhanNoch keine Bewertungen
- EEN01a-L EXPERIMENT NO.4 - Online (ME)Dokument14 SeitenEEN01a-L EXPERIMENT NO.4 - Online (ME)Elizabeth De GalaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ohms Law and Kirchhoffs Law Lab ReportDokument8 SeitenOhms Law and Kirchhoffs Law Lab Reportlove to readNoch keine Bewertungen
- Experiment No. 1 Kirchhoff'S Law I. ObjectivesDokument6 SeitenExperiment No. 1 Kirchhoff'S Law I. ObjectivesKzenetteNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lab 1Dokument5 SeitenLab 1javelNoch keine Bewertungen
- Presentation On EEE 2122Dokument37 SeitenPresentation On EEE 2122shafiulNoch keine Bewertungen
- LCA Lab1Dokument13 SeitenLCA Lab1Rizwan HanifNoch keine Bewertungen
- Series and Parallel DC CircuitsDokument8 SeitenSeries and Parallel DC CircuitsFrobles120% (1)
- Experiment #5: Parallel CircuitsDokument7 SeitenExperiment #5: Parallel CircuitsJustine G. ViñasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Experiment No Experiment Name ObjectiveDokument12 SeitenExperiment No Experiment Name ObjectiveZareen Rashid ChoudhuryNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lab Report 3.0Dokument8 SeitenLab Report 3.0Mesake Manumalo TofingaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Eec 115 Practical - Electrical EngineeringDokument35 SeitenEec 115 Practical - Electrical EngineeringVietHungCao89% (9)
- EXPERIMENT 3 F This ShitDokument3 SeitenEXPERIMENT 3 F This ShitatenhyunaeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lab 8 Kirchhoffs Laws - College-Physics-2Dokument6 SeitenLab 8 Kirchhoffs Laws - College-Physics-2Thom Ashley Shappit GanironNoch keine Bewertungen
- Prelab Louise Tang Shi Yuan CE210002 Ts. Wan Nur Hafsha Binti Wan KhairuddinDokument11 SeitenPrelab Louise Tang Shi Yuan CE210002 Ts. Wan Nur Hafsha Binti Wan KhairuddindharwinNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mae156b Ethics LectureDokument49 SeitenMae156b Ethics LectureMd Asif HossainNoch keine Bewertungen
- Basic Bank FinalDokument15 SeitenBasic Bank FinalMd Asif HossainNoch keine Bewertungen
- FB Ads Targeting SampleDokument2 SeitenFB Ads Targeting SampleMd Asif HossainNoch keine Bewertungen
- SBL Rec So o Oc Wirtten Passed PDFDokument12 SeitenSBL Rec So o Oc Wirtten Passed PDFtitas31Noch keine Bewertungen
- East West University: EngineeringDokument6 SeitenEast West University: EngineeringMd Asif HossainNoch keine Bewertungen
- NSPE Code of EthicsDokument2 SeitenNSPE Code of EthicsRizka WidyariniNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mid Solutions 2010Dokument6 SeitenMid Solutions 2010Md Asif HossainNoch keine Bewertungen
- NSPE Code of EthicsDokument2 SeitenNSPE Code of EthicsRizka WidyariniNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lecture 2bDokument7 SeitenLecture 2bMd Asif HossainNoch keine Bewertungen
- Exercise 1Dokument2 SeitenExercise 1Md Asif HossainNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lecture Eee DesignDokument14 SeitenLecture Eee DesignMd Asif HossainNoch keine Bewertungen
- Scan0003Dokument1 SeiteScan0003Leka AmuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Transformer Nameplate ParametersDokument1 SeiteTransformer Nameplate ParametersMd Asif HossainNoch keine Bewertungen
- Electronics Exercise 2: The 555 Timer and It's Applications: ObjectiveDokument5 SeitenElectronics Exercise 2: The 555 Timer and It's Applications: ObjectiveMichael AjayiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Exercise 1Dokument2 SeitenExercise 1Md Asif HossainNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sta102 StemDokument2 SeitenSta102 StemMd Asif HossainNoch keine Bewertungen
- Corporate Finance FormulasDokument3 SeitenCorporate Finance FormulasMustafa Yavuzcan83% (12)
- Fundamentals of Electronics, Book - 1 PDFDokument319 SeitenFundamentals of Electronics, Book - 1 PDFjramongv83% (12)
- Fan7930b 92897Dokument23 SeitenFan7930b 92897VinhNoch keine Bewertungen
- Products t1 Brochure TrioDokument8 SeitenProducts t1 Brochure TrioAhmed El-ShafeiNoch keine Bewertungen
- CH 07 Solutions Practice ProblemsDokument4 SeitenCH 07 Solutions Practice ProblemsChris RosasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Prog Controller Wiring SystemsDokument208 SeitenProg Controller Wiring SystemsKyle StackNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pixtend v1 3 Datasheet ENDokument74 SeitenPixtend v1 3 Datasheet ENOldGeekNoch keine Bewertungen
- DX DiagDokument34 SeitenDX DiagjNoch keine Bewertungen
- Design and Simulation of 80 KHZ High Frequency Converter Using CD 4047IC CMOSDokument6 SeitenDesign and Simulation of 80 KHZ High Frequency Converter Using CD 4047IC CMOSEditor IJTSRD100% (1)
- DC Circuits Class Test Ratio Resistances Series ParallelDokument1 SeiteDC Circuits Class Test Ratio Resistances Series ParallelShinde JayakrishnaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Wireless World 1948 12Dokument78 SeitenWireless World 1948 12Jan PranNoch keine Bewertungen
- Title: Model Ut601: Operating ManualDokument26 SeitenTitle: Model Ut601: Operating ManualScott TylerNoch keine Bewertungen
- LAN TopologiesDokument31 SeitenLAN TopologiesDinku Minda100% (1)
- Tando 700 Brochure EnuDokument8 SeitenTando 700 Brochure Enu159753Noch keine Bewertungen
- IR Audio Product GuideDokument8 SeitenIR Audio Product Guidejean grangeonNoch keine Bewertungen
- S1 Uvr2Dokument1 SeiteS1 Uvr2Sindhu PandreNoch keine Bewertungen
- Review On SIW TechnologyDokument6 SeitenReview On SIW TechnologyNitinNoch keine Bewertungen
- Folheto s7300 eDokument16 SeitenFolheto s7300 eHector GANoch keine Bewertungen
- Hanstar SMD 'Hot Air' Rework StationsDokument5 SeitenHanstar SMD 'Hot Air' Rework StationsFerdinand EstanislaoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Acn CSDokument4 SeitenAcn CSLeo100% (1)
- Lab Gruppen FP 10000q User GuideDokument31 SeitenLab Gruppen FP 10000q User GuideHari SemprulNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bp308 Installation Manual GBDokument154 SeitenBp308 Installation Manual GBReynold SuarezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Two approaches for control unit designDokument48 SeitenTwo approaches for control unit designhub23Noch keine Bewertungen
- Power Amplifiers for Proportional Electro-Hydraulic ControlsDokument23 SeitenPower Amplifiers for Proportional Electro-Hydraulic ControlsNguyen Van ChungNoch keine Bewertungen
- ONGAKU Manual SmallerDokument15 SeitenONGAKU Manual SmallerEsteban BikicNoch keine Bewertungen
- Datasheet - X-DA4125EN With 24 VDC - EN2.5Dokument2 SeitenDatasheet - X-DA4125EN With 24 VDC - EN2.5Walid DerradjiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Data Sheet: Mcu For DSLDokument49 SeitenData Sheet: Mcu For DSLradioscribdNoch keine Bewertungen
- PCA9511A: 1. General DescriptionDokument24 SeitenPCA9511A: 1. General DescriptionGuilherme Ribeiro BarbosaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Driver Backlight PSP 2000Dokument12 SeitenDriver Backlight PSP 2000Jhonny GuillermoNoch keine Bewertungen
- LTC135 DS en V04Dokument2 SeitenLTC135 DS en V04Nirmal mehtaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Intel Interview QuestionsDokument3 SeitenIntel Interview QuestionsgfhdNoch keine Bewertungen