Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
1 Basic Concepts of Chemistry and Laws Structure of Atom Periodic Law Periodic System o
Hochgeladen von
anon_533839304Originalbeschreibung:
Originaltitel
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
1 Basic Concepts of Chemistry and Laws Structure of Atom Periodic Law Periodic System o
Hochgeladen von
anon_533839304Copyright:
Verfügbare Formate
ATOM and ITS STRUCTURE
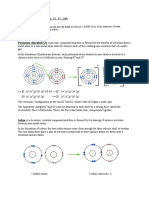
Atom has basically two parts, nucleus and electrons. Nucleus is located in the center of atom and electrons are rotating around nucleus with high speed. 2. Subatomic Particles Today it is well known that atoms have subatomic particles, called protons, neutrons and electrons. Protons are positively charged particles found in the nucleus of an atom, and denoted by p. Neutrons are neutral particles found in the nucleus of an atom, and denoted by n. Electrons are negatively charged particles placed around the nucleus of an atom, and shown by e . Protons and neutrons almost have the same masses, but electrons have negligible mass with respect to protons and neutrons. Neutral atoms have the equal number of protons and electrons. Electrons are rotating in certain places called orbit, energy level or shell. Energy levels are represented by letters, K, L, M, N, Oetc, or numbers, 1, 2, 3, 4, etc. Each shell can hold a certain number of electrons calculated by the equation of 2n2 where n refers to number of shell. The electrons located in the outermost shell of atoms are called valance electrons. st 2 In the 1 shell, No. of e = 2x1 = 2e nd 2 In the 2 shell, No. of e = 2x2 = 8e rd 2 In the 3 shell, No. of e = 2x3 = 18e th 2 In the 4 shell, No. of e = 2x4 = 32e Example 1 Show the electron configuration of 6C and 13Al atoms. Solution 6C: 2) 4) 13Al: 2) 8) 3) 3. Isotopes Isotope atoms have the same number of protons but different number of neutrons. Example 2 Example 3
atoms are isotones. Each have 16 neutrons but 15 and 16 protons respectively. Isotone atoms are completely different atoms, they have different chemical and physical characteristics. 4. Ions Electrically charged atoms are called ions. When an atom loses electrons it becomes positively charged ion, called cation. When an atom gains electrons it becomes negatively charged ion, called anion. Charge of an atom, q , can be found with q = p - e.
Example 4 Find the charge and ion type of atom. Atom Fe Al O P Cl Solution Atom Fe Al Proton 26 13 8 15 17 Electron 24 10 10 15 18 Charge +2 +3 -2 0 -1 Ion Cation Cation Anion Neutral Anion Proton 26 13 8 15 17 Electron 24 10 10 15 18 Charge Ion
atoms are isotopes. All they have 6 protons but 6, 7 and 8 neutrons respectively. They have similar chemical properties but different physical properties. Isotones, atoms with the same number of neutrons, but different numbers of protons.
O P Cl
Example 5 +1 +2 +3 +4 Li , Ca , Al , Pb are cations. -1 -2 -3 F , O , P are anions.
Solution +2 = p 28 p = 30 A = 30 + 35 A = 65 Example 8 +3 Cr ion has 21 electrons and its atomic mass number is 52. What is the number of neutrons for Cr ? Solution 3 = p 21 p = 24 52 = 24 + n n = 28 THE PERIODIC TABLE Introduction Dmitri Mendeleev is the father of periodic table. He arranged elements in a table according to atomic masses. He discovered many elements and left blank spaces for the undiscovered ones. Henry Moseley solved the puzzle of periodic table after the discovery of noble gases. He arranged elements in his table according to atomic numbers. After his study the modern periodic table appeared. It is arranged according to increasing atomic numbers. Horizontal rows are called periods. There are 7 periods beginning with a metal and ending with a noble gas. Vertical columns are called groups or family. There are 8A and 8B groups. The group 8B contains 3 columns. A groups are called main or representative groups. And B groups are called transition metals. The periodic table and Electron configuration The elements which have almost similar chemical and physical properties are put in the same groups. They have similar electron configurations as well. Valance electron configurations of the elements in the same group are the same. Their physical properties gradually change. Periods There are seven periods of which three are short, two are medium, and two are long. In the first period there are 2 elements, both of them are gases. He is inert and put among noble gases. Groups There are two types of groups, A and B. 1A and 2A groups belong to s-block. 3A, 4A, 5A, 6A, 7A, and 8A groups belong to p-block. The elements of group B belong to d-block, transition metals.
5. The Atomic Terminology 1. Atomic Number, Z Atomic number = Number of Protons Each type of atom has different number of protons. For a neutral atom, Atomic number = Number of protons = Number of electrons Z=p=e 2. Atomic Mass Number, A Atomic mass number = Number of Protons + Number of Neutrons A=p+n Example 6 Fill in the blanks in the table below. Atom Ti Al S Br Solution Atom Ti Al S Br p 22 13 16 35 n 26 14 16 45 Z 22 13 16 35 A 48 27 31 80 16 p 22 14 16 45 35 n Z A 48 27
Example 7 What is the number of protons and atomic mass number of Zn.
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Von EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Bewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (121)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryVon EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (231)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceVon EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (588)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaVon EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (266)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItVon EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (838)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerVon EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (271)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingVon EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (400)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeVon EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (5794)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyVon EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (2259)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeVon EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (537)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreVon EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (1090)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersVon EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (344)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnVon EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (234)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesVon EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (821)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceVon EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (895)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaVon EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (45)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureVon EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (474)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealVon EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (74)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Von EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Bewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (98)
- Water For Injection-By AnamDokument20 SeitenWater For Injection-By AnamMuhammad Bilal TahirNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cathodic Protection Design Using ImpressDokument80 SeitenCathodic Protection Design Using ImpressAyub Yaakob100% (1)
- NMAT Mock Exam For ChemDokument16 SeitenNMAT Mock Exam For ChemMDreamer100% (2)
- Science9 q2 Mod3 Formation of Ions v.2Dokument32 SeitenScience9 q2 Mod3 Formation of Ions v.2Kristine Ibarreta-Jazul50% (2)
- 42 - Extensive Feedwater Quality Control and Monitoring Concept For Preventing Chemistry-Related Failures of Boiler Tubes in A Subcritical Thermal Power PlantDokument12 Seiten42 - Extensive Feedwater Quality Control and Monitoring Concept For Preventing Chemistry-Related Failures of Boiler Tubes in A Subcritical Thermal Power PlantBehnam RamouzehNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fiitjee: Topic: Periodic Phase - I Class: Xi (Chemistry) PropertiesDokument4 SeitenFiitjee: Topic: Periodic Phase - I Class: Xi (Chemistry) PropertiesSudhanshu JhaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Types of Intermolecular ForcesDokument7 SeitenTypes of Intermolecular ForcesRhenczell Angela VelascoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Xiao CHM4130L Lab Manual 2013-1Dokument35 SeitenXiao CHM4130L Lab Manual 2013-1visa1032Noch keine Bewertungen
- 4 Impact of OilDokument21 Seiten4 Impact of OilkayNoch keine Bewertungen
- Faculty Selection Test Chemistry: Pre-Foundation Sample PaperDokument7 SeitenFaculty Selection Test Chemistry: Pre-Foundation Sample PaperRam Ji PandeyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chemical Bonding Graphic Organizer RubricDokument1 SeiteChemical Bonding Graphic Organizer Rubricapi-439932199100% (1)
- HW1Dokument5 SeitenHW1Nathan YangNoch keine Bewertungen
- SNC1W Final Exam Review Package 5Dokument21 SeitenSNC1W Final Exam Review Package 5Jaismeen CheemaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Science ExperimentDokument12 SeitenScience Experiment4c945f8kd2Noch keine Bewertungen
- WiFi in Schools Nov 2011 Andrew Goldsworthy A 1Dokument1 SeiteWiFi in Schools Nov 2011 Andrew Goldsworthy A 1odhiseoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Downstream Processing AssignmentDokument9 SeitenDownstream Processing AssignmentPalak AgarwalNoch keine Bewertungen
- 396-1558-2-RV (1) NewDokument19 Seiten396-1558-2-RV (1) NewMe MeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Compressld: Points To RememberDokument8 SeitenCompressld: Points To RememberAnjali PanigrahiNoch keine Bewertungen
- ChemitryDokument44 SeitenChemitrygiridharrajuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sulfur CycleDokument6 SeitenSulfur CycleJoel Santilices BulawanNoch keine Bewertungen
- CBSE QUESTION BANK D and F Block ElementsDokument2 SeitenCBSE QUESTION BANK D and F Block ElementsVishnuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Atomic Structure WorksheetsDokument5 SeitenAtomic Structure WorksheetsYến Nhi LêNoch keine Bewertungen
- Year 10 Chemistry Revision Schedule BookletDokument8 SeitenYear 10 Chemistry Revision Schedule BookletDermot ChuckNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bonding and StructuresDokument10 SeitenBonding and StructuresFatema KhatunNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cape Chemistry, 2016, U1, P2, Q#4Dokument4 SeitenCape Chemistry, 2016, U1, P2, Q#4Mariah BissoonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Gen Chem 2 q3 Module 1a Properties of Matter and Intermolecular Forces of AttractionDokument23 SeitenGen Chem 2 q3 Module 1a Properties of Matter and Intermolecular Forces of AttractionMarian Margarette PegaridoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cole-Parmer Ammonia Gas-Sensing Electrode Instruction Manual General InstructionsDokument23 SeitenCole-Parmer Ammonia Gas-Sensing Electrode Instruction Manual General InstructionsHương PhạmNoch keine Bewertungen
- Carbon and Its Compounds One Shot GYAANI KEEDA PDFDokument34 SeitenCarbon and Its Compounds One Shot GYAANI KEEDA PDFFakeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chemistry Second YearDokument31 SeitenChemistry Second YearMalik Mohammad AsifNoch keine Bewertungen
- Kertas2 PPT T4 - Soalan SMSSIDokument18 SeitenKertas2 PPT T4 - Soalan SMSSINurliana Roslan0% (1)