Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Selenoid Valves
Hochgeladen von
Mohsin ShahOriginalbeschreibung:
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Selenoid Valves
Hochgeladen von
Mohsin ShahCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
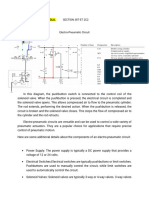
SOLENOID VALVES:
A valve is a mechanical device for controlling the flow of a fluid or a substance. A solenoid valve is an electromagnetic valve for use with liquid or gas controlled by running or stopping an electrical current through a solenoid, which is a coil of wire, thus changing the state of the valve.
PRINCIPLE OF WORKING:
The operation of a solenoid valve is similar to that of a light switch, but typically controls the flow of air or water, whereas a light switch typically controls the flow of electricity. A solenoid valve has two main parts: the solenoid and the valve. The solenoid converts electrical energy into mechanical energy which, in turn, opens or closes the valve mechanically. Solenoid valves may use metal seals or rubber seals, and may also have electrical interfaces to allow for easy control. A spring may be used to hold the valve opened or closed while the valve is not activated When current flows in the coil, magnetic field is generated and it reduces the air gap. Generally spring is used to create gap when coil is not energized. Small signal can operate solenoids. Large back emf is generated when coil is switched off. Diode is used to suppress the back emf and it prevents the control electronics from damage.
VALVE WORKING:
CLASSIFICATION OF SELENOID VALVES:
Types of Solenoid Valves: Solenoid valves may have two or more ports: in the case of a two-port valve the flow is switched on or off; in the case of a three-port valve, the outflow is switched between the two outlet ports. Multiple solenoid valves can be placed together on a manifold. A two-way valve has two ports. When power is applied, the pressure flows from one port to the other. With pressure off, the flow ceases.
A three-way valve has three ports. When power is on, one of the ports is connected to the common port, and pressure flows through to extend the pneumatic cylinder. When power is off, the other port is connected to the common port, and pressure is exhausted to reset the cylinder This is the pneumatic equivalent of a single-pole single-throw electrical switch.
A four-way valve has four ports. With power on, one set of ports is connected straight through to the other set of ports. With power off, the connection is reversed.
If a valve has more ports than you need, you can plug them up to get a lesser configuration. A four-way valve can act as a three-way by plugging one of the ports.
A three-way valve can act as a two-way by plugging one of the ports.
SELECTION CRITERIA FOR SELENOID VALVES:
Coil voltage, current, AC or DC, and intermittent versus continuous duty. Valve type Aperture size Pressure rating, such as "50 PSI" Materials (medium) that it can control, such as "air/water" Type of connection to each port, such as "1/4" NPT".
APPLICATIONS:
Solenoid valves are also used in industry to control the flow of all sorts of fluids. A common use for 2 way solenoid valves is in central heating. These are controlled by an electrical signal from the thermostat to regulate the flow of heated water from a heat pump to the in room radiators. Such valves are particularly useful when multiple heating zones are driven by a single heat pump.
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Automatic Rapping SystemDokument8 SeitenAutomatic Rapping SystemAnonymous j0aO95fgNoch keine Bewertungen
- Discrete Control ElementsDokument44 SeitenDiscrete Control ElementswaqasahmadzNoch keine Bewertungen
- Solenoid ValveDokument3 SeitenSolenoid ValveSaravanapriya Karthik0% (1)
- Objective: Apparatus:: Solenoid ValveDokument4 SeitenObjective: Apparatus:: Solenoid ValveAbid HameedNoch keine Bewertungen
- Klent - Solenoid PrintDokument6 SeitenKlent - Solenoid PrintRich Samuel AlmazarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Solenoid Valve - How They Work: Normally Open Normally ClosedDokument7 SeitenSolenoid Valve - How They Work: Normally Open Normally Closedmuhammad aliNoch keine Bewertungen
- SolenoidDokument4 SeitenSolenoidVivekanandhan Porselvan100% (1)
- Solenoid Switching Using TransistorDokument6 SeitenSolenoid Switching Using TransistorZaid MustafaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Solenoid Valve: From Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaDokument3 SeitenSolenoid Valve: From Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaNatrajj SivakumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Solenoid Valve TypesDokument6 SeitenSolenoid Valve Typeschdi0% (1)
- Act8 InstrumentationDokument4 SeitenAct8 InstrumentationErvin MedranoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Report About Motorized and Solenoid ValvesDokument7 SeitenReport About Motorized and Solenoid ValvesMøhåmëd Êl Kñäwý UwkNoch keine Bewertungen
- What Is Solenoid Valve and Its Types With PDFDokument8 SeitenWhat Is Solenoid Valve and Its Types With PDFpntnhan21thNoch keine Bewertungen
- Solenoid ValveDokument5 SeitenSolenoid ValvetkaneeshNoch keine Bewertungen
- Electromechanical Valve Liquid Gas Electric Current SolenoidDokument3 SeitenElectromechanical Valve Liquid Gas Electric Current SolenoidAjay KaundalNoch keine Bewertungen
- MarusujufawoDokument3 SeitenMarusujufawonileshnk2000Noch keine Bewertungen
- Electromechanically Valve Electric Current SolenoidDokument11 SeitenElectromechanically Valve Electric Current SolenoidLoga NathanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hassan SalahDokument10 SeitenHassan SalahAsst. Prof. Dr. Ahmed Hameed KaleelNoch keine Bewertungen
- Water QuatDokument36 SeitenWater QuatHrishi PhulsundarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Solenoid OperationDokument3 SeitenSolenoid Operationchamara kumarasingheNoch keine Bewertungen
- Details About HardwareDokument4 SeitenDetails About Hardwaredhirajsingh_avitNoch keine Bewertungen
- A Solenoid Valve Is An Electromechanical Valve For Use With Liquid or GasDokument3 SeitenA Solenoid Valve Is An Electromechanical Valve For Use With Liquid or GasNaresh KumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Different Types of Solenoid ValvesDokument2 SeitenDifferent Types of Solenoid ValvesJe MaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Electromechanically Valve Electric Current Solenoid Manifold FluidicsDokument1 SeiteElectromechanically Valve Electric Current Solenoid Manifold FluidicsArunkumar SudhakaranNoch keine Bewertungen
- Directional Control ValveDokument6 SeitenDirectional Control Valvevishnu kumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- What Are Solenoid Valves?Dokument1 SeiteWhat Are Solenoid Valves?uetian729Noch keine Bewertungen
- Module 4Dokument67 SeitenModule 4Achsah K VijuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Directional Control Valves Fall Into One of Two CategoriesDokument0 SeitenDirectional Control Valves Fall Into One of Two CategoriessprotkarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hydraulic Control ValvesDokument22 SeitenHydraulic Control ValvesUdayanka Madushan100% (2)
- GEVEROLA - Electro-Pneumatic CircuitDokument2 SeitenGEVEROLA - Electro-Pneumatic Circuitbirdsflying193Noch keine Bewertungen
- Unit 4 Study MaterialDokument11 SeitenUnit 4 Study MaterialDishaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Electro Hydraulicsystem 131229110325 Phpapp02Dokument47 SeitenElectro Hydraulicsystem 131229110325 Phpapp02mangyan100% (1)
- Chapter 4 Control ValveDokument91 SeitenChapter 4 Control ValveNebiyou KorraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Guidelines For Selecting Valves Guidelines For SelectingDokument5 SeitenGuidelines For Selecting Valves Guidelines For Selectingebbys89Noch keine Bewertungen
- ValvesDokument76 SeitenValvesN NandiniNoch keine Bewertungen
- Final Control Element - Hassan ElBanhawiDokument1 SeiteFinal Control Element - Hassan ElBanhawijesus_manrique2753Noch keine Bewertungen
- Valve Selection GuideDokument5 SeitenValve Selection Guiderajeshn1100% (1)
- Control ValvesDokument11 SeitenControl ValvesKrushnasamy SuramaniyanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lesson 6. Directional Control ValvesDokument18 SeitenLesson 6. Directional Control ValvesYunah VelosoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Electro Hydraulic System Components and Their OperationDokument3 SeitenElectro Hydraulic System Components and Their OperationAtul NarkhedeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pneumatic Control ValvesDokument2 SeitenPneumatic Control ValvesMuhammad Attiq Ur RahmanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Control Valve (Actuator)Dokument31 SeitenControl Valve (Actuator)Junior7100% (1)
- Electro PneumaticsDokument51 SeitenElectro Pneumaticshansanadesilva098Noch keine Bewertungen
- Valve SelectionDokument8 SeitenValve SelectionShreya Sahajpal KaushalNoch keine Bewertungen
- 3-2-Way Pneumatic ValveDokument6 Seiten3-2-Way Pneumatic ValveĐặng Trung AnhNoch keine Bewertungen
- Discrete Control ElementDokument13 SeitenDiscrete Control Elementjovanarga66Noch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 4Dokument46 SeitenChapter 4Thành CôngNoch keine Bewertungen
- Unit 3 Control Components in Hydraulic SystemDokument16 SeitenUnit 3 Control Components in Hydraulic SystemAbhishek KumbalurNoch keine Bewertungen
- Control Components in Hydraulic SystemDokument68 SeitenControl Components in Hydraulic SystemYashwanth Mg100% (1)
- Principle Design Solenoid ValvesDokument28 SeitenPrinciple Design Solenoid Valveshassan alrokabNoch keine Bewertungen
- Control Valve ActuatorsDokument31 SeitenControl Valve ActuatorsMuhammad ImtiazNoch keine Bewertungen
- Proportional ValvesDokument7 SeitenProportional ValvesSummer AshleyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Control ValveDokument31 SeitenControl ValveMohammed AhmedNoch keine Bewertungen
- Prevention of Actuator Emissions in the Oil and Gas IndustryVon EverandPrevention of Actuator Emissions in the Oil and Gas IndustryNoch keine Bewertungen
- PNEUMATICS AND AIR CIRCUITS UNDERSTANDING THE CASCADE VALVE AND PLC UNDERSTANDINGVon EverandPNEUMATICS AND AIR CIRCUITS UNDERSTANDING THE CASCADE VALVE AND PLC UNDERSTANDINGNoch keine Bewertungen
- A Guide to the Home Electric System: Home Guide Basics Series, #2Von EverandA Guide to the Home Electric System: Home Guide Basics Series, #2Noch keine Bewertungen
- Antiblock AgentsDokument3 SeitenAntiblock AgentsMohsin ShahNoch keine Bewertungen
- Environmental Stress Crack Resistance of PEDokument6 SeitenEnvironmental Stress Crack Resistance of PEMohsin ShahNoch keine Bewertungen
- RIFT Technique For Composite FabricationDokument15 SeitenRIFT Technique For Composite FabricationMohsin ShahNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sajjad CVDokument1 SeiteSajjad CVMohsin ShahNoch keine Bewertungen
- Comp Amp Turbine COURS 9001EDokument27 SeitenComp Amp Turbine COURS 9001Enabil160874100% (1)
- Typical Guest House Solar SolutionDokument1 SeiteTypical Guest House Solar Solutionpeter LamurenNoch keine Bewertungen
- Clean Energy Handbook For Financial Service InstitutionDokument227 SeitenClean Energy Handbook For Financial Service Institutionhannyjberchmans-1Noch keine Bewertungen
- Class 5 EVS Chapter 13 Amazing EnergyDokument5 SeitenClass 5 EVS Chapter 13 Amazing EnergyragharikaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Wind Energy Systems ClassificationsDokument16 SeitenWind Energy Systems ClassificationsSubheesh KTNoch keine Bewertungen
- Natural ResourceDokument2 SeitenNatural ResourceYuli Macias VivancoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Thermal Power Plant Simulator TPP 200 Laboratory Exercise Tutorial N1: Rolling Up of Turbine Train and Connection of Generator To The GridDokument13 SeitenThermal Power Plant Simulator TPP 200 Laboratory Exercise Tutorial N1: Rolling Up of Turbine Train and Connection of Generator To The GridPriyajit SahooNoch keine Bewertungen
- A Practical Study For New Design of Essential OilsDokument17 SeitenA Practical Study For New Design of Essential OilsEmmanuel PlazaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Test 3 - Advanced Word Form 1: Wouldn't Want To Do Anything To Displease HimDokument2 SeitenTest 3 - Advanced Word Form 1: Wouldn't Want To Do Anything To Displease Him32Nguyễn Ngọc Nguyên Nhung9A4Noch keine Bewertungen
- Hassyan Energy Hassyan Gas Power Plant IPP Phase 1 2 Dubai - Profile - 070222Dokument17 SeitenHassyan Energy Hassyan Gas Power Plant IPP Phase 1 2 Dubai - Profile - 070222salman Khan100% (1)
- Francis AssignmentDokument21 SeitenFrancis AssignmentAlok YadavNoch keine Bewertungen
- Solar Irradiance Monitoring in Solar Energy ProjectsDokument8 SeitenSolar Irradiance Monitoring in Solar Energy ProjectsAlfan AlfrsyNoch keine Bewertungen
- AAC BlocksDokument20 SeitenAAC BlocksJithesh DharmadasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Answer Key Physical ScienceDokument8 SeitenAnswer Key Physical ScienceFrancis Ho HoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mek Motor BMP KMDokument8 SeitenMek Motor BMP KMVenkatarama KrishnanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Overpressure Protection and Relief Valves: Process Training School 2004/5Dokument62 SeitenOverpressure Protection and Relief Valves: Process Training School 2004/5Ekundayo JohnNoch keine Bewertungen
- 01 Variable LoadDokument11 Seiten01 Variable LoadPaul CamuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Shasi DR StoryDokument6 SeitenShasi DR Storyapi-3723321Noch keine Bewertungen
- Portable Gensets Honda ProductsDokument20 SeitenPortable Gensets Honda ProductsRajan KumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Presentation-3 - Exp - Flex Options - Tech WS - 181114 - V4Dokument65 SeitenPresentation-3 - Exp - Flex Options - Tech WS - 181114 - V4Juniko ParhusipNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cisco CSR ReviewDokument4 SeitenCisco CSR ReviewVikram JeetNoch keine Bewertungen
- HTTPDokument5 SeitenHTTPJorge VillagomezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Modelling and Control of Large WindDokument122 SeitenModelling and Control of Large WindAjay SinghNoch keine Bewertungen
- Question Bank All Units With VTU Old Questions With Front PageDokument11 SeitenQuestion Bank All Units With VTU Old Questions With Front PageHareesha N GNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ds Datasheet Erhard Twin Air Air Valves enDokument7 SeitenDs Datasheet Erhard Twin Air Air Valves enthawdarNoch keine Bewertungen
- APS1005 Problem Data-SetV3Dokument6 SeitenAPS1005 Problem Data-SetV3daveix3Noch keine Bewertungen
- Steam CondenserDokument53 SeitenSteam CondenserGeorge Markas100% (1)
- Bladeless WindmillDokument22 SeitenBladeless WindmillSudarsan reddyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Rajasthan Solar Energy Policy 2019Dokument46 SeitenRajasthan Solar Energy Policy 2019V S MITTALNoch keine Bewertungen
- Solar Policy GoaDokument13 SeitenSolar Policy Goajim mehtaNoch keine Bewertungen