Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Capitalism
Hochgeladen von
amarsinha1987Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Capitalism
Hochgeladen von
amarsinha1987Copyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Capitalism Capitalism is a particular way of organizing the economic activities of a society.
It can be defined in two dimension: 1) Nature of its class relation
Class relation Worker Capitalist
Controlled and owned Producer of means production
2) Central Mechanism of the economic Coordination It is a provide free market It is a mode of production in which capital in its various forms is the principal means of production Characteristics of Capitalism: Production for market rather own use The separation of the producer from his means of production The concentration of the means of production in the hands of one class, the bourgeoisie Labour power is too commodity, it is sold or brought and mode of exchange is money in form of the wage Limited barter system Capitalist is controller of everything such as means of production process, choose of technique, quality of output and input, working condition, deciding wage, the arrangement for selling and buying of the output. Capitalism- increase competition-forced to capitalist to adopt new technique and improved machinery-reduce cost of production and accumulation of wealth in one hand Technical progress is most essential feature of the capitalism Capitalism- The division of labour-specialization of the task of productivityunprecedented growth of output and productivity- development and growth Incentive of profit-main driving force With increasing desire for profit, the demand for labour was rising tremendously with the result that the merchant capitalists were hiring more and more workers. The final product as well as the entire profit was appropriated by the capitalist.
Capital: Capital is an asset which can generate an income flow for its owner. It could be Merchandise, sum of money any other money carrying interest Capitalist Society: The production of capital predominates, and dominates every other sort of production
Feudal Framework Work was generally done in the homes of the producers and not under the factory shades of modern industries Not full-scale machines, but simple tools were used for manufacturing. And many a times these factors of production were owned by the workers themselves. factors of production were limited, manufacturing was also on a much smaller scale as compared to goods produced in factories One man, i.e., the merchant entrepreneur, controlled the whole process from start to finish
Transition from feudalism to Capitalism Exchange relation or external trade demolished the feudal mode of production Inner contradiction like exploitation of the peasants by nobles Unproductive use of the economic surplus like expenditure on war and labour were responsible for breakdown of the feudalism Demographic Factors Commerce and capital accumulated to be crucial link between risk of capitalism and decline of feudalism.
Mercantilism In the 17th century, Europe was under the influence of a set of economic ideas and practice known as Mercantilism. State controlled economy policy with aim to regulating trade and commerce as well as its factories and manufacturer with the primary purpose of ultimately to concentrate and wield political power by building fleets, equipping army etc. Characteristics: The state policy should be formulated in such manner that the state should get maximum share of trade Precious metals (Gold and Silver) Desirable form of the national wealth, if nation did not possess it, the chief way to get them was trade.
In order to accumulate precious metals, the government should ensure favorable balance of trade (Export> Import) To preserve and increase this balance, higher tariff should be imposed on the manufactured good, low tariff should be imposed on cheap raw material and bounties should be given on export. The state should take all possible efforts to promote export such as state run workshop, regulating guild etc. Colonies could prove to be useful for export market of manufacturing good and as source of supply of raw materials and if possible precious metals. If necessary, war must be waged against economic rivalry for acquisition and protection of the colonies. Negative Impact of Capitalism in our Society
1) Human Suffering Exploitation Negative social externalities of technologies Technology changes- Key ways for capitalist to increase productivity Make skill of worker obsolete and demand for new skill Profit maximizing competition Low wages- For reduction of production cost- concentration of wealth in one hand While capitalism is an engine of growth, it is also inherent generate poverty, deprivation and marginalization. Recommendation: Capitalist economy-Material growth in one hand. So we need creation of the some sort of counter capitalism institution capable of neutralizing the destructive impact of capitalism 2) Inequality Material Inequality and flourishing Inequalities in access to interesting and challenging work Destructive competition
3) Curtailment of Individual freedom and autonomy The relations of domination within capitalist workplaces constitute pervasive restrictions on individual autonomy and self-direction. At the core of the institution of private property is the power of owners to decide how their property is to be used.
4) violates liberal egalitarian principles of social justice
Capitalism Capitalist Opportunity of their Children proletariate
Oppertunity of their Children
Children of the both classes do not have equal opportunity. The children of capitalist can access better education, Health, development etc. while in the proletariat, they can not
Violate the principle of equal opportunity for all
5) Inefficient in crucial respects Public goods: Under production of the public goods Many public goods are important for quality of life and economic productivity. It is not wise to rely on market to produce them Under pricing for natural resources: Capitalism- profit motivated-Means to make all possible efforts to reduce production cost- It leads to underpricing of natural resources because the value of natural resources are not registered Negative Externalities: Capitalism-promote industrialization and with profit motivated- indiscriminate use of the natural resources- excessive pollution and scarcity of sustainable resources because of uncontrolled use of resources
6) Environmentally destructive Capitalist firms face competitive pressures to reduce costs, and externalizing those costs on the environment is a good strategy of doing this. This pressure cannot be countered by the market itself; it requires some form of non-capitalist intervention either by the state or by organized social forces
Natural resources are systematically underpriced in the market since their value to people in the future is not registered in the dynamics of supply and demand in the present 7) Capitalist commodification threatens important values Commodification of the certain things are seen by most people as monstrous violation of moral value of Human being For instances: Commodification of Babies (production and adoption of Babies) Slavery Market at which you are allow yourself to sell voluntary into slavery Commodification of the body parts and its organs Commodification of children care 8) Corrode community Community is a social unit within which people are concerned for the well-being of other people and feel solidarity and obligations towards others. Capitalism, as a system of organizing economic activity, has an intensely contradictory relation to community as a way of organizing social cooperation. 9) Capitalism limit democracy Exclusion of democratic bodies from control over the allocation of investments The inability of democratic bodies to control the movement of capital undermines the ability of democracy to set collective priorities over even those activities which capitalist firms themselves do not directly organize Positive impact of Capitalism 1) Economic effects: Increase production Increase export Become prominent industrial power in the world Growth of urbanization Capital formation
2) Social Effect: The renaissance strengthened the middle class values; but the middle class could not exhibit its power in the society for long time. The industrial revolution unfolded the power of the middle class
3) Political Effect: Various laws were enacted in order to protect the interest of both worker and manufacturer. E.g. Factory act-decided working hour minimum wage and other things by Dipak Patel
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- CapitalDokument10 SeitenCapitalSamantha Dela Cruz0% (1)
- Introduction of Economic SystemDokument11 SeitenIntroduction of Economic SystemPruthviraj Rathore100% (1)
- Capitalism Vs Socialism PDFDokument14 SeitenCapitalism Vs Socialism PDFMohandas PeriyasamyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Biotechnology Regulatory Authority of India BillDokument5 SeitenBiotechnology Regulatory Authority of India Billamarsinha1987Noch keine Bewertungen
- Term Sheet EquityDokument8 SeitenTerm Sheet EquitygargramNoch keine Bewertungen
- National Income and Economic System: by Dr. Forum DaveDokument42 SeitenNational Income and Economic System: by Dr. Forum DaveVatsal ChangoiwalaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ethical Issues in Capitalism and MarketDokument16 SeitenEthical Issues in Capitalism and MarketAashu AroraNoch keine Bewertungen
- What Are The Features and Merits of SocialismDokument8 SeitenWhat Are The Features and Merits of SocialismViral Modi100% (1)
- Profit Motive:: (3) Price MechanismDokument15 SeitenProfit Motive:: (3) Price MechanismSshivam AnandNoch keine Bewertungen
- CHAPTER 1 Unit 2 - BASIC PROBLEMS OF AN ECONOMY AND ROLE OF PRICE MECHANISMDokument8 SeitenCHAPTER 1 Unit 2 - BASIC PROBLEMS OF AN ECONOMY AND ROLE OF PRICE MECHANISMIJAZ AHAMED S 2212053Noch keine Bewertungen
- Module 3 - Economic Systems - v1Dokument22 SeitenModule 3 - Economic Systems - v1divyansh srivastavaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Economic SystemDokument11 SeitenEconomic SystemAjithkumar kuttappanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Capitalism 1Dokument2 SeitenCapitalism 1manoramatiwary827Noch keine Bewertungen
- Notes On CapitalismDokument12 SeitenNotes On Capitalismshanayub496Noch keine Bewertungen
- General Growth ModelDokument24 SeitenGeneral Growth ModelNar Carlo Corpuz ArpilledaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Notes On EconomicsDokument13 SeitenNotes On EconomicsJello De CastroNoch keine Bewertungen
- Government, Market and Industrial Policy in Emerging EconomiesDokument35 SeitenGovernment, Market and Industrial Policy in Emerging Economieshearthelord66Noch keine Bewertungen
- COMPLETE NOTES Business Envt UNIT IIDokument26 SeitenCOMPLETE NOTES Business Envt UNIT IIAyush LohiyaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Indian Economy 1950-1990Dokument9 SeitenIndian Economy 1950-1990Tarun VermaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Economics ReportDokument5 SeitenEconomics ReportgamedeziphozekhetheloNoch keine Bewertungen
- Comparative Economic SystemsDokument22 SeitenComparative Economic SystemsArun WadhawanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Macroeconomics Definitions ReviewerDokument6 SeitenMacroeconomics Definitions ReviewerArizza NocumNoch keine Bewertungen
- UNIT I-MG2452-Engineering Economics and Financial Accounting NotesDokument18 SeitenUNIT I-MG2452-Engineering Economics and Financial Accounting NotesMohammed AsifNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lecture Notes in Economics With LRT PrelimsDokument5 SeitenLecture Notes in Economics With LRT PrelimsArvin DecastroNoch keine Bewertungen
- UNIT I-MG2452-Engineering Economics and Financial Accounting NotesDokument18 SeitenUNIT I-MG2452-Engineering Economics and Financial Accounting Notesanon_331279695100% (1)
- Economic Systems: CapitalismDokument7 SeitenEconomic Systems: CapitalismNajeeb khanNoch keine Bewertungen
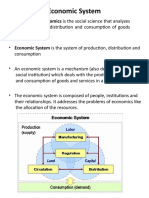
- Economic System: Economic System Is The System of Production, DistributionDokument23 SeitenEconomic System: Economic System Is The System of Production, DistributionPooja SheoranNoch keine Bewertungen
- Capitalism: Max Weber & Karl MarxDokument83 SeitenCapitalism: Max Weber & Karl MarxTania KochetkovaNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Economic Systems HandoutDokument7 SeitenThe Economic Systems Handoutbed_bugNoch keine Bewertungen
- Class 3 Adam Smith and The Wealth of Nations 28012021Dokument26 SeitenClass 3 Adam Smith and The Wealth of Nations 28012021Ngân Hải PhíNoch keine Bewertungen
- Economic WorksheetDokument5 SeitenEconomic WorksheetAhmed GmNoch keine Bewertungen
- CEP Chapter 2 To 5Dokument49 SeitenCEP Chapter 2 To 5Juliana Mae FabrigarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Summary - Chap 2Dokument3 SeitenSummary - Chap 2Nhan Trinh NgocNoch keine Bewertungen
- Section 1 D, E, F, GDokument26 SeitenSection 1 D, E, F, Gtaona madanhireNoch keine Bewertungen
- What Is Capitalism?: Free Markets May Not Be Perfect But They Are Probably The Best Way To Organize An EconomyDokument2 SeitenWhat Is Capitalism?: Free Markets May Not Be Perfect But They Are Probably The Best Way To Organize An EconomyNoNameUNINoch keine Bewertungen
- Economic System: Mr. Rohit Kumar Vishwakarma Asst. Professor UIMDokument14 SeitenEconomic System: Mr. Rohit Kumar Vishwakarma Asst. Professor UIMPrachi BharadwajNoch keine Bewertungen
- Business EthicsDokument27 SeitenBusiness EthicsSehrish HabibNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter1 5Dokument27 SeitenChapter1 5Arya ChatautNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lesson 2 ONLINEDokument10 SeitenLesson 2 ONLINEFrancis Dave Nagum Mabborang IINoch keine Bewertungen
- (Economics) : Managing Within The Dynamic Business Environment: Taking Risks and Making ProfitsDokument42 Seiten(Economics) : Managing Within The Dynamic Business Environment: Taking Risks and Making ProfitsRafayet Omar ShuvoNoch keine Bewertungen
- 7.) Chapter 2 (How Economic Issues Affect Business)Dokument7 Seiten7.) Chapter 2 (How Economic Issues Affect Business)John AustinNoch keine Bewertungen
- Features of Capitalist EconomyDokument51 SeitenFeatures of Capitalist EconomyAmit ParasramkaNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Growth of CapitalismDokument6 SeitenThe Growth of CapitalismSAMADHAN KAKADENoch keine Bewertungen
- The Political Economy: PS 215, Global Issues - MHCCDokument25 SeitenThe Political Economy: PS 215, Global Issues - MHCCAzmaine SanjanNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Economy and WorkDokument24 SeitenThe Economy and WorkmoatlhodiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Principles of FairnessDokument7 SeitenPrinciples of FairnessAli Longasa CortezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Assignment On The History of Economic SystemsDokument3 SeitenAssignment On The History of Economic SystemsLove BirdNoch keine Bewertungen
- Topic 4 - The Nature of Capitalism (Week 2)Dokument10 SeitenTopic 4 - The Nature of Capitalism (Week 2)Pei JuanNoch keine Bewertungen
- BMO2004 L1 & L2 Week 3 Capitalism and Socialism Students'Dokument26 SeitenBMO2004 L1 & L2 Week 3 Capitalism and Socialism Students'annesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tutorial 4Dokument5 SeitenTutorial 4seee CelinaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Economics1 114333Dokument7 SeitenEconomics1 114333ITACHI UCHIHANoch keine Bewertungen
- CAPITALISMDokument9 SeitenCAPITALISMHimanshu DarganNoch keine Bewertungen
- Macroeconomics Week 3Dokument9 SeitenMacroeconomics Week 3Mhavs CasimiroNoch keine Bewertungen
- Definitions of EconomyDokument10 SeitenDefinitions of EconomyAyush KumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Capitalism. 1Dokument3 SeitenCapitalism. 1Tom JarryNoch keine Bewertungen
- Economics Notes - Introduction To EconomicsDokument16 SeitenEconomics Notes - Introduction To Economicskkesarwani727Noch keine Bewertungen
- Capitalism, Socialism, and Mixed Economy-Ppt-1Dokument24 SeitenCapitalism, Socialism, and Mixed Economy-Ppt-1nandini swami100% (1)
- Capitalism: Why Is It Bad?: I. AbstractDokument4 SeitenCapitalism: Why Is It Bad?: I. Abstractdot dotNoch keine Bewertungen
- MIXED ECO Final FDDokument26 SeitenMIXED ECO Final FDRishi SehgalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Summary Of "Thesis About The Theory Of The State" By Claus Offe: UNIVERSITY SUMMARIESVon EverandSummary Of "Thesis About The Theory Of The State" By Claus Offe: UNIVERSITY SUMMARIESNoch keine Bewertungen
- Indian Art & Culture - IAS 51 Rank (Nitin Singhaniya) - 5Dokument30 SeitenIndian Art & Culture - IAS 51 Rank (Nitin Singhaniya) - 5amarsinha1987Noch keine Bewertungen
- Indian Art & Culture - IAS 51 Rank (Nitin Singhaniya) - 2Dokument30 SeitenIndian Art & Culture - IAS 51 Rank (Nitin Singhaniya) - 2amarsinha1987Noch keine Bewertungen
- Indian Art & Culture - IAS 51 Rank (Nitin Singhaniya) - 1Dokument30 SeitenIndian Art & Culture - IAS 51 Rank (Nitin Singhaniya) - 1amarsinha1987100% (3)
- Indian Art & Culture - IAS 51 Rank (Nitin Singhaniya) - 4Dokument30 SeitenIndian Art & Culture - IAS 51 Rank (Nitin Singhaniya) - 4amarsinha1987Noch keine Bewertungen
- Indo China Relations Aditya RavichandranDokument27 SeitenIndo China Relations Aditya Ravichandranamarsinha1987100% (1)
- Iran Is Important in Geopolitical Balance-NehaDokument4 SeitenIran Is Important in Geopolitical Balance-Nehaamarsinha1987Noch keine Bewertungen
- Indian Art & Culture - IAS 51 Rank (Nitin Singhaniya) 6 PDFDokument28 SeitenIndian Art & Culture - IAS 51 Rank (Nitin Singhaniya) 6 PDFelcmas.saeculaNoch keine Bewertungen
- AptitudeDokument14 SeitenAptitudeamarsinha1987Noch keine Bewertungen
- FRBM ActDokument2 SeitenFRBM Actrajesh_scribd1984Noch keine Bewertungen
- Natarajar Temple Case Explained - Yuva RajDokument4 SeitenNatarajar Temple Case Explained - Yuva Rajamarsinha1987Noch keine Bewertungen
- Astronomy-Sphere of Influence, Mars Mission, OrbitDokument16 SeitenAstronomy-Sphere of Influence, Mars Mission, Orbitcrackmains2014Noch keine Bewertungen
- Future Markets, Put and Option Contracts, Derivative Markets and MechanismDokument8 SeitenFuture Markets, Put and Option Contracts, Derivative Markets and Mechanismamarsinha1987Noch keine Bewertungen
- Optional - English Literature Optional Strategy by Kumar UjjwalDokument2 SeitenOptional - English Literature Optional Strategy by Kumar Ujjwalamarsinha1987Noch keine Bewertungen
- National Early Childhood Care and Education Policy 2012Dokument5 SeitenNational Early Childhood Care and Education Policy 2012amarsinha1987Noch keine Bewertungen
- TNPSC Pattern, PreparationDokument6 SeitenTNPSC Pattern, Preparationamarsinha1987Noch keine Bewertungen
- Motivation Time ManagementDokument5 SeitenMotivation Time Managementamarsinha1987Noch keine Bewertungen
- Bugets-Basics & Terminologies-Ankur SachanDokument8 SeitenBugets-Basics & Terminologies-Ankur Sachanamarsinha1987Noch keine Bewertungen
- Patent Laws and Issues - MarudavananDokument8 SeitenPatent Laws and Issues - Marudavananamarsinha1987Noch keine Bewertungen
- Multilateral Export Control RegimesDokument8 SeitenMultilateral Export Control Regimesmossad86Noch keine Bewertungen
- Future Markets, Put and Option Contracts, Derivative Markets and MechanismDokument8 SeitenFuture Markets, Put and Option Contracts, Derivative Markets and Mechanismamarsinha1987Noch keine Bewertungen
- Diplomatic Immunity by ArunaDokument4 SeitenDiplomatic Immunity by ArunaAsim MahatoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Patent Laws and Issues - MarudavananDokument8 SeitenPatent Laws and Issues - Marudavananamarsinha1987Noch keine Bewertungen
- Air Pollution-Some PointsDokument4 SeitenAir Pollution-Some Pointsamarsinha1987Noch keine Bewertungen
- Contribution of Thinkers From India & World-GurleenDokument6 SeitenContribution of Thinkers From India & World-Gurleenamarsinha1987Noch keine Bewertungen
- 1st Estate 2nd Estate 3rd Estate: - Clergy - Churchman - Noble - Royal Family - Poor Peasants - Common ManDokument6 Seiten1st Estate 2nd Estate 3rd Estate: - Clergy - Churchman - Noble - Royal Family - Poor Peasants - Common Manamarsinha1987Noch keine Bewertungen
- Non-Alignment Movement AnkitDokument6 SeitenNon-Alignment Movement Ankitamarsinha1987Noch keine Bewertungen
- Clouds Various TypesDokument3 SeitenClouds Various Typesamarsinha1987Noch keine Bewertungen
- Biodiversity Some PointsDokument4 SeitenBiodiversity Some Pointsamarsinha1987Noch keine Bewertungen
- EssayonEthics PDFDokument5 SeitenEssayonEthics PDFJukonti K ReddiNoch keine Bewertungen
- 5 Solar Stocks That Should Be On Your Radar: XOM CVX BP $60 A BarrelDokument3 Seiten5 Solar Stocks That Should Be On Your Radar: XOM CVX BP $60 A BarrelGautam SinghalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Role of Financial Institutions in The GRDokument142 SeitenRole of Financial Institutions in The GRNejash Abdo IssaNoch keine Bewertungen
- FIN 352 Solutions Chapter 8Dokument3 SeitenFIN 352 Solutions Chapter 8yamjam123Noch keine Bewertungen
- Capital Structure ManagementDokument12 SeitenCapital Structure ManagementRentsenjugder NaranchuluunNoch keine Bewertungen
- BCG Economic Value Added Oct1996Dokument2 SeitenBCG Economic Value Added Oct1996anahata2014Noch keine Bewertungen
- Project On Corporate GovernanceDokument28 SeitenProject On Corporate GovernanceRashmiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hero CyclesDokument87 SeitenHero Cyclesanon_61822950% (4)
- A) Instituted, Dispute B) Established, Doubt C) Entrenched, Barricade D) Began, AcceptanceDokument3 SeitenA) Instituted, Dispute B) Established, Doubt C) Entrenched, Barricade D) Began, AcceptanceShaswata ChoudhuryNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2point2 - Investor Presentation 202101Dokument13 Seiten2point2 - Investor Presentation 202101OneappNoch keine Bewertungen
- CDBLDokument5 SeitenCDBLsmg_dreamNoch keine Bewertungen
- Why Jpmorgan Chase Did Not Purchase Ownership of 615b Worth of Wamu Loans in Three Simple Steps 07242017Dokument2 SeitenWhy Jpmorgan Chase Did Not Purchase Ownership of 615b Worth of Wamu Loans in Three Simple Steps 07242017api-293779854100% (1)
- SWOTDokument3 SeitenSWOTSajid Ali0% (1)
- 20-1 To 20-13Dokument16 Seiten20-1 To 20-13Jesica Vargas0% (2)
- SWOT AnalysisDokument3 SeitenSWOT Analysissidlbsim100% (1)
- Travel InsuranceDokument4 SeitenTravel InsuranceAvinash ChauhanNoch keine Bewertungen
- FT Partners FinTech September 2020Dokument111 SeitenFT Partners FinTech September 2020Sergey PostnovNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Boeing Company Finacial AanalysisDokument6 SeitenThe Boeing Company Finacial Aanalysisalan NgunjiriNoch keine Bewertungen
- ILAEAnnual Report2015Dokument80 SeitenILAEAnnual Report2015LunaFiaNoch keine Bewertungen
- China-Pakistan Economic CorridorDokument50 SeitenChina-Pakistan Economic CorridorAbid HussainNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lebanese Association of Certified Public Accountants - IFRS KEY July Exam 2019Dokument5 SeitenLebanese Association of Certified Public Accountants - IFRS KEY July Exam 2019jad NasserNoch keine Bewertungen
- Introduction Iasb Conceptual FrameworkDokument55 SeitenIntroduction Iasb Conceptual FrameworkEtiel Films / ኢትኤል ፊልሞችNoch keine Bewertungen
- RMR 01-02Dokument8 SeitenRMR 01-02matinikkiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Unit 2 Financial Statement and Cash Flows BBS Notes EduNEPAL - InfoDokument1 SeiteUnit 2 Financial Statement and Cash Flows BBS Notes EduNEPAL - InfoGrethel Tarun MalenabNoch keine Bewertungen
- E-Commerce:: E-Business Is The Use of The Internet and Other Networks andDokument13 SeitenE-Commerce:: E-Business Is The Use of The Internet and Other Networks andImroz MahmudNoch keine Bewertungen
- Basic Accounting Concepts, Conventions, Bases & Policies, Concept of Balance SheetDokument44 SeitenBasic Accounting Concepts, Conventions, Bases & Policies, Concept of Balance SheetVivan Menezes86% (7)
- Cpa Review School of The Philippines Mani LaDokument6 SeitenCpa Review School of The Philippines Mani LaSophia PerezNoch keine Bewertungen
- GIPC IP Index 2017 ReportDokument148 SeitenGIPC IP Index 2017 Reportbluemerlelv5205Noch keine Bewertungen
- Pid 39 Panchratna 14 Jul-Sep17Dokument21 SeitenPid 39 Panchratna 14 Jul-Sep17pmlprasadNoch keine Bewertungen