Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
HW Sol1
Hochgeladen von
Asad Ur RehmanOriginaltitel
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
HW Sol1
Hochgeladen von
Asad Ur RehmanCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Chapter 1, Solution 2
(a) i = dq/dt = 3 mA
(b) i = dq/dt = (16t + 4) A
(c) i = dq/dt = (-3e
-t
+ 10e
-2t
) nA
(d) i=dq/dt = 1200 120 t t cos t pA
(e) i =dq/dt = +
e t t
t 4
80 50 1000 50 ( cos sin ) A
Chapter 1, Solution 8
C 15 1 10
2
1 10
idt q = +
= =
}
Chapter 1, Solution 12
For 0 < t < 6s, assuming q(0) = 0,
q t idt q tdt t
t t
( ) ( ) . = + = + =
} }
0 3 0 15
0
2
0
At t=6, q(6) = 1.5(6)
2
= 54
For 6 < t < 10s,
q t idt q dt t
t t
( ) ( ) = + = + =
} }
6 18 54 18 54
6 6
At t=10, q(10) = 180 54 = 126
For 10<t<15s,
q t idt q dt t
t t
( ) ( ) ( ) = + = + = +
} }
10 12 126 12 246
10 10
At t=15, q(15) = -12x15 + 246 = 66
For 15<t<20s,
q t dt q
t
( ) ( ) = + =
}
0 15 66
15
Thus,
q t
t
t
t
( )
.
,
=
+
15
18 54
12 246
66
2
C, 0 < t < 6s
C, 6 < t < 10s
C, 10 < t < 15s
C 15 < t < 20s
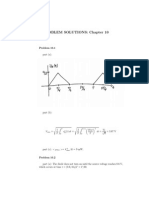
The plot of the charge is shown below.
Chapter 1, Solution 18
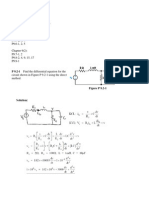
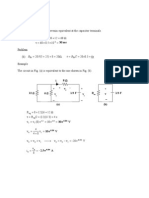
Calculate the power absorbed or supplied by each element in Fig. 1.29
4A + 6V I
o
= 3A + 10 V
4A
+ 1
3V 3I
o
+
2
3A
5V +
(a) (b)
Figure 1.29
For Prob. 1.18
0 5 10 15 20
0
20
40
60
80
100
120
140
t
q
(
t
)
24V 9V
2
1
+
+
Solution: Note, we will express absorbed power as positive terms and delivered power as
negative power absorbed.
(a) For the 9-V voltage source, p = -4 (9) = 36 W
For element 1, p = 4 (6) = 24W
For element 2, p = 4 (3) = 12W
(b) For the 24-V voltage source, p = 24 (-3) = 72W
For the current-controlled voltage source,
0
p 3 I (3) 27W = = = 27 W
For element 1, p = 10 (3) = 30 W
For element 2, p = 3 (5) = 15 W
Chapter 1, Solution 26
A 12-V car battery supported a current of 150mA to a bulb. Calculate: (a) the power absorbed by
the bulb, (b) the energy absorbed by the bulb over an interval of 20 minutes.
Solution:
3
(a) p = vi = 12 150 10 = 1.8 W
(b) w = pt = 1.8 20 60 = 2.16 kJ
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- EEP - 8 Steps To Begin Circuit DesignDokument3 SeitenEEP - 8 Steps To Begin Circuit DesignSugeng SumarnoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Test Bank for Precalculus: Functions & GraphsVon EverandTest Bank for Precalculus: Functions & GraphsBewertung: 5 von 5 Sternen5/5 (1)
- A Brief Introduction to MATLAB: Taken From the Book "MATLAB for Beginners: A Gentle Approach"Von EverandA Brief Introduction to MATLAB: Taken From the Book "MATLAB for Beginners: A Gentle Approach"Bewertung: 2.5 von 5 Sternen2.5/5 (2)
- Instructor's Manual to Accompany CALCULUS WITH ANALYTIC GEOMETRYVon EverandInstructor's Manual to Accompany CALCULUS WITH ANALYTIC GEOMETRYNoch keine Bewertungen
- Working Principle of Diesel EngineDokument30 SeitenWorking Principle of Diesel EngineShahzaibUsmanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Solution Manual For Fundamentals of Electric Circuits 5th Edition by AlexanderDokument40 SeitenSolution Manual For Fundamentals of Electric Circuits 5th Edition by Alexandera251630941Noch keine Bewertungen
- Solution Manual For Fundamentals of Electric Circuits 6th Edition by AlexanderDokument40 SeitenSolution Manual For Fundamentals of Electric Circuits 6th Edition by Alexandera25163094125% (4)
- Chapter 3 - Resistive CircuitsDokument50 SeitenChapter 3 - Resistive CircuitsGeoFurriel100% (1)
- Matrices with MATLAB (Taken from "MATLAB for Beginners: A Gentle Approach")Von EverandMatrices with MATLAB (Taken from "MATLAB for Beginners: A Gentle Approach")Bewertung: 3 von 5 Sternen3/5 (4)
- Answers to Selected Problems in Multivariable Calculus with Linear Algebra and SeriesVon EverandAnswers to Selected Problems in Multivariable Calculus with Linear Algebra and SeriesBewertung: 1.5 von 5 Sternen1.5/5 (2)
- Cable Calculations Worked ExamplesDokument676 SeitenCable Calculations Worked Examplesagan sitompul100% (1)
- Solution Manual for an Introduction to Equilibrium ThermodynamicsVon EverandSolution Manual for an Introduction to Equilibrium ThermodynamicsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cascade and Cascode ConfigurationsDokument21 SeitenCascade and Cascode ConfigurationsPrasit50% (2)
- Sadiku 5th Edition SolutionDokument1.972 SeitenSadiku 5th Edition SolutionarkaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 9 Homework SolutionDokument27 SeitenChapter 9 Homework Solutionjoe100% (3)
- A Comparison of BS en 287 Part 1 and ISO 9606Dokument3 SeitenA Comparison of BS en 287 Part 1 and ISO 9606Joe ClarkeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Inventory Database - All Parts Inc (8/20/20)Dokument2.835 SeitenInventory Database - All Parts Inc (8/20/20)All Parts Inc.Noch keine Bewertungen
- Gate by RK KanodiaDokument440 SeitenGate by RK KanodiaAfshan KhanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Electric Power TransmissionDokument6 SeitenElectric Power TransmissionLimuel John Vera CruzNoch keine Bewertungen
- Gardner Denver S.R.L. Spare Parts Price List Gds 10Dokument140 SeitenGardner Denver S.R.L. Spare Parts Price List Gds 10Tina Manousi100% (2)
- HDSD may cắt hàn màng nhiệtDokument20 SeitenHDSD may cắt hàn màng nhiệtsetavietnamNoch keine Bewertungen
- ECE 2004: Electric Circuit Analysis: T T T T QDokument3 SeitenECE 2004: Electric Circuit Analysis: T T T T QPao JJNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 1 - Electric Circuit Variables: ExercisesDokument8 SeitenChapter 1 - Electric Circuit Variables: ExercisesMinYong SungNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 1 - Electric Circuit Variables: ExercisesDokument8 SeitenChapter 1 - Electric Circuit Variables: ExercisesRulierNoch keine Bewertungen
- P.P.6.1 40V 2.4mJ: February 5, 2006Dokument5 SeitenP.P.6.1 40V 2.4mJ: February 5, 2006thebrown girlNoch keine Bewertungen
- P.P.6.1 40V 2.4mJ: February 5, 2006Dokument5 SeitenP.P.6.1 40V 2.4mJ: February 5, 2006thebrown girlNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapt 06 PP060205Dokument5 SeitenChapt 06 PP060205John RamelbNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 6 Problem 2 A 20 F Capacitor Has Energy 10cos 377Dokument5 SeitenChapter 6 Problem 2 A 20 F Capacitor Has Energy 10cos 377Wad ZzupNoch keine Bewertungen
- Solution Topic 5Dokument3 SeitenSolution Topic 5mimie20063808Noch keine Bewertungen
- Problem Set A Capacitors & Inductors: Te V, Find The Current and The Power V (T) 2te V VDokument4 SeitenProblem Set A Capacitors & Inductors: Te V, Find The Current and The Power V (T) 2te V VJohn A. CenizaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Staticki Odredjeni Nosaci Zadaci Dio1Dokument25 SeitenStaticki Odredjeni Nosaci Zadaci Dio1Kc TanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 6Dokument115 SeitenChapter 6heryj12Noch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 6, Solution 1Dokument40 SeitenChapter 6, Solution 1api-3701823Noch keine Bewertungen
- Tutorial EE1Dokument5 SeitenTutorial EE1Azra Musić50% (2)
- Practice Assignment 1-SolutionsDokument26 SeitenPractice Assignment 1-SolutionsJingyu ZhangNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sem1 1314 SolutionDokument16 SeitenSem1 1314 SolutionThinesh StNoch keine Bewertungen
- ProblemasDokument18 SeitenProblemasAnxo Do ForteNoch keine Bewertungen
- Analysis of AC Circuits: VT and V T, and The Mesh Currents, It and I TDokument4 SeitenAnalysis of AC Circuits: VT and V T, and The Mesh Currents, It and I TYahya ElamraniNoch keine Bewertungen
- Voltage and Current Division in DC and AC CircuitsDokument3 SeitenVoltage and Current Division in DC and AC CircuitsWilson AdrianoNoch keine Bewertungen
- EE 201 - HW 1 Solutions W2007Dokument11 SeitenEE 201 - HW 1 Solutions W2007mrm3zaNoch keine Bewertungen
- W=− F ∙Dl=− Pa ∙Dl=− Pdv W=− Pdv =− Α V Dv =−Α V Dv U Du= U N+1 W =−Α V V W =−5 Atm M M Atm M W =−35 Atm M Pa AtmDokument2 SeitenW=− F ∙Dl=− Pa ∙Dl=− Pdv W=− Pdv =− Α V Dv =−Α V Dv U Du= U N+1 W =−Α V V W =−5 Atm M M Atm M W =−35 Atm M Pa AtmSebastian Torres SanchezNoch keine Bewertungen
- UEE Assignments 1,2,3Dokument11 SeitenUEE Assignments 1,2,3Kaone OsupileNoch keine Bewertungen
- Examination Nov 2012Dokument16 SeitenExamination Nov 2012Mahesh SinghNoch keine Bewertungen
- HW2 SolutionDokument5 SeitenHW2 SolutionAndrewNoch keine Bewertungen
- CH 01 Sec 5Dokument5 SeitenCH 01 Sec 5김성준Noch keine Bewertungen
- Taller 1 ElectrotecniaDokument17 SeitenTaller 1 ElectrotecniaAlejoGonzalezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Experiment-11 Time Response of R-C CircuitDokument8 SeitenExperiment-11 Time Response of R-C CircuitabhimanyuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ee PDFDokument8 SeitenEe PDFabhimanyuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Engr240HW1 PDFDokument9 SeitenEngr240HW1 PDFJames JamesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tarea 1 CNC 2016 (Solución)Dokument24 SeitenTarea 1 CNC 2016 (Solución)Camilo Ignacio Arriagada JaraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Elec9713-11 Tutorial 1 Solution PDFDokument7 SeitenElec9713-11 Tutorial 1 Solution PDFRajeev ValunjkarNoch keine Bewertungen
- ch06 IsmDokument34 Seitench06 IsmQuero22Noch keine Bewertungen
- ch07 Ism PDFDokument95 Seitench07 Ism PDFSebastian Mora OyarzunNoch keine Bewertungen
- Forced and Total Response in RL and RC CircuitsDokument11 SeitenForced and Total Response in RL and RC CircuitsDr. Omar Sh. AlyozbakyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Problem Solutions: Chapter 10Dokument10 SeitenProblem Solutions: Chapter 10arcg89Noch keine Bewertungen
- Problem Solutions: V V P I V R R VDokument24 SeitenProblem Solutions: V V P I V R R Vapi-3741518Noch keine Bewertungen
- Practica de Circuitos Eléctricos I Ing. Telecomunicaciones Problema 1 .-Si Vi 10 Senwt (Voltios) I (T) (Ma) I (T) .Grafique I (T), Vo (T)Dokument4 SeitenPractica de Circuitos Eléctricos I Ing. Telecomunicaciones Problema 1 .-Si Vi 10 Senwt (Voltios) I (T) (Ma) I (T) .Grafique I (T), Vo (T)lector161Noch keine Bewertungen
- B Network 09-09-16 1494Dokument10 SeitenB Network 09-09-16 1494arunNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tutorial 3 LoadDokument6 SeitenTutorial 3 LoadIriest SumaryantoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Capitulo 11-12Dokument6 SeitenCapitulo 11-12CESAR ADALBERTO GARNICA ALCIVARNoch keine Bewertungen
- Process Modelling, Simulation and Control For Chemical Engineers. Solved Problems. Chapter 10 Laplace Domain Analysis of Conventional Feedback Control SystemsDokument34 SeitenProcess Modelling, Simulation and Control For Chemical Engineers. Solved Problems. Chapter 10 Laplace Domain Analysis of Conventional Feedback Control SystemsViajante_santosNoch keine Bewertungen
- ECON 4301 Midterm Solutions PDFDokument8 SeitenECON 4301 Midterm Solutions PDFHumam HassanNoch keine Bewertungen
- 29.RLC Part 3 - Complete ResponseDokument19 Seiten29.RLC Part 3 - Complete ResponseIbrahim GhunaimNoch keine Bewertungen
- Soln 11060Dokument1 SeiteSoln 11060LUIS ALEXANDER RODRIGUEZ ZAPATANoch keine Bewertungen
- Electrical and Electronic Principles 3 Checkbook: The Checkbook SeriesVon EverandElectrical and Electronic Principles 3 Checkbook: The Checkbook SeriesNoch keine Bewertungen
- 7 KGCOE-EEEE-374-EM-Fields and Transmission Lines - RIT Dubai - TliliDokument4 Seiten7 KGCOE-EEEE-374-EM-Fields and Transmission Lines - RIT Dubai - TliliAsad Ur RehmanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 6 BJT ACDokument23 SeitenChapter 6 BJT ACAsad Ur RehmanNoch keine Bewertungen
- EEEE-120 - Lecture 2 - Logic Circuits - 1 PDFDokument27 SeitenEEEE-120 - Lecture 2 - Logic Circuits - 1 PDFAsad Ur RehmanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Basic Integration FormulaDokument1 SeiteBasic Integration FormulaAsad Ur RehmanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Homework 1Dokument1 SeiteHomework 1Asad Ur RehmanNoch keine Bewertungen
- UG Orientation Overview 2014-2015 WEBDokument13 SeitenUG Orientation Overview 2014-2015 WEBAsad Ur RehmanNoch keine Bewertungen
- RIT Dubai Bachelor Tuition 2015-16 PDFDokument1 SeiteRIT Dubai Bachelor Tuition 2015-16 PDFAsad Ur RehmanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Charting The Heavens: Lecture OutlineDokument9 SeitenCharting The Heavens: Lecture OutlineAsad Ur RehmanNoch keine Bewertungen
- COE221 Lect2 Numbersystems 2sDokument23 SeitenCOE221 Lect2 Numbersystems 2sAsad Ur RehmanNoch keine Bewertungen
- ELE 351L Lab 3Dokument11 SeitenELE 351L Lab 3Asad Ur RehmanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 2, Solution 4 I 15/100 150 Ma I 15/150 100 Ma Chapter 2, Solution 7Dokument4 SeitenChapter 2, Solution 4 I 15/100 150 Ma I 15/150 100 Ma Chapter 2, Solution 7Asad Ur RehmanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Charting The Heavens: Lecture OutlineDokument9 SeitenCharting The Heavens: Lecture OutlineAsad Ur RehmanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mbackpaper 18Dokument6 SeitenMbackpaper 18Aakash PathakNoch keine Bewertungen
- Global System For Mobile Communications (GSM) : 1 Summer Internship ReportDokument51 SeitenGlobal System For Mobile Communications (GSM) : 1 Summer Internship ReportAvay SinghNoch keine Bewertungen
- Semester Project Report: Group MembersDokument10 SeitenSemester Project Report: Group Membersraja badarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Utmost TFT Training Part1Dokument96 SeitenUtmost TFT Training Part1gideontargrave7Noch keine Bewertungen
- Francis and Kaplan Reaction TurbinesDokument5 SeitenFrancis and Kaplan Reaction TurbinesfahadNoch keine Bewertungen
- Jquery SummaryDokument8 SeitenJquery Summaryraj06740Noch keine Bewertungen
- Input-Output Tracking System For Process MeasurementDokument4 SeitenInput-Output Tracking System For Process MeasurementVipen MahajanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fulcrum Summer IssueDokument20 SeitenFulcrum Summer IssuewillwnetNoch keine Bewertungen
- 03-Application List Moto, ATVDokument97 Seiten03-Application List Moto, ATVΗλίας ΓεωργιάδηςNoch keine Bewertungen
- Work With Linked ServersDokument44 SeitenWork With Linked ServersioiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Au GP1012 PDFDokument1 SeiteAu GP1012 PDFAkmalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Deltascope FMP10 Isoscope FMP10 Dualscope FMP20: Operators ManualDokument152 SeitenDeltascope FMP10 Isoscope FMP10 Dualscope FMP20: Operators ManualMarcelino Navarrete EvaristoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Medium Voltage Ac Drives Selection Guide: Powerflex 7000 - Direct-To-Drive™ Technology - Air-Cooled - Liquid-CooledDokument36 SeitenMedium Voltage Ac Drives Selection Guide: Powerflex 7000 - Direct-To-Drive™ Technology - Air-Cooled - Liquid-CooledRamesh Gandhasiri50% (2)
- The Visual Basic Editor: School of ConstructionDokument43 SeitenThe Visual Basic Editor: School of Constructionavdesh7777Noch keine Bewertungen
- DriPak - Prod - Mark - SHT - AFP 1 120F NewDokument2 SeitenDriPak - Prod - Mark - SHT - AFP 1 120F NewsandroNoch keine Bewertungen
- Power Xpert Power Quality Meters: Product FocusDokument20 SeitenPower Xpert Power Quality Meters: Product FocusMike MendozaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Wood AshDokument5 SeitenWood AshJohn loyd hernandezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Kool Calc GuideDokument24 SeitenKool Calc GuideAlonso MejíaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Flocculation and ClarifiersDokument17 SeitenFlocculation and ClarifiersOnelNoch keine Bewertungen
- Dead LoadsDokument1 SeiteDead LoadsShokry AlkissyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Printing, Laminating & Encoding Solutions: Fargo® Dtc5500LmxDokument6 SeitenPrinting, Laminating & Encoding Solutions: Fargo® Dtc5500Lmxgroovey9040Noch keine Bewertungen
- Difference Between PPM and PPMVDokument2 SeitenDifference Between PPM and PPMVKhanh TrangNoch keine Bewertungen
- Low Density Parity Check CodesDokument21 SeitenLow Density Parity Check CodesPrithvi Raj0% (1)