Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
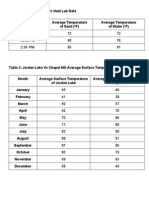
Ds82-Dna Replication Laboratory
Hochgeladen von
api-110789702Originaltitel
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Ds82-Dna Replication Laboratory
Hochgeladen von
api-110789702Copyright:
Verfügbare Formate
UNIT 7: DNA Structure & Replication DAYSHEET 82-DNA Replication Laboratory
Name: _______________________________
BIOLOGY I
Date: _______________
Bellringer: Use your previous daysheets to help you answer the following review questions.
1) If you were given the one strand of DNA below, what would the complementary strands bases be?
___ ___ ___ ___ ___ ___ ___ ___ ___
2) What is the picture of? _____________________________________ 3) Who created this picture? __________________________________
4) What are the building blocks of DNA? __________________________ 5) Label the picture of the DNA nucleotide below:
Objective: Students will learn how DNA replicates, or makes copies of itself. Homework: HW 82 is due next class! Your Unit 7 Exam is next Tues/Wed!!!!!
Activity 1: Candy DNA Replication Laboratory
Introduction Now that you have an understanding of the structure of the DNA molecule and the base pairing rules, you are going to investigate DNA replication. Each time a cell divides it makes an exact copy of itself. The process that DNA makes an exact copy of itself is called DNA replication. During DNA replication the double helix is unwound by the enzyme helicase and complementary nucleotides are attached to each of the 2 original strands of DNA by the enzyme DNA polymerase. Materials 4 Toothpicks Scissors 2 pieces of red licorice 2 pieces of black licorice 4 yellow marshmallows/gummy bears = Adenine 4 orange marshmallows/gummy bears = Thymine 4 green marshmallows/gummy bears = Cytosine 4 pink/red marshmallows/gummy bears = Guanine
Directions 1. Use your two red pieces of licorice to assemble a strand of DNA with the following nucleotide sequence A-T-C-G. You will use the toothpicks to attach the nitrogen bases (marshmallows) to the sugar-phosphate backbones (licorice). 2. Attach the complementary nucleotides to the other side of the toothpick (if you have an A, attach a T, or G with C) and then attach the other red licorice piece to this side of the strand. 3. Carefully color code and label your original strand of candy DNA in the space provided, using all the labels listed in the directions on the observations table. 4. Using the scissors, separate the two strands by cutting down the middle (think about what the action of the cutting scissors represents in DNA replication). 5. You and your partner will both take one of the single strands from the original molecule and add the NEW complementary base pairs. 6. Once the new base pairs are added you will close the molecule by attaching the new backbone (black licorice). 7. Lay these two new strands next to one another so that both pieces of black licorice are in the middle and both pieces of red licorice are on the outside. 8. Carefully color code and label your new strands of candy DNA in the space provided, using all the labels listed in the directions on the observations table. 9. Complete the analysis questions.
Observations Your diagrams should include the following labels and colors: Original Strand (RED), New Strand (BLACK), Adenine (YELLOW), Guanine (PINK), Thymine (ORANGE), Cytosine (GREEN)
Parent DNA strand
Daughter DNA strands
Analysis Questions: 1. How are your original and new strands SIMILAR? _____ 2. How are your original and new strands DIFFERENT?
3. What did the following parts of your DNA model represent:
DNA Replication EX: Adenine Guanine Cytosine Thymine Red licorice Black licorice Toothpicks Helicase DNA polymerase Represented by in your model The yellow marshmallows
4. Why is it necessary for DNA replication to occur?
_____
5. What kind of mistakes could happen in DNA replication (be specific)? How do you think this could affect an organism?
________________________
Homework 82: Cellular Respiration Flip-Flop Name: ___________________________________
Biology I Date: __________________
FLIP
Energy All living things need energy. But where does that energy come from? Most of us would probably say our energy comes from the food we eat. But what does this mean? I cant see the energy in my sandwich, so where is it? Energy comes in many forms, including light, heat, and electricity. Energy can be stored in the chemical bonds between atoms and molecules. When these bonds are broken, energy is released. So when you say that there is energy in your food, you are really saying that energy is stored in the food. Our body can break apart the atoms in the food to release the energy. ATP There is one molecule in our bodies that is particularly good at storing and releasing energy. This molecule is called adenosine triphosphate (or ATP for short). ATP consists of adenine, a 5-carbon sugar called ribose, and 3 phosphate groups. The 3 phosphate groups are where ATP gets its name adensine triphosphate. ATP stores energy in the chemical bond between the 2nd and 3rd phosphate groups. When a cell needs energy, it can break this bond, releasing the energy.
FLOP
1. Where is energy stored?
2. How is energy released?
3. Label the 3 parts of the ATP molecule:
4. What are some things a cell might need energy for?
ATP is so good at storing and releasing energy that it is considered the universal energy source for cells. All living things from bacteria, to plants, to animals, use ATP to carry out important functions.
Making ATP Our cells make ATP by breaking down food molecules, specifically the sugar glucose. This process is called respiration. There are two types of respiration - aerobic respiration and anaerobic respiration.
5. SOL Blitz: Energy is released from ATP when A.ATP is exposed to sunlight B. a phosphate group is removed C. adenine bonds to ribose D.a phosphate group is added 6. What are the 2 types of respiration?
FLIP Aerobic respiration Aerobic respiration happens at two levels. At the organism level, it involves your body taking in air that contains oxygen, and breathing out carbon dioxide. At the cell level, it involves using the oxygen you breathe to help break down glucose and release energy. This energy is used to put together ATP molecules, which the cell can then use as energy for all its important functions. Carbon dioxide and water are waste products. Here is the chemical equation for aerobic respiration: oxygen + glucose water + carbon dioxide + ATP! In the cell, aerobic respiration takes place in the mitochondria. Thats why the mitochondria are called the powerhouses of the cell, because this is where food is broken down to make ATP energy. One molecule of glucose can be used to create 36 molecules of ATP!
FLOP
7. What are the reactants of aerobic respiration? 9. What are the procuts of aerobic respiration? 10. Where does aerobic respiration take place?
11. What are 2 differences between aerobic respiration and anaerobic respiration?
Anaerobic Respiration Aerobic respiration can only happen when an organism has oxygen. So what happens when oxygen is not present? For example, bacteria that live in deep in the soil do not have oxygen. A process called anaerobic respiration, or fermentation, can occur when there is no oxygen available. Anaerobic respiration does not make as much energy as aerobic respiration only 2 ATP but its better than nothing. Fermentation produces some interesting products besides ATP. In one type of fermentation, ethanol and carbon dioxide are produced as waste products. This type of fermentation called alcoholic fermentation is used to make beer and wine, and to make bread rise. The other type of fermentation lactic acid fermentation makes lactic acid as a waste product. This often happens in our muscle cells when we exercise or participate in a strenuous activity. Our muscle cells run out of oxygen and start using fermentation to produce ATP. But the fermentation also makes lactic acid, which causes your muscles to feel like they are burning, and makes them sore the next day.
12. Usain Bolt is practicing for the 2012 summer Olympics. Hes been running all day, and now has a burning sensation in his leg muscles but doesnt know why. Explain to Usain why his muscles are burning:
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- GoosechaseplannerDokument2 SeitenGoosechaseplannerapi-110789702Noch keine Bewertungen
- Symbiosis Practice QuizDokument11 SeitenSymbiosis Practice Quizapi-110789702Noch keine Bewertungen
- IntroductiontochemicalequationspodcastnotesDokument4 SeitenIntroductiontochemicalequationspodcastnotesapi-110789702Noch keine Bewertungen
- Icecores 2015Dokument2 SeitenIcecores 2015api-110789702Noch keine Bewertungen
- AnswerkeyofwaterqualitynotesstudentsDokument2 SeitenAnswerkeyofwaterqualitynotesstudentsapi-110789702Noch keine Bewertungen
- Station Number What Was Done? What Can You Observe? Was It A Physical or Chemical Change?Dokument2 SeitenStation Number What Was Done? What Can You Observe? Was It A Physical or Chemical Change?api-110789702Noch keine Bewertungen
- Example 1: Some Finches (Birds) Had A That Gave Them Thinner Beaks Than OthersDokument2 SeitenExample 1: Some Finches (Birds) Had A That Gave Them Thinner Beaks Than Othersapi-110789702Noch keine Bewertungen
- FossilstationsDokument3 SeitenFossilstationsapi-110789702Noch keine Bewertungen
- GraphinginstructionsDokument1 SeiteGraphinginstructionsapi-110789702Noch keine Bewertungen
- MmiummealDokument1 SeiteMmiummealapi-110789702Noch keine Bewertungen
- Picture Put Events (Letters / Numbers) in Order From Oldest To YoungestDokument2 SeitenPicture Put Events (Letters / Numbers) in Order From Oldest To Youngestapi-110789702Noch keine Bewertungen
- ConvergentboundariesDokument1 SeiteConvergentboundariesapi-110789702Noch keine Bewertungen
- Station #1: Evaporation and TranspirationDokument6 SeitenStation #1: Evaporation and Transpirationapi-110789702Noch keine Bewertungen
- Bolin Creek - September 24, 2015Dokument4 SeitenBolin Creek - September 24, 2015api-110789702Noch keine Bewertungen
- RockcyclecrayonlabDokument2 SeitenRockcyclecrayonlabapi-110789702Noch keine Bewertungen
- Hydrologyeogreviewnotes 2014Dokument5 SeitenHydrologyeogreviewnotes 2014api-110789702Noch keine Bewertungen
- BolincreekmealplanningDokument2 SeitenBolincreekmealplanningapi-110789702Noch keine Bewertungen
- NameDokument4 SeitenNameapi-110789702Noch keine Bewertungen
- Eogchemistryreviewnotes 2014Dokument4 SeitenEogchemistryreviewnotes 2014api-110789702Noch keine Bewertungen
- TakealookgraphtablesheetDokument1 SeiteTakealookgraphtablesheetapi-110789702Noch keine Bewertungen
- SpecificheatdataDokument1 SeiteSpecificheatdataapi-110789702Noch keine Bewertungen
- Waterqualityreadings 2015Dokument17 SeitenWaterqualityreadings 2015api-110789702Noch keine Bewertungen
- Them e A L ParagraphDokument2 SeitenThem e A L Paragraphapi-110789702Noch keine Bewertungen
- HydrologylearningmapDokument3 SeitenHydrologylearningmapapi-110789702Noch keine Bewertungen
- Symbiosis QuizDokument18 SeitenSymbiosis Quizapi-110789702Noch keine Bewertungen
- Food / Energy & Disease Eog Review!!! Countdown To Success: 3 Days!!!Dokument4 SeitenFood / Energy & Disease Eog Review!!! Countdown To Success: 3 Days!!!api-110789702Noch keine Bewertungen
- EnergyflowpodcastnotesDokument8 SeitenEnergyflowpodcastnotesapi-110789702Noch keine Bewertungen
- Coral Reef Adventure Quiz: NameDokument2 SeitenCoral Reef Adventure Quiz: Nameapi-110789702Noch keine Bewertungen
- Symbiosis QuizDokument18 SeitenSymbiosis Quizapi-110789702Noch keine Bewertungen
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeVon EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (5784)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Von EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Bewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (98)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItVon EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (838)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeVon EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (537)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerVon EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (271)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceVon EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (890)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingVon EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (399)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnVon EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (234)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceVon EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (587)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaVon EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (265)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryVon EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (231)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealVon EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (72)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureVon EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (474)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersVon EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (344)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaVon EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (45)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyVon EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (2219)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreVon EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Von EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Bewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (119)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesVon EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (821)
- The Aspects of GENE THERAPYDokument12 SeitenThe Aspects of GENE THERAPYJasmin Prindiana100% (6)
- Central Dogma of Life: Transcription and TranslationDokument13 SeitenCentral Dogma of Life: Transcription and TranslationLamia AkterNoch keine Bewertungen
- Strawberry Dna LabDokument4 SeitenStrawberry Dna Labapi-393031110Noch keine Bewertungen
- Proteoglycans and Glycoproteins: DR - Nuruddin Mohammed NurDokument39 SeitenProteoglycans and Glycoproteins: DR - Nuruddin Mohammed NurIffah IrdinaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bio 1Dokument13 SeitenBio 1Mary Ann FriasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mulungushi University final exam covers genetics conceptsDokument15 SeitenMulungushi University final exam covers genetics conceptsPrince-SimonJohnMwanza100% (1)
- Recombinant DNA TechnologyDokument3 SeitenRecombinant DNA TechnologyMaika Pilley DaduboNoch keine Bewertungen
- Assessment of Tumor Response To Percutaneous Ablation by Using Glyceraldehyde-3-Phosphate Dehydrogenase AntagonistsDokument12 SeitenAssessment of Tumor Response To Percutaneous Ablation by Using Glyceraldehyde-3-Phosphate Dehydrogenase Antagonistsnguyen hoang nganNoch keine Bewertungen
- Forensic DNA Fingerprinting Using Restriction EnzymesDokument33 SeitenForensic DNA Fingerprinting Using Restriction Enzymesbharad wajNoch keine Bewertungen
- Transfer RNA Synthesis RegulationDokument17 SeitenTransfer RNA Synthesis RegulationAfif BerlianNoch keine Bewertungen
- Healthcare in BDDokument20 SeitenHealthcare in BDAl AminNoch keine Bewertungen
- Barba Et Al-2014-Molecular Ecology ResourcesDokument18 SeitenBarba Et Al-2014-Molecular Ecology ResourcesAndrés FrankowNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mindoro State College of Agriculture and Technology: I. ObjectivesDokument7 SeitenMindoro State College of Agriculture and Technology: I. ObjectivesJunjun CaoliNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cell Surface Biotinylation - Sorting Nexin-27 Regulates AMPA ReceptorsDokument32 SeitenCell Surface Biotinylation - Sorting Nexin-27 Regulates AMPA ReceptorsEshaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Intraneuronal Signalling Pathways: Chair Person: Dr. S. Kiran Kumar Presenter: Dr. G - Sangha MitraDokument20 SeitenIntraneuronal Signalling Pathways: Chair Person: Dr. S. Kiran Kumar Presenter: Dr. G - Sangha Mitrasangha_mitra_2Noch keine Bewertungen
- Retinoic Acid and Its Derivatives in SkinDokument14 SeitenRetinoic Acid and Its Derivatives in SkinBryan NguyenNoch keine Bewertungen
- Introduction To Genetic Analysis 11Th Edition Griffiths Solutions Manual Full Chapter PDFDokument36 SeitenIntroduction To Genetic Analysis 11Th Edition Griffiths Solutions Manual Full Chapter PDFarthur.hendricks257100% (12)
- COVID vaccination certificateDokument2 SeitenCOVID vaccination certificateGeorge HonciugNoch keine Bewertungen
- CloningDokument6 SeitenCloningAngel L.Noch keine Bewertungen
- Genetics A Conceptual Approach 5th Edition Pierce Test Bank DownloadDokument18 SeitenGenetics A Conceptual Approach 5th Edition Pierce Test Bank DownloadMax Martinez100% (25)
- Being Asked in Each of The Boxes. (Note: You Can Insert A Textbox Where You Can Insert Your Answer.)Dokument4 SeitenBeing Asked in Each of The Boxes. (Note: You Can Insert A Textbox Where You Can Insert Your Answer.)Reign PedrosaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Genome Wide Analysis Reveals A Rhamnolipid DependentDokument16 SeitenGenome Wide Analysis Reveals A Rhamnolipid DependentTiago Souza SallesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Campbell DNA and TechnologyDokument14 SeitenCampbell DNA and TechnologyIntan Karnina PutriNoch keine Bewertungen
- @NeoPlex COVID-19 Technical Information 20200324 - Rev1Dokument17 Seiten@NeoPlex COVID-19 Technical Information 20200324 - Rev1Theresia Lumban GaolNoch keine Bewertungen
- Energy & Respiration NotesDokument5 SeitenEnergy & Respiration Notesaimee simarnoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Activity 1 Group TaskDokument5 SeitenActivity 1 Group Taskfranchesca marie t. uyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Vaccines and Vaccination History and Emerging IssuesDokument15 SeitenVaccines and Vaccination History and Emerging IssuesMěđ SimoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Coarse-Grained Simulations of Macromolecules: From DNA To NanocompositesDokument23 SeitenCoarse-Grained Simulations of Macromolecules: From DNA To NanocompositesDavide MandelliNoch keine Bewertungen
- Restriction Enzyme DigestionDokument5 SeitenRestriction Enzyme DigestionAqsa ImtiazNoch keine Bewertungen
- Marieb Ch3aDokument45 SeitenMarieb Ch3aNorhayna DadiaNoch keine Bewertungen