Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Test Papers
Hochgeladen von
Bhaskar BhaskiCopyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Test Papers
Hochgeladen von
Bhaskar BhaskiCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
BHASKAR TUTORIALS BUSINESS STATISTICS PART A (5 MARKS) 1. Write a critical note on distrust of statics (June 2008) 2.
Explain the difference between sampling and census method (Dec2007) 3. What is tabulation? Mention the parts of a statistical table (Dec 2007,Dec 2009) PART B (10 MARKS) 1. Define statistics. Explain the scope and functions of statics (may 07) 2. Draw a blank table to show the number of students in a college according to a. Sex b. Studying class : PUC and Degree c. Faculty : Arts , Commerce, Science PART C (15 MARKS) 1. Present the following in a tabular form. In 1990 out of the total of 3500 workers of factory. 2400 were the member of trade. The number of women employed was 400 of which 350 did not belong to a trade union. In 1995 the number of union workers increased to 3160 of which 2580 were men. On the other hand the number of non-union members fell down to 416 of which 360 were men. In 2000, there were 3600 workers who belong to a trade union and 100 who did not belong to a trade union. Of all the workers in 2000, 600 were women of whom only 16 did not belong to a trade union. 2. The data given below relate to the height and weight of 20 persons, you are required to form a two way frequency table with class intervals 62 to 64, 64 to 66 and so on and 115 to 125 lbs,125lbs to 135lbs. Sl No. 1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9,10,11,12,13,14,15,16,17,18,19,20 Weight in LBS: 170,135,136,137,148,124,117,128,143,129,163,139,129,134,140,132,120,148,129,152 Height in inches: 70,65,65,64,69,63,65,70,71,62,70,67,62,68,67,69,66,68,67,67
BHASKAR TUTORIALS BUSINESS STATISTICS PART A(5 MARKS) 1. What are the limitations of statistics? Explain (May 07) 2. Explain the advantages of sampling method and census method (June 2008,Dec 2009) 3. What are the main rules of tabulation (Dec08) PART B (10 MARKS) 1. State the function of Statics. 2. Draft a blank table to show the exports of 3 companies A,B and C to 5 countries UK,USA,RUSSIA, FRANCE,GERMANY in each of the years 2000-2004 PART C (15 MARKS) 3. Present the following in a tabular form. In 1990 out of the total of 3500 workers of factory. 2400 were the member of trade. The number of women employed was 400 of which 350 did not belong to a trade union. In 1995 the number of union workers increased to 3160 of which 2580 were men. On the other hand the number of non-union members fell down to 416 of which 360 were men. In 2000, there were 3600 workers who belong to a trade union and 100 who did not belong to a trade union. Of all the workers in 2000, 600 were women of whom only 16 did not belong to a trade union. 4. The data given below relate to the height and weight of 20 persons, you are required to form a two way frequency table with class intervals 62 to 64, 64 to 66 and so on and 115 to 125 lbs,125lbs to 135lbs. Sl No. 1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9,10,11,12,13,14,15,16,17,18,19,20 Weight in LBS: 170,135,136,137,148,124,117,128,143,129,163,139,129,134,140,132,120,148,129,152 Height in inches: 70,65,65,64,69,63,65,70,71,62,70,67,62,68,67,69,66,68,67,67
BHASKAR TUTORIALS COST ACCOUNTING
1. 2. 3.
4. 5.
PART A(5 MARKS) Write brief the limitations of Cost Accounting What is direct expenses? Give examples PART B (10 MARKS) Prepare a cost sheet form the information's given below for the year ended 31-03-10 Opening stock : RM 110000 WIP 55000 FG 140000 Closing stock : RM 82000 WIP 60000 FG 105000 RM Purchased 600000 Carriage on purchase 4000 Direct wages 450000 Direct expenses 210000 RM Returned 4000 Factory expenses 325000 Administrative expenses 245000 Income tax 22000 Dividends 28000 Selling expenses 88000 Sale of FG 2200000 State the difference between cost accounting and financial accounting PART C (15 MARKS) From the following particulars prepare cost sheet showing Prime cost, Works Cost , Total cost, %of Work OH to Wages, %of OfficeOH to WC Stock on 1-1-10 FG 112000 RM 51200 Stock on 31-12-10 FG 70720 RM 156000 Purchase of RM 1518400 Sale of FG 3078400 Productive wages 1032000 Work OH 258000 Office OH 100000 On the basis of the above information assuming that a unit with cost Rs.2500 towards direct materials and Rs.1500 towards productive wages prepare a quotation for the year 2010 by maintaining the same %of works OH and office OH as in the previous year. The firm expects to recover 20% profit on cost price.
BHASKAR TUTORIALS COST ACCOUNTING
PART A(5 MARKS) 1. Define costing? State the different methods od costing 2. Explain the advantages of cost accouting PART B (10 MARKS) 3. From the following particulars prepare cost sheet showing Prime cost, Works Cost , Cost of production, Profit Stock on 1-1-10 RM 28000 WIP 23000 Stock on 31-12-10 RM 23000 WIP 8500 Purchase of RM 250000 Octoria 8500 Carriage outwards 14000 Wages 50000 Sales 480000 Salaries to salesman 9000 Power(10% to sales office) 14000 Salaries to office staff 12000 Rent,rates and taxes(20% to sales office) 10000 P and S 4000 Sale of scrap 3000 Interest 15000 Publicity expenses 21500 Commission on sales staff 16000 4. State the difference between cost accounting and financial accounting PART C (15 MARKS) 5. From the following particulars prepare cost sheet showing Prime cost, Works Cost , Total cost, %of Work OH to Wages, %of OfficeOH to WC Stock on 1-1-10 FG 112000 RM 51200 Stock on 31-12-10 FG 70720 RM 156000 Purchase of RM 1518400 Sale of FG 3078400 Productive wages 1032000 Work OH 258000 Office OH 100000 On the basis of the above information assuming that a unit with cost Rs.2500 towards direct materials and Rs.1500 towards productive wages prepare a quotation for the year 2010 by maintaining the same %of works OH and office OH as in the previous year. The firm expects to recover 20% profit on cost price.
1. What is an Average? Name the different types of averages. 2. Calculate Am from the following data under Short cut method, Step deviation method No of students : 20,15,30,35,40,28,12,8,7,5 Marks ; 10, 15, 20, 25, 30, 35, 40, 45, 50, 55 3. From the data given below calculate mean, median and mode. Weight in Kgs 10.-19 20-29 30-39 No of Students 8 32 81 80-89 2
40-49 152
50-59 92
60-69 24
70-79 9
1. What is mode? How it is calculated in unmoral and bimodal series? 2.Calculate AM from the following data Temperature : -40 to -30, -30 to -20, -20 to -10, -10 to 0, 0 to 10, 10 to 20, 20 to 30 No of days : 10, 28, 30, 42, 65, 180, 10 3. Calculate mean, median and mode from the following distribution 10-15, 15-20, 20-25, 25-30, 30-35, 35-40, 40-45, 45-50, Variable 50-55, 55-60 12, 19, 31, 55, 79, 58, 40, 22, Frequency 13, 11 1. What are the requisites of a good average? 2.From the following data find the missing frequency when the mean is 15.38 Central Value : 10,12,14,16,18,20 Frequency : 3,7,?,20,8,5
3. From the following data calculate Arithmatic, Mean, Median and Mode Marks obtained No of students. Above 0 430 Above 10 408 Above 20 374 Above 30 322 Above 40 235 Above 50 191 Above 60 142 Above 70 102 Above 80 68 Above 90 24
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Data Interpretation Guide For All Competitive and Admission ExamsVon EverandData Interpretation Guide For All Competitive and Admission ExamsBewertung: 2.5 von 5 Sternen2.5/5 (6)
- Tutorial Questions: Quantitative Methods IDokument5 SeitenTutorial Questions: Quantitative Methods IBenneth YankeyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Supply Chain Management and Business Performance: The VASC ModelVon EverandSupply Chain Management and Business Performance: The VASC ModelNoch keine Bewertungen
- Question Bank MbaDokument173 SeitenQuestion Bank MbanamrataNoch keine Bewertungen
- Statistics Revision WorksheetDokument2 SeitenStatistics Revision Worksheetkaashvi goyalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lcci BS 1Dokument17 SeitenLcci BS 1Kyaw Htin WinNoch keine Bewertungen
- Statistics 1Dokument20 SeitenStatistics 1Saran RannyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mean, Median and Mode - Module1Dokument8 SeitenMean, Median and Mode - Module1Ravindra BabuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bumastics QP Final1Dokument16 SeitenBumastics QP Final1Ravindra BabuNoch keine Bewertungen
- MBA Question Papers 2007Dokument27 SeitenMBA Question Papers 2007Rakesh_Bhati_1182100% (1)
- Business Statistics ExercisesDokument5 SeitenBusiness Statistics Exercisesvictor18576184Noch keine Bewertungen
- Business Statistics ExercisesDokument8 SeitenBusiness Statistics ExercisesQuạt MoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bank&InsurDokument14 SeitenBank&Insurammusamaya1416Noch keine Bewertungen
- Business StatsDokument3 SeitenBusiness Statssaha apurva100% (1)
- Subject Code:: Prepared byDokument6 SeitenSubject Code:: Prepared byDarmmini MiniNoch keine Bewertungen
- XIME-QT-1 Assignment-IIDokument2 SeitenXIME-QT-1 Assignment-IIRiya SinghNoch keine Bewertungen
- Question Paper Mba 2018Dokument15 SeitenQuestion Paper Mba 2018Karan Veer SinghNoch keine Bewertungen
- MS 4solvedpapersDokument20 SeitenMS 4solvedpapersexsonuNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2nd Assignment Managerial Economics Please Submit The Hand Written Assignment On 22nd September Before 12:30 PM. Answer All The Five QuestionsDokument1 Seite2nd Assignment Managerial Economics Please Submit The Hand Written Assignment On 22nd September Before 12:30 PM. Answer All The Five QuestionsvikasNoch keine Bewertungen
- 08MBA14 May - June 2010Dokument3 Seiten08MBA14 May - June 2010nitte5768Noch keine Bewertungen
- Assignment or BCADokument5 SeitenAssignment or BCAkuku288Noch keine Bewertungen
- PPC Question BankDokument20 SeitenPPC Question BankMyameSirameNoch keine Bewertungen
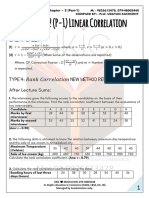
- Chapter: 2 (P-1) Linear Correlation: Cheat SheetDokument4 SeitenChapter: 2 (P-1) Linear Correlation: Cheat SheetHet Patel100% (1)
- Anjuman Institute of Technology and Management Department of Manegement Studies Mba 1 Sem 1 Internal Assessment TestDokument1 SeiteAnjuman Institute of Technology and Management Department of Manegement Studies Mba 1 Sem 1 Internal Assessment TestZahid HassanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mean, Median and Mode - Module 1Dokument8 SeitenMean, Median and Mode - Module 1Ravindra Babu0% (1)
- Excel Assignment (2) 1 1Dokument29 SeitenExcel Assignment (2) 1 1Sonali ChauhanNoch keine Bewertungen
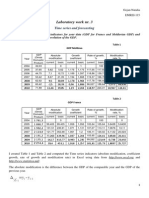
- Laboratory Work Nr. 3: Time Series and ForecastingDokument10 SeitenLaboratory Work Nr. 3: Time Series and ForecastingNataliaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 3740 Introduction To Econometrics, Fall 2010: I I I I IDokument10 Seiten3740 Introduction To Econometrics, Fall 2010: I I I I IRobert SherNoch keine Bewertungen
- CAT DI Combination Graph M05Dokument8 SeitenCAT DI Combination Graph M05vatsadbgNoch keine Bewertungen
- 12 01Dokument9 Seiten12 01Zahid RaihanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Eco 162: Microeconomics: Website: Universiti Teknologi MaraDokument14 SeitenEco 162: Microeconomics: Website: Universiti Teknologi MaraQaseh Acewin100% (1)
- Kings: Introduction To EconomicsDokument8 SeitenKings: Introduction To EconomicsVenkatesh ArumugamNoch keine Bewertungen
- Announces Q2 Results (Standalone) & Limited Review Report (Standalone) For The Quarter Ended September 30, 2016 (Result)Dokument8 SeitenAnnounces Q2 Results (Standalone) & Limited Review Report (Standalone) For The Quarter Ended September 30, 2016 (Result)Shyam SunderNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bcom 3 Sem Quantitative Techniques For Business 1 19102079 Oct 2019Dokument3 SeitenBcom 3 Sem Quantitative Techniques For Business 1 19102079 Oct 2019lightpekka2003Noch keine Bewertungen
- Standalone Financial Results, Limited Review Report For September 30, 2016 (Result)Dokument8 SeitenStandalone Financial Results, Limited Review Report For September 30, 2016 (Result)Shyam SunderNoch keine Bewertungen
- DI Workshop 2Dokument4 SeitenDI Workshop 2Aravinth RameshNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bba2002 2022janDokument4 SeitenBba2002 2022janpsubburajNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ii Pu Statistics QPDokument12 SeitenIi Pu Statistics QPLokesh RaoNoch keine Bewertungen
- LDP 609-Revision Questions. Statistics PDFDokument27 SeitenLDP 609-Revision Questions. Statistics PDFKen MugambiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Gujarat Technological University: InstructionsDokument2 SeitenGujarat Technological University: InstructionsVasim ShaikhNoch keine Bewertungen
- QBDokument34 SeitenQBAadeel NooraniNoch keine Bewertungen
- S1 4 SampleQDokument3 SeitenS1 4 SampleQAzail SumNoch keine Bewertungen
- Monthly Earnings (In 00 RS.) : Month Jan A BDokument2 SeitenMonthly Earnings (In 00 RS.) : Month Jan A BPoulami PrasadNoch keine Bewertungen
- BBA I Sem Information Technology Pratical QPDokument5 SeitenBBA I Sem Information Technology Pratical QPFarheen AsmaNoch keine Bewertungen
- All Semesters PDFDokument92 SeitenAll Semesters PDFkiranNoch keine Bewertungen
- Graphical Representation of Statistical DataDokument56 SeitenGraphical Representation of Statistical Dataxaxif8265100% (5)
- Additonal Mathematics Project Work 2013 Selangor (Project 2)Dokument15 SeitenAdditonal Mathematics Project Work 2013 Selangor (Project 2)farhana_hana_982% (11)
- 2020 AgFood Final ExamDokument3 Seiten2020 AgFood Final ExamSolomiya PikhNoch keine Bewertungen
- Assignment 2 M Eco FDokument5 SeitenAssignment 2 M Eco FRazaRanaNoch keine Bewertungen
- QM Assignment For Section-BDokument1 SeiteQM Assignment For Section-Bsunru24Noch keine Bewertungen
- MBA I Semeste Model Question Papers W.E.F (2011-13) StudentsDokument8 SeitenMBA I Semeste Model Question Papers W.E.F (2011-13) Studentsvikramvsu100% (2)
- 3 Honours Excel Practical ListDokument8 Seiten3 Honours Excel Practical ListBala KrishnaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Introductory Econometrics Midterm Examnation INSTRUCTIONS: - This Is The Open-Book ExamDokument2 SeitenIntroductory Econometrics Midterm Examnation INSTRUCTIONS: - This Is The Open-Book ExamNguyễn Hồng DươngNoch keine Bewertungen
- ExamsDokument74 SeitenExamsSuraj SinghNoch keine Bewertungen
- Statistics-Plural: Refers To Set of Figures. E.g.: Production and Sale of Textiles TV Sets Etc.Dokument20 SeitenStatistics-Plural: Refers To Set of Figures. E.g.: Production and Sale of Textiles TV Sets Etc.kkv_phani_varma5396Noch keine Bewertungen
- Eco401 Midterm Subjective by Adil AlviDokument11 SeitenEco401 Midterm Subjective by Adil AlviMaryam AshrafNoch keine Bewertungen
- Business Statistics L3 Past Paper Series 2 2011Dokument7 SeitenBusiness Statistics L3 Past Paper Series 2 2011Haznetta HowellNoch keine Bewertungen
- Maths EnglishDokument32 SeitenMaths EnglishBhaskar BhaskiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Electronics IndustryDokument2 SeitenElectronics IndustryBhaskar BhaskiNoch keine Bewertungen
- VpdStockStatement2 4 2016Dokument1 SeiteVpdStockStatement2 4 2016Bhaskar BhaskiNoch keine Bewertungen
- New Microsoft Office Word DocumentDokument7 SeitenNew Microsoft Office Word DocumentBhaskar BhaskiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Consumer ElectronicsDokument9 SeitenConsumer ElectronicsBhaskar BhaskiNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1 How Often Do You Visit SHREE HARIPRIYA PVT LTD?: SL No Particulars No of Respondents PercentageDokument12 Seiten1 How Often Do You Visit SHREE HARIPRIYA PVT LTD?: SL No Particulars No of Respondents PercentageBhaskar BhaskiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Search Results: LG Washing Machine Products Ask For It To Be CreatedDokument5 SeitenSearch Results: LG Washing Machine Products Ask For It To Be CreatedBhaskar BhaskiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Edp TedpDokument117 SeitenEdp TedpBhaskar Bhaski100% (1)
- Network: From Wikipedia, The Free Encyclopedia Look Up or in Wiktionary, The Free DictionaryDokument2 SeitenNetwork: From Wikipedia, The Free Encyclopedia Look Up or in Wiktionary, The Free DictionaryBhaskar BhaskiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Theory: CertaintyDokument4 SeitenTheory: CertaintyBhaskar BhaskiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Info at A GlanceDokument2 SeitenInfo at A GlanceBhaskar BhaskiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Serial NumberDokument1 SeiteSerial NumberBhaskar BhaskiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Employee Reponse: YES 45 90 NO 5 10Dokument8 SeitenEmployee Reponse: YES 45 90 NO 5 10Bhaskar BhaskiNoch keine Bewertungen
- KofDokument80 SeitenKofBhaskar Bhaski100% (1)
- AcknowledgementDokument1 SeiteAcknowledgementBhaskar BhaskiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Date DSE Name Customer Name Mob No. Place Model ApplicationDokument2 SeitenDate DSE Name Customer Name Mob No. Place Model ApplicationBhaskar BhaskiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Resume of Kishan Bedre, ChitradurgaDokument1 SeiteResume of Kishan Bedre, ChitradurgaBhaskar BhaskiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Purchasing, Inventory, and Cash Disbursements: Common Frauds and Internal ControlsVon EverandPurchasing, Inventory, and Cash Disbursements: Common Frauds and Internal ControlsBewertung: 5 von 5 Sternen5/5 (1)
- Getting to Yes: How to Negotiate Agreement Without Giving InVon EverandGetting to Yes: How to Negotiate Agreement Without Giving InBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (652)
- I Will Teach You to Be Rich: No Guilt. No Excuses. No B.S. Just a 6-Week Program That Works (Second Edition)Von EverandI Will Teach You to Be Rich: No Guilt. No Excuses. No B.S. Just a 6-Week Program That Works (Second Edition)Bewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (13)
- The Science of Prosperity: How to Attract Wealth, Health, and Happiness Through the Power of Your MindVon EverandThe Science of Prosperity: How to Attract Wealth, Health, and Happiness Through the Power of Your MindBewertung: 5 von 5 Sternen5/5 (231)
- The E-Myth Chief Financial Officer: Why Most Small Businesses Run Out of Money and What to Do About ItVon EverandThe E-Myth Chief Financial Officer: Why Most Small Businesses Run Out of Money and What to Do About ItBewertung: 5 von 5 Sternen5/5 (13)
- A Beginners Guide to QuickBooks Online 2023: A Step-by-Step Guide and Quick Reference for Small Business Owners, Churches, & Nonprofits to Track their Finances and Master QuickBooks OnlineVon EverandA Beginners Guide to QuickBooks Online 2023: A Step-by-Step Guide and Quick Reference for Small Business Owners, Churches, & Nonprofits to Track their Finances and Master QuickBooks OnlineNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Accounting Game: Learn the Basics of Financial Accounting - As Easy as Running a Lemonade Stand (Basics for Entrepreneurs and Small Business Owners)Von EverandThe Accounting Game: Learn the Basics of Financial Accounting - As Easy as Running a Lemonade Stand (Basics for Entrepreneurs and Small Business Owners)Bewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (33)
- The ZERO Percent: Secrets of the United States, the Power of Trust, Nationality, Banking and ZERO TAXES!Von EverandThe ZERO Percent: Secrets of the United States, the Power of Trust, Nationality, Banking and ZERO TAXES!Bewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (14)
- LLC Beginner's Guide: The Most Updated Guide on How to Start, Grow, and Run your Single-Member Limited Liability CompanyVon EverandLLC Beginner's Guide: The Most Updated Guide on How to Start, Grow, and Run your Single-Member Limited Liability CompanyBewertung: 5 von 5 Sternen5/5 (1)
- How to Start a Business: Mastering Small Business, What You Need to Know to Build and Grow It, from Scratch to Launch and How to Deal With LLC Taxes and Accounting (2 in 1)Von EverandHow to Start a Business: Mastering Small Business, What You Need to Know to Build and Grow It, from Scratch to Launch and How to Deal With LLC Taxes and Accounting (2 in 1)Bewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (5)
- Accounting 101: From Calculating Revenues and Profits to Determining Assets and Liabilities, an Essential Guide to Accounting BasicsVon EverandAccounting 101: From Calculating Revenues and Profits to Determining Assets and Liabilities, an Essential Guide to Accounting BasicsBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (7)
- The One-Page Financial Plan: A Simple Way to Be Smart About Your MoneyVon EverandThe One-Page Financial Plan: A Simple Way to Be Smart About Your MoneyBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (37)
- SAP Foreign Currency Revaluation: FAS 52 and GAAP RequirementsVon EverandSAP Foreign Currency Revaluation: FAS 52 and GAAP RequirementsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tax-Free Wealth: How to Build Massive Wealth by Permanently Lowering Your TaxesVon EverandTax-Free Wealth: How to Build Massive Wealth by Permanently Lowering Your TaxesNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Credit Formula: The Guide To Building and Rebuilding Lendable CreditVon EverandThe Credit Formula: The Guide To Building and Rebuilding Lendable CreditBewertung: 5 von 5 Sternen5/5 (1)
- Excel for Beginners 2023: A Step-by-Step and Quick Reference Guide to Master the Fundamentals, Formulas, Functions, & Charts in Excel with Practical Examples | A Complete Excel Shortcuts Cheat SheetVon EverandExcel for Beginners 2023: A Step-by-Step and Quick Reference Guide to Master the Fundamentals, Formulas, Functions, & Charts in Excel with Practical Examples | A Complete Excel Shortcuts Cheat SheetNoch keine Bewertungen
- Finance Basics (HBR 20-Minute Manager Series)Von EverandFinance Basics (HBR 20-Minute Manager Series)Bewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (32)
- How to Measure Anything: Finding the Value of "Intangibles" in BusinessVon EverandHow to Measure Anything: Finding the Value of "Intangibles" in BusinessBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (28)
- Warren Buffett and the Interpretation of Financial Statements: The Search for the Company with a Durable Competitive AdvantageVon EverandWarren Buffett and the Interpretation of Financial Statements: The Search for the Company with a Durable Competitive AdvantageBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (109)
- Controllership: The Work of the Managerial AccountantVon EverandControllership: The Work of the Managerial AccountantNoch keine Bewertungen
- 7 Financial Models for Analysts, Investors and Finance Professionals: Theory and practical tools to help investors analyse businesses using ExcelVon Everand7 Financial Models for Analysts, Investors and Finance Professionals: Theory and practical tools to help investors analyse businesses using ExcelNoch keine Bewertungen
- I'll Make You an Offer You Can't Refuse: Insider Business Tips from a Former Mob Boss (NelsonFree)Von EverandI'll Make You an Offer You Can't Refuse: Insider Business Tips from a Former Mob Boss (NelsonFree)Bewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (24)
- Financial Accounting For Dummies: 2nd EditionVon EverandFinancial Accounting For Dummies: 2nd EditionBewertung: 5 von 5 Sternen5/5 (10)
- Financial Intelligence: A Manager's Guide to Knowing What the Numbers Really MeanVon EverandFinancial Intelligence: A Manager's Guide to Knowing What the Numbers Really MeanBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (79)
- Start, Study and Pass The CPA Exam FAST - Proven 8 Step CPA Exam Study PlaybookVon EverandStart, Study and Pass The CPA Exam FAST - Proven 8 Step CPA Exam Study PlaybookBewertung: 5 von 5 Sternen5/5 (4)