Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
p240w12 Mid1-2
Hochgeladen von
shlaeaOriginalbeschreibung:
Originaltitel
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
p240w12 Mid1-2
Hochgeladen von
shlaeaCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
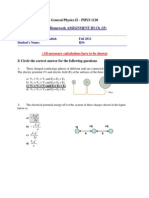
Version 2 Page 1
Form # = version# on bottom of inside page
Physics 240 First Exam Winter 2012
1. Last Name:____________________ First Name:_____________________
2. Please circle your discussion instructor and section below:
Instructor Time Section
David Gidley 9-10 am 100
David Winn 10-11 am 200
3. Special Scantron Instructions:
a) Bubble in UNIQ-NAME in last name field
b) Bubble in 8 digit UM student ID numberthis is critical
c) Bubble in Form #=version# (critical) and section number
d) Print your name in shaded upper right signature box
4. There are 20 multiple choice problems worth 5 points each for a total of 100
points. Choose the one best answer and transfer it to the scantron sheet. You
must mark the correct answer on the scantron sheet to get credit for the
problem. There is no penalty for guessing, so be sure to enter an answer for
every question even if it is just a best guess.
5. At the end of the exam hand in only your scantron to a proctor. Keep your
exam booklet for future reference. Your instructor only sees the scantron so make
sure it has all the correct information.
6. This is a closed book, 90 minute exam. Turn off and put away all electronic
devices. You may use a calculator and one 3x5 note card or equivalent.
k = 1/4
0
=9x10
9
Nm
2
/C
2
0
= 8.85x10
-12
C
2
/Nm
2
e = 1.6x10
-19
C 1 eV= 1.6x10
-19
J
= micro =10
-6
g = 9.8 m/s
2
m
e
= 9.1 x 10
-31
kg M
P
=1.67 x 10
-27
kg
Version 2 Page 2
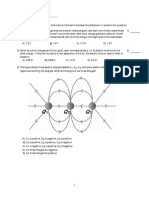
1. Positive charge +Q is uniformly distributed on the upper half of a rod and a negative
charge Q is uniformly distributed on the lower half. What is the direction of force on
an electron placed at point P on the perpendicular bisector.
.
r
+Q
-Q
P
A) zero
B)
+
C)
D)
E)
|
2. A particle with mass m and, charge q is projected with speed v
0
into the region between
two parallel plates as shown. The potential difference between the two plates is V and
their separation is d. The change in kinetic energy of the particle as it traverses this
region is:
A)
B) qV
C)
D) qV
E) none of these
Version 2 Page 3
3. A solid conducting sphere of radius a carries an excess charge of +6 C. This sphere is
located at the center of a hollow conducting sphere with an inner radius b and an outer
radius of c, as shown. The hollow sphere carries zero net charge.
Which one of the following figures shows a qualitatively accurate sketch of the electric
field lines in and around this system? (Hint: each arrow represents the same amount of
electric flux).
A) a
B) b
C) c
D) d
E) e
Version 2 Page 4
4. A hollow conductor is positively charged. A small uncharged metal ball is lowered by a
silk thread through a small opening in the top of the conductor and allowed to touch its
inner surface. After the ball is removed, it will have:
A) a positive charge
B) a negative charge
C) no appreciable charge
D) a charge whose sign depends on what part of the inner surface it touched
E) a charge whose sign depends on where the small hole is located in the conductor
5.
If the electric potential is
2 2 2
( , , )
kq
V x y z
x y z
=
+ +
, then what is the magnitude of the
electric force acting on a particle of charge Q placed at the location (x
0
, y
0
, z
0
) ?
A)
2 2 2
0 0 0
kqQ
x y z + +
B)
0 0 0
2 2 2 3/ 2
0 0 0
( )
( )
kqQ x y z
x y z
+ +
+ +
C)
2 2 2 3/ 2
0 0 0
( )
kqQ
x y z + +
D)
0
kqQ
x
E)
2
0
kqQ
y
Version 2 Page 5
6. How much charge is contained within a cubical volume 2 meters on a side if the electric
field is given (in N/C) by
( , , ) 2 1.5 6 E x y z i j k = + + . The cube is located with one
corner at the origin and with edges along the +x, +y, and +z directions.
(0,0,0) .
(2,2,2)
X
Y
Z
A) 8.5 x 10
-10
C
B) 7.1 x 10
-10
C
C) 2.1 x 10
-9
C
D) 4.2 x 10
-10
C
E) 0 C
7.
An infinitely long line of negative charge (dashed line) with linear charge density =
-6.0 x 10
-9
C/m runs right down the center of a long rectangular solid with square cross
sectional area (each square side is 0.10 m in length). What is the electric flux (in
Nm
2
/C) through the shaded side if it is 3.0 meters long (into page).
A) 5.1 x 10
2
B) 8.5 x 10
1
C) -1.7 x 10
2
D) -1.5 x 10
3
E) 3.4 x 10
2
Version 2 Page 6
8. Two particles have point charges Q and Q (equal magnitude and opposite sign). For a
net forceof zero to be exerted on a third point charge (NOT located at distance) this
third charge must be placed:
-Q +Q
I II III
A) on the dashed perpendicular bisector of the line joining Q and Q
B) in region II on the line joining the charges
C) in region I on the line joining the charges
D) in region III on the line joining the charges
E) at none of these places (there is no place)
9. A large ring with charge Q uniformly distributed around it and with radius 2R is
positioned so that its axis coincides with the axis of a smaller ring of uniform charge q
and radius R. A point on the axis is a distance R from the smaller ring and 2R from the
larger ring as shown. What must Q be such that the electric field at the point due to the
two rings is zero?
R
R 2R
2R
Q
q
A) -2q
B) +2q
C) +q/2
D) +4q
E) -4q
Version 2 Page 7
10. Four identical charges with Q = +1.0 x 10
-6
C are arranged at the corners of a square
with 1 meter sides. If we put a proton at the center of the square and give it just an
infinitesimal displacement out from the plane of the square how much kinetic energy
will the proton have when it is very far from the charges?
Q
Q
Q
Q
A) 3.7 x 10
-9
J
B) zero
C) 2.3 x 10
-4
J
D) 8.4 x 10
-12
J
E) 8.1 x 10
-15
J
11. Two very large, identical, copper metal plates of area A are separated by a uniform,
short distance, x. Neither has any net charge. Then we start to transfer charge from one
plate to the other until an electric potential difference of V exists between the plates.
What is the total charge on the plate with the lower potential? (You can neglect
distortions in the electric field at the edges of the plates.)
A)
0
V A
x
c A
B)
0
V A
x
c A
+
C)
0
Vx
A c
A
+
D) 0
E)
0
Vx
A c
A
Version 2 Page 8
12. A proton is projected into a region where the electric field lines are shown as dashed
arrows in the figure. Which trajectory best describes the path of the proton?
A) A
B) B
C) C
D) D
E) E
13. Three conducting hollow spheres each carry the net charge shown: sphere A has -7 C,
spheres B and C have +9 C and -3 C, respectively. In addition there is a -8 C point
charge at the center. How much charge is on the outer surface of sphere B?
-8C
-7C
+9C
-3C
A B C
A) -6 C
B) 0 C
C) -3 C
D) +6 C
E) +15 C
Version 2 Page 9
14. An electric dipole is held at rest so its dipole moment of 0.10 C-m makes a small angle
of only 2 degrees with a uniform electric field of 400 N/C. If we release the dipole so it
is free to turn with its moment of inertia of I = 0.60 kg-m
2
what is the dipole's
approximate angular frequency of oscillation, , in radians/second?
A) 8.2
B) 3.4
C) 2.2
D) 0.052
E) 0.35
15. What is the electric potential on the z-axis, relative to a zero potential infinitely far away
from the disk?
A)
0
2
Q
V
a t c
=
B)
2
2 2
0 0
2
a
Q rdr
V
a
r z
t c
=
+
}
C)
2 2 2 3/ 2
0 0
2 ( )
a
Q zdr
V
a r z t c
=
+
}
D)
2
2 2
0 0
2
a
Q zdz
V
a
r z
t c
=
+
}
E)
2
0
2
Qz
V
a t c
=
Version 2 Page 10
16. A cylindrically symmetric charge distribution has a volume charge density that depends
on the radial position, r, as follows:
0
( ) (1 )
r
r
a
= , where
0
is the charge density at
the central axis and "a" is just a size constant. What is the electric field at r = 2a? (For
direction + means out along radius and - means in along radius.)
A)
0
0
6
a
c
+
B)
0
0
3
a
c
C)
0
0
4
a
c
+
D) 0
E)
0
0
2
a
c
Version 2 Page 11
17. What is the x-component of the electric field at point P a distance R out on the
perpendicular from one end of a uniformly negatively charged rod of length L and
charge -Q?
L
P
R
- - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - -
x
A)
2 2
0
L
kQ dx
L x R +
}
B)
2 2
0
L
kQ xdx
L
x R
+
}
C)
2 2 3/ 2
0
( )
L
kQ xdx
L x R +
}
D)
2 2
0
L
kQ Rdx
L
x R +
}
E)
2 2 3/ 2
0
( )
L
kQ xdx
L x R
+
}
Version 2 Page 12
18. Two conducting spheres, one having three times the diameter of the other (labelled 1
and 3), are separated by a distance that is very large compared to their diameters.
Initially, the smaller sphere (1) is uncharged and the larger sphere (3) has charge Q. The
spheres are then connected by a long conducting wire and this two-sphere conductor
system is allowed to reach equilibrium. (The charge on the conducting wire is
negligible). What is the ratio of electric field magnitudes just immediately above each
sphere's surface, E
3
/E
1
?
3
1
A) 1
B) 1/3
C) 9
D) 3
E) 2/3
19. Charge Q is distributed uniformly throughout a spherical insulator of radius R. What
is the potential at the center of the insulator relative to zero an infinite distance away?
A)
0
16
Q
V
R tc
=
B) V=0
C)
0
8
Q
V
R tc
=
D)
0
3
8
Q
V
R tc
=
E)
0
3
16
Q
V
R tc
=
Version 2 Page 13
20. Two charged particles of identical mass, m, and charge, Q, are fired straight at each
other from a great distance. One particle has initial velocity v, while the second
particle has initial velocity of 5v. How close will they come to each other, i.e. what is
their minimum separation? Here, k is the Coulomb constant.
A)
2
2
3kQ
mv
B)
2
2
9
kQ
mv
C)
2
2
3
kQ
mv
D)
2
kQ
mv
E)
2
2
3
13
kQ
mv
Version 2 Page 14
Answer Key
1. E
2. D
3. C
4. C
5. A
6. E
7. A
8. E
9. D
10. E
11. A
12. A
13. A
14. A
15. B
16. B
17. C
18. B
19. D
20. B
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Electron Beam-Specimen Interactions and Simulation Methods in MicroscopyVon EverandElectron Beam-Specimen Interactions and Simulation Methods in MicroscopyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Practice Exam - 1 + Answers Winn F10Dokument13 SeitenPractice Exam - 1 + Answers Winn F10Billy PozehlNoch keine Bewertungen
- Practice Questions Chs 21-24 1Dokument40 SeitenPractice Questions Chs 21-24 1jevanjunior0% (1)
- Test1 16FDokument8 SeitenTest1 16FJasper LuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Previous Exams Questions Ch23-24-With NotesDokument11 SeitenPrevious Exams Questions Ch23-24-With NotesaamerbolookiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Classroom Assignment 3 With AnswersDokument3 SeitenClassroom Assignment 3 With AnswersBishoy EmileNoch keine Bewertungen
- PG Brainstormer - 1 H (Electromagneticsm)Dokument6 SeitenPG Brainstormer - 1 H (Electromagneticsm)Harsh VardhanNoch keine Bewertungen
- 07 08 II ms1Dokument5 Seiten07 08 II ms1Mahmoud FariedNoch keine Bewertungen
- 07 08 I FinalDokument9 Seiten07 08 I FinalMahmoud FariedNoch keine Bewertungen
- W2016 PHYS259 Final Booklet I AnswersDokument12 SeitenW2016 PHYS259 Final Booklet I AnswersYasmeenNoch keine Bewertungen
- Prac FinaleDokument14 SeitenPrac FinaleadadafasfasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Two Small Spheres in MotionDokument12 SeitenTwo Small Spheres in MotionharshanauocNoch keine Bewertungen
- Physics 1653 Exam 3 - Review Questions: Sphere A Sphere BDokument39 SeitenPhysics 1653 Exam 3 - Review Questions: Sphere A Sphere BPi PoliNoch keine Bewertungen
- 3 Soln Practice Assignment Ch25Dokument7 Seiten3 Soln Practice Assignment Ch25Eng MohammedNoch keine Bewertungen
- Emf Gate QuestionsDokument6 SeitenEmf Gate QuestionsvijaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Physics 220 Homework: Spring 2008Dokument27 SeitenPhysics 220 Homework: Spring 2008Jeff Pratt100% (1)
- PhysicsDokument17 SeitenPhysicspaninikumar0000Noch keine Bewertungen
- Phys 272 Final Exam PracticeDokument16 SeitenPhys 272 Final Exam Practiceheehee2010Noch keine Bewertungen
- Electrostatic 1 Shot DPP 1Dokument8 SeitenElectrostatic 1 Shot DPP 1Ayush JainNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bài tập VL2 CLCDokument12 SeitenBài tập VL2 CLCbnthanh2209Noch keine Bewertungen
- Electrostatics ExerciseDokument20 SeitenElectrostatics ExerciseUtkarsh Mittal86% (7)
- Electric Potential Capacitance Multiple Choice 2014-03-13Dokument14 SeitenElectric Potential Capacitance Multiple Choice 2014-03-13Zeeshan sharifNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2019 PHY 2 CLC BTapDokument15 Seiten2019 PHY 2 CLC BTapzuuuNoch keine Bewertungen
- 111年下A卷題庫Dokument10 Seiten111年下A卷題庫陳奕安Noch keine Bewertungen
- Final Exam 259 Answer KeyDokument20 SeitenFinal Exam 259 Answer KeyYasmeenNoch keine Bewertungen
- Final ExamA1Dokument3 SeitenFinal ExamA1LÂN HỒ THANHNoch keine Bewertungen
- E1a 121 s06txtDokument4 SeitenE1a 121 s06txtBob TheBuilderNoch keine Bewertungen
- In Your Name Where Indicated in The Upper Right Corner Then (2) Do The Same With YourDokument12 SeitenIn Your Name Where Indicated in The Upper Right Corner Then (2) Do The Same With YouradadafasfasNoch keine Bewertungen
- 10 Electrostaticsand Electric FieldsDokument14 Seiten10 Electrostaticsand Electric Fieldssteve223255313251Noch keine Bewertungen
- Https Attachment - Fbsbx.com File DownloadDokument22 SeitenHttps Attachment - Fbsbx.com File DownloadSoham ChatterjeeNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2021 PHY2 CLC Problems BaitapDokument13 Seiten2021 PHY2 CLC Problems BaitapThinh Nguyen100% (1)
- Previous Exams Questions Ch21-22-With NotesDokument7 SeitenPrevious Exams Questions Ch21-22-With NotesaamerbolookiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Electrostatics Type 2 PART 2 of 3 ENGDokument20 SeitenElectrostatics Type 2 PART 2 of 3 ENGSubhashChandraMishraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Electrostatics Assignment: Gravity ClassesDokument6 SeitenElectrostatics Assignment: Gravity Classesjagan9912342495Noch keine Bewertungen
- Major Test 4 2015-16 Paper 1Dokument24 SeitenMajor Test 4 2015-16 Paper 1Sarvesh DubeyNoch keine Bewertungen
- JEE ADV and ManisDokument14 SeitenJEE ADV and Manisbrm1shubhaNoch keine Bewertungen
- DR - Hannan Saadeh Solved Problems PDFDokument50 SeitenDR - Hannan Saadeh Solved Problems PDFAbdNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 21: Electric Charge and Electric FieldDokument30 SeitenChapter 21: Electric Charge and Electric FieldNguyễn Ngoc AnhNoch keine Bewertungen
- Physics 72: University of The PhilippinesDokument14 SeitenPhysics 72: University of The PhilippinesVic Nelson LuceroNoch keine Bewertungen
- Electrostatics Solved QBPDFDokument75 SeitenElectrostatics Solved QBPDFMohammed Aftab AhmedNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ch22 SSM-1Dokument31 SeitenCh22 SSM-1alyxs_1Noch keine Bewertungen
- Physics Electrostatics MCQDokument8 SeitenPhysics Electrostatics MCQSrijan Chakraborty100% (1)
- Unit-5 QMDokument7 SeitenUnit-5 QMMANIVANNAN MNoch keine Bewertungen
- ElectrostaticsDokument39 SeitenElectrostaticsanon_9323536550% (1)
- Electrostatics ProblemsDokument2 SeitenElectrostatics Problemsquasar2138Noch keine Bewertungen
- Review Test 1314Dokument11 SeitenReview Test 1314Hassan AliNoch keine Bewertungen
- Phys2 Midterm Exam F2019 20 With NotesDokument12 SeitenPhys2 Midterm Exam F2019 20 With NotesaamerbolookiNoch keine Bewertungen
- WORKSHEET12Dokument8 SeitenWORKSHEET12Anfeli JamesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Practice Midterm 1.2 v2Dokument5 SeitenPractice Midterm 1.2 v2golemisgreeaaaatNoch keine Bewertungen
- Electromagnetic Wave ExerciseDokument10 SeitenElectromagnetic Wave ExerciseAnkit VatsaNoch keine Bewertungen
- PHYS 259 W2017 - Final ExamDokument19 SeitenPHYS 259 W2017 - Final ExamYasmeenNoch keine Bewertungen
- JEE Main Solved Paper 2010Dokument24 SeitenJEE Main Solved Paper 2010chithrasajeevNoch keine Bewertungen
- MOS Integrated Circuit DesignVon EverandMOS Integrated Circuit DesignE. WolfendaleNoch keine Bewertungen
- Electricity and Magnetism: Problems in Undergraduate PhysicsVon EverandElectricity and Magnetism: Problems in Undergraduate PhysicsBewertung: 5 von 5 Sternen5/5 (1)
- Feynman Lectures Simplified 2C: Electromagnetism: in Relativity & in Dense MatterVon EverandFeynman Lectures Simplified 2C: Electromagnetism: in Relativity & in Dense MatterNoch keine Bewertungen
- Interactions between Electromagnetic Fields and Matter: Vieweg Tracts in Pure and Applied PhysicsVon EverandInteractions between Electromagnetic Fields and Matter: Vieweg Tracts in Pure and Applied PhysicsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Vacuum Nanoelectronic Devices: Novel Electron Sources and ApplicationsVon EverandVacuum Nanoelectronic Devices: Novel Electron Sources and ApplicationsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Piezoelectric Sensors & Actuators: MECH 466 Microelectromechanical SystemsDokument15 SeitenPiezoelectric Sensors & Actuators: MECH 466 Microelectromechanical SystemsSanjay LahareNoch keine Bewertungen
- Electric Fields: Coulomb's LawDokument7 SeitenElectric Fields: Coulomb's LawMax TennerNoch keine Bewertungen
- EMW - Module - 2Dokument47 SeitenEMW - Module - 2ROHITH MYSURUNoch keine Bewertungen
- Physics DPP 1Dokument1 SeitePhysics DPP 1Crazy iitphysicsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Quest Review 4 Electric Force, Magnetic Fields KEYDokument16 SeitenQuest Review 4 Electric Force, Magnetic Fields KEYJ PNoch keine Bewertungen
- eALOM General Chemistry PDFDokument128 SeiteneALOM General Chemistry PDFHARRY POTTERNoch keine Bewertungen
- Atom Inside Out DLPDokument6 SeitenAtom Inside Out DLPJohn Bernard Rili100% (1)
- 58714.Đề tuyển sinh đề số 1Dokument9 Seiten58714.Đề tuyển sinh đề số 1Nguyễn Hoàng NamNoch keine Bewertungen
- Introduction To ElectricityDokument12 SeitenIntroduction To ElectricityRomel PanisNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mechanism of HeatingDokument1 SeiteMechanism of HeatingManish PrasadNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ch-1 Basic Elctrical Enginnering Paramters RevisedDokument39 SeitenCh-1 Basic Elctrical Enginnering Paramters Revisedtemesgen adugnaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Physics Electrostatics 2Dokument55 SeitenPhysics Electrostatics 2kishore_subrama3240Noch keine Bewertungen
- Coulombs Charges and Field Multiple QuestionsDokument9 SeitenCoulombs Charges and Field Multiple QuestionsjitenhrtNoch keine Bewertungen
- 21 Magnetic Forces and FieldsDokument11 Seiten21 Magnetic Forces and Fieldssoe0303Noch keine Bewertungen
- Electricity - Part 1Dokument21 SeitenElectricity - Part 1Anonymous CommentatorNoch keine Bewertungen
- Newsletter 79 EngDokument12 SeitenNewsletter 79 EngMahmoud Al HomranNoch keine Bewertungen
- PH MiracleDokument272 SeitenPH MiracleNeomorpheous90Noch keine Bewertungen
- Fine Structure Constant and The Golden SectionDokument37 SeitenFine Structure Constant and The Golden SectionRaskoJovanovicNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 3 Outline Atoms: The Building Blocks of Matter ChapterDokument5 SeitenChapter 3 Outline Atoms: The Building Blocks of Matter ChapterTomás Monzón100% (1)
- PythonDokument12 SeitenPythonprakhar jaiswalNoch keine Bewertungen
- What Is The Relation Between Electric Field and Drift Velocity PDFDokument2 SeitenWhat Is The Relation Between Electric Field and Drift Velocity PDFLeon MathaiosNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1.current ElectricityDokument147 Seiten1.current ElectricityYogy YNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 11 Static Electricity ReviewDokument2 SeitenChapter 11 Static Electricity ReviewjohnsmithNoch keine Bewertungen
- Interactive Textbook 2 PDF 4 2 AtomsDokument9 SeitenInteractive Textbook 2 PDF 4 2 Atomsapi-240094705100% (1)
- Laboratory REPORT Physics Electric FieldDokument4 SeitenLaboratory REPORT Physics Electric FieldAishah Yahya33% (3)
- Electrostatics: Related StoriesDokument12 SeitenElectrostatics: Related StoriesmadhurNoch keine Bewertungen
- Question 2 - Kam Eu Siang (Chinese & English)Dokument1 SeiteQuestion 2 - Kam Eu Siang (Chinese & English)2012PhCNoch keine Bewertungen
- Subatomic Particles of AtomsDokument8 SeitenSubatomic Particles of AtomsRose Ann Marie BabiaNoch keine Bewertungen
- ScienceDokument15 SeitenScienceJezz Betiz VergaraNoch keine Bewertungen
- EMI Chapter4 p1Dokument42 SeitenEMI Chapter4 p1Riaz Ahmad0% (1)