Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
BS 2779-1986 Ó ÖÆ ÇÃÜ Â ÜÂÝÎÆ (BSP)
Hochgeladen von
Vaibhav ShuklaOriginalbeschreibung:
Originaltitel
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
BS 2779-1986 Ó ÖÆ ÇÃÜ Â ÜÂÝÎÆ (BSP)
Hochgeladen von
Vaibhav ShuklaCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
BRITISH STANDARD
BS 2779:1986
Specification for
Licensed Copy: AUB User, na, Sun Mar 25 13:38:08 GMT+00:00 2007, Uncontrolled Copy, (c) BSI
Pipe threads for tubes and fittings where pressure-tight joints are not made on the threads (metric dimensions)
UDC 621.643.414:621.882.082.1
BS 2779:1986
Committees responsible for this British Standard
This British Standard was entrusted by the Piping Systems Components Standards Committee (PSE/-) to Technical Committee PSE/9, upon which the following bodies were represented: Association of Hydraulic Equipment Manufacturers British Compressed Air Society British Engine Group of the Society of Motor Manufacturers and Traders British Gas Corporation British Hydromechanics Research Association British Malleable Tube Fittings Association British Steel Industry British Valve Manufacturers Association Ltd. Copper Tube Fittings Manufacturers Association Department of Trade and Industry (National Engineering Laboratory) Energy Industries Council Engineering Equipment and Materials Users Association Gauge and Tool Makers Association Institution of Civil Engineers Institution of Gas Engineers Institution of Public Health Engineers Institution of Water Engineers and Scientists Water Authorities Association Water Companies Association Wrought Fitting Makers Association
Licensed Copy: AUB User, na, Sun Mar 25 13:38:08 GMT+00:00 2007, Uncontrolled Copy, (c) BSI
This British Standard, having been prepared under the direction of the Piping Systems Components Standards Committee, was published under the authority of the Board of BSI and comes into effect on 29 August 1986 BSI 12-1998 First published December 1956 First revision April 1973 Second revision August 1986 The following BSI references relate to the work on this standard: Committee reference PSE/9 Draft for comment 85/75381 DC ISBN 0 580 15212 X
Amendments issued since publication Amd. No. Date of issue Comments
BS 2779:1986
Contents
Committees responsible Foreword Page Inside front cover ii 1 1 1 4 5 5 6 8 4 5 7 8 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 3 5 9 10 11 13 14
Licensed Copy: AUB User, na, Sun Mar 25 13:38:08 GMT+00:00 2007, Uncontrolled Copy, (c) BSI
1 2 3 4
Scope Symbols Classification and designation Thread details
Appendix A Special truncated form of the Whitworth thread for class A external threads Appendix B Notes on tolerancing system structure Appendix C Method of verification of thread size and form by means of limit gauges Appendix D Gauges for the method given in appendix C Figure 1 Thread profile and tolerance zones Figure 2 Special truncated external thread Figure 3 NOT GO screw calliper gauge Figure 4 Start of complete thread Figure 5 Chamfer of start of thread Figure 6 Thread profiles of GO ring gauges and their check plugs Figure 7 Relative positions of pitch diameter tolerance zones for GO ring gauges and their check plugs Figure 8 Thread profiles of NOT GO ring gauges and their check plugs and calliper gauges Figure 9 Relative positions of pitch diameter tolerance zones for NOT GO ring gauges, calliper gauges and their check plugs Figure 10 Thread profiles of Go and NOT GO plug gauges Figure 11 Relative positions of pitch diameter tolerance zones for GO and NOT GO plug gauges Table 1 Basic dimensions and tolerances Table 2 Special truncated fastening threads, class A external threads Table 3 Dimensions for GO and NOT GO gauges and their check plugs for class A external threads and for GO gauges and their check plugs for class B external threads Table 4 Other values for GO and NOT GO gauges and their check plugs for class A and class B external threads as a function of the pitch, P Table 5 Dimensions for NOT GO gauges and their check plugs for class B external threads Table 6 Dimensions for threaded GO and NOT GO plug gauges Table 7 Other values for GO and NOT GO plug gauges as a function of the pitch, P Publications referred to
Inside back cover
BSI 12-1998
BS 2779:1986
Foreword
This revision of BS 2779 has been prepared under the direction of the Piping Systems Components Standards Committee. It supersedes BS 2779:1973, which is withdrawn. This standard is based on and is technically equivalent to the two Parts of ISO 228 Pipe threads where pressure-tight joints are not made on the threads, namely ISO 228/1-1982 Designation, dimensions and tolerances, and ISO/2-1980 Verification by means of limit gauges; both Parts are published by the International Organization for Standardization (ISO). This standard provides a range of thread sizes which are considered to be necessary to fulfil general requirements. Dimensions are given in metric units only. For ease of production, it has been found convenient to reproduce the figures from ISO 228/2-1980 for Figure 4, Figure 5, Figure 7, Figure 10 and Figure 11 of this standard. A British Standard does not purport to include all the necessary provisions of a contract. Users of British Standards are responsible for their correct application. Compliance with a British Standard does not of itself confer immunity from legal obligations.
Licensed Copy: AUB User, na, Sun Mar 25 13:38:08 GMT+00:00 2007, Uncontrolled Copy, (c) BSI
Summary of pages This document comprises a front cover, an inside front cover pages i and ii, pages 1 to 14, an inside back cover and a back cover. This standerd has been updated (see copyright date) and may have had amendments incorporated. This will be indicated in the amendment table on the inside front cover. ii
BSI 12-1998
BS 2779:1986
1 Scope Licensed Copy: AUB User, na, Sun Mar 25 13:38:08 GMT+00:00 2007, Uncontrolled Copy, (c) BSI
This British Standard specifies requirements for the designation and dimensions of Whitworth form Td fastening pipe threads having a thread size designation in the range 1/16 to 6 inclusive. This standard applies to pipe threads where Td2 pressure-tight joints are not made on the threads1). Dimensions are given in metric units. The tolerance TD1 on the crests of the threads allows for truncation (see 4.1). TD,2
NOTE 1 The pipe threads covered by this standard are generally used for fastening purposes, such as the mechanical assembly of the component parts of fittings, cocks and valves, etc. NOTE 2 The titles of the publications referred to in this standard are listed on the inside back cover.
Tcp
TPL TR u WGO WNG ZPL ZR
2 Symbols
For the purposes of this British Standard, the following symbols apply.
Symbol Term
b3 d d1 d2 D D1 D2 h H m
Width of clearance groove at the major and minor diameter of the thread profile with shortened flanks. Basic major diameter of the external thread. Basic minor diameter of the external thread (d1 = d 1.280 654P).
Basic major diameter of the internal thread (D = d). Basic minor diameter of the internal thread (D1 = D 1.280 654P = d1).
Basic pitch diameter of the external thread (d2 = d 0.640 327 P).
Tolerance on the pitch diameter of GO and NOT GO threaded check plugs and wear check plugs. Tolerance on the basic major diameter of the external thread. Tolerance on the basic pitch diameter of the external thread. Tolerance on the basic minor diameter of the internal thread. Tolerance on the basic pitch diameter of the internal thread. Tolerance on the pitch diameter of GO and NOT GO threaded plug gauges. Tolerance on the pitch diameter of GO and NOT GO threaded ring gauges. A length equal to twice the radial height of rounding at crest of root and thread (u = 0.147 84P). Average amount available for the permissible wear of GO threaded plug gauge and GO threaded ring gauge. Average amount available for the permissible wear of NOT GO threaded plug gauge and NOT GO threaded ring gauge. Distance between the middle of the tolerance zone TPL of the GO threaded plug gauge and the lower limit of the thread. Distance between the middle of the tolerance zone TR of the GO threaded ring gauge and the upper limit of the thread.
3 Classification and designation
3.1 Classes of external and internal threads For internal threads, one class of tolerance on the pitch diameter has been provided. For external threads, two classes of tolerance on the pitch diameter have been established, as follows: a) class A tolerance, entirely negative value equivalent to the internal thread tolerance (see Table 1); b) class B tolerance, entirely negative value twice that of the class A tolerance (see Table 1).
NOTE 1 Where no class reference is stated, class B should be assumed. NOTE 2 The tolerance zones are shown in Figure 1. NOTE 3 The choice of fit for a particular purpose rests with the purchasers designer.
Basic pitch diameter of the internal thread (D2 = D 0.640 327P = d2). Height of the thread profile with rounded crests and roots. Height of the triangle of the thread profile. Distance between the middle of the tolerance zone TR of the threaded ring gauge and the middle of the tolerance zone TCP of the GO check plug. Pitch. Radius of rounded crests and roots. Displacement of the clearance groove with shortened flanks. Tolerance on b3.
P r s S
1)
Reference should be made to BS 21 for requirements for pipe threads where pressure-tight joints are made on the threads.
BSI 12-1998
BS 2779:1986
3.2 Designation Internal and external threads shall be designated by the letter G followed by the thread size designation given in Table 1, and, for external threads, the class reference: for example, G for an internal thread, G A for a class A external thread, and G B for a class B external thread.
NOTE Where no class reference is stated, class B should be assumed.
Licensed Copy: AUB User, na, Sun Mar 25 13:38:08 GMT+00:00 2007, Uncontrolled Copy, (c) BSI
Where threads are full form (see 4.1.2), the letter F shall be added to the designation, e.g. G F for internal threads and G AF for class A external threads. Where external threads have the special truncated Whit-worth form in accordance with Table 2, the letter T shall be added to the designation, e.g. G AT.
BSI 12-1998
Licensed Copy: AUB User, na, Sun Mar 25 13:38:08 GMT+00:00 2007, Uncontrolled Copy, (c) BSI
Table 1 Basic dimensions and tolerances
2 Number of Thread size threads designation in 25.4 mm 1 3 Pitch 4 Depth of thread, h mm 5 6 Basic diameters 7 8 9 10 11
b
BSI 12-1998
12
Tolerances on the basic pitch diameter Internal thread, TD2 Lower deviation mm Upper deviation
13 14 15 16 Tolerance on the Tolerance on the basic basic minor diameter major diameter Internal thread, TD1 Lower deviation Upper deviation External thread, Td Lower deviation Upper deviation
External thread, Td2 Lower Lower Upper deviation, deviation, deviation class A class B mm mm mm
P
a1 a1
Major d=D mm
Pitch d2 = D 2 mm
Minor d1= D1 mm
/16 /8
28 28 19 19 14 14 14 14 11 11 11 11 11 11 11 11 11 11 11 11 11 11 11 11 sizes.
0.907 0.581
mm
7.723 9.728
7.142 9.147
6.561 0 8.566 0
+ 0.107
mm
0.107
0.214
0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
mm
+ 0.282
mm
0.214
mm
0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
mm
0.907 0.581 1.337 0.856 1.337 0.856 1.814 1.162 1.814 1.162 1.814 1.162 1.814 1.162 2.309 1.479 2.309 1.479 2.309 1.479 2.309 1.479 2.309 1.479 2.309 1.479 2.309 1.479 2.309 1.479 2.309 1.479 2.309 1.479 2.309 1.479 2.309 1.479 2.309 1.479 2.309 1.479 2.309 1.479 2.309 1.479
+ 0.107 + 0.125 + 0.125 + 0.142 + 0.142 + 0.142 + 0.142 + 0.180 + 0.180 + 0.180 + 0.180 + 0.180 + 0.180 + 0.217 + 0.217 + 0.217 + 0.217 + 0.217 + 0.217 + 0.217 + 0.217 + 0.217 + 0.217
0.107 0.125 0.125 0.142 0.142 0.142 0.142 0.180 0.180 0.180 0.180 0.180 0.180 0.217 0.217 0.217 0.217 0.217 0.217 0.217 0.217 0.217 0.217
0.214 0.250 0.250 0.284 0.284 0.284 0.284 0.360 0.360 0.360 0.360 0.360 0.360 0.434 0.434 0.434 0.434 0.434 0.434 0.434 0.434 0.434 0.434
0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
+ 0.282 + 0.445 + 0.445 + 0.541 + 0.541 + 0.541 + 0.541 + 0.640 + 0.640 + 0.640 + 0.640 + 0.640 + 0.640 + 0.640 + 0.640 + 0.640 + 0.640 + 0.640 + 0.640 + 0.640 + 0.640 + 0.640 + 0.640
0.214 0.250 0.250 0.284 0.284 0.284 0.284 0.360 0.360 0.360 0.360 0.360 0.360 0.434 0.434 0.434 0.434 0.434 0.434 0.434 0.434 0.434 0.434
a1/ 4 a3/ 8 a1 5 a3
13.157 16.662 20.955 22.911 26.441 30.201 33.249 37.897 41.910 47.803 53.746 59.614 65.710 75.184 81.534 87.884 100.330
12.301 15.806 19.793 21.749 25.279 29.039 31.770 36.418 40.431 46.324 52.267 58.135 64.231 73.705 80.055 86.405 98.851
11.445 0 14.950 0 18.631 0 20.587 0 24.117 0 27.877 0 30.291 0 34.939 0 38.952 0 44.845 0 50.788 0 56.656 0 62.752 0 72.226 0 78.576 0 84.926 0 97.372 0
/2
/8 /8
7 a
/4
1 /8 a11/ 4 a 1 1 / 13/4
a2 a a21/ 4
1 2 /2
3 2 /4
a3 a
1 3 /2 4 41/2
a
113.030 111.551 110.072 0 125.730 124.251 122.772 0 138.430 136.951 135.472 0 151.130 149.651 148.172 0 163.830 162.351 160.872 0
BS 2779:1986
5 51/
a6
a Preferred b For
thin walled parts, the tolerances on pitch diameters apply to the mean pitch diameter, which is the arithmetical mean of twodiameters measured at right angles to each other.
BS 2779:1986
4 Thread details
4.1 Form of thread
4.3 Compliance
NOTE No method is specified for verification of compliance with the requirements o f 4.1 and 4.2, but the method described in appendix C, using the gauges described in appendix D, is recommended.
Licensed Copy: AUB User, na, Sun Mar 25 13:38:08 GMT+00:00 2007, Uncontrolled Copy, (c) BSI
information on the tolerancing system structure. Tolerance zones are shown in Figure 1. NOTE 2 The tolerances for the basic pitch diameter of internal threads given in Table 1 correspond to the positive deviation of the tolerances on the diameter specified in BS 21, with the exception of the tolerances for the following thread size designations, for which slightly higher tolerances have been specified: 1/16, 1/8, 1/4, 3/8, 21/2, 3, 4, 5, and 6.
If tested in accordance with appendices C and D, the threads shall be deemed to comply with the standard if they are in accordance with the 4.1.2 For internal threads, the crests of the thread following. shall have one of the following forms: a) For external threads: a) the full form, as shown in Figure 1; or 1) with the solid threaded GO ring gauge, the b) the truncated form, with crests truncated to gauge shall pass over the whole length of the the tolerances given in Table 1. thread; NOTE The form of thread should be agreed between the manufacturer and the purchaser. 2) with the NOT GO screw calliper gauge, at any position, the gauge shall not pass over a 4.1.3 For external threads, the crests of the thread threaded part, except for the first two threads shall have one of the following forms: of the part thread; a) the full form, as shown in Figure 1; or 3) with the solid threaded NOT GO ring gauge, b) the truncated form, with crests truncated to using either side of the gauge, it shall not be the tolerances given in Table 1; or possible to screw the gauge on to the thread by c) for class A threads only, the special truncated more than two turns of thread. In addition, the form, in accordance with appendix A. gauge shall not pass completely over a NOTE The special truncated form of thread is used where threaded part having a length of three threads galling of the threads may occur. or less. 4.2 Dimensions and tolerances b) For internal threads: 4.2.1 Dimensions. The basic dimensions for the 1) with the threaded GO plug gauge, the gauge threads shall be as given i n Table 1, except for class shall pass through the whole length of the A external threads with the special truncated form thread; [see 4.1.3 c)]. 2) with the threaded NOT GO plug gauge, the 4.2.2 Tolerances. Tolerances for the major, pitch and gauge shall not enter either end of the thread minor diameters shall be as given n i Table 1, except by more than two turns of thread. In addition, for class A external threads with the special the gauge shall not pass completely through a truncated form [see 4.1.3 c)]. threaded part with a length of three threads or NOTE 1 Reference should be made to appendix B for further less.
NOTE This form is identical with that specified for the parallel thread in BS 21.
4.1.1 The basic form of the thread shall be the basic Whitworth form, as shown in Figure 1.
Figure 1 Thread profile and tolerance zones 4
BSI 12-1998
BS 2779:1986
Appendix A Special truncated form of the Whitworth thread for class A external threads Licensed Copy: AUB User, na, Sun Mar 25 13:38:08 GMT+00:00 2007, Uncontrolled Copy, (c) BSI
The dimensions of the special truncated Whitworth form shall be in accordance with Table 2. The thread form shall be as shown in Figure 2.
NOTE 1 These threads should only be supplied when specified on a component drawing. NOTE 2 In the truncated Whitworth form of external thread, the basic rounded crest at the major diameter is removed at the junction with the straight flanks of the basic thread form. This reduction from the basic major diameter is equal to 0.147 84P (see Figure 2). The resulting flat crest of the thread is given a suitable manufacturing tolerance.
Lengths of engagement are not specified; these will depend upon the application. However, for long lengths of engagement (e.g. more tha n 15 pitches), it is essential that care be taken to ensure that there is not excessive deviation from the pitch, roundness or straightness of the threads, particularly when using class A external threads.
Table 2 Special truncated fastening threads, class A external threads
1 2 Number of threads in 25.4 mm 3 4 5 External thread major diameter
Thread size designation
maximum tolerance minimum mm mm mm
1 1
/16 /8
28 28 19 19 14 14 14 14 11 11
7.590 9.594 12.959 16.464 20.686 22.642 26.172 29.931 32.908 41.570
0.122 0.122 0.144 0.144 0.170 0.170 0.170 0.170 0.198 0.198
7.468 9.472 12.815 16.320 20.516 22.472 26.002 29.761 32.710 41.372 Figure 2 Special truncated external thread
1/ 4 3/ 8 1/ 2 5/ 8 3 7
/4 /8
1
Tolerances are not specified for the minor diameters of external threads nor for the major diameters of internal threads. In practice, these diameters will 1 11 47.462 0.198 47.264 1 /2 be controlled by the profiles of the tools used to cut the threads. The minor diameter of external threads Appendix B Notes on tolerancing should not be greater than the basic minor system structure diameter, while the major diameter of internal In Table 1, the pitch diameter tolerances, which are threads should not be smaller than the basic major intended to include the diametral effect of pitch and diameter. angle errors, have been calculated from the general It should be noted that the internal thread minor diameter tolerances are such as to permit a tapping formula: 0.0625 multiplied by the deviation on the drill of ample size to be used. If full advantage is internal thread length of BS 21. Thus: taken of these generous minor diameter tolerances, a) the positive deviation of internal the crests of the internal threads will be flat. It threads = + 0.0625 length deviation; should also be noted that the external thread major b) the negative deviation of class A external diameter tolerances are generally such as to permit threads = 0.0625 length deviation; crests which do not have a complete radius. c) the negative deviation of class B external threads = 0.125 length deviation. 1 /4
BSI 12-1998
BS 2779:1986
Licensed Copy: AUB User, na, Sun Mar 25 13:38:08 GMT+00:00 2007, Uncontrolled Copy, (c) BSI
Errors in the pitch and flank angles of a thread virtually increase the pitch diameter of an external thread and decrease the pitch diameter of an internal thread. The minimum material limits stated in Table 1 and Table 2 apply to the simple pitch diameter (as measured along the pitch line of the thread); the maximum material limits apply to the pitch diameter as virtually increased (for external threads) or decreased (for internal threads) by the diametral equivalents of any errors present in the flank angles and in the pitch over the length of engagement. For thin-walled parts, the tolerances on pitch diameters apply to the mean pitch diameter, which is the arithmetical mean of two diameters measured at right angles to each other.
C.1.2 Gauges. The gauges shall be in accordance with appendix D. Since the 55 profile has different elements to be verified, it is necessary to provide for several GO and NOT GO gauges. C.1.3 Control of solid threaded ring gauges C.1.3.1 New gauges. Check the GO and NOT GO ring gauges with the GO check plug (see D.2.1.2 and D.2.2.2.1) of the appropriate size, by attempting to screw the check plug, by hand and without using excessive force, through the gauge. Check that the check plug will pass completely through the ring gauge. Check that the maximum size of the pitch diameter of the ring gauge is not exceeded, either using the NOT GO check plug (see D.2.1.2 and D.2.2.2.1) or by some other method. If theNOT GO check plug is used, attempt to screw the appropriate check plug, by hand and without using excessive force, into both ends of the gauge. Remove the check plug, counting the turns of thread, and ensure that the check plug has not engaged the ring gauge by more than one turn. Record the number of turns of thread. C.1.3.2 Checking for wear. Check the GO and NOT GO ring gauges regularly with the appropriate wear check plug (see D.2.1.2 and D.2.2.2.1). Attempt to screw the wear check plug, by hand and without using excessive force, into both ends of the gauge. Remove the check plug, counting the turns of thread, and ensure that the check plug has not engaged the ring gauge by more than one turn. Record the number of turns of thread. C.1.4 Procedure for gauging threads C.1.4.1 Solid threaded GO ring gauge. Without using excessive force, attempt to screw the gauge by hand over the whole length of the thread. C.1.4.2 Solid threaded NOT GO ring gauge. Without using excessive force and using either side of the gauge, screw the gauge by hand on to the thread for as many turns as possible. Unscrew the gauge and record the number of turns engaged. C.1.4.3 NOT GO screw calliper gauge C.1.4.3.1 Setting the gauge. Use the setting plug appropriate to the gauge in use to set the anvils of the gauge. Attempt to pass the gauge over the plug, under its own weight or under a fixed load.
NOTE The gauge may be moved slightly to and fro in a circumferential direction during this process.
Appendix C Method of verification of thread size and form by means of limit gauges
C.1 External threads C.1.1 Principles
C.1.1.1 Solid threaded GO ring gauge. The gauge checks the virtual size of the internal thread on the GO side, i.e. it gauges the virtual pitch diameter. This is done by checking the maximum material limit of the pitch diameter. During this process the following factors, which produce an apparent enlargement of the pitch diameter (represented by the dimension, virtual pitch diameter), are taken into account. a) Deviations from the form. b) Departures from roundness. c) Lack of straightness of the thread axis over the gauge length. d) Pitch errors. e) Helix variations. f) Errors in the flank angles. In addition, this gauge checks that the rounding at the root of the profile does not encroach too far upon the flank of the thread. It also verifies that the thread crest form does not transgress the maximum material profile. C.1.1.2 NOT GO Screw Calliper Gauge. The gauge is used to check the minimum limit of the pitch diameter. C.1.1.3 Solid threaded NOT GO ring gauge. The gauge is used to check whether the actual pitch diameter exceeds the specified minimum size.
If the gauge will not pass over the plug or if there is a clearance, adjust the anvils of the gauge and repeat the procedure.
BSI 12-1998
BS 2779:1986
Licensed Copy: AUB User, na, Sun Mar 25 13:38:08 GMT+00:00 2007, Uncontrolled Copy, (c) BSI
C.1.4.3.2 Main procedure. In at least three positions evenly distributed over the circumference, attempt to pass the gauge over the thread, under its own weight or under a fixed load.
NOTE The gauge may be moved slightly to and fro in a circumferential direction during this process.
If the gauge shown in Figure 3(b) is used, repeat each check after having displaced the gauge from one pitch to the other. Record the positions of the thread the gauge passes over. C.2 Internal threads C.2.1 Principles C.2.1.1 Threaded GO plug gauge. The gauge checks the virtual size of the internal thread on the GO side, i.e. it gauges the virtual pitch diameter. This is done by checking the minimum material limit of the pitch diameter. During this process the following factors, which produce an apparent reduction of the pitch diameter (represented by the dimension, virtual pitch diameter), are taken into account. a) Deviations from the form. b) Departures from roundness. c) Lack of straightness of the thread axis over the gauge length.
d) Pitch errors. e) Helix variations. f) Errors in the flank angles. In addition, this gauge checks both the minimum limit of the major diameter and also that the rounding at the root of the profile does not encroach too far upon the flank of the thread. C.2.1.2 Threaded NOT GO plug gauge. The gauge is used to check whether the actual pitch diameter exceeds the specified maximum size. C.2.2 Gauges. The gauges shall be in accordance with appendix D. C.2.3 Control of plug gauges. Examine the GO and NOT GO plug gauges regularly for wear by measurement.
NOTE The worn threads of a NOT GO plug gauge may be removed, provided that at least three turns of thread remain.
C.2.4 Procedure for gauging threads C.2.4.1 Threaded GO plug gauge. Without using excessive force, attempt to screw the gauge by hand through the whole length of the thread. C.2.4.2 Threaded NOT GO plug gauge. Without using excessive force, screw the gauge by hand into the thread for as many turns as possible. Unscrew the gauge and record the number of turns engaged.
Figure 3 NOT GO screw calliper gauge
BSI 12-1998
BS 2779:1986
Appendix D Gauges for the method given in appendix C Licensed Copy: AUB User, na, Sun Mar 25 13:38:08 GMT+00:00 2007, Uncontrolled Copy, (c) BSI
D.1 General D.1.1 Taylor principle. All gauges and their setting plugs and check plugs should be designed to be in accordance with the Taylor principle as far as possible, except for the solid threaded NOT GO ring gauge.
D.2 Ring gauges and calliper gauges for external threads D.2.1
GO
side
D.2.1.1 Gauges D.2.1.1.1 Solid threaded GO ring gauges for class A and class B external threads shall be in accordance with Table 3 and Table 4. Ring gauge thread profiles shall be as shown in Figur e 6.
NOTE 1
NOTE 1 The Taylor principle is a statement to the effect that the maximum material limits of as many related elements or dimensions as practicable should be incorporated in the GO gauge, whereas the minimum material limit of each related element or dimension may be gauged only by individual minimum material limit gauges or gauging methods. NOTE 2 Checking with a solid threadedNOT GO ring gauge does not correspond to the Taylor principle. For non-rigid machined pieces, the departure from the Taylor principle is of less importance because of the flexibility of the pieces.
The values of d, d1 and d2 shall be as given in Table 1.
NOTE 2 The values specified in Table 3 and Table 4 for pitch, P, and tolerance on basic pitch diameter, T d2, are identical with those given in Table 1.
Tolerance zones are shown in Figure 7.
D.1.2 Entry of the thread, incomplete threads, even if they are chamfered, are still sharp enough to break or deform. In order that checking will not be affected, it is recommended that the incompletely formed part of the thread be removed (se e Figure 4) or, if this is not possible, that a chamfer to the thread root of 2730 be applied (see Figure 5).
D.2.1.1.2 The length of the thread on the gauge shall be at least 80 % of the thread length of the engaging part or component (i.e. the thread length of, for example, a nut). D.2.1.2 Check plugs
NOTE The GO and NOT GO check plugs for the solid threadedGO ring gauge are used to check the limits of the pitch diameter of a new gauge. The wear check plug is used to ascertain that the pitch diameter of the solid threaded GO ring gauge has not exceeded the wear limit. It embodies the pitch diameter of the solid threaded GO ring gauge at the prescribed limit of wear. GO, NOT GO
and wear check plugs for ring gauges for class A and class B external threads shall be in accordance with D.2.1.1.1. D.2.2
NOT GO
side
D.2.2.1 Gauges D.2.2.1.1 Solid threaded NOT GO ring gauges and NOT GO screw calliper gauges for class A external threads shall be in accordance-with Table 3 and Table 4. Ring gauges and calliper gauges for class B external threads shall be in accordance with Table 4 and Table 5. Thread profiles shall be shown in Figure 8. The values of d, d1 and d2 shall be as given in Table 1.
NOTE Tolerance zones are shown in Figure 9.
Figure 4 Start of complete thread
Figure 5 Chamfer of start of thread
BSI 12-1998
BS 2779:1986
Table 3 Dimensions for GO and NOT GO gauges and their check plugs for class A external threads and for GO gauges and their check plugs for class B external threads
Thread size designation
Licensed Copy: AUB User, na, Sun Mar 25 13:38:08 GMT+00:00 2007, Uncontrolled Copy, (c) BSI
1 1 1
/16 and 1/8a /4 and 3/8
7
107
Td2 4m
15
TR 4m
10
TPL 4m
9 9 10 10 13 13
TCP 4m
17 17
m 4m
2 2
ZR 4m
13 13
WNG 4m
18 18
WGO 4m
125 142 180 217 217
15 20 20 25 25
10 12 12 15 15
/2 up to and including /8 1 up to and including 2 21/4 up to and including 4 41/2 up to and including 6
20 20 24 24
9 9 13 13
17 17 21 21
23 23 28 28
a For 1/16 and 1/8 GO ring gauges, for a pitch of 0.907 mm, a profile is permitted with a radius without an internal diameter, in millimetres, increased by the following. (d1 +0.134 + TR/2) TR/2 = d1 +0.142 0.0075 [see Figure 6(a)].
Figure 6 Thread profiles of GO ring gauges and their check plugs 9
BSI 12-1998
BS 2779:1986
Table 4 Other values for GO and NOT GO gauges and their check plugs for class A and class B external threads as a function of the pitch, P
Licensed Copy: AUB User, na, Sun Mar 25 13:38:08 GMT+00:00 2007, Uncontrolled Copy, (c) BSI
Thread size designation
Pitch, P
Number of threads in 25.4 mm
Width of clearance groove at the major and minor diameter of the thread profile with shortened flanks, b3 Nominal or as in note Tolerance S mm
Tolerance on the half angle (27 30) of check plugs and ring gauges minutes
mm 1 1 1
mm
/16 and /8 /4 and 3/8 /2 up to and including 7/8
1 up to and including 6
0.907 0.005a 1.337 0.005a 1.814 0.005a 2.309 0.005a
28 19 14 11
0 0.4 0.5 0.8
0.04 + 0,05 0.05
15 13 11 10
NOTE The maximum displacement permitted between the middle of the groove of width b3 and that of the profile is equal to S.if the effective displacement, s, is less than S, it is permissible for the upper limit of b3 (nominal b3 + S) to be exceeded by twice the difference S s; this is the equivalent of accepting for the distance between each lateral face of the groove and the middle of the profile the equal [(nominal b3 + S)/2] S
a When
measured between any two threads over the length of the gauge or check plug.
Figure 7 Relative positions of pitch diameter tolerance zones for GO ring gauges and their check plugs
10
BSI 12-1998
BS 2779:1986
Licensed Copy: AUB User, na, Sun Mar 25 13:38:08 GMT+00:00 2007, Uncontrolled Copy, (c) BSI
Figure 8 Thread profiles of NOT GO ring gauges and their check plugs and calliper gauges Table 5 Dimensions for NOT GO gauges and their check plugs for class B external threads
Thread size designation 1/ 16 1/ 4 1/ 2 Td2 TR TPL TCP m WNG m m m m m m
and
1/ 8
214 250 284 360 434 434
25 25 25 33 33 33
15 15 15 20 20 20
13 13 13 17 17 17
24 24 24 30 30 30
21 21 21 28 28 28
and 3/8 up to and including 7/8 up to and including 4
1 up to and including 2 21/
4
41/2 up to and including 6
BSI 12-1998
11
BS 2779:1986
Licensed Copy: AUB User, na, Sun Mar 25 13:38:08 GMT+00:00 2007, Uncontrolled Copy, (c) BSI
Figure 9 Relative positions of pitch diameter tolerance zones for NOT GO ring gauges, calliper gauges and their check plugs D.2.2.1.2 The solid threaded NOT GO ring gauge shall have a length of thread of at least three turns of thread. Each anvil of the NOT GO screw calliper gauge shall be so designed that it contacts the machined piece thread on no more than two flanks [see Figure 3(a) and (b)]. On fine pitch gauges, these flanks shall be situated not more than three pitches apart. D.2.2.2 Check plugs and setting plugs D.2.2.2.1 Check plugs for NOT GO ring gauge
NOTE
D.2.2.2.2 Setting plugs for NOT GO screw calliper gauge. Setting plugs shall be in accordance wit h D.2.2.1.1. Each setting plug shall have at least three complete threads. D.3 GO and NOT GO plug gauges The gauges shall be in accordance with Table 6 and Table 7. Thread profiles shall be as shown in Figure 10.
NOTE Tolerance zones are shown in Figure 11. The GO and NOT GO check plugs for the solid threaded ring gauge are used to check the pitch diameter limits of The values of D, D1 and D2 shall be as given a new gauge. The threaded GO check plug makes sure that the clearance diameter of the gauge is not too small. The wear check in Table 1. plug is used to check whether the pitch diameter of the gauge has The length of thread on the GO plug gauge shall be exceeded the wear limit. It embodies the pitch diameter of the at least 80 % of the thread length of the engaging threaded NOT GO ring gauge at the prescribed limit of wear.
NOT GO
GO, NOT GO
part or component (i.e. the thread length of, for and wear check plugs for ring gauges for example, a nut). The NOT GO plug gauge shall have class A and class B external threads shall be in a length of thread of at least three complete threads. accordance with D.2.2.1.1.
12
BSI 12-1998
BS 2779:1986
Table 6 Dimensions for threaded GO and
Thread size designation TD2 m ZPL m
NOT GO TPL m
plug gauges
WNG m WGO m
Licensed Copy: AUB User, na, Sun Mar 25 13:38:08 GMT+00:00 2007, Uncontrolled Copy, (c) BSI
1 1 1
/16 and
1 a /8
107 125 142 180 217 217
8 8 13 13 18 18
10 10 12 12 15 15
10 10 13 13 17 17
14 14 19 19 23 23
/4 and 3/8 /2 up to and including 7/8
1
1 up to and including 2
2 /4 up to and including 4 41/2 up to and including 6
a
For 1/16 and 1/8 GO plug gauges, for a pitch of 0.907 mm, a profile is permitted without a radius with an external diameter, in millimetres, increased by the following: (D 0.134 TPL/2) TPL/2 = D 0.139 0.005 (see Figure 10)
Figure 10 Thread profiles of GO and NOT GO plug gauges
BSI 12-1998
13
BS 2779:1986
Table 7 Other values for GO and NOT GO plug gauges as a function of the pitch, P
Thread size designation Pitch, P Number of threads in 25.4 mm Width of clearance groove at the major and minor diameter of the thread profile with shortened flanks,b3 Nominal 1 1 1 Tolerance S or as in note Tolerance on the half angle (27 30)
Licensed Copy: AUB User, na, Sun Mar 25 13:38:08 GMT+00:00 2007, Uncontrolled Copy, (c) BSI
/16 and /8 /4 and 3/8 /2 up to and including 7/8
1 up to and including 6
0.907 0.005a 1.337 0.005a 1.814 0.005a 2.309 0.005a
mm
28 19 14 11
0 0.4 0.5 0.8
mm
mm
15 13 11 10
minutes
0.04 0.05 0.05
NOTE The maximum displacement permitted between the middle of the groove of width b3 and that of the profile is equal to S. If the effective displacement, s, is less than S, it is permissible for the upper limit of b3 (nominal b3 + S) to be exceeded by twice the difference S s; this is the equivalent of accepting for the distance between each lateral face of the groove and the middle of the profile the value [(nominal b3 + S)/2] S.
a
When measured between any two threads over the length of the plug gauge.
Figure 11 Relative positions of pitch diameter tolerance zones for GO and Not Go plug gauges
14
BSI 12-1998
BS 2779:1986
Publications referred to
BS 21, Specification for pipe threads for tubes and fittings where pressure-tight joints are made on the threads (metric dimensions). ISO 228, Pipe threads where pressure-tight joints are not made on the threads2). Part 1 Designation, dimensions and tolerances. Part 2 Verification by means of limit gauges.
Licensed Copy: AUB User, na, Sun Mar 25 13:38:08 GMT+00:00 2007, Uncontrolled Copy, (c) BSI
2) Referred
to in the foreword only.
BSI 12-1998
BSI 389 Chiswick High Road London W4 4AL
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
BSI British Standards Institution
BSI is the independent national body responsible for preparing British Standards. It presents the UK view on standards in Europe and at the international level. It is incorporated by Royal Charter. Revisions British Standards are updated by amendment or revision. Users of British Standards should make sure that they possess the latest amendments or editions. It is the constant aim of BSI to improve the quality of our products and services. We would be grateful if anyone finding an inaccuracy or ambiguity while using this British Standard would inform the Secretary of the technical committee responsible, the identity of which can be found on the inside front cover. Tel: 020 8996 9000. Fax: 020 8996 7400. BSI offers members an individual updating service called PLUS which ensures that subscribers automatically receive the latest editions of standards. Buying standards Orders for all BSI, international and foreign standards publications should be addressed to Customer Services. Tel: 020 8996 9001. Fax: 020 8996 7001. In response to orders for international standards, it is BSI policy to supply the BSI implementation of those that have been published as British Standards, unless otherwise requested. Information on standards BSI provides a wide range of information on national, European and international standards through its Library and its Technical Help to Exporters Service. Various BSI electronic information services are also available which give details on all its products and services. Contact the Information Centre. Tel: 020 8996 7111. Fax: 020 8996 7048. Subscribing members of BSI are kept up to date with standards developments and receive substantial discounts on the purchase price of standards. For details of these and other benefits contact Membership Administration. Tel: 020 8996 7002. Fax: 020 8996 7001. Copyright Copyright subsists in all BSI publications. BSI also holds the copyright, in the UK, of the publications of the international standardization bodies. Except as permitted under the Copyright, Designs and Patents Act 1988 no extract may be reproduced, stored in a retrieval system or transmitted in any form or by any means electronic, photocopying, recording or otherwise without prior written permission from BSI. This does not preclude the free use, in the course of implementing the standard, of necessary details such as symbols, and size, type or grade designations. If these details are to be used for any other purpose than implementation then the prior written permission of BSI must be obtained. If permission is granted, the terms may include royalty payments or a licensing agreement. Details and advice can be obtained from the Copyright Manager. Tel: 020 8996 7070.
Licensed Copy: AUB User, na, Sun Mar 25 13:38:08 GMT+00:00 2007, Uncontrolled Copy, (c) BSI
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- ISO 228-1-2000 Pipe Threads Where Pressure-Tight Joints Are Not Made On The Threads-Part 1 Dimensions, Tolerances and DesignationDokument12 SeitenISO 228-1-2000 Pipe Threads Where Pressure-Tight Joints Are Not Made On The Threads-Part 1 Dimensions, Tolerances and DesignationM Alim Ur Rahman100% (3)
- Din 3357-1Dokument7 SeitenDin 3357-1gm_revankar39420% (1)
- BS 00084-2007Dokument66 SeitenBS 00084-2007jjdNoch keine Bewertungen
- RTFE (Reinforced Teflon®: 85% PTFE, 15% Glass Fiber) : RTFE Pressure vs. TemperatureDokument2 SeitenRTFE (Reinforced Teflon®: 85% PTFE, 15% Glass Fiber) : RTFE Pressure vs. TemperatureErhan100% (1)
- Asme B18.3.1MDokument30 SeitenAsme B18.3.1MApurva GuptaNoch keine Bewertungen
- DIN125ADokument1 SeiteDIN125AManoj PatilNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sae J514 37Dokument1 SeiteSae J514 37deepakg9Noch keine Bewertungen
- Din 6915 PDFDokument3 SeitenDin 6915 PDFa.tabkhi1980100% (3)
- ISO 8434 6 - 2007 60 Code Cone Connectors With or Without O-RingDokument50 SeitenISO 8434 6 - 2007 60 Code Cone Connectors With or Without O-RingDiyan IrawanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Asme B 1.9Dokument37 SeitenAsme B 1.9Marcel BurlacuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ansiasme B1.2-1983 (Revision of Ansi B1.2-1974) PDFDokument190 SeitenAnsiasme B1.2-1983 (Revision of Ansi B1.2-1974) PDFrzurabaezaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Federal Screw Thread Standards for Pipes, Gas Cylinders and HosesDokument126 SeitenFederal Screw Thread Standards for Pipes, Gas Cylinders and HosesMisaelNoch keine Bewertungen
- 13-08-26 List of GPS Relevant ISO-Standards - August 2013 - Edition 25 - Publication Date OrderDokument21 Seiten13-08-26 List of GPS Relevant ISO-Standards - August 2013 - Edition 25 - Publication Date OrderGabriel RoqueNoch keine Bewertungen
- DIN 915 EN-1980 Hexagon Socket Set Screws With Dog PointDokument4 SeitenDIN 915 EN-1980 Hexagon Socket Set Screws With Dog Pointthachpn100% (1)
- Arandelas Asme b18.22.1Dokument8 SeitenArandelas Asme b18.22.1Beto HurtadoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Trapezoidal ISO ThreadsDokument4 SeitenTrapezoidal ISO Threadsnicholas_j_vaughanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mil H 25579Dokument22 SeitenMil H 25579Senthil KumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Metric Plain Washers: American National StandardDokument16 SeitenMetric Plain Washers: American National StandardSubrata Das100% (2)
- Asme B1.2 - 1983 PDFDokument189 SeitenAsme B1.2 - 1983 PDFKristin Jones100% (1)
- DIN ISO Equivalent FastenersDokument12 SeitenDIN ISO Equivalent FastenersGunnie PandherNoch keine Bewertungen
- Asme B4.1-1967 (2009)Dokument28 SeitenAsme B4.1-1967 (2009)vijay pawar100% (3)
- Din 8140 AmecoilDokument1 SeiteDin 8140 Amecoiljuanpalomo74Noch keine Bewertungen
- Iso 14582 - Hexalobular Socket Countersunk Flat Head Screws, High Head PDFDokument5 SeitenIso 14582 - Hexalobular Socket Countersunk Flat Head Screws, High Head PDFMitesh MakvanaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bs 3293Dokument18 SeitenBs 3293nguyenmainam0% (1)
- Din 477-5Dokument6 SeitenDin 477-5mutluNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hexagon Socket Head Cap Screws - IsO 4762-1992Dokument6 SeitenHexagon Socket Head Cap Screws - IsO 4762-1992Corneliu VilcuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Iso 6149-1Dokument1 SeiteIso 6149-1Manjunath Shankaran100% (3)
- En10083 2Dokument2 SeitenEn10083 2Sezgin BayrakNoch keine Bewertungen
- BS EN ISO 228-1: 2003 Table 1 Thread Dimensions British Pipe Thread (Whitworth Form) - Parallel (BSPP/BSPF) - (G)Dokument3 SeitenBS EN ISO 228-1: 2003 Table 1 Thread Dimensions British Pipe Thread (Whitworth Form) - Parallel (BSPP/BSPF) - (G)Sergio Hurtado AvellaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Iso 642-1999Dokument24 SeitenIso 642-1999jerfmos100% (3)
- Iso 4029Dokument9 SeitenIso 4029ellisforheroesNoch keine Bewertungen
- X DIN 6885Dokument3 SeitenX DIN 6885bee140676Noch keine Bewertungen
- Asme B18.2.2 - 2010Dokument40 SeitenAsme B18.2.2 - 2010leandro_estudo100% (1)
- Din 6885 KeysDokument3 SeitenDin 6885 KeysJJ100% (2)
- Iso 104-2002 PDFDokument20 SeitenIso 104-2002 PDFsandip277Noch keine Bewertungen
- Asme B107.17M 1997Dokument14 SeitenAsme B107.17M 1997Roberto Poblete HernandezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sae J343-2010Dokument9 SeitenSae J343-2010Job-AngelNoch keine Bewertungen
- BS 4500-2009 îºÍÅäºÏ.× ÐÎÅäºÏÏ Í ºÍ ÓC 13 1500, È Ó6mm 630mmö СÓÚ ÈÓÚ500mm Ä× ÐÎ Ä Îï ÍDokument50 SeitenBS 4500-2009 îºÍÅäºÏ.× ÐÎÅäºÏÏ Í ºÍ ÓC 13 1500, È Ó6mm 630mmö СÓÚ ÈÓÚ500mm Ä× ÐÎ Ä Îï Ísaj_ash82Noch keine Bewertungen
- Internal Snap Rings DIN 7993 Part B SizesDokument2 SeitenInternal Snap Rings DIN 7993 Part B SizesRajaSekarsajja100% (1)
- Astm A 217 - 04Dokument4 SeitenAstm A 217 - 04Raul Humberto Mora VillamizarNoch keine Bewertungen
- ISO 2341-1986 EN 22341-1992 Clevis Pins With Head PDFDokument6 SeitenISO 2341-1986 EN 22341-1992 Clevis Pins With Head PDFAddul Omman NailNoch keine Bewertungen
- Asme B1.20.5 PDFDokument66 SeitenAsme B1.20.5 PDFBala Murugan100% (1)
- BS 4368-1 1998Dokument22 SeitenBS 4368-1 1998virajNoch keine Bewertungen
- Iso - 8434 3 2005Dokument8 SeitenIso - 8434 3 2005Morez BarikaniNoch keine Bewertungen
- Asme B1.8Dokument42 SeitenAsme B1.8jithinjose86Noch keine Bewertungen
- Din 2353 EgDokument10 SeitenDin 2353 Egxuanphuong2710100% (1)
- Astm A646 A646mDokument5 SeitenAstm A646 A646mJosé de Paula MoreiraNoch keine Bewertungen
- DIN 128 en PDFDokument3 SeitenDIN 128 en PDFDaniel PuiaNoch keine Bewertungen
- DIN EN 1563e 2005-10Dokument29 SeitenDIN EN 1563e 2005-10bell_15477100% (1)
- ISO 7-1 Pipe ThreadsDokument11 SeitenISO 7-1 Pipe ThreadsFarzad SadrNoch keine Bewertungen
- BS 21 - 1985Dokument22 SeitenBS 21 - 1985Anonymous gFPYO5Iv6100% (2)
- 2643 2005Dokument14 Seiten2643 2005govimanoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Is - 01879 - 2010Dokument31 SeitenIs - 01879 - 2010sangitaghaisasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mjitfjjl: Pipe Supports and Hangers Part 3: Middle Connection Attachment and Building Structure AttachmentsDokument37 SeitenMjitfjjl: Pipe Supports and Hangers Part 3: Middle Connection Attachment and Building Structure AttachmentsIRELECNoch keine Bewertungen
- BS 143 & 1256: 2000Dokument30 SeitenBS 143 & 1256: 2000thanh_79Noch keine Bewertungen
- Disclosure To Promote The Right To InformationDokument34 SeitenDisclosure To Promote The Right To InformationKashyap PatelNoch keine Bewertungen
- SANS282 - Steel Detailing CodeDokument31 SeitenSANS282 - Steel Detailing CodeSarisha Harrychund100% (1)
- BS 302 - 1-1987 Stranded Steel Wire Ropes PDFDokument16 SeitenBS 302 - 1-1987 Stranded Steel Wire Ropes PDFAlsonChin0% (1)
- Is 8805 2002Dokument18 SeitenIs 8805 2002Mani KandanNoch keine Bewertungen
- BSP ThreadsDokument6 SeitenBSP ThreadsVinod YbNoch keine Bewertungen
- Progress Test 18Dokument8 SeitenProgress Test 18Vaibhav ShuklaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Standard Astm b456Dokument11 SeitenStandard Astm b456Vaibhav ShuklaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Esi ProCAST PDFDokument16 SeitenEsi ProCAST PDFanwarsitangangNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ubc 1997-0068Dokument123 SeitenUbc 1997-0068Vaibhav ShuklaNoch keine Bewertungen
- FORM ED1 Invest PunjabDokument1 SeiteFORM ED1 Invest PunjabVaibhav ShuklaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Procast Manual PDFDokument471 SeitenProcast Manual PDFPhan Dinh Sy0% (2)
- Ubc 1997-0068Dokument123 SeitenUbc 1997-0068Vaibhav ShuklaNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Effect of Heat Transfer Coefficient and Cooling Schedule On Porosity Sizes of Low Pressure Die Casting Aluminium Alloy WheelsDokument8 SeitenThe Effect of Heat Transfer Coefficient and Cooling Schedule On Porosity Sizes of Low Pressure Die Casting Aluminium Alloy WheelsVaibhav ShuklaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Metals 10 01418Dokument24 SeitenMetals 10 01418Vaibhav ShuklaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1 en 3 Chapter AuthorDokument14 Seiten1 en 3 Chapter AuthorVaibhav ShuklaNoch keine Bewertungen
- FORM ED1 Invest PunjabDokument1 SeiteFORM ED1 Invest PunjabVaibhav ShuklaNoch keine Bewertungen
- HTC CoefficientDokument20 SeitenHTC CoefficientVaibhav ShuklaNoch keine Bewertungen
- BS 2779-1986 Ó ÖÆ ÇÃÜ Â ÜÂÝÎÆ (BSP)Dokument20 SeitenBS 2779-1986 Ó ÖÆ ÇÃÜ Â ÜÂÝÎÆ (BSP)Vaibhav ShuklaNoch keine Bewertungen
- ANSI ASME B1.20.1, NPT Pipe Threads PDFDokument31 SeitenANSI ASME B1.20.1, NPT Pipe Threads PDFVaibhav Shukla75% (4)
- Grohe Cat 03Dokument144 SeitenGrohe Cat 03FERCONoch keine Bewertungen
- HIWINDokument1 SeiteHIWINVaibhav ShuklaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Disclosure To Promote The Right To InformationDokument21 SeitenDisclosure To Promote The Right To InformationVaibhav ShuklaNoch keine Bewertungen
- GST Chapter Wise RateDokument213 SeitenGST Chapter Wise RateMoneycontrol News92% (280)
- Spares Pricelist HB-86Dokument2 SeitenSpares Pricelist HB-86Vaibhav ShuklaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Brass MachiningDokument68 SeitenBrass MachiningVaibhav ShuklaNoch keine Bewertungen
- ServeCAST - Non-Fe - Sand, Die Casting - Input Data FormatDokument3 SeitenServeCAST - Non-Fe - Sand, Die Casting - Input Data FormatVaibhav ShuklaNoch keine Bewertungen
- GST Chapter Wise RateDokument213 SeitenGST Chapter Wise RateMoneycontrol News92% (280)
- Exploded View & Part List HB-86-XxxDokument3 SeitenExploded View & Part List HB-86-XxxVaibhav ShuklaNoch keine Bewertungen
- FP241 1Dokument4 SeitenFP241 1Vaibhav ShuklaNoch keine Bewertungen
- User Guide Dual Action Hand Spray Gun HB-86, HB-35 & DJ-10Dokument12 SeitenUser Guide Dual Action Hand Spray Gun HB-86, HB-35 & DJ-10Vaibhav ShuklaNoch keine Bewertungen
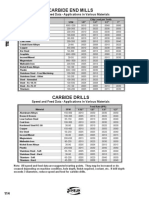
- Technical data on carbide end mills and drillsDokument1 SeiteTechnical data on carbide end mills and drillsenricoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Speedchart For MachiningDokument1 SeiteSpeedchart For MachiningVaibhav ShuklaNoch keine Bewertungen
- A Man's Caftan and Leggings From The North Caucasus of The Eighth To TenthDokument32 SeitenA Man's Caftan and Leggings From The North Caucasus of The Eighth To TenthdgzinnackNoch keine Bewertungen
- Masks For All OccasionsDokument2 SeitenMasks For All OccasionsFer JoãoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Conditions of Entry - Skypark Observation DeckDokument3 SeitenConditions of Entry - Skypark Observation DeckxxcarxxNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lord of The Mysteries Vol. 1 ClownDokument2.458 SeitenLord of The Mysteries Vol. 1 ClownrakushakohakuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Herodotus' Catalogues of The Persian Empire in The Light of The Monuments and The Greek Literary Tradition, O. Kimball ArmayorDokument10 SeitenHerodotus' Catalogues of The Persian Empire in The Light of The Monuments and The Greek Literary Tradition, O. Kimball ArmayorΕΣΤΙΤΙΣΣΙΩΝΤΙΣΙΣNoch keine Bewertungen
- Terms and ConditionsDokument3 SeitenTerms and ConditionsNagarjuna MuthineniNoch keine Bewertungen
- Full Peasant Dress Pattern 12 Mo To 14Dokument15 SeitenFull Peasant Dress Pattern 12 Mo To 14Maria MourãoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Scentsy Catalog Fall Winter 2016Dokument38 SeitenScentsy Catalog Fall Winter 2016Kristy PoolNoch keine Bewertungen
- Stories of The NightDokument90 SeitenStories of The NightfahdalirazaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mohan and His AmmaDokument6 SeitenMohan and His Ammarbhairavi198440% (5)
- Arc Welding Safety PrecautionsDokument14 SeitenArc Welding Safety PrecautionsMarcelito MorongNoch keine Bewertungen
- GI A2 U3 Vocabulary BasicsDokument1 SeiteGI A2 U3 Vocabulary BasicsVanessa VNoch keine Bewertungen
- Wellwits Women's Keyhole Mesh Bell Long Sleeve Knee Swing Cocktail Dress Amazon - Co.uk FashionDokument1 SeiteWellwits Women's Keyhole Mesh Bell Long Sleeve Knee Swing Cocktail Dress Amazon - Co.uk Fashion21ddumanfNoch keine Bewertungen
- Little Black Dress PDFDokument19 SeitenLittle Black Dress PDFEsther Bravo Mozo100% (2)
- Year End Paper 2 English Year 1Dokument5 SeitenYear End Paper 2 English Year 1ETHAN BONG YU ZHE MoeNoch keine Bewertungen
- An Overview of Knitting Industry of IndiaDokument18 SeitenAn Overview of Knitting Industry of IndiaJyoti BarwarNoch keine Bewertungen
- PAGEANT MECHANICS and CRITERIA FOR JUDGINGDokument2 SeitenPAGEANT MECHANICS and CRITERIA FOR JUDGINGRegie BenesioNoch keine Bewertungen
- Learning Driving A Semi-Manual MotorcycleDokument3 SeitenLearning Driving A Semi-Manual MotorcycleVonna Cristalyn VeluzNoch keine Bewertungen
- Talla 46 Moldes de Bermuda Cargo Dockers Classic Fit hm1305b PDFDokument1 SeiteTalla 46 Moldes de Bermuda Cargo Dockers Classic Fit hm1305b PDFleandrobuenoiNoch keine Bewertungen
- syllabus-B.Sc Fashion Technology 2017-18Dokument43 Seitensyllabus-B.Sc Fashion Technology 2017-18Md Marfat aliNoch keine Bewertungen
- Studio Pictures and Dress Rehearsal 2020Dokument1 SeiteStudio Pictures and Dress Rehearsal 2020api-215005036Noch keine Bewertungen
- Shadow of The Silk Road (Travellers Tales Essay)Dokument3 SeitenShadow of The Silk Road (Travellers Tales Essay)Joey Mai VanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Never Late Never Away Chapter 21 25Dokument17 SeitenNever Late Never Away Chapter 21 25Tejumola Taiwo75% (4)
- Handloom Jacquard GuideDokument37 SeitenHandloom Jacquard GuideSammers Hbr0% (1)
- Slow Fashion in A Fast Fashion World: Promoting Sustainability and ResponsibilityDokument9 SeitenSlow Fashion in A Fast Fashion World: Promoting Sustainability and ResponsibilityLia Amellya LNoch keine Bewertungen
- General Flight Information: GSO - Strategy, Support and LogisticsDokument26 SeitenGeneral Flight Information: GSO - Strategy, Support and LogisticsIliyanPetrovNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Scarecrows On Parade English - Low ResDokument20 SeitenThe Scarecrows On Parade English - Low ResHitesh VashistNoch keine Bewertungen
- Medical TextileDokument32 SeitenMedical TextileMusa Eltayeb100% (1)
- loveFMD Magazine Issue5Dokument116 SeitenloveFMD Magazine Issue5loveFMD100% (1)