Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Acute Bronchitis
Hochgeladen von
Fecky Fihayatul IchsanCopyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Acute Bronchitis
Hochgeladen von
Fecky Fihayatul IchsanCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Click image to enlarge
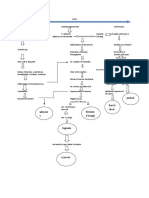
Acute Bronchitis
What is bronchitis?
Bronchitis is an inflammation of the large breathing tubes (airways) that are called bronchi, which causes increased production of mucus and other changes. Although there are several different types of bronchitis, the two most common are acute and chronic (primarily affects adults).
What is acute bronchitis?
Acute bronchitis is the inflammation of mucous membranes of the bronchial tubes.
What causes acute bronchitis?
Acute bronchitis is usually caused by infectious agents such as bacteria or viruses. It may also be caused by physical or chemical agents - dusts, allergens, strong fumes, and those from chemical cleaning compounds, or tobacco smoke. (Acute asthmatic bronchitis may happen as the result of an asthma attack, or it may be the cause of an asthma attack.) In children, the most common cause of bronchitis is a virus, although in children over years of age, it can be caused by bacteria. Acute bronchitis is usually a mild condition. Acute bronchitis may follow the common cold or other viral infections in the upper respiratory tract. It may also occur in children with chronic sinusitis, allergies, or those with enlarged tonsils and adenoids. !neumonia is a complication that can follow bronchitis.
What are the symptoms of acute bronchitis?
"he following are the most common symptoms for acute bronchitis. #owever, each child may e$perience symptoms differently. %ymptoms may include&
runny nose, usually before a cough starts malaise (an overall body discomfort or not feeling well) chills slight fever
back and muscle pain sore throat
In the earlier stages of the condition, children may e$perience a dry, non-productive cough which progresses later to an abundant mucus-filled cough. 'ounger children may have some vomiting or gagging with the cough. "he symptoms of bronchitis usually last seven to () days, but may also persist for three to four weeks. "he symptoms of acute bronchitis may resemble other conditions or medical problems. *onsult your child+s physician for a diagnosis.
How is acute bronchitis diagnosed?
Bronchitis is usually diagnosed solely on the history and physical e$amination of the child. ,any tests may be ordered to rule out other diseases, such as pneumonia or asthma. In addition, the following tests may be ordered to help confirm diagnosis&
chest x-rays - a diagnostic test which uses invisible electromagnetic energy beams to produce images of internal tissues, bones, and organs onto film. blood tests pulse oximetry - an o$imeter is a small machine that measures the amount of o$ygen in the blood. "o obtain this measurement, a small sensor (like a BandAid) is taped onto a finger or toe. -hen the machine is on, a small red light can be seen in the sensor. "he sensor is painless and the red light does not get hot. sputum cultures lung tests
Treatment for acute bronchitis
%pecific treatment for acute bronchitis will be determined by your child+s physician based on&
your child+s age, overall health, and medical history e$tent of the condition your child+s tolerance for specific medications, procedures, or therapies e$pectations for the course of the condition your opinion or preference
In many cases, antibiotic treatment is not necessary to treat acute bronchitis, since most of the infections are caused by viruses. .ven children who have been coughing for longer that eight to (/ days usually do not need antibiotics. ,ost of the treatment is supportive of the symptoms your child may have, and may include&
analgesics, such as acetaminophen (for fever and discomfort)
cough medicine increased fluid intake cool mist humidifier in the room may be helpful
Antihistamines should be avoided, in most cases, because they dry up the secretions and can make the cough worse.
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeVon EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (5794)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Von EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Bewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (98)
- Fecky F Ichsan - Wound HealingDokument60 SeitenFecky F Ichsan - Wound HealingFecky Fihayatul IchsanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fecky F Ichsan - LiverDokument6 SeitenFecky F Ichsan - LiverFecky Fihayatul IchsanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Garuda - Garba Rujukan Digital SURGERYDokument638 SeitenGaruda - Garba Rujukan Digital SURGERYFecky Fihayatul IchsanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Machine Learning1Dokument8 SeitenMachine Learning1Fecky Fihayatul IchsanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Machine Learning Is A Branch ofDokument2 SeitenMachine Learning Is A Branch ofFecky Fihayatul IchsanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Report Frank GabelDokument13 SeitenReport Frank GabelFecky Fihayatul IchsanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ad PcosDokument9 SeitenAd PcosFecky Fihayatul IchsanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hemorrhagic StrokeDokument35 SeitenHemorrhagic StrokeFecky Fihayatul IchsanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ectopic PregnancyDokument39 SeitenEctopic PregnancyFecky Fihayatul IchsanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Reproductive Health Prof Biran AfandiDokument44 SeitenReproductive Health Prof Biran AfandiFecky Fihayatul IchsanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Uremic NeuropathyDokument10 SeitenUremic NeuropathyFecky Fihayatul IchsanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Use of Vital Statistics in Obstetry and GynecologyDokument4 SeitenUse of Vital Statistics in Obstetry and GynecologyFecky Fihayatul IchsanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ectopic Pregnancy WilliamsDokument9 SeitenEctopic Pregnancy WilliamsFecky Fihayatul IchsanNoch keine Bewertungen
- MDGs PDFDokument4 SeitenMDGs PDFHarshal NimjeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Acute Fulminant Pseudomembranous Colitis Which Developed After Ileostomy Closure and Required Emergent Total ColectomyDokument10 SeitenAcute Fulminant Pseudomembranous Colitis Which Developed After Ileostomy Closure and Required Emergent Total ColectomyFecky Fihayatul IchsanNoch keine Bewertungen
- EpiglotitisDokument12 SeitenEpiglotitisFecky Fihayatul IchsanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pocket Guide To Antimicrobial Therapy in Otolaryngology - Head and Neck Surgery 13th EditionDokument115 SeitenPocket Guide To Antimicrobial Therapy in Otolaryngology - Head and Neck Surgery 13th EditionFecky Fihayatul IchsanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Oto Primary Care FINALhigh NonumberDokument139 SeitenOto Primary Care FINALhigh NonumberNurprianto TenggarongNoch keine Bewertungen
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryVon EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (231)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceVon EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (895)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingVon EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (400)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeVon EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (537)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItVon EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (838)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureVon EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (474)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceVon EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (588)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerVon EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (271)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealVon EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (74)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnVon EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (234)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaVon EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (266)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersVon EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (344)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyVon EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (2259)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreVon EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (1090)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaVon EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (45)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Von EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Bewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (121)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesVon EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (821)
- Monday Tuesday Wednesday Thursday Friday: I. ObjectivesDokument4 SeitenMonday Tuesday Wednesday Thursday Friday: I. ObjectivesMary Joselyn BodionganNoch keine Bewertungen
- Summative Test 1st QuarterDokument4 SeitenSummative Test 1st QuarterChai BarcelonNoch keine Bewertungen
- ABG InterpretationDokument38 SeitenABG Interpretationmahmod omerNoch keine Bewertungen
- Respiratory Therapy Skills ChecklistDokument3 SeitenRespiratory Therapy Skills Checklistnorthweststaffing50% (2)
- T V NG TACN1Dokument18 SeitenT V NG TACN1Thanh ToànNoch keine Bewertungen
- Francisco, Ma. Theresa Q. 1bsn-Ui (Session 19-Lec)Dokument5 SeitenFrancisco, Ma. Theresa Q. 1bsn-Ui (Session 19-Lec)DANICA JEAN PRIANES100% (1)
- BLOODBUFFERSDokument2 SeitenBLOODBUFFERSkulangkatunNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pumonary Drug Delivery Sy 3856380Dokument30 SeitenPumonary Drug Delivery Sy 3856380Chaitanya Kumar ReddyNoch keine Bewertungen
- OCMDokument7 SeitenOCMchimboriNoch keine Bewertungen
- NCP Pleural EffusionDokument7 SeitenNCP Pleural EffusionKristian Karl Bautista Kiw-isNoch keine Bewertungen
- Case Study-Pleural EffusionDokument51 SeitenCase Study-Pleural EffusionJames J. Salazar100% (4)
- Figure 1 Human Nervous System Source:courses - Lumenlearning.c Om/microbiology/chapter/anato My-Of-The-Nervous-SystemDokument14 SeitenFigure 1 Human Nervous System Source:courses - Lumenlearning.c Om/microbiology/chapter/anato My-Of-The-Nervous-SystemShekaina Faith Cuizon LozadaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pneumonia Clinical Case Study BSN 2 2 Group 4Dokument43 SeitenPneumonia Clinical Case Study BSN 2 2 Group 4Precious Jenichris TamayoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Kudinkula BiologyDokument113 SeitenKudinkula BiologylufeyocliftonNoch keine Bewertungen
- What Do The Lungs Do, and How Do They Function?: StructureDokument15 SeitenWhat Do The Lungs Do, and How Do They Function?: StructurethenameisvijayNoch keine Bewertungen
- English Homework 2Dokument2 SeitenEnglish Homework 2Teodora TanaseNoch keine Bewertungen
- Oxygen Therapy For NurseDokument46 SeitenOxygen Therapy For NurseselviiNoch keine Bewertungen
- MSDS Ammonium Hydroxide PDFDokument1 SeiteMSDS Ammonium Hydroxide PDFciscaNoch keine Bewertungen
- CPR Chapter 41 OutlineDokument6 SeitenCPR Chapter 41 OutlineFarhad AmaniNoch keine Bewertungen
- COPD PathophysiologyDokument1 SeiteCOPD PathophysiologyJustin Ahorro-Dionisio33% (3)
- Nursing Care Plan For Pneumonia NCPDokument3 SeitenNursing Care Plan For Pneumonia NCPderic79% (133)
- The Speech MechanismDokument5 SeitenThe Speech MechanismSittie HijaraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lungs and Thorax Assessment - PPTX RAHEEM KHANDokument60 SeitenLungs and Thorax Assessment - PPTX RAHEEM KHANRabia IsrafilNoch keine Bewertungen
- 10 Respiratory System 2Dokument73 Seiten10 Respiratory System 2Angel BumanglagNoch keine Bewertungen
- Passable 350 Q&aDokument76 SeitenPassable 350 Q&aDavid Yousef100% (1)
- Clinical Manifestations and Assessment of Respiratory Disease 5th Edition Jardins Test BankDokument36 SeitenClinical Manifestations and Assessment of Respiratory Disease 5th Edition Jardins Test Bankgeincupola.06zi100% (23)
- StridorDokument48 SeitenStridorMahindra Kumar100% (1)
- Asthma Thesis StatementDokument4 SeitenAsthma Thesis Statementfjnev0hc100% (2)
- Basic Human Needs Mobility & The Hazards of ImmobilityDokument54 SeitenBasic Human Needs Mobility & The Hazards of ImmobilityZsuzsanna MesterNoch keine Bewertungen
- c64 Section3 Spirometry 2014Dokument19 Seitenc64 Section3 Spirometry 2014Mihai PetrescuNoch keine Bewertungen