Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Cystic Fibrosis Outline
Hochgeladen von
Dominique PorterCopyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Cystic Fibrosis Outline
Hochgeladen von
Dominique PorterCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Cystic Fibrosis
I.
II.
III.
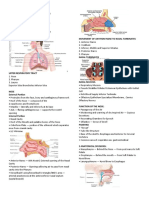
Definition A. an inherited disease characterized by an abnormality in the glands that produce sweat and mucus B. thick, sticky mucus to form in the lungs, pancreas, and other organs C. mucus blocks the airways, causing lung damage, making it hard to breathe, and leading to serious lung infections Epidemiology A. second most common life-shortening, inherited disorder occurring in childhood in the United States B. Approximately 30,000 Americans have CF C. 1,000 new cases diagnosed each year D. equally in male & female and affect every race E. most commonly in caucasians of Northern European descent F. one in 2,500 caucasians are born affected each year Signs & Symptoms A. Vary depending on severity B. may worsen as time passes C. Respiratory S&S: 1. clogs the tubes that carry air in and out of your lungs a) A persistent cough that produces thick spit (sputum) and mucus b) Wheezing c) Breathlessness d) A decreased ability to exercise e) Repeated lung infections f) Inflamed nasal passages or a stuffy nose D. Digestive S&S: 1. The thick mucus can also block tubes that carry digestive enzymes from your pancreas to your small intestine. Without these digestive enzymes, your intestines can't fully absorb the nutrients in the food you eat a) Foul-smelling, greasy stools b) Poor weight gain and growth c) Intestinal blockage, particularly in newborns (meconium ileus) d) Severe constipation
IV.
How is it diagnosed? A. newborn screening B. sweat test 1. measures amount of salt present
C. chemical test D. chest x-rays E. lung function test F. sputum cultures G. stool evaluations H. for babies who cannot produce enough sweat, blood may be used V. Treatment A. non curable B. Management of problems that cause lung obstruction, which may involve: 1. Physical therapy 2. Exercise to loosen mucus, stimulate coughing, and improve overall physical condition 3. Medications to reduce mucus and help breathing 4. Antibiotics to treat infections 5. Anti-inflammatory medications C. Management of digestive problems, which may involve: 1. Appropriate diet 2. Pancreatic enzymes to aid digestion 3. Vitamin supplements 4. Treatments for intestinal obstructions D. Medications: 1. Antibiotics a) treat and prevent lung infections 2. Mucus-thinning drugs a) help you cough up the mucus, which improves lung function 3. Bronchodilators a) help keep your airways open by relaxing the muscles around your bronchial tubes 4. Oral pancreatic enzymes a) help your digestive tract absorb nutrients VI. Prognosis A. survival age was 37.4 years B. on average people diagnosed with cystic fibrosis live to their mid to late 30 VII. Prevention
A. undergo genetic testing with your significant other to see if either of you carry the gene
Links: http://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/cystic-fibrosis/basics/definition/con-20013731 http://www.hopkinsmedicine.org/healthlibrary/conditions/adult/respiratory_disorders/cystic_fibr osis_85,P01306/ http://www.lung.org/assets/documents/publications/solddc-chapters/cf.pdf http://www.webmd.com/children/tc/cystic-fibrosis-topic-overview
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Asthma and CopdDokument44 SeitenAsthma and CopdBeer Dilacshe100% (1)
- Lung Abscess Handout PDFDokument3 SeitenLung Abscess Handout PDFTansanee MalivalayaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Neonatal Conjunctivitis Prevention and TreatmentDokument7 SeitenNeonatal Conjunctivitis Prevention and TreatmentKathie88100% (1)
- Women's Pneumonia ReportDokument9 SeitenWomen's Pneumonia ReportNohaira SADANGNoch keine Bewertungen
- Respiratory Failure Nursing Care and ManagementDokument19 SeitenRespiratory Failure Nursing Care and ManagementYudionoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lung Abscess Treatment and ManagementDokument36 SeitenLung Abscess Treatment and ManagementPalanki Gopal100% (1)
- Pediatric Lung Diseases: Empyema and Lung AbscessDokument39 SeitenPediatric Lung Diseases: Empyema and Lung AbscessFaisal MoidunnyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Rsexm 170207141549Dokument72 SeitenRsexm 170207141549gpete321Noch keine Bewertungen
- Bronchiectasis: Prepared By: Michelle TamorDokument17 SeitenBronchiectasis: Prepared By: Michelle TamorMichelle TamorNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lung Abscess: Dr. Ravi Gadani MS, FmasDokument20 SeitenLung Abscess: Dr. Ravi Gadani MS, FmasRaviNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lung Abscess Bronchoectasis PleurisynDokument19 SeitenLung Abscess Bronchoectasis Pleurisynmarco luenaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Oxygenation NCM 103Dokument10 SeitenOxygenation NCM 103Richmond LacadenNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bronchial AsthmaDokument95 SeitenBronchial AsthmaBrian BrownNoch keine Bewertungen
- Respiratory EmergenciesDokument30 SeitenRespiratory EmergenciesNovriefta NugrahaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Case Discussion - CopdDokument63 SeitenCase Discussion - CopdrajeshNoch keine Bewertungen
- Empyema 171013100219Dokument23 SeitenEmpyema 171013100219Mahmoud Abdel MoneimNoch keine Bewertungen
- Infectious Disease Medications ModuleDokument8 SeitenInfectious Disease Medications ModuleSheril MarekNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pulmonary Tuberculosis 2016Dokument17 SeitenPulmonary Tuberculosis 2016Nikka Moreen DagdagNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cystic FibrosisDokument23 SeitenCystic Fibrosisclarytah0% (1)
- BRONCHIECTASISDokument36 SeitenBRONCHIECTASISVince Peliño De MesaNoch keine Bewertungen
- ARDSDokument27 SeitenARDSChloie Marie RosalejosNoch keine Bewertungen
- 13Lec-Approach To Neonates With Suspected Congenital InfectionsDokument56 Seiten13Lec-Approach To Neonates With Suspected Congenital InfectionsMinerva Stanciu100% (1)
- Lung Abscess - Lecture 2015Dokument19 SeitenLung Abscess - Lecture 2015Okta Dwi Kusuma AyuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Practice Questions: Respiratory SystemDokument6 SeitenPractice Questions: Respiratory SystemTraceyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pneumonia: DefinitionDokument5 SeitenPneumonia: DefinitionhemaanandhyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bronchiectasis and Lung Abscess Diagnosis and TreatmentDokument56 SeitenBronchiectasis and Lung Abscess Diagnosis and TreatmentMansi GandhiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bronchial AsthmaDokument46 SeitenBronchial AsthmaKhor Kee GuanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome (Ards)Dokument12 SeitenAcute Respiratory Distress Syndrome (Ards)Vin Grace Tiqui - GuzmanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lung AbsesDokument48 SeitenLung AbsesAvhindAvhindNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bronchiectasis: By: Karunesh KumarDokument21 SeitenBronchiectasis: By: Karunesh KumarAnkan DeyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Treatment: Chest Tube (Chest Drain or Tube Thoracostomy) Is A Flexible Plastic Tube That Is InsertedDokument7 SeitenTreatment: Chest Tube (Chest Drain or Tube Thoracostomy) Is A Flexible Plastic Tube That Is Insertedmegrace_martinezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lower Respiratory Tract Infections: Manali H Solanki F.Y.M.Sc - Nursing J G College of NursingDokument95 SeitenLower Respiratory Tract Infections: Manali H Solanki F.Y.M.Sc - Nursing J G College of NursingRI NANoch keine Bewertungen
- BronchiectasisDokument39 SeitenBronchiectasischarles_wangsadjajaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD)Dokument51 SeitenChronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD)api-19641337Noch keine Bewertungen
- Coanal AtresiaDokument4 SeitenCoanal AtresiaBkas GrgNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chemo ReceptorDokument8 SeitenChemo ReceptorCheryl Lyn SanchezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Empyema 2Dokument31 SeitenEmpyema 2Michelle SalimNoch keine Bewertungen
- Acute Dyspnea First RevisionDokument56 SeitenAcute Dyspnea First RevisionAradhanaRamchandaniNoch keine Bewertungen
- Risk Factors and Management of Community Acquired PneumoniaDokument53 SeitenRisk Factors and Management of Community Acquired PneumoniaAtif100% (1)
- Anatomy and Physiology of the ConjunctivaDokument43 SeitenAnatomy and Physiology of the ConjunctivaVincentius Okta VidiandickaNoch keine Bewertungen
- ... 2 Finals Pulmonary PhysiologyDokument9 Seiten... 2 Finals Pulmonary PhysiologyELIZABETH GRACE AMADOR100% (1)
- Pneumonia: Submitted To:Ms Lisette Cruz Submitted By: Ms. Mely Rose AbanadorDokument26 SeitenPneumonia: Submitted To:Ms Lisette Cruz Submitted By: Ms. Mely Rose AbanadorJoyce Catherine Buquing UysecoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lung abscess diagnosis and treatmentDokument25 SeitenLung abscess diagnosis and treatmentIskandar HasanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Viral Exanthem (Main)Dokument94 SeitenViral Exanthem (Main)Starlet Rhonadez Bito-onon OrielNoch keine Bewertungen
- Asthma: A. DefinitionDokument6 SeitenAsthma: A. DefinitionElvando SimatupangNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tuberculosis Unit 1 Lecture - 1Dokument39 SeitenTuberculosis Unit 1 Lecture - 1Kubra Rasool100% (1)
- Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome (Ards)Dokument17 SeitenAcute Respiratory Distress Syndrome (Ards)joyrena ochondra0% (1)
- COPD and Other Chronic Pulmonary DiseasesDokument41 SeitenCOPD and Other Chronic Pulmonary DiseasesKristine CastilloNoch keine Bewertungen
- Epid COPDDokument9 SeitenEpid COPDAgung WistaraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chest Injuries: DR Rodwell Gundo Medical/Surgical Nursing DepartmentDokument47 SeitenChest Injuries: DR Rodwell Gundo Medical/Surgical Nursing Departmentpaul kaundaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Respiratorydisease 170426125838Dokument69 SeitenRespiratorydisease 170426125838Hayder MaqsadNoch keine Bewertungen
- PneumothoraxDokument3 SeitenPneumothoraxSanthosh.S.UNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pulmonary Embolism Guide: Causes, Symptoms & DiagnosisDokument60 SeitenPulmonary Embolism Guide: Causes, Symptoms & DiagnosisRafika RaraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pathophysiology ARDSDokument2 SeitenPathophysiology ARDSKim AmboyaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Dyspnea: Ahammed Naseem Roll No: 3 Second Year BSC Nursing Al-Mas College of NursingDokument19 SeitenDyspnea: Ahammed Naseem Roll No: 3 Second Year BSC Nursing Al-Mas College of NursingNaseem Bin YoosafNoch keine Bewertungen
- Neet TB MCQDokument3 SeitenNeet TB MCQslimon100% (1)
- Pulmonology Division COPD GuideDokument59 SeitenPulmonology Division COPD GuideKarenmedicalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Complication of MI (Myocardial Infarction)Dokument2 SeitenComplication of MI (Myocardial Infarction)Zahid QamarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Everything You Need to Know About Lung AbscessDokument46 SeitenEverything You Need to Know About Lung AbscessJeevitha VanithaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsVon EverandAcute Respiratory Distress Syndrome, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Benign Prostatic Hypertrophy OutlineDokument2 SeitenBenign Prostatic Hypertrophy OutlineDominique PorterNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cystitis OutlineDokument3 SeitenCystitis OutlineDominique PorterNoch keine Bewertungen
- Type 2 Diabetes Disease Overview OulineDokument3 SeitenType 2 Diabetes Disease Overview OulineDominique PorterNoch keine Bewertungen
- Type 1 Diabetes OutlineDokument2 SeitenType 1 Diabetes OutlineDominique PorterNoch keine Bewertungen
- Congestive Heart Failure OutlineDokument4 SeitenCongestive Heart Failure OutlineDominique PorterNoch keine Bewertungen
- Academic Writing Siap CetakDokument90 SeitenAcademic Writing Siap CetakRetno OktavianiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Social PsychologyDokument6 SeitenSocial PsychologyRaxNoch keine Bewertungen
- Module 2 Planet JockeyDokument2 SeitenModule 2 Planet Jockeyapi-562124758100% (1)
- Uts PDFDokument3 SeitenUts PDFGiro AnthonyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Second Use For Old Reverse Osmosis Membranes: Wastewater TreatmentDokument8 SeitenSecond Use For Old Reverse Osmosis Membranes: Wastewater TreatmentMokni skanderNoch keine Bewertungen
- Soulmaking (Art Making)Dokument36 SeitenSoulmaking (Art Making)Theios DG100% (2)
- Data Science: What Is Data Science and Who Is Data ScientistDokument26 SeitenData Science: What Is Data Science and Who Is Data ScientistZaib KhanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lesson Plan Science 5Dokument9 SeitenLesson Plan Science 5Marj Reña LunaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Adsorption Tank Specification SheetDokument16 SeitenAdsorption Tank Specification SheetKristine AmbasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Counting Atoms ClassworkDokument2 SeitenCounting Atoms ClassworkBrayden BiggsNoch keine Bewertungen
- AdityaL1 Mission BrochureDokument8 SeitenAdityaL1 Mission Brochurejagadeesh Kumaran B (Jagan Jagadeesh)Noch keine Bewertungen
- Factorial Design ScreeningDokument30 SeitenFactorial Design Screeningnelson.rodriguezm6142Noch keine Bewertungen
- A Remark On The Integration by Parts Formula For TDokument12 SeitenA Remark On The Integration by Parts Formula For TdwayneNoch keine Bewertungen
- 10math RemovedDokument72 Seiten10math RemovedA KennedyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lesson PlanDokument1 SeiteLesson PlanNovah Mary A/P Guruloo IPGKTARNoch keine Bewertungen
- CA - Commissioning - Guide - New - California - CostDokument84 SeitenCA - Commissioning - Guide - New - California - Costlong minn2Noch keine Bewertungen
- School Memo No 9 S. 2022Dokument4 SeitenSchool Memo No 9 S. 2022DINA MAE FLOR JAPSONNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cainta Catholic College: Academic Year 2021 - 2022Dokument3 SeitenCainta Catholic College: Academic Year 2021 - 2022Angelo lacandiliNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fables of Response/abilityDokument34 SeitenFables of Response/abilitymihneamircanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Research Project BCOM (H) - 312 Guidelines BCOM VI Semester 2020-2023Dokument7 SeitenResearch Project BCOM (H) - 312 Guidelines BCOM VI Semester 2020-2023Aryan MishraNoch keine Bewertungen
- XBit 80 DatasheetDokument13 SeitenXBit 80 DatasheetAlexis AlvaradoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Vocabulary TestDokument5 SeitenVocabulary Testmeiluz molina rodriguezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Parameter Technical - KemenkesDokument1 SeiteParameter Technical - KemenkesAlkes PKRTNoch keine Bewertungen
- Children S Functional Health Pattern Assessment Student 3Dokument7 SeitenChildren S Functional Health Pattern Assessment Student 3Tommy PangandahengNoch keine Bewertungen
- TRIALOG 106 FreeDownloadDokument64 SeitenTRIALOG 106 FreeDownloadAmos Pangihutan SNoch keine Bewertungen
- Handbook of Analytical Spectroscopy - Theory and ApplicationsDokument1.793 SeitenHandbook of Analytical Spectroscopy - Theory and Applicationssankar_chakmaNoch keine Bewertungen
- A Concise Introduction To Existential Counselling. AdamsDokument161 SeitenA Concise Introduction To Existential Counselling. Adamsjen100% (1)
- MCQ Chemistry PDFDokument19 SeitenMCQ Chemistry PDFV Srinivasa RaoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Study Methods and Academic Performance of Management Accounting StudentsDokument81 SeitenStudy Methods and Academic Performance of Management Accounting StudentsNonay BananNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lecture Guide 2 in Engineering Data Analysis Engr. Theresa Lean Roma Tuliao-SumerDokument17 SeitenLecture Guide 2 in Engineering Data Analysis Engr. Theresa Lean Roma Tuliao-SumerJustin Paul TumaliuanNoch keine Bewertungen