Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
AMBO205 - Business Transformation Assignment
Hochgeladen von
Anant BhargavaOriginaltitel
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
AMBO205 - Business Transformation Assignment
Hochgeladen von
Anant BhargavaCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
SEMESTER-II
Subject Name Study COUNTRY Roll Number (Reg.No.) Student Name : Business Transformation : : :
INSTRUCTIONS a) Students are required to submit all three assignment sets. ASSIGNMENT Assignment A Assignment B Assignment C b) c) d) e) DETAILS Five Subjective Questions Three Subjective Questions + Case Study 40 Objective Type Questions MARKS 10 10 10
Total weightage given to these assignments is 30%. OR 30 Marks All assignments are to be completed as typed in word/pdf. All questions are required to be attempted. All the three assignments are to be completed by due dates and need to be submitted for evaluation by Amity University. f) The students have to attached a scan signature in the form.
Signature : Date :
_________________________________ _________________________________
( ) Tick mark in front of the assignments submitted Assignment Assignment B Assignment C A
Business Transformation Assignment A
Q . 1 B u s i n e s s t r a n s f o r m a t i o n b u i l d s o n t h e dynamic interplay among value, complexity, and change. What are the major considerations that usually revolve around any transformation process?Also Discuss the various types of Business Transformation.
Q . 2 Write short Notes on
a) Business Model Innovation b) Incremental Strategy Development c) Elements of Strategic Decision-making Process
Q . 3 a ) How does Environmental Scanning using SWOT ,can keep a close watch over environmental
factors that affect your start-up and prepare adequately to face the emerging challenges? b ) VRIO is an acronym for the four question framework. Discuss the Questions which can help a firm attain the competitive Advantage. Q . 4 a ) What are critical questions answered by corporate-level strategists. Discuss the various types of Corporate Strategies and how does Stricklands Grand Strategy Selection Matrix help in Making strategic Choices? b) Differentiate between BCG and GE Matrix. Also cite the demerits of BCG matrix in brief.
Q . 5 Organizational structures imply formal relationships with well defined duties and responsibilities.
Discuss the various types of Organizational Structures.
A s s i g n me n t B :
Q . 1 Explain the term Strategic Decision Making .Do you agree that in Strategic decision making
situations-Options are consequential, situations may not have clear cause-and-effect outcomes. Q . 2 The balanced scorecard suggests that we view the organization from four perspectives, and to develop metrics, collect data and analyze it relative to each of these perspectives. Explain the same with the help of example and relevant model Q . 3 . The understanding for any business is that its core competency is rooted in the process of transformation itself, rather than being focused rather narrowly on competitive advantage in service or delivery of product. Comment.
Case Study
Section - C : Compulsory question
Nestl (NESN) has long been known for making chocolate treats for the common man. Think Kit Kat or Crunch bars. But demand for pricier premium chocolates is growing faster than that of plain old candy. So the Vevey (Switzerland)-based company has devised a novel strategy to move up the value chain: customized confections. Internet shoppers in Switzerland and Liechtenstein can now order a taster pack from Nestls Maison Cailler line of expensive Swiss chocolates. After nibbling the samples of five kinds of Ecuador-sourced chocolate with various cocoa content, consumers complete an online survey to determine their chocolate personality. They then can order larger boxes of the candies, marrying their favored chocolate with preferred fillings ranging from peppercorn and vanilla to raspberry and verbena. The bespoke chocolate experience doesnt come at Baby Ruth prices. A 16-piece box of the Maison Cailler chocolates costs 26 Swiss francs ($28.30). Thats just 128 grams of chocolate, or slightly more than 4 ounces, so these custom sweets price out to more than $100 a pound. Yet such luxe pricing can succeed even amid the economic downturn, says Laurent Freixe, head of Nestls European business. It may sound counterin tuitive, but whats happening in the [financial] crisis is a quest by consumers for value, for more-affordable product, but also for products that overtake their expectations.
In high-end chocolate, Nestl hopes to mimic a strategy it used to build demand for its Nespresso capsule, which helped create the luxury home-coffee market. That single-serving espresso-maker business began in only two countries in 1986, with Nestl introducing online sales in the 1990s and stores in 2002. Now its a 3 billion Swiss franc ($3.3 billion) brand, with about half its sales coming from the Internet and more than 250 boutiques worldwide. Nestl already has tried its hand at other premium, customized goods. The company in 2011 began selling BabyNes formula milk capsules, which fit its own $272 single-serving machine. A year earlier it debuted pricey Special.T pods containing top-quality tea in France. While Kit Kat bars are the worlds ninth-biggest chocolate brand, according to Euromonitor International, the company has had mixed success in the premium sweets segment in the past. Nestl, which merged with Cailler in 1929, sought to revamp the brand in 2006 with higher prices and packaging designed by architect Jean Nouvel. The overhaul was scrapped after it failed to boost revenue. Cailler still isnt well-known outside of Switzerland, with only 8 percent of sales coming from abroad. Nestl is a strong player in the mass -market, but in the premium segment, it doesnt have a strong reputation, says Patrick Hasenboehler, an analyst at Bank Sarasin in Zurich.
Chocolate producers including Swiss rival Lindt & Sprngli Group (LISP) already sell online, but only for
standard products. Bespoke chocolate is generally sold by niche chocolatiers. Maison Caillers online store will generate the bulk of its revenue, although some sales will come from a boutique in Broc, Switzerland, home to the 193-year-old Cailler brand. Nestl plans to expand the custom candies to neighboring countries beginning next year. The big objective is to make it sustainable, make it something which will enter into consumption habits and which will not be just a one-off, Freixe says.
Case Study Questions
Q.1 Discuss the Value Chain adopted by Nestle to enhance Value for its Target Audience while competing with their counterparts? Q.2. Nestl does a big business in low-priced candy bars. Now its selling $100-a-pound chocolates customized to buyers personal tastes. Comment on the Generic Business Strategy followed here. Assignment C (40 Multi ple choice questions)
A tendency of individuals to adopt the perspective of the group as a whole. It occurs when decision makers dont question 1 the underlying assumptions.
Think Tank
Group Think
Out of Box Thinking
Questionable Thinking
Clusters of firms within an industry that share certain critical asset configurations and follow 2 common strategies.
Strategic Business Units
Strategic Groups
Sectoral Groups
Rival Groups
Focus the firms efforts and 3 resources in one industry.
Diversification
Concentration
Integration
Outsourcing
The costs incurred when a buyer switches from one supplier to 4 another.
Fixed Costs
Switching Costs
Transfer Cost
Variable Costs
Aggressiveness in Pricing by a firm against its rivals with the intent of driving them out of 5 business.
Penetration Pricing
Predatory Pricing
Skim Pricing
Mark Up Pricing
Factors that reduce entry of new players or entrants into an 6 industry.
Exit Barriers
Entry Barriers
Mobility Barriers
Defensive Barriers
To monitor, evaluate and disseminate information from the external environment to key 7 people within the firm.
Information Sharing
Environmental Scanning
Data Churning
Data Mining
An unfavorable trend or development in the firms external environment that may lead to an erosion of the firms 8 competitive position.
Weaknesses
Threats
Strengths
Opportunities
statements indicating the desired strategic future for the 9 firm
Purpose
Vision
Mission
Objective
The rate over time at which 10 innovations are copied by rivals
Learning Curve
Diffusion Curve
Life Cycle Curve
Innovation Curve
Looking inside the business and identifying strengths and 11 weaknesses of the firm
External Appraisal
Internal Appraisal
SWOT Analysis
ETOP Analysis
Each product and enterprise is considered as an individual responsibility center for purposes 12 of strategy formulation.
Parenting Anlaysis
Portfolio Analysis
Pareto Analysis
PEST Analysis
Individuals and groups inside and outside the firm who have an interest in the actions and 13 decisions of the firm.
Shareholders
Stakeholders
Human Capital
Directors
A checklist of questions that provide an assessment of a firms strategic position and 14 performance.
Strategic Schedule
Strategic Audit
Strategic Questionnaire
Strategic Accounting
Unplanned strategy that emerge 15 from within the organization
intended Strategy
Emergent Strategy
Deliberate Strategy
Realised Strategy
The development of long-range plans for the management of environmental opportunities and threats, in light of the firms 16 strengths and weaknesses.
Strategy Formulation
Strategy Analysis
Strategy Implementatio n
Strategy Evaluation
Compares performance with desired results and provides the feedback for management to evaluate results and take 17 corrective action.
Strategy Controls
Strategy Objectives
Strategy Actions
Strategy statements
A strategy serving a specialized 18 part of the market
Focus
Cost Leadership
Differentiation
Best Solution Provider
The process by which strategies and policies are put into action through the development of programs, budgets, and 19 procedures.
Strategy Implementation
Strategy Evaluation
Strategy Formulation
Strategy Analysis
Fit between what the environment wants and what the 20 firm has to offer
Strategic Fit
Strategic Direction
Strategic Disparity
Strategic Balance
Where one firm has full ownership and control over all the stages in the production of a 21 product
Full integration
Taper Intergration
Quasi Integration
Horizontal Integration
A portfolio planning model based on analysing the relative market share and market growth rates for a companys products and/or 22 strategic business units These units typically generate cash in excess of the amount of cash needed to maintain the business. They are regarded as staid and boring, in a "mature" market, and every corporation would be thrilled to own as many 23 as possible. The business unit has low market share compared to competitors, however it is doing business in high-growth market. Most of the new businesses start in this quadrant. There are well established businesses in this market and new businesses try to grow and capture more market share. This market is growing and there are opportunities for 24 new businesses.
BCG Matrix
Probability Matrix
PIMS Matrix
GE Matrix
Cash Cows
Dogs
Stars
Question Marks
Question Marks
Cash Cows
Dogs
Stars
GE Matrix compares different products or businesses on "Business Strength" and "Market Attractiveness" variables and in addition the size of the bubbles represents the market size.It is 25 also known as It is a collection of businesses ranging from primary producers, processors, distributors and retailers that progressively create consumer value in a specific 26 market segment. It is positive disposition of a customer toward a particular enterprise. It however, also includes intangible assets or qualities of the company, or its management, that cause people to 27 hold the company in high regard.
Multifactor Portfolio Analysis Model
ETOP Model
Hofer Model
Ansoff Model
Value chain
Supply Chain
Distribution Chain
Food Chain
Goodwill
Patents
Copyrights
Competencies
It is the return of information about the impact of an activity. In other uses it can also mean the return of a portion of the output 28 of a process as new input. These are resources under the control of an enterprise that are typically non-physical and not of a monetary nature, and that are critical for the success of the business. These resources include things such as brand image, customer and employee loyalty, quality of business relationships, 29 social standing
Feedback
Reverse Logistics
Reverse Information
Relative Input
Intangible Resouces
Tangible Resources
Valuable Resources
Human Resources
It is an organization that is able to adapt to change, move forward, and transform itself by acquiring new knowledge, skills, 30 or behaviors.
Learning Organisation
Lean Organisation
Flat Organisation
Tall Organisation
It is a cost/benefit comparison of the cost of an investment or activity compared with the financial and/or non-financial 31 benefits that result.
Cost of Return
Cost of investment
Break Even
Return on Investment
A _________ is appropriate where the target customer segment is not price-sensitive, the market is competitive or saturated, customers have very specific needs which are possibly under-served, and the firm has unique resources and capabilities which enable it to satisfy these needs in ways that are difficult to 32 copy A _________ should target market segments that are less vulnerable to substitutes or where a competition is weakest to earn above-average return on 33 investment. The Primary Activities of the Value Chain which are the transformation activities that change inputs into outputs that are sold to customers. Here, your 34 operational systems create value. These are all the processes related to receiving, storing, and distributing inputs internally. Your supplier relationships are a 35 key factor in creating value here. These are a company's support systems, and the functions that allow it to maintain daily operations. Accounting, legal, administrative, and general management are examples of necessary infrastructure that businesses can use to their 36 advantage. Restitching business portfolio according to changes in market requirements allows corporate managers to focus on the best 37 market opportunities. Ability of two or more business units to generate greater value working together than they could working apart, synergy has its sources in shared resources, knowledge and skills, coordinated strategies, vertical integration or establishing 38 internal alliances in enterprise
Best Solution Strategy
Focus strategy
Cost Leadership Strategy
differentiation strategy
Best Solution Strategy
Cost Leadership Strategy
differentiation strategy
focused strategy
Operations
Logistics
Marketing
Customer Service
Inbound Logistics
Outbound Logistics
Warehousing
Transportation
Infrastructure
Human Resource Management
Procurement
Research and Technology
Patching
Co evolving
Regeneration
Refocus
Co-Evolution
Diversification
Differentiation
Business Splits
It is usually a restructuring plan and is adopted when a turnaround has been attempted but has proved to be unsuccessful or it 39 was ignored.
Divestment
Captive Company
Bankruptcy
Stability
It is any combination of Data, Information, and Knowledge concerning the Business environment in which a company operates that, when acted upon, will confer a significant Competitive advantage or enable 40 sound decisions to be made
Action with Intelligence
Innovation with Business Intellegence Intelligence
Business Decisions
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Bi Scorecard Process SummaryDokument5 SeitenBi Scorecard Process SummarySaving ValleyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Business Improvement Districts: An Introduction to 3 P CitizenshipVon EverandBusiness Improvement Districts: An Introduction to 3 P CitizenshipNoch keine Bewertungen
- Business 9609 Assignment TemplateDokument24 SeitenBusiness 9609 Assignment TemplateShenal NethminNoch keine Bewertungen
- Strategic Business Unit A Complete Guide - 2020 EditionVon EverandStrategic Business Unit A Complete Guide - 2020 EditionNoch keine Bewertungen
- Post-merger integration A Complete Guide - 2019 EditionVon EverandPost-merger integration A Complete Guide - 2019 EditionNoch keine Bewertungen
- Product Line Management A Complete Guide - 2019 EditionVon EverandProduct Line Management A Complete Guide - 2019 EditionNoch keine Bewertungen
- Transformation Plan A Complete Guide - 2019 EditionVon EverandTransformation Plan A Complete Guide - 2019 EditionNoch keine Bewertungen
- Business Process Re-engineering A Complete Guide - 2019 EditionVon EverandBusiness Process Re-engineering A Complete Guide - 2019 EditionNoch keine Bewertungen
- Musgrave's Business Environment AssignmentDokument19 SeitenMusgrave's Business Environment AssignmentDerrick FranklinNoch keine Bewertungen
- FIA Sem 2 PACT002 AssignmentDokument20 SeitenFIA Sem 2 PACT002 AssignmentMohammad Fazrul Amin Bin Ramlee100% (1)
- Sales Capacity Planning A Complete Guide - 2021 EditionVon EverandSales Capacity Planning A Complete Guide - 2021 EditionNoch keine Bewertungen
- Growth Strategy Process Flow A Complete Guide - 2020 EditionVon EverandGrowth Strategy Process Flow A Complete Guide - 2020 EditionNoch keine Bewertungen
- Accenture Archetypes Winning Geographically Diverse and Digital WorldDokument20 SeitenAccenture Archetypes Winning Geographically Diverse and Digital WorldDang PhuongNoch keine Bewertungen
- Feedback - Form-WWLP Asgn 4Dokument4 SeitenFeedback - Form-WWLP Asgn 4Danish SayedNoch keine Bewertungen
- Assignment Brief (Business Decision Making)Dokument8 SeitenAssignment Brief (Business Decision Making)Nguyen Dac ThichNoch keine Bewertungen
- Critical Financial Review: Understanding Corporate Financial InformationVon EverandCritical Financial Review: Understanding Corporate Financial InformationNoch keine Bewertungen
- Integrated Business Planning A Complete Guide - 2020 EditionVon EverandIntegrated Business Planning A Complete Guide - 2020 EditionNoch keine Bewertungen
- Business Law-Assignment December 2018Dokument8 SeitenBusiness Law-Assignment December 2018KKNoch keine Bewertungen
- Business Operations Group AssignmentDokument7 SeitenBusiness Operations Group Assignmentankit gangeleNoch keine Bewertungen
- Business Strategic AssignmentDokument15 SeitenBusiness Strategic AssignmentSheetal JasmeetNoch keine Bewertungen
- Assignment 412 Answers: Retail POS CustomersDokument12 SeitenAssignment 412 Answers: Retail POS CustomersPradeep DhanushkaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Dell Inc.Dokument6 SeitenDell Inc.Fahad Umar100% (1)
- Business AssignmentDokument7 SeitenBusiness AssignmentariefahNoch keine Bewertungen
- Business Ethics AssignmentDokument4 SeitenBusiness Ethics AssignmentNext PersonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Business Stratergies AssignmentDokument4 SeitenBusiness Stratergies AssignmentAnkur SrivastavaNoch keine Bewertungen
- CRM in Virtual Business PDFDokument5 SeitenCRM in Virtual Business PDFIndika SampathNoch keine Bewertungen
- Business Environment AssignmentDokument9 SeitenBusiness Environment AssignmentAbdul RahimNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cambodian Mekong University: Understanding Business AssignmentDokument19 SeitenCambodian Mekong University: Understanding Business AssignmentAli GMNoch keine Bewertungen
- Market Research in Business (Unit 10) Assignment BriefDokument12 SeitenMarket Research in Business (Unit 10) Assignment BriefRubaiyatrNoch keine Bewertungen
- Unit 7 Business Strategy AssignmentDokument7 SeitenUnit 7 Business Strategy AssignmentMohammadAhmad100% (2)
- The Balanced Scorecard - SummaryDokument10 SeitenThe Balanced Scorecard - SummaryGuest HouseNoch keine Bewertungen
- P&G UnileverDokument7 SeitenP&G UnileverPratyusha DashNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bmo6624-Organisation Change Management - Assessment 4 (Final Version)Dokument30 SeitenBmo6624-Organisation Change Management - Assessment 4 (Final Version)abcdpitt4722Noch keine Bewertungen
- Mas 21226 SolutionDokument14 SeitenMas 21226 SolutionAditiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ebusiness AssignmentDokument18 SeitenEbusiness AssignmentRakesh Sheokand50% (2)
- Dixons Retail PLC - Assignment Business EnvironmentDokument11 SeitenDixons Retail PLC - Assignment Business EnvironmentAndrei TomyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sample Assignment For The Course of International BusinessDokument14 SeitenSample Assignment For The Course of International BusinessAnonymous RoAnGpANoch keine Bewertungen
- Managing Radical ChangeDokument30 SeitenManaging Radical ChangeDeepan BaalanNoch keine Bewertungen
- E-Business Model of CitiBankDokument1 SeiteE-Business Model of CitiBankKnt Nallasamy GounderNoch keine Bewertungen
- HND Business AssignmentDokument2 SeitenHND Business AssignmentShahzaib AzharNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nike Company/ Essay / PaperDokument8 SeitenNike Company/ Essay / PaperAssignmentLab.com100% (1)
- AS 17 Segment Reporting - Objective Type Question PDFDokument44 SeitenAS 17 Segment Reporting - Objective Type Question PDFrsivaramaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Business Communiication AssignmentDokument4 SeitenBusiness Communiication AssignmentAbid Zain Alam0% (1)
- BCOS-183 Computer Application and Business EDokument4 SeitenBCOS-183 Computer Application and Business EAnupama SahNoch keine Bewertungen
- 3.6.7 - UAT Test Script Details - AXDokument11 Seiten3.6.7 - UAT Test Script Details - AXVishal VermaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Business To Business Marketing AssignmentDokument2 SeitenBusiness To Business Marketing Assignmentsirisha_bvsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Business Communication Assignment No 1 Autumn 2020Dokument15 SeitenBusiness Communication Assignment No 1 Autumn 2020Mujtaba AhmedNoch keine Bewertungen
- Business PCL I HR Human Resourse Planning Module AssignmentDokument3 SeitenBusiness PCL I HR Human Resourse Planning Module AssignmentPrabhjot Singh RekhiNoch keine Bewertungen
- CLAP - Brief To MentorsDokument19 SeitenCLAP - Brief To Mentorsd2687681Noch keine Bewertungen
- MysticMonkCoffeeCaseStudy TravisHuberDokument7 SeitenMysticMonkCoffeeCaseStudy TravisHuberTravisJohnHuber50% (2)
- 12 Managing Business With Sap Planning Implementation and Evaluation 2004Dokument349 Seiten12 Managing Business With Sap Planning Implementation and Evaluation 2004praveen78619371Noch keine Bewertungen
- Customer Relationship Management in India - Case of Volkswagen IndiaDokument20 SeitenCustomer Relationship Management in India - Case of Volkswagen IndiaPratik Mohapatra94% (17)
- Esoft Marketing Assignment 2Dokument8 SeitenEsoft Marketing Assignment 2sheran230% (1)
- UMACRQ-15-M Strategic Management Accounting: Session 6: Activity-Based Costing (ABC) RevisitedDokument24 SeitenUMACRQ-15-M Strategic Management Accounting: Session 6: Activity-Based Costing (ABC) RevisitedAhmed MunawarNoch keine Bewertungen
- International Business - India and Latin AmericaDokument2 SeitenInternational Business - India and Latin AmericasankalppatkarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Assigning Business Roles SAPDokument5 SeitenAssigning Business Roles SAPNeeraj MelayilNoch keine Bewertungen
- Important Note: Booked & Payable at Goibibo: Total Has Been Rounded Off To Next Rupee ValueDokument4 SeitenImportant Note: Booked & Payable at Goibibo: Total Has Been Rounded Off To Next Rupee ValueAnant BhargavaNoch keine Bewertungen
- ADL 16 Total Quality Management V4ADokument1 SeiteADL 16 Total Quality Management V4AAnant BhargavaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Performance Appraisal FormDokument10 SeitenPerformance Appraisal FormAnant BhargavaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Marketing Strategies of Toyota in IndiaDokument51 SeitenMarketing Strategies of Toyota in IndiaAnant Bhargava50% (2)
- Asodl GhuiopDokument5 SeitenAsodl GhuiopAnant BhargavaNoch keine Bewertungen
- DoneDokument2 SeitenDoneAnant BhargavaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Given That P 0.995138, How Many Persons Age 46 Can Be Expected To Die Before Reaching Age 47 Out of A Group of 1,000,000?Dokument1 SeiteGiven That P 0.995138, How Many Persons Age 46 Can Be Expected To Die Before Reaching Age 47 Out of A Group of 1,000,000?Anant BhargavaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Objectives of StudyDokument19 SeitenObjectives of StudyAnant BhargavaNoch keine Bewertungen
- GopeshDokument2 SeitenGopeshAnant BhargavaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Q2.Marital Status?Dokument11 SeitenQ2.Marital Status?Anant BhargavaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Average: Interpretation of DataDokument17 SeitenAverage: Interpretation of DataAnant BhargavaNoch keine Bewertungen
- A Project Report On " Brand Equity Analysis of Icici Prudential Life Insurance Products Within The Contemprory Insurance Product Market"Dokument16 SeitenA Project Report On " Brand Equity Analysis of Icici Prudential Life Insurance Products Within The Contemprory Insurance Product Market"Anant BhargavaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Major Findings and Interpretation of ThestudyDokument6 SeitenMajor Findings and Interpretation of ThestudyAnant BhargavaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Project Report: Introduction of The ProblemDokument1 SeiteProject Report: Introduction of The ProblemAnant BhargavaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Theoretical Perspective:: Objective & ScopeDokument1 SeiteTheoretical Perspective:: Objective & ScopeAnant BhargavaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Declaration: Distribution of Respondents Based On AgeDokument25 SeitenDeclaration: Distribution of Respondents Based On AgeAnant BhargavaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Methodology: Objective & ScopeDokument1 SeiteMethodology: Objective & ScopeAnant BhargavaNoch keine Bewertungen
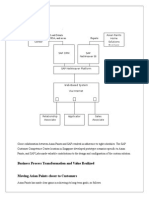
- Business Process Transformation and Value RealizedDokument4 SeitenBusiness Process Transformation and Value RealizedAnant BhargavaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Declaration: Please Mark Envelope Strictly Confidential'Dokument4 SeitenDeclaration: Please Mark Envelope Strictly Confidential'Anant BhargavaNoch keine Bewertungen
- It Skills: Ms Dos, Windows 98 & Xp. Ms Office (Word Excel, Powerpoint) - Tally 6.3, SageDokument1 SeiteIt Skills: Ms Dos, Windows 98 & Xp. Ms Office (Word Excel, Powerpoint) - Tally 6.3, SageAnant BhargavaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lead Details SOA, and So On Reports Asian Paints Home Solutions Business Customer Interaction CenterDokument5 SeitenLead Details SOA, and So On Reports Asian Paints Home Solutions Business Customer Interaction CenterAnant BhargavaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Etec 6223 Educational ReportDokument13 SeitenEtec 6223 Educational Reportapi-310826346Noch keine Bewertungen
- Google Case StudyDokument5 SeitenGoogle Case StudyKaushik Sarkar100% (1)
- Multiple Choice QuizDokument4 SeitenMultiple Choice QuizMuthusamy SenthilkumaarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Deloitte Change Vision To Value Full Pursuit Package - Nov2018Dokument182 SeitenDeloitte Change Vision To Value Full Pursuit Package - Nov2018M Victoria MNoch keine Bewertungen
- Aetna Diversity Case 1Dokument32 SeitenAetna Diversity Case 1Echo ZhanNoch keine Bewertungen
- ELECTIVE FCC12 Financial Management For Agribusiness EnterpriseDokument3 SeitenELECTIVE FCC12 Financial Management For Agribusiness EnterpriseJov'z GuerreroNoch keine Bewertungen
- Introduction To Private and Public IntelligenceDokument170 SeitenIntroduction To Private and Public IntelligenceCharbak Quazi100% (1)
- Strategic Management SberbankDokument16 SeitenStrategic Management SberbankJan BudaevNoch keine Bewertungen
- The-Business-Model-Canvas IKEADokument1 SeiteThe-Business-Model-Canvas IKEAPasukan EliteNoch keine Bewertungen
- Strategic Management NotesDokument52 SeitenStrategic Management Notesyogesh verma96% (28)
- Horizontal MergersDokument12 SeitenHorizontal MergersRahul Aggarwal100% (2)
- STR - Implementation - Abridged Aug Sep 14Dokument19 SeitenSTR - Implementation - Abridged Aug Sep 14ankit274Noch keine Bewertungen
- Moving From Transactional To Transformational HRDokument3 SeitenMoving From Transactional To Transformational HRSalman Hakkani100% (2)
- Coca ColaDokument64 SeitenCoca ColaRachit JoshiNoch keine Bewertungen
- CRM BrochureDokument9 SeitenCRM BrochureMehdi AbdelNoch keine Bewertungen
- Activity 1 3Dokument6 SeitenActivity 1 3Christian VillaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sales & Promotion at Coca ColaDokument87 SeitenSales & Promotion at Coca Colajagruti0% (2)
- Final Marketing Strategy ICICIDokument36 SeitenFinal Marketing Strategy ICICIAbhishek MishraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Role of The CIO in Effective IT: Strategic IT Planning Through Corporate GovernanceDokument9 SeitenRole of The CIO in Effective IT: Strategic IT Planning Through Corporate GovernanceIvoryNoch keine Bewertungen
- Boundary Permeability and Online-Offline Hybrid Organization A Case Study of Suning, ChinaDokument13 SeitenBoundary Permeability and Online-Offline Hybrid Organization A Case Study of Suning, ChinaAANoch keine Bewertungen
- Executive Summary: Tyson Foods, IncDokument15 SeitenExecutive Summary: Tyson Foods, IncJeannie GussNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pestel AnalysisDokument2 SeitenPestel AnalysisstyledbystunnaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Restaurant Business PlanDokument34 SeitenRestaurant Business Planmohe80% (10)
- ID26Dokument21 SeitenID26Ashish BaidyanathanNoch keine Bewertungen
- VP Global Strategic Marketing in New York City Resume Nancy SheaDokument3 SeitenVP Global Strategic Marketing in New York City Resume Nancy SheaNancySheaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Management Technology and InnovationDokument28 SeitenManagement Technology and InnovationSabbir Ahmed SolaimanNoch keine Bewertungen
- White Ocean StrategiDokument9 SeitenWhite Ocean StrategiMIRA AISA INDINoch keine Bewertungen
- HDFC N SbiDokument129 SeitenHDFC N SbiShruti PoddarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 2 ReviewDokument3 SeitenChapter 2 ReviewStibin ilibinNoch keine Bewertungen
- Standard Costing: Mcgraw-Hill/IrwinDokument92 SeitenStandard Costing: Mcgraw-Hill/IrwinelmarcomonalNoch keine Bewertungen