Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
INFS1602 Ch1 Notes
Hochgeladen von
yeungkaseyOriginalbeschreibung:
Originaltitel
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
INFS1602 Ch1 Notes
Hochgeladen von
yeungkaseyCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Ch1: Info Sys in Global Business today 1.
1 Role of Info Sys in Business today Whats new in Management info sys? Technology: Cloud Computing platform emerges as a major business area of innovation. More powerful, energy efficient computer processing and storage devices Growth in Software as a Service (Saas) Netbooks emerge often using open source software. Mobile digital platform emerges Management: Adopt online collaboration and social networking software to improve coordination, collaboration and knowledge sharing Business intelligence application acceleratemore powerful data analytics and interactive dash boards to provide real-time performance information to managers to enhance management control and decision making. Adopt mobile tools such as smartphones and mobile Internet devices to accelerate decision making and improve performance emerging mobile platform greatly enhances the accuracy, speed, and richness of decision making as well as responsiveness to customers because mobile phones are convenient for managers to bring around and get updated or make respond quickly. Virtual meetings grow adopt video conferencing and web conferencing tech to reduce travel time and cost while improving collaboration and decision making. Organisation: Web 2.0 applications are widely adopted by firms enable employees to interact as online communities using blogs, wikis and instant messaging services. Social networking sites create new opportunity for business to collaborate with customers and vendors. Telework gains momentum in workplace (internet, wireless laptops, iPhones, Blackberrys) make possible to work away from traditional office. Outsourcing production firms learn to use new tech to outsource production work to low wage countries. Co-creation of business value shift from product based value creation to solutions and experiences from internal sources, network of suppliers and collaboration with customers. The Emerging Digital Firm: one in which organisations significant business relations with customers, suppliers, and employees are digitally enabled and mediated. Core business processes accomplished through digital network, key corporate assets managed through digital means. Allows time shifting and space shifting. Strategic Business Objectives of Info Sys: 1. Operational Excellence: efficiency in operations such as Wal-Mart that uses RetailLink system which digitally link its suppliers so that as soon as a customer purchases an item, the supplier monitoring the item knows to ship replacement to the shelf. 2. New products, services, and business models (describes how company produces, delivers, and sells a g/s to create wealth) 3. Customers and suppliers Intimacy: e.g Hotels use computers to keep track of guests preferences such as preferred room temp, television programs and music. Can be used to find patterns(selling size, colours, styles) to help reduce overproduction and its associated inventory storage cost. 4. Improved decision making: real time data from marketplace reduce overproduction, misallocation of resources and poor response time. 5. Competitive advantage: from achieving the above points hence realising higher profits competitors cannot match. E.g Toyota implement TPS and produce vehicles based on what customers have actually ordered reduce wastage. 6. Survival: become necessities e.g. driven by industry-level change such as ATMs first introduced by Citibank now is a requirement of being in and surviving in retail banking business. The above shows that in contemporary sys there is a growing interdependence between a firms info sys and its business capabilities. Changes in strategy, rules and biz processes increasingly require changes in hardware, software, databases and telecommunication (collectively known as info sys). Often, what the organisation would like to do depends on what its sys will permit it to do.
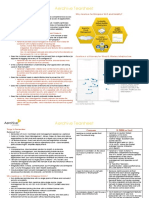
1.2 Perspective of Info Sys What is Info Sys: set of interrelated components that collect, process, store and distribute information to support decision making. Consist of all hardware and software. Data: raw facts information: when data have been shaped into a form that is meaningful and useful to human. Inputs: captures, collect raw data internally or externally process: converts raw input into meaningful form output: transfer processed info to whom will use it. Feedback: output that is returned to help evaluate or correct input stage. Dimension of Info Sys: Organisation Key elements: people; Hierarchical structure consisting of senior mgmt (long term strategic decisions and ensures financial performance of firm), middle mgmt (carries out programs and plans of senior mgmt), operational mgmt (responsible for monitoring daily activities); Business processes include formal rules that have been developed for accomplishing task (could be automate) or informal work practices; Politics is the conflicting views and interest between different levels and specialities for how firm is run and how resources and rewards be distributed; Culture is the fundamental set of assumptions, values, and ways of doing things, that has been accepted by most of its members. Management Manage what already exist (coordinate, strategy and planning, identify problem and solutions and make decision) and creatively create new g/s driven by new knowledge and info and even re-create the organisation. Technology Hardware, software, data management tech, networking and telecommunications tech, and Internet along with people required to ryn and manage them constitute the firms information technology infrastructure. Information systems literacy: understand all 3 dimensions above. Computer literacy: is only knowledge on the technology dimension. Complementary Assets required to optimise returns from IT investments Organisational assets Supportive organisational culture, appropriate biz model, efficient biz processes, decentralised authority, distributed decision-making rights, strong IS development team. Managerial assets Strong senior mgmt support for tech investment, mgmt culture that values flexibility and knowledgebased decision making, incentives for mgmt innovation, teamwork and collaborative work environments, training programs to enhance mgmt decision making skills Social assets Internet and telecommunication infrastructure, IT rich educational programs 1.3. Contemporary approaches to info sys Technical Approach: focus on formal models and capabilities of system Computer science, management science and operations research. Behavioural approach: focus on design, implementation, and business impact of systems Psychology, sociology and economics. Sociotechnical view of systems considers both technical and social features of systems and solutions that represent the best fit between them.
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Solidworks Workgroup PDM InstallationDokument7 SeitenSolidworks Workgroup PDM InstallationmecanicajcNoch keine Bewertungen
- HIL Configuration Using MatlabDokument13 SeitenHIL Configuration Using MatlabVimal RauNoch keine Bewertungen
- How Management An Art or A Science (REHAN)Dokument2 SeitenHow Management An Art or A Science (REHAN)Rehan AhmadNoch keine Bewertungen
- Computer Networks Lab Manual LatestDokument45 SeitenComputer Networks Lab Manual LatestKande Archana K100% (16)
- BMS 841 Course OutlineDokument3 SeitenBMS 841 Course OutlineMutevu SteveNoch keine Bewertungen
- Architecting and Deploying Splunk 6.4Dokument200 SeitenArchitecting and Deploying Splunk 6.4Leandro de MatosNoch keine Bewertungen
- Automotive Telematics: 1.0 Executive SummaryDokument7 SeitenAutomotive Telematics: 1.0 Executive SummaryRaghav NevatiaNoch keine Bewertungen
- GIS Work Book - teoretical curs - русDokument74 SeitenGIS Work Book - teoretical curs - русblah2224Noch keine Bewertungen
- Taylor Scientific ManagementDokument2 SeitenTaylor Scientific ManagementworkingfolksNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cyber Power & National SecurityDokument664 SeitenCyber Power & National Securitydecember152011100% (6)
- 1.trends in Information SystemDokument16 Seiten1.trends in Information Systemmathewscj1Noch keine Bewertungen
- Objectives of FASDEP II SummarizedDokument3 SeitenObjectives of FASDEP II SummarizedDanielNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Technical Approach: Advantages of Client Server Networks Over Peer To Peer NetworksDokument2 SeitenThe Technical Approach: Advantages of Client Server Networks Over Peer To Peer NetworksChaya SheikhNoch keine Bewertungen
- Director of Big DataDokument2 SeitenDirector of Big DataBugNoch keine Bewertungen
- Industrial EngineeringDokument2 SeitenIndustrial EngineeringIrina0% (1)
- Application of Operation Reasearch in Hospital ManagementDokument3 SeitenApplication of Operation Reasearch in Hospital ManagementBoobalan RNoch keine Bewertungen
- Foundations of Simplex AlgorithmDokument3 SeitenFoundations of Simplex AlgorithmnishanthNoch keine Bewertungen
- RRLDokument3 SeitenRRLHarold CarvajalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Anjani Kumar SinghDokument3 SeitenAnjani Kumar SinghUllas PandeyNoch keine Bewertungen
- WorkDokument3 SeitenWorkAnkit TiwariNoch keine Bewertungen
- Seatwork in Management Science & Maximization Model-1Dokument1 SeiteSeatwork in Management Science & Maximization Model-1Blu3NPinkNoch keine Bewertungen
- Daftar PustakaDokument2 SeitenDaftar PustakaSuviiana RNoch keine Bewertungen
- Supporting Documents: General Business & ManagementDokument3 SeitenSupporting Documents: General Business & ManagementMitzulica1011Noch keine Bewertungen
- Information Is The Basis For Every Decision Taken in An OrganizationDokument2 SeitenInformation Is The Basis For Every Decision Taken in An OrganizationHony HonyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Curriculum VitaeDokument3 SeitenCurriculum VitaeCristian GintingNoch keine Bewertungen
- FB11001 Summary Where Are New Theories of OrganizationDokument2 SeitenFB11001 Summary Where Are New Theories of OrganizationDr-Akshay Bhat0% (1)
- Cranfield School of ManagementDokument2 SeitenCranfield School of ManagementTien NguyenNoch keine Bewertungen
- Matthew Stark ResumeDokument1 SeiteMatthew Stark ResumeSt. Bonaventure Students in Money ManagementNoch keine Bewertungen
- Q. What Is A Risk Management Consultant?: Don'T All Insurance Professionals Advise or Offer Professional Advice?Dokument3 SeitenQ. What Is A Risk Management Consultant?: Don'T All Insurance Professionals Advise or Offer Professional Advice?hafiz_yaakopNoch keine Bewertungen
- Justin A. Catalan - Bs in Management IvDokument3 SeitenJustin A. Catalan - Bs in Management IvJustin CatalanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fayol&TaylorDokument2 SeitenFayol&TayloransaradnanNoch keine Bewertungen
- What Is Operational Research?: Why Is OR Needed?Dokument3 SeitenWhat Is Operational Research?: Why Is OR Needed?Suvidha DixitNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Era of Scientific Management, Operations ManagementDokument1 SeiteThe Era of Scientific Management, Operations Managementakamalapuri388Noch keine Bewertungen
- Is Management Science or Arts?Dokument3 SeitenIs Management Science or Arts?FFC129Noch keine Bewertungen
- Management Science - UMDokument3 SeitenManagement Science - UMEly IseijinNoch keine Bewertungen
- Library of Abbottabad University of Science and TechnologyDokument2 SeitenLibrary of Abbottabad University of Science and TechnologySubhan AliNoch keine Bewertungen
- Management Trainee Job DescriptionDokument1 SeiteManagement Trainee Job DescriptionumeshjmangroliyaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Background of UNITAR International UniversityDokument3 SeitenBackground of UNITAR International UniversityAin NadiaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Keyterm Chap 1Dokument3 SeitenKeyterm Chap 1HuynhGiangNoch keine Bewertungen
- MGT508 Operations ManagementDokument3 SeitenMGT508 Operations ManagementTrungKiemchacsuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Historical Theories of ManagementDokument3 SeitenHistorical Theories of ManagementokwesiliezeNoch keine Bewertungen
- OperationsDokument2 SeitenOperationsjskjunior77Noch keine Bewertungen
- Management Science Assignment 1Dokument2 SeitenManagement Science Assignment 1Saleamlak AfireNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ulrich Körner, PHDDokument2 SeitenUlrich Körner, PHDAlpinum Investment ManagementNoch keine Bewertungen
- ReportDokument2 SeitenReportTawfik OussaidNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 1 Reviewer Operations ManagementDokument3 SeitenChapter 1 Reviewer Operations ManagementsssilencersevenNoch keine Bewertungen
- Operations Management AssignmentDokument2 SeitenOperations Management AssignmentRichard LaneNoch keine Bewertungen
- 24mba Production and Operations Management Set1Dokument2 Seiten24mba Production and Operations Management Set1SRINIVASA RAO GANTANoch keine Bewertungen
- Supply Chain Management (MEC6009) - Course PlanDokument3 SeitenSupply Chain Management (MEC6009) - Course PlanpitchipooNoch keine Bewertungen
- Operations Management Case Bill's HardwareDokument2 SeitenOperations Management Case Bill's HardwareravindramahadurageNoch keine Bewertungen
- Following Are The Key Characteristics of MIS:: System ApproachDokument2 SeitenFollowing Are The Key Characteristics of MIS:: System ApproachAnanya SarangiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Operations Management AssignmentDokument2 SeitenOperations Management AssignmentRichard LaneNoch keine Bewertungen
- Workbased Assignment - Financial ManagementDokument2 SeitenWorkbased Assignment - Financial Managementsuemwinza0% (1)
- Operations Management QuestionsDokument2 SeitenOperations Management QuestionsSyed QutubuddinNoch keine Bewertungen
- MMH717 OperationsmanagementDokument2 SeitenMMH717 OperationsmanagementSri HarshaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Practical Problems in Breakeven PointDokument3 SeitenPractical Problems in Breakeven Pointnerisa econas0% (1)
- Managment AssignmentDokument33 SeitenManagment AssignmentRiyad AhsanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Myk Ogbinar 2019 CV 0318Dokument2 SeitenMyk Ogbinar 2019 CV 0318Myk OgbinarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Erp Application Operations Management PDF in HindiDokument2 SeitenErp Application Operations Management PDF in HindiMensurNoch keine Bewertungen
- Case StudyDokument3 SeitenCase StudyJane Koay100% (5)
- Cost Accounting Course OutlineDokument7 SeitenCost Accounting Course OutlineFurqan AhmedNoch keine Bewertungen
- National Institute of Business Management: Chennai - 020 Second Semester Emba/Mba Subject: Management Information SystemDokument14 SeitenNational Institute of Business Management: Chennai - 020 Second Semester Emba/Mba Subject: Management Information SystemAtul Raut100% (1)
- Scientific ManagementDokument3 SeitenScientific ManagementKristian_Matth_6269Noch keine Bewertungen
- Technology Unit 4Dokument20 SeitenTechnology Unit 4feba100% (1)
- 102 EABD CourseNoteDokument55 Seiten102 EABD CourseNoteDr. Rakesh BhatiNoch keine Bewertungen
- ICT Lesson 1 - Introduction To ICTDokument72 SeitenICT Lesson 1 - Introduction To ICTOTIENO ELIJAHNoch keine Bewertungen
- 3rd Semester Mis Notes 1Dokument56 Seiten3rd Semester Mis Notes 1Sanjay JaisiNoch keine Bewertungen
- INFS1602CH10 NotesDokument2 SeitenINFS1602CH10 NotesyeungkaseyNoch keine Bewertungen
- INFS1602Ch11 NotesDokument2 SeitenINFS1602Ch11 NotesyeungkaseyNoch keine Bewertungen
- INFS1602 CH9 NotesDokument2 SeitenINFS1602 CH9 NotesyeungkaseyNoch keine Bewertungen
- INFS1602CH8 NotesDokument2 SeitenINFS1602CH8 NotesyeungkaseyNoch keine Bewertungen
- INFS1602CH7 NotesDokument3 SeitenINFS1602CH7 NotesyeungkaseyNoch keine Bewertungen
- INFS1602 CH 6 NotesDokument3 SeitenINFS1602 CH 6 NotesyeungkaseyNoch keine Bewertungen
- INFS1602Ch3 NotesDokument3 SeitenINFS1602Ch3 NotesyeungkaseyNoch keine Bewertungen
- INFS1602Ch5 NotesDokument3 SeitenINFS1602Ch5 NotesyeungkaseyNoch keine Bewertungen
- INFS1602Ch4 NotesDokument4 SeitenINFS1602Ch4 NotesyeungkaseyNoch keine Bewertungen
- INFS1602 Ch1 NotesDokument2 SeitenINFS1602 Ch1 NotesyeungkaseyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Read and Understand Electronic Radar 1920s: SignalsDokument14 SeitenRead and Understand Electronic Radar 1920s: SignalsAdrian TerrazasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Preferred ResumeDokument2 SeitenPreferred ResumeAnonymous P3sQECwNoch keine Bewertungen
- Avaya IP Office: Delivering Intelligent Communications To Small BusinessesDokument131 SeitenAvaya IP Office: Delivering Intelligent Communications To Small Businessespk8barnesNoch keine Bewertungen
- GatewayTrapsG250G350G430G450G700AvayaS8xxxServers TrisoftCopy March27 2014 PDFDokument128 SeitenGatewayTrapsG250G350G430G450G700AvayaS8xxxServers TrisoftCopy March27 2014 PDFEzio LopesNoch keine Bewertungen
- MEC1000 Operation ManualDokument159 SeitenMEC1000 Operation ManualTECNOVIGILANCIA HOSPITAL CALARCANoch keine Bewertungen
- Dell EMC Data Domain DD3300 Data Protection PDFDokument2 SeitenDell EMC Data Domain DD3300 Data Protection PDFdsadrac100% (1)
- Wi-Fi Solution For Government: AXILSPOT CommunicationDokument4 SeitenWi-Fi Solution For Government: AXILSPOT CommunicationArgon UsmanNoch keine Bewertungen
- GSM Network Planning and Optimization Single Site Verification Work Guidebook V1.0Dokument41 SeitenGSM Network Planning and Optimization Single Site Verification Work Guidebook V1.0Tongai Naison MutengwaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Presentation - Oracle Exadata Architecture OverviewDokument34 SeitenPresentation - Oracle Exadata Architecture Overviewkinan_kazuki104Noch keine Bewertungen
- Fiche Technique VideoDokument19 SeitenFiche Technique Videop4s8wt8x86Noch keine Bewertungen
- 258 BLUECOAT-SGOS Vol3 IMStreaming 5.2.2 PDFDokument96 Seiten258 BLUECOAT-SGOS Vol3 IMStreaming 5.2.2 PDFMISPOLJNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2623-Article Text-4858-1-10-20210620Dokument10 Seiten2623-Article Text-4858-1-10-20210620ELERIA JOHNPATRICKNoch keine Bewertungen
- Connecting Audiocodes SBC To Microsoft Teams Direct Routing Hosting Model Configuration NoteDokument66 SeitenConnecting Audiocodes SBC To Microsoft Teams Direct Routing Hosting Model Configuration NoteerikaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Troubleshooting VoLTE &Dokument3 SeitenTroubleshooting VoLTE &AmbujNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ipela PCS-XG55, PCS-XG55SDokument8 SeitenIpela PCS-XG55, PCS-XG55SMilenko RiverosNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ict CSS SHS12 Q2 Las5 FinalDokument20 SeitenIct CSS SHS12 Q2 Las5 FinalLucky JuanNoch keine Bewertungen
- IPOLiS NW Design Tool UserGuideDokument33 SeitenIPOLiS NW Design Tool UserGuideQuyềnTrầnNoch keine Bewertungen
- M900-M1800 BSC V300R002 System Description 200603Dokument35 SeitenM900-M1800 BSC V300R002 System Description 200603Thats MyName100% (1)
- Aerohive Primer PDFDokument2 SeitenAerohive Primer PDFMichele BrunelliNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2900 NewbridgeDokument8 Seiten2900 NewbridgeallpabloNoch keine Bewertungen
- Profibus Module (Opmp) Operating Instructions: EnglishDokument22 SeitenProfibus Module (Opmp) Operating Instructions: EnglishchochoroyNoch keine Bewertungen
- 3G Enterprise Power Solutions - EPS2 SeriesDokument2 Seiten3G Enterprise Power Solutions - EPS2 SeriesEagan Wafi IndrastaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Exampdf: Higher Quality, Better Service!Dokument8 SeitenExampdf: Higher Quality, Better Service!Marcio KatanNoch keine Bewertungen