Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Driving Force For Fluid Flow
Hochgeladen von
Alphy ThomasOriginaltitel
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Driving Force For Fluid Flow
Hochgeladen von
Alphy ThomasCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Driving force for fluid flow
Driving force for fluid flow Driving force for fluid flow is Energy per unit mass or total head available at the point of location.
Justification:
If you observe the flow in venturi meter, it will become more clear. consider 3 points as shown in the below figure.
Assume P1, P2, P3 are pressures at 1, 2 and 3 points. Here according to cross section area variation we can say P1 > P2 < P3. It shows that P3 > P2 but fluid is moving from 2 point to 3 point, so we can say pressure is not the driving force. Similarly we can say velocity is also not the driving force. Why distillation? Why not adsorbption or leaching ?
In distillation the new phase generated is different from the original by phase, or heat content only. This heat can be removed or added by easy operations. But in case of adsorption or leaching the a foreign substance is introduced to separate the phases. Thenew phase generated using these processes is a new solution which in turn may be separated using other separation methods unless the new solution is directly useful. This makes thedistillation process to more economical. Distillation process depends on the relative volatilities of the components. If the difference is too low separation is difficult and it makes the process as more expensive.
When reflux ratio to the column is minimum and zero, what are the requirements in column When reflux ratio is minimum, column requires maximum number of trays and minimum reboiler load for a required separation. To avoid this problem of infinite trays we use optimum reflux ratio. Define Intensive and extensive properties, give examples for them Intensive and Extensive properties: Extensive property: Is defined as one which depends on quantityof matter specified in the system. Examples: Total mass, volume, Energy, enthalpy, Intensive property: It is defined as one which depends on the quantity of matter present in the sysytem.
Examples: Temperature, pressure,Molar enthalpy, molar v What is jigging and where it is used ? Jigging: Jigging is a separation method in which the particle are separated by using the density difference between them. Jigging is a method of gravitational preparation of natural resources, based on separation of mineral mixture on density in vertically oscillating water stream. Usually it is used to separate metal slag form metals. What is Differential Distillation, Simple Distillation, Rayleigh distillation,Rayleigh equation, material Balance equation Differential Distillation: Simple distillation, also known as Rayleigh distillation ordifferential distillation, is the most elementary example of batchdistillation. In this distillation system, the vapor is removed from the still during a particular time interval and is condensed in the condenser. The more volatile component is richer in the vapor than in the liquid remaining in the still. Over time, the liquid remaining in the still begins to experience a decline in the concentration of the more
volatile component, while the distillate collected in the condenser becomes progressively more enriched in the more volatile component. Schematic representation of differential distillation is as shown in in fig.1 Fig:1 Differential distillation
No reflux is returned to the still, and no stages or packing materials are provided inside the column; therefore, the various operating approaches are not applicable to this distillation system. The early analysis of this process for a binary system, proposed by Rayleigh is given below. Let F be the initial binary feed to the still (mol) and xF be the mole fraction of the more volatile component (A) in the feed. Let B be the amount of compound remaining in the still, xB be the mole fraction of component A in the still, and xD be the mole fraction of component A in the vapor phase. The differential material balancefor component A can then be written as: xD dB = d ( B xB ) = B dxB + xB dB Upon integration:
or
In this simple distillation process, it is assumed that the vapor formed within a short period is in thermodynamic equilibrium with the liquid; hence, the vapor composition (xD) is related to the liquid composition (xB) by an equilibrium relation of the form xD = F(xB). The exact relationship for a particular mixture may be obtained from a thermodynamic analysis depending on temperature and pressure. For a system following the ideal behavior given by Raoults law, the equilibrium relationship between the vapor composition y (or xD) and liquid composition X (or xB) of the more volatile component in a binary mixture can be approximated using the concept of constant relative volatility (), which is given by:
Substitution of the above equation in Equation (2)
Although the analysis of simple distillation historically represents the theoretical start of batch distillation research, a complete separation using this process is impossible unless the relativevolatility of the mixture is infinite. Therefore, the application of simple distillation is restricted to laboratory-scale distillation, where high purities are not required, or when the mixture is easily separable. what is a first order system and what physical phenomena give rise to first order system(It's transfer function)?
WHAT IS A FIRST-ORDER SYSTEM? A first-order system is one whose output, y(t), is modeled by a first order,linear differential equation
Define,
p is known as the time constant of the process and KP is called the steady state gain or static gain or simply the gainof the process. From eqn, it is easily found that the transfer function of a firstorder process is given by;
A first-order process with a transfer function given by above eqn. is also known as: first-order lag, linear lag, exponential transfer lag.
If on the other hand, a0 = 0, then from eqn. we take
which gives a transfer function
In such case the process is called purely capacitive or pure integrator
where f(t) is the input (forcing function). If a0 # 0, then above eqation yields,
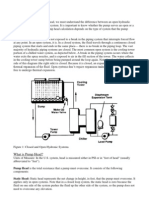
Dew Point: It is the temperature at which the partial pressure of the water vapour in the mixture is equal to the vapour pressure of water. It can also be defines as, the temperature where condensate formation will start upon constant cooling of vapour mixture . Dew point is a saturation temperature Dew point is always lower than or equal to the dry bulb temperature. Dew point is always lower than or equal to the wet-bulb temperature. At 100% saturation : Dry bulb temperature = wet bulb temperature = Dew point. What is volute in centrifugal pump, uses of volute in centrifugal pump
Centrifugal pump is as shown in the figure. In this figure observe the vanes shape and impeller direction.
Volute: It is the gap between the casing and the impeller. There are two uses with volute of the centrifugal pump. 1. In this volute kinetic energy is converted into pressure energy. As the cross section area increases, the volute reduces the velocity of the liquid and increases the pressure of the liquid. 2. One of the main purposes of a volute casing is to help balance the hydraulic pressure on the shaft of the pump. However, this occurs best at the manufacturer's recommended capacity. Running volute-style pumps at a lower capacity than the manufacturer recommends can put lateral stress on the shaft of the pump, increasing wear-and-tear on the seals and bearings, and on the shaft itself.
Centrifugal pumps are used for large discharge through smaller heads. What are differences between pipe and tube,Birmingham wire gauge,schedule number Pipes and tubes are specified in terms of their diameter and wall thickness. Pipes: Heavy walled Relatively large in diameter comes in moderate lengths (20 to 40 ft) Threading is not possible Pipe walls are rough Lengths of pipes are joined by screwed, flanged and welded fittings Made by welding , casting, or piercing a billet in a piercing mill The wall thickness of the pipe is indicated usingschedule number Size of the pipe is indicated as nominal diameter Tubes: Thin walled Less diameter available in the form of coils also, several hundred meters Can be threaded Tube walls are smooth
These are joined by compression fittings, flare fittings, or soldered fittings These can be cold drawn Tube thickness is indicated using BWG (Birminghamwire gauge) Size of the tube is indicated as outside diameter NPSH is an acronym for Net Positive Suction Head. In any cross-section of a generic hydraulic circuit, the NPSH parameter shows the difference between the actual pressure of a liquid in a pipeline and the liquid's vapor pressure at a given temperature. NPSH is an important parameter to take into account when designing a circuit: whenever the liquid pressure drops below the vapor pressure, liquid boiling occurs, and the final effect will be cavitation: vapor bubbles may reduce or stop the liquid flow, as well as damage the system.
Considering the circuit shown in the picture
where hL is the head loss between 0 and 1 p0 is the pressure at the water surface pv is the vapour pressure (saturation pressure) for the fluid at the temperature T1 at 1 z is the difference in height z1 z0 (shown as H on the diagram) from the water surface to the location 1 is the fluid density g is gravitational acceleration
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Advantages of Distilled WaterDokument7 SeitenAdvantages of Distilled Waterapi-3827527100% (5)
- Pump Head CalculationDokument15 SeitenPump Head CalculationYashapuja100% (1)
- Batch Distillation ExperimentsDokument29 SeitenBatch Distillation Experimentsytconstance50% (4)
- Lab Report 2 - Head Loss in Pipe & BendsDokument20 SeitenLab Report 2 - Head Loss in Pipe & BendsChris Ang76% (21)
- Exp.2-Principles of Saturation Pressure MeasurementDokument65 SeitenExp.2-Principles of Saturation Pressure MeasurementAmir Hamzah25% (4)
- Pump Head CalculationsDokument4 SeitenPump Head CalculationsPrabhjot Singh SahiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Calculation K ValueDokument12 SeitenCalculation K ValueAshrafMostafaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Reboiler and VaporiserDokument56 SeitenReboiler and Vaporiserjihad jamareiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Flow Measurement Techniques and SensorsDokument5 SeitenFlow Measurement Techniques and SensorsTAREK ALMAHDYNoch keine Bewertungen
- Using DIERS Two-Phase Equations To Estimate Tube Rupture FlowratesDokument8 SeitenUsing DIERS Two-Phase Equations To Estimate Tube Rupture FlowratesAugusto Jorge Lozada100% (1)
- Linde V Stapler h40d h40t h45d h45t h50d h50t Series 394 Service Training Manual deDokument23 SeitenLinde V Stapler h40d h40t h45d h45t h50d h50t Series 394 Service Training Manual dekathleenjames170285xep98% (99)
- Centrifugal Pump - HandbookDokument26 SeitenCentrifugal Pump - HandbookPrafull Dhakate100% (2)
- Separation TechniquesDokument17 SeitenSeparation Techniquesdenise adrieneNoch keine Bewertungen
- Experiment 4 - Flow MeasurementDokument24 SeitenExperiment 4 - Flow MeasurementKhairil Ikram67% (6)
- Working Guide to Vapor-Liquid Phase Equilibria CalculationsVon EverandWorking Guide to Vapor-Liquid Phase Equilibria CalculationsBewertung: 5 von 5 Sternen5/5 (1)
- Vacuum TheoryDokument79 SeitenVacuum TheoryrusyadNoch keine Bewertungen
- P&IDDokument34 SeitenP&IDAz Zahra Assyifa UshwahNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fluid Mechanics Tutorial 8C Pumped Piped Systems: Let's Start by Examining The Meaning of Specific Speed of PumpsDokument17 SeitenFluid Mechanics Tutorial 8C Pumped Piped Systems: Let's Start by Examining The Meaning of Specific Speed of Pumps12Noch keine Bewertungen
- Distillation Lecture Note-2Dokument20 SeitenDistillation Lecture Note-2BasseyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chem Note SS1 1st TermDokument32 SeitenChem Note SS1 1st TermVictor Okosun94% (16)
- Selection of Reboiler Type Design ProceduresDokument0 SeitenSelection of Reboiler Type Design ProcedurestpchoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Reciprocating CompressorDokument7 SeitenReciprocating CompressorAlphy Thomas100% (1)
- Calculating Pump HeadDokument8 SeitenCalculating Pump HeadPascal SayahNoch keine Bewertungen
- RocketDokument45 SeitenRocketDefenceDog100% (1)
- TRG Control ValveDokument13 SeitenTRG Control Valvemilton1987Noch keine Bewertungen
- Produxction of Vinyl Acetate From EthyleneDokument9 SeitenProduxction of Vinyl Acetate From EthyleneSajid AliNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pharmaceutical Organic Chemistry I Lab ManualDokument57 SeitenPharmaceutical Organic Chemistry I Lab ManualDeep Mali100% (1)
- Using DIERS Two Phase Equations To Estimate Tube Rupture FlowratesDokument8 SeitenUsing DIERS Two Phase Equations To Estimate Tube Rupture FlowratesNoirchevalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Report-Design of A Vertical Flash ColumnDokument7 SeitenReport-Design of A Vertical Flash ColumnSehry SyedNoch keine Bewertungen
- Basics of VacuumDokument7 SeitenBasics of Vacuumsanthosh_yash1Noch keine Bewertungen
- Part-A Laminar Flow: The Flow of A Fluid When Each Particle of The Fluid Follows A Smooth PathDokument28 SeitenPart-A Laminar Flow: The Flow of A Fluid When Each Particle of The Fluid Follows A Smooth PathAmirthavalli PE - Asst ProfNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lab Cheat Sheet, Distill and ArtificalDokument5 SeitenLab Cheat Sheet, Distill and ArtificalFarhan M JafrINoch keine Bewertungen
- Working Principle: Q DQ DT DM DT - Cp. TDokument6 SeitenWorking Principle: Q DQ DT DM DT - Cp. TBhakteshNoch keine Bewertungen
- Heat Exchanger Design and Drawing FundamentalsDokument11 SeitenHeat Exchanger Design and Drawing Fundamentalsjeevanantham 5846Noch keine Bewertungen
- Liquid Recirculation System-1Dokument8 SeitenLiquid Recirculation System-1Behnam AshouriNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hydraulics and Env. Engg Final ReportDokument14 SeitenHydraulics and Env. Engg Final ReportZohaib AliNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lab Report 1Dokument26 SeitenLab Report 1ParvinNoch keine Bewertungen
- FFODokument8 SeitenFFOmehfuzansari1Noch keine Bewertungen
- 3b. Packec Column DesignDokument48 Seiten3b. Packec Column DesignFahim RahmanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Energy Analysis of Pipes and FittingsDokument4 SeitenEnergy Analysis of Pipes and FittingsEymann JalaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Training Material DistillationDokument10 SeitenTraining Material DistillationjokishNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mass, Momentum and Energy EquationsDokument25 SeitenMass, Momentum and Energy Equationslassi19a100% (1)
- Engineering Thermodynamics ExperimentDokument5 SeitenEngineering Thermodynamics ExperimentinxludezNoch keine Bewertungen
- IT Module - N2 Equipment & CalculationsDokument7 SeitenIT Module - N2 Equipment & CalculationsMohamedNoch keine Bewertungen
- Absorption Calculation 8Dokument36 SeitenAbsorption Calculation 8adeebNoch keine Bewertungen
- CHE 220 Flow of Compressible FluidsDokument53 SeitenCHE 220 Flow of Compressible FluidsMay May MagluyanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fluid FrictionDokument18 SeitenFluid Frictioncakhoa100% (2)
- Formal ReportxDokument7 SeitenFormal ReportxDarshan ShaarmaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mechanically-Pumped-Liquid_Overfeed-EvaporatorsDokument10 SeitenMechanically-Pumped-Liquid_Overfeed-Evaporators霍广东Noch keine Bewertungen
- Week 10 of Aqs110 Fluid Mechanics PDFDokument16 SeitenWeek 10 of Aqs110 Fluid Mechanics PDFGeva GarradoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Composition Measurements: IndirectDokument14 SeitenComposition Measurements: IndirectBogdan CalinescuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Demonstration On Bernoulli's TheoremDokument22 SeitenDemonstration On Bernoulli's TheoremMahe RukhNoch keine Bewertungen
- II Law Analysis: by Dr. Kannan. ADokument69 SeitenII Law Analysis: by Dr. Kannan. AppkNoch keine Bewertungen
- Conservation of Energy: The Bernoulli Equation: Figure 1. A Very Large Venturi MeterDokument8 SeitenConservation of Energy: The Bernoulli Equation: Figure 1. A Very Large Venturi Meterdist2235Noch keine Bewertungen
- TFR ExperimentDokument25 SeitenTFR ExperimentSiti Norbaya100% (1)
- Interview Que.Dokument7 SeitenInterview Que.PrimalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Multicomponent DistillationDokument10 SeitenMulticomponent DistillationDAMP ChemicalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hydrodynamic Study of Fixed Beds With Cocurrent Upflow and DownflowDokument6 SeitenHydrodynamic Study of Fixed Beds With Cocurrent Upflow and DownflowAbdelhamid OughanemNoch keine Bewertungen
- Answer No 3Dokument15 SeitenAnswer No 3Politik Itu KejamNoch keine Bewertungen
- Autopipe Reference Information: Fluid Transient MethodDokument6 SeitenAutopipe Reference Information: Fluid Transient MethodJohn NashNoch keine Bewertungen
- SJV Selection EjectorsDokument9 SeitenSJV Selection Ejectorskumarvns111Noch keine Bewertungen
- Libro de BombasDokument260 SeitenLibro de BombasBoris SalazarNoch keine Bewertungen
- What Is The Difference Between Newtonian and Non-Newtonian Fluid and Give Example For Each Case?Dokument11 SeitenWhat Is The Difference Between Newtonian and Non-Newtonian Fluid and Give Example For Each Case?MOHAMED ABD ELGHANYNoch keine Bewertungen
- Vacuum Science and TechnologyDokument7 SeitenVacuum Science and TechnologywestewrNoch keine Bewertungen
- Specific Gravity Vs StrengthDokument5 SeitenSpecific Gravity Vs StrengthAlphy ThomasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Organ Culture: FeaturesDokument3 SeitenOrgan Culture: FeaturesAlphy ThomasNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1 Department 2 Name of Post 3 Scale of Pay 4 Number of VacanciesDokument3 Seiten1 Department 2 Name of Post 3 Scale of Pay 4 Number of VacanciesAlphy ThomasNoch keine Bewertungen
- ChromatographyDokument2 SeitenChromatographyAlphy ThomasNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1 2 Vacuum PumpsDokument14 Seiten1 2 Vacuum PumpsgyirgaNoch keine Bewertungen
- SumDokument1 SeiteSumAlphy ThomasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Agricultural UseDokument1 SeiteAgricultural UseAlphy ThomasNoch keine Bewertungen
- MiceDokument6 SeitenMiceTewedage TweNoch keine Bewertungen
- Affinity ChromatographyDokument2 SeitenAffinity ChromatographyAlphy ThomasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Heat Transfer CoefficientsDokument1 SeiteHeat Transfer CoefficientsAlphy ThomasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bank Rate, Also Referred To As The Discount Rate in American EnglishDokument4 SeitenBank Rate, Also Referred To As The Discount Rate in American EnglishAlphy ThomasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fluid VelocitiesDokument1 SeiteFluid VelocitiesAlphy ThomasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Practice TechniquesDokument1 SeitePractice TechniquesAlphy ThomasNoch keine Bewertungen
- ScribdDokument1 SeiteScribdNg JohnNoch keine Bewertungen
- Urea Silo BasisDokument24 SeitenUrea Silo BasisAlphy Thomas0% (1)
- VLC DiagramDokument1 SeiteVLC DiagramAlphy ThomasNoch keine Bewertungen
- ReservoirsDokument1 SeiteReservoirsAlphy ThomasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Angle of Repose MeasurementDokument1 SeiteAngle of Repose MeasurementAlphy ThomasNoch keine Bewertungen
- PDDDokument43 SeitenPDDAlphy ThomasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hrs SapDokument8 SeitenHrs SapAlphy Thomas100% (1)
- Van de Graaff Generator ExplainedDokument2 SeitenVan de Graaff Generator ExplainedAlphy ThomasNoch keine Bewertungen
- New Mechanisms of LNG Pricing in Asia PacificDokument15 SeitenNew Mechanisms of LNG Pricing in Asia PacificAlphy ThomasNoch keine Bewertungen
- From Our StudyDokument1 SeiteFrom Our StudyAlphy ThomasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Major Fertilizer Companies by CountryDokument1 SeiteMajor Fertilizer Companies by CountryAlphy ThomasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tonnage Dia Height 20000 29411.76471 40 23.4170101 15000 22058.82353 40 17.5627576Dokument2 SeitenTonnage Dia Height 20000 29411.76471 40 23.4170101 15000 22058.82353 40 17.5627576Alphy ThomasNoch keine Bewertungen
- NP Plants ListDokument1 SeiteNP Plants ListAlphy ThomasNoch keine Bewertungen
- A 841MWelding Procedures and Performance Qualifications Shall Be Conducted ForDokument1 SeiteA 841MWelding Procedures and Performance Qualifications Shall Be Conducted ForAlphy ThomasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Large Scale Ammonia Storage and HandlingDokument37 SeitenLarge Scale Ammonia Storage and HandlingAlphy ThomasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fluids Lab Friction LossesDokument35 SeitenFluids Lab Friction LossesNana AzmilNoch keine Bewertungen
- Problem 11 4 5Dokument10 SeitenProblem 11 4 5Yahyah NahabooNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ponchon-Savarit NotesDokument19 SeitenPonchon-Savarit Noteskyle2kdNoch keine Bewertungen
- Humboldt Catalog #7Dokument240 SeitenHumboldt Catalog #7Wagdi Alhajj100% (1)
- Solomon Hailemariam - Extraction and Characterization of Essential OilDokument108 SeitenSolomon Hailemariam - Extraction and Characterization of Essential Oiljennifer.germiniani.cardozoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Curriculum Vitae (CV)Dokument4 SeitenCurriculum Vitae (CV)Muhammad Fitrah SaidussuhurNoch keine Bewertungen
- Gafar 2022 IOP Conf. Ser. Earth Environ. Sci. 950 012035Dokument11 SeitenGafar 2022 IOP Conf. Ser. Earth Environ. Sci. 950 012035rburhansyah4625Noch keine Bewertungen
- Design of packed absorber column for multi-component gas scrubbingDokument104 SeitenDesign of packed absorber column for multi-component gas scrubbingNana kwadwoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Matter in Our SurroundingDokument62 SeitenMatter in Our SurroundingSumit ManeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sea Der 1977 WesterbergDokument4 SeitenSea Der 1977 WesterbergValeria OchoaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Exctractive Distillation ChemcadDokument7 SeitenExctractive Distillation Chemcadingbarragan87Noch keine Bewertungen
- Determination and Prediction of CO Minimum Miscibility PressuresDokument11 SeitenDetermination and Prediction of CO Minimum Miscibility PressuresDarryan DhanpatNoch keine Bewertungen
- Quotation of Automatic Carbon Residue Tester - LabtechDokument2 SeitenQuotation of Automatic Carbon Residue Tester - LabtechOmar SaaedNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pedal Powered Water PurifierDokument30 SeitenPedal Powered Water PurifierAnuj TripathiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lecture 2Dokument10 SeitenLecture 2Omar Al-KubaisiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Column Object - Startup and Tuning GuideDokument9 SeitenColumn Object - Startup and Tuning GuideIkhtiander IkhtianderNoch keine Bewertungen
- MA180-005 SubPUR-duoPUR User ManualDokument34 SeitenMA180-005 SubPUR-duoPUR User ManualSukrisdianto DiantoNoch keine Bewertungen
- HTTPSWWW - Google.aesearchq Bull+Bosh+Vodka&Client Safari&Hl en-GB&Prmd Inv&Sxsrf ALiCzsbhr ZBgnxFwA9HuKpeOiup a6ORw16562672Dokument1 SeiteHTTPSWWW - Google.aesearchq Bull+Bosh+Vodka&Client Safari&Hl en-GB&Prmd Inv&Sxsrf ALiCzsbhr ZBgnxFwA9HuKpeOiup a6ORw16562672shailesh jhaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chemistry of DistillationDokument18 SeitenChemistry of DistillationdeepakattavarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Experiment: 4: Physical Separation TechniquesDokument5 SeitenExperiment: 4: Physical Separation TechniquesDCRUZNoch keine Bewertungen
- Demineralized Water Purity GuideDokument1 SeiteDemineralized Water Purity GuideeltonNoch keine Bewertungen
- On The Energy Efficiency of Stripping-Type Crude DistillationDokument7 SeitenOn The Energy Efficiency of Stripping-Type Crude DistillationAnonymous tdxdh519MNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tray Columns - DesignDokument6 SeitenTray Columns - Designframon.chem35Noch keine Bewertungen
- CF BraunDokument4 SeitenCF BraunTito EcheverriaNoch keine Bewertungen