Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Niche
Hochgeladen von
Martín EcheverriaOriginaltitel
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Niche
Hochgeladen von
Martín EcheverriaCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Leopards:
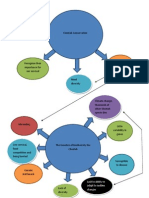
Habitat/spatial: They are mostly found in woodlands, grassland savannahs and forests. Temporal: Usually rest by day and hunt by night. Behaviour: They mark their territory with urine, feces, and claw marks and communicate with conspecifics by growling, roaring, and spitting when aggravated, and purring when content.1 Feeding: They approach their prey silently by crouching to the ground, they are ambush predators, it pounces on its prey then brakes its neck after this it carries it to a feeding location. Reproductive: They are promiscuous, since they have multiple mates. Females attract males by excreting pheromones through their urine.
Cheetahs:
Habitat/spatial: Found in grasslands and deserts. They hunt by ground but occasionally they tend to climb trees. Temporal: Hunt during the day. Behaviour: Males mark their territory with urine; they defend their territory from other males which facilitate the access of other females or preys. mark territory by ranking the ground with their hind paws, claws at trees, flatten grass by rolling, or deposit feces on prominent land features2 Feeding: Knocks the prey down with his forepaws, then it proceeds to strangle its throat with his jaw. Reproductive: They are promiscuous. Males associate with females only at mating, they will mate with as many females as possible.
Hyenas:
Habitat/spatial: Common in dry, semi-desert, savannah acacia bush and mountainous forest habitats. Temporal: Tend to hunt mostly by night Behaviour: Females are dominant to the males. The females remain in their natal clan for the rest of their lives, while the males disperse upon reaching sexual maturity.
1
Animal Diversity Web (ADW), Panthera Pardus, leopard, by Ashley Hunt, available at: http://animaldiversity.ummz.umich.edu/accounts/Panthera_pardus/#behavior 2 ADW, Acinonyx Jubatus, cheetah, by Erin R. Lehnert, available at: http://animaldiversity.ummz.umich.edu/accounts/Acinonyx_jubatus/#behavior
Feeding: Typically hyenas split into hunting groups, 70% of the food were from direct kills, not from scavenging. Reproductive: Males perform a bowing display before mating; since the females are dominant the males will retreat immediately if the female shows any signs of aggression.
Lions:
Habitat/spatial: Lions live in very big plain lands, savannah habitats where there is large amount of pray and cover available. Temporal: Tend to hunt mostly by night or in the early mornings. Behaviour: In engaged fight, they are capable of injuring or killing other lions. Females within a pride do not compete/fight or show any kind of dominance. Feeding: Usually hunt in groups, but the killing is done by an individual lion.
Reproductive: Lions breed year-round and are usually polygynous.3 It is estimated that it copulates 3000 times for every cub that survives over a year.
Niches depend on different things such as the environment, the behaviour of an animal or also it could depend on the time in the day/night the animal hunts. The particular Niche between these big predators is the way all of them can live in the same place, but they avoid competition since the time and places where they hunt are different for example the Leopards hunt in a different time to a Cheetah (in the day), and though it hunts at the same time as the lion and the hyena (in the night), it hunts in a different area.
Bibliography: http://animaldiversity.ummz.umich.edu/accounts/Crocuta_crocuta/ http://animaldiversity.ummz.umich.edu/accounts/Acinonyx_jubatus/ http://animaldiversity.ummz.umich.edu/accounts/Panthera_leo/ http://animaldiversity.ummz.umich.edu/accounts/Panthera_pardus/
ADW, Panthera leo, lion, by Erin Harrington, available at: http://animaldiversity.ummz.umich.edu/accounts/Panthera_leo/#reproduction
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceVon EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (895)
- Notes From Book A Short History of Nearly EverythingDokument1 SeiteNotes From Book A Short History of Nearly EverythingMartín EcheverriaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItVon EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (838)
- Peppered MothDokument1 SeitePeppered MothMartín EcheverriaNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Von EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Bewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (98)
- End of Q2 ReflectionsDokument2 SeitenEnd of Q2 ReflectionsMartín EcheverriaNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeVon EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (5794)
- Planning Q2: Which Activities Do You Plan To Participate in This Quimester?Dokument4 SeitenPlanning Q2: Which Activities Do You Plan To Participate in This Quimester?Martín EcheverriaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeVon EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (537)
- Self Review and Perosonal Goals.Dokument4 SeitenSelf Review and Perosonal Goals.Martín EcheverriaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaVon EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (266)
- Interspecific Interactions Simple Assignment 2ak6ehlDokument8 SeitenInterspecific Interactions Simple Assignment 2ak6ehlMartín EcheverriaNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingVon EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (400)
- Inter Specific RelationshipDokument3 SeitenInter Specific RelationshipMartín EcheverriaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureVon EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (474)
- Definiton of Words.Dokument1 SeiteDefiniton of Words.Martín EcheverriaNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Values of Being VegetarianDokument2 SeitenThe Values of Being VegetarianMartín EcheverriaNoch keine Bewertungen
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryVon EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (231)
- CheetahDokument1 SeiteCheetahMartín EcheverriaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceVon EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (588)
- ICT PresentationDokument9 SeitenICT PresentationMartín EcheverriaNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerVon EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (271)
- Presentation1 HawaiiDokument1 SeitePresentation1 HawaiiMartín EcheverriaNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaVon EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (45)
- The Meaning of SpeciesDokument2 SeitenThe Meaning of SpeciesMartín EcheverriaNoch keine Bewertungen
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealVon EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (74)
- Hotspot WorksheetDokument2 SeitenHotspot WorksheetMartín EcheverriaNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersVon EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (344)
- Project Review On T - Shirt DesignDokument1 SeiteProject Review On T - Shirt DesignMartín EcheverriaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnVon EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (234)
- Spider Key - BiologyDokument3 SeitenSpider Key - BiologyMartín EcheverriaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Project ReviewDokument1 SeiteProject ReviewMartín EcheverriaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Project Review ICTDokument2 SeitenProject Review ICTMartín EcheverriaNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreVon EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (1090)
- Working With Selections Martin EcheverriaDokument1 SeiteWorking With Selections Martin EcheverriaMartín EcheverriaNoch keine Bewertungen
- History of The Israeli - Palestinian ConflictDokument1 SeiteHistory of The Israeli - Palestinian ConflictMartín EcheverriaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 06Dokument98 Seiten06Mladen LazićNoch keine Bewertungen
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyVon EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (2259)
- Report Text About CheetahDokument2 SeitenReport Text About Cheetahmoerla 16Noch keine Bewertungen
- Carnivores Vs Herbivores Update Lesson Plan-1 - 0Dokument5 SeitenCarnivores Vs Herbivores Update Lesson Plan-1 - 0Bianca Anamaria Zoţ VălcanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Endangerd AnimalsDokument2 SeitenEndangerd AnimalsCandy KittyNoch keine Bewertungen
- The CheetahDokument1 SeiteThe Cheetahsanada_shinjiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Savannah Biome v4Dokument4 SeitenSavannah Biome v4Adam WhiteNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Von EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Bewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (121)
- Animal OlympicsDokument2 SeitenAnimal OlympicsmohammadjunaidNoch keine Bewertungen
- ES5 ArgueDokument71 SeitenES5 ArgueLeyla AbbasovaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Soal UAS Kelas 9 Bhs Inggris Smt1-CandraedukasiDokument6 SeitenSoal UAS Kelas 9 Bhs Inggris Smt1-CandraedukasiSeilinNoch keine Bewertungen
- 7 PM Compilation May 2023Dokument99 Seiten7 PM Compilation May 2023Vaibhav RajNoch keine Bewertungen
- Jess 102 NCERT X SSDokument9 SeitenJess 102 NCERT X SSKumara55Noch keine Bewertungen
- Jl. Mana-Saja Km.12 Kp. Suka Kamu Ds. Cuitan Kec. Suka KamuDokument3 SeitenJl. Mana-Saja Km.12 Kp. Suka Kamu Ds. Cuitan Kec. Suka KamuNadiah Nuraini RahmawatiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Geo - NcertDokument98 SeitenGeo - NcertMegan CruzNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Natural World: Unit ContentsDokument13 SeitenThe Natural World: Unit ContentsMarco RomeroNoch keine Bewertungen
- Academic Reading Practice Test 1Dokument8 SeitenAcademic Reading Practice Test 1Ashwin AlsiNoch keine Bewertungen
- TIẾNG ANHDokument3 SeitenTIẾNG ANHThu HangNoch keine Bewertungen
- UTS Ganjil Bahasa InggrisDokument100 SeitenUTS Ganjil Bahasa InggrisNana PutriNoch keine Bewertungen
- Unit 2 Factual ReportDokument6 SeitenUnit 2 Factual ReportFabiolaIvonyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Wildlife Conservation in Namibia: CHEETAH Population. The Wildlife Population in Namibia Has Been On The RISE Because TheDokument4 SeitenWildlife Conservation in Namibia: CHEETAH Population. The Wildlife Population in Namibia Has Been On The RISE Because TheSimonaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Problem Solving - The Cat Family (Standard) : Name DateDokument2 SeitenProblem Solving - The Cat Family (Standard) : Name DateToso LaurenceNoch keine Bewertungen
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesVon EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (821)
- Soal 9.1Dokument5 SeitenSoal 9.1eewuanNoch keine Bewertungen
- 7th Grade Pre-Post Test Student's EditionDokument11 Seiten7th Grade Pre-Post Test Student's Editionfranciscojoel1100% (1)
- Resolution Exercises L12024Dokument17 SeitenResolution Exercises L12024Grisha AdamyanNoch keine Bewertungen
- African Animals Trivia QuizDokument4 SeitenAfrican Animals Trivia QuizMarxela MTNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cambridge IGCSE: Biology 0610/42Dokument24 SeitenCambridge IGCSE: Biology 0610/42Fatima TayyabNoch keine Bewertungen
- Animales en Peligro de Extinción en InglesDokument7 SeitenAnimales en Peligro de Extinción en InglesDarl GarcíaNoch keine Bewertungen
- PersianLeopard V4Dokument8 SeitenPersianLeopard V4mohsen72474Noch keine Bewertungen
- Guided Cloze Practice 05Dokument3 SeitenGuided Cloze Practice 05Khoa Dang0% (2)
- Soal Bhs Inggris Kelas Ix Semester 1Dokument6 SeitenSoal Bhs Inggris Kelas Ix Semester 1loebdakaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Latihan Soal UN SMP NitipDokument21 SeitenLatihan Soal UN SMP NitipNathan Blue SilenceNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tales from Both Sides of the Brain: A Life in NeuroscienceVon EverandTales from Both Sides of the Brain: A Life in NeuroscienceBewertung: 3 von 5 Sternen3/5 (18)
- Gut: the new and revised Sunday Times bestsellerVon EverandGut: the new and revised Sunday Times bestsellerBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (393)
- Why We Die: The New Science of Aging and the Quest for ImmortalityVon EverandWhy We Die: The New Science of Aging and the Quest for ImmortalityBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (5)