Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Anatomy - Chapter 1 Vocab
Hochgeladen von
aaauutCopyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Anatomy - Chapter 1 Vocab
Hochgeladen von
aaauutCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Chapter 6 Vocabulary
1) Actin - a protein that forms (together with myosin) the contractile filaments of muscle cells, and
is also involved in motion in other types of cells.
2) Aerobic respiration - A form of cellular respiration that requires oxygen in order to generate
energy.
3) All-or-none - Characterized by either a complete response or by a total lack of response or
effect, as in neurological action above a threshold:
4) Antagonist - any muscle that opposes the action of another
5) Cardiac muscle - The principal tissue of the vertebrate heart; composed of a syncytium of
striated muscle fibers.
6) Endomysium - The connective tissue layer surrounding an individual skeletal muscle fiber.
7) Epimysium - The connective-tissue sheath surrounding a skeletal muscle.
8) Fixator - A muscle whose action tends to hold a body part in a certain position or limit its
movement
9) Insertion - the act of implanting, or the condition of being implanted.
10) Involuntary - done without will or conscious control.
11) Isometric Contractions - Isometric exercise or isometrics are a type of strength training in which
the joint angle and muscle length do not change during contraction. Isometrics are done in static
positions, rather than being dynamic through a range of motion.
12) Isontic contractions - Exercise in which isotonic muscular contraction is used to strengthen
muscles and improve joint mobility.
13) Motor unit - a motor neuron and the muscle fibers innervated by its axon.
14) Myofibrils - any of the elongated contractile threads found in striated muscle cells.
15) Myofilaments - Any of the ultramicroscopic filaments, made up of actin and myosin, that are the
structural units of a myofibril.
16) Myosin - a protein of the myofibril, occurring chiefly in the A band; with actin it forms
actomyosin, which is responsible for the contractile properties of muscle.
17) Neuromuscular Junction - the area of contact between the ends of a large myelinated nerve
fiber and a fiber of skeletal muscle.
18) Neurotransmitter - a substance released from the axon terminal of a presynaptic neuron on
excitation, which diffuses across the synaptic cleft to either excite or inhibit the target cell
19) Origin - used when describing muscles, tendons, ligaments, nerves, and blood and lymph vessels
20) Oxygen debt - The amount of extra oxygen required by muscle tissue to oxidize lactic acid and
replenish depleted ATP and phosphocreatine following vigorous exercise.
21) Perimysium - The fibrous sheath enveloping each of the primary bundles of skeletal muscle
fibers.
22) Prime mover - a muscle that acts directly to bring about a desired movement.
23) Sacromere - a structural unit of a myofibril in striated muscle, consisting of a dark band and the
nearer half of each adjacent pale band.
24) Skeletal muscle - a muscle that is connected to the skeleton to form part of the mechanical
system that moves the limbs and other parts of the body.
25) Sliding filament mechanism - the process by which striated muscles change length, the overlap
of thin and thick filaments increasing as the muscle shortens and decreasing as it lengthens.
Describes the manner in which these length changes occur, but is not an explanation of the
mechanism of active shortening.
26) Smooth muscle - muscle tissue in which the contractile fibrils are not highly ordered, occurring
in the gut and other internal organs and not under voluntary control.
27) Striated - Marked with striae; striped, grooved, or ridged.
28) Synergist - a substance, organ, or other agent that participates in an effect of synergy.
29) Tendon - a flexible but inelastic cord of strong fibrous collagen tissue attaching a muscle to a
bone.
30) Voluntary - done, given, or acting of one's own free will.
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- IES Blogger - Personal StatementDokument1 SeiteIES Blogger - Personal StatementaaauutNoch keine Bewertungen
- READMEDokument1 SeiteREADMEaaauutNoch keine Bewertungen
- 6 MacKinnon 2012 Consent of The Networked Ch1-2 PDFDokument22 Seiten6 MacKinnon 2012 Consent of The Networked Ch1-2 PDFaaauutNoch keine Bewertungen
- Final Exam Review- Quarter 4 Ch 17 Thermochemistry Practice Test MatchingDokument8 SeitenFinal Exam Review- Quarter 4 Ch 17 Thermochemistry Practice Test MatchingaaauutNoch keine Bewertungen
- Statement of Financial ResponsibilityDokument1 SeiteStatement of Financial ResponsibilityaaauutNoch keine Bewertungen
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItVon EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (838)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeVon EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (537)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeVon EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (5794)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Von EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Bewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (98)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceVon EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (894)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingVon EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (399)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureVon EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (474)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryVon EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (231)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceVon EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (587)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaVon EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (265)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealVon EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (73)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerVon EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (271)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersVon EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (344)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaVon EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (45)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnVon EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (234)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyVon EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (2219)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreVon EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Von EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Bewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (119)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesVon EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (821)
- Gabinete STS Activity1Dokument2 SeitenGabinete STS Activity1Anthony GabineteNoch keine Bewertungen
- Vector 4114NS Sis TDSDokument2 SeitenVector 4114NS Sis TDSCaio OliveiraNoch keine Bewertungen
- NLP Business Practitioner Certification Course OutlineDokument11 SeitenNLP Business Practitioner Certification Course OutlineabobeedoNoch keine Bewertungen
- 4 Influencing Factors of Learners Career Choice Parents Choice Vs Personal DescisionDokument24 Seiten4 Influencing Factors of Learners Career Choice Parents Choice Vs Personal Descisionmatteo mamaloNoch keine Bewertungen
- CS210 Lecture 32 Magical Application Binary Tree IIIDokument38 SeitenCS210 Lecture 32 Magical Application Binary Tree IIIOshoNoch keine Bewertungen
- DBMS Architecture FeaturesDokument30 SeitenDBMS Architecture FeaturesFred BloggsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Induction ClassesDokument20 SeitenInduction ClassesMichelle MarconiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Strategies For StartupDokument16 SeitenStrategies For StartupRoshankumar BalasubramanianNoch keine Bewertungen
- Inventory ControlDokument26 SeitenInventory ControlhajarawNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hipotension 6Dokument16 SeitenHipotension 6arturo castilloNoch keine Bewertungen
- Masteringphys 14Dokument20 SeitenMasteringphys 14CarlosGomez0% (3)
- Steps To Christ AW November 2016 Page Spreaad PDFDokument2 SeitenSteps To Christ AW November 2016 Page Spreaad PDFHampson MalekanoNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2010 HD Part Cat. LBBDokument466 Seiten2010 HD Part Cat. LBBBuddy ButlerNoch keine Bewertungen
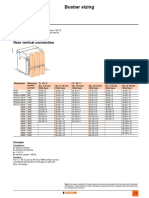
- Busbar sizing recommendations for Masterpact circuit breakersDokument1 SeiteBusbar sizing recommendations for Masterpact circuit breakersVikram SinghNoch keine Bewertungen
- Training Customer CareDokument6 SeitenTraining Customer Careyahya sabilNoch keine Bewertungen
- Test Bank For Fundamental Financial Accounting Concepts 10th by EdmondsDokument18 SeitenTest Bank For Fundamental Financial Accounting Concepts 10th by Edmondsooezoapunitory.xkgyo4100% (48)
- Managerial EconomicsDokument3 SeitenManagerial EconomicsGuruKPONoch keine Bewertungen
- Gapped SentencesDokument8 SeitenGapped SentencesKianujillaNoch keine Bewertungen
- !!!Логос - конференц10.12.21 копіяDokument141 Seiten!!!Логос - конференц10.12.21 копіяНаталія БондарNoch keine Bewertungen
- A Database of Chromatographic Properties and Mass Spectra of Fatty Acid Methyl Esters From Omega-3 ProductsDokument9 SeitenA Database of Chromatographic Properties and Mass Spectra of Fatty Acid Methyl Esters From Omega-3 ProductsmisaelNoch keine Bewertungen
- EN 12449 CuNi Pipe-2012Dokument47 SeitenEN 12449 CuNi Pipe-2012DARYONO sudaryonoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Letter From Attorneys General To 3MDokument5 SeitenLetter From Attorneys General To 3MHonolulu Star-AdvertiserNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mil STD 2154Dokument44 SeitenMil STD 2154Muh SubhanNoch keine Bewertungen
- 202112fuji ViDokument2 Seiten202112fuji ViAnh CaoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Draft SemestralWorK Aircraft2Dokument7 SeitenDraft SemestralWorK Aircraft2Filip SkultetyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Jesd8 15aDokument22 SeitenJesd8 15aSridhar PonnurangamNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lab StoryDokument21 SeitenLab StoryAbdul QadirNoch keine Bewertungen
- PeopleSoft Security TablesDokument8 SeitenPeopleSoft Security TablesChhavibhasinNoch keine Bewertungen
- Kate Elizabeth Bokan-Smith ThesisDokument262 SeitenKate Elizabeth Bokan-Smith ThesisOlyaGumenNoch keine Bewertungen