Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Infrared Absorption Frequencies
Hochgeladen von
Asep Muhamad SamsudinCopyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Infrared Absorption Frequencies
Hochgeladen von
Asep Muhamad SamsudinCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
6/3/13
Infrared Absorption Frequencies
Infrared Absorption Frequencies
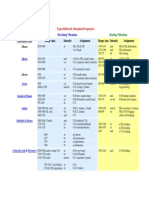
Numbers separated by dashes are ranges; when two numbers are separated by a comma, both absorptions are expected. Individual numbers not components of a range should be considered 5 cm-1. Intensity of absorptions (relative height of peak) is keyed by letter: s = strong; m = medium; w = weak; v = very; br = broad. Compound Class Structure n , cm -1 2850-3000 Alkanes RCH2CH3 1450-1470 1370-1380 720-725 3040-3140 Alkenes RCH=CH2 1655 910, 990 3080-3140 R2C=CH2 1650 890 3020 Z- RCH=CHR 1660 675-725 (a) 3-ring (b) 4-ring (c) 5-ring (d) 6-ring (e) 7-ring
chemistry.umeche.maine.edu/CHY251/IR-Table.html
Intensity s s s m m m s s m s w w m w w w w w
Assignment CH stretch CH2 and CH3 bending modes =C-H stretch C=C stretch =CH out of plane =C-H stretch C=C stretch =CH out of plane =C-H stretch C=C stretch =CH out of plane C=C stretch " " " "
1/5
1641 1566 1611 1649 1651
6/3/13
Infrared Absorption Frequencies
(f) 8-ring
1653 3020
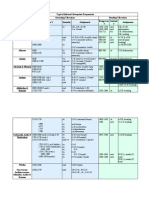
w w w s w w s vw to missing s m s vw to missing s s s out of range varies s varies s s s s s
" =C-H stretch C=C stretch
=CH out of plane
E- RCH=CHR
1675 970 3020
=C-H stretch C=C stretch =CH out of plane C=C stretch CH stretch CC stretch C-H bend C C stretch C-F stretch C-Cl stretch C-Br stretch C-I stretch OH stretch C-O stretch OH stretch C-O stretch OH stretch C-O stretch C=O stretch C=O stretch
2/5
R2C=CHR
1670 790-840
R2C=CR2
1670 3300
Alkynes
RC CH
2100-2140 600-700
RC CR Alkyl Halides R-F R-Cl R-Br R-I Alcohols RCH2OH
2190-2260 1000-1350 750-850 500-680 200-500 3400-3600 1050 3400-3600 1100 3400-3600 1070-1150 1725 1685
R2CHOH R3COH Ethers Aldehydes R-O-R RCHO C=CCHO
chemistry.umeche.maine.edu/CHY251/IR-Table.html
6/3/13
Infrared Absorption Frequencies
ArCHO All aldehydes Ketones R2CO (a) 4-ring (b) 5-ring (c) 6-ring C=CCOR ArCOR
1700 2720, 2820 (both) 1715 1780 1745 (doublet) 1715 1675 1690 3400
s m s " " " m s s s s (broad) s s s s (broad) s
>m "
C=O stretch CHO out of plane C=O stretch " " " " " monomer OH monomer C=O dimer OH dimer C=O monomer OH monomer C=O dimer OH dimer C=O C-O stretch " C=O stretch " " " " NH stretch (free)
3/5
Carboxylic Acids
RCO2H
1760 2800-3400 1710 3400 1720
C=CCO2H
2800-3400 1690
RCO2Esters RCO2R' (a) 5-ring (b) 6-ring C=CCO2R ArCO2R
1550-1610 1400 1735 1770 1735 1720 1720 3500
s s s s s m
chemistry.umeche.maine.edu/CHY251/IR-Table.html
6/3/13
Infrared Absorption Frequencies
1690 Amides RCONH2 3400 1650 1600-1640 3440 1680 RCONHR 3330 1650 1530-1550 (a) 4-ring (b) 5-ring (c) 6-ring RCONR2 Anhydrides Acid Chloride RCO2COR RCOCl 1745 1700 1640 1650 1760, 1820 (both) 1800 3400, 3500 (both) Amines RNH2 1560-1640 1030-1230 R2NH 3310-3350 1030-1230 3450 1250-1360 730-770 690-710
s m s s m s m s m s " " m s s w s m w m w s m m
C=O stretch (free) NH str. (H-bond) C=O str. (H-bond) NH out of plane NH stretch (free) C=O stretch (free) NH str. (H-bond) C=O str. (H-bond) NH out of plane C=O stretch " " C=O stretch C=O stretch; symm., unsymm. C=O stretch NH stretch NH2 in plane bend C-N stretch NH stretch C-N stretch NH stretch Ar-N stretch CH out of plane bending
4/5
Ar2NH
Benzenes
monosubst.
chemistry.umeche.maine.edu/CHY251/IR-Table.html
6/3/13
Infrared Absorption Frequencies
ortho-disub. meta-disub. para-disub. 1,2,3-trisub.
735-770 750-810 690-710 810-840 760-780 705-745 810-865 675-730 805-825 870-885 800-810 855-870 840-850 870 References
m m m m m m m m m m m m m w
" " " "
1,3,5-trisub.
"
1,2,4-trisub. 1,2,3,4tetrasub. 1,2,4,5tetrasub. 1,2,3,5tetrasub. 1,2,3,4,5pentasub.
" " " " "
1. Bellamy, L. J., "The Infrared Spectra of Complex Molecules", 2nd edition, John Wiley & Sons, New York, 1961. 2. Nakanishi, K. "Infrared Absorption spectroscopy - Practical", Holden-Day, Inc., San Francisco, 1962.
This page last modified 11:18 AM on Thursday October 1st, 2009. Webmaster, Department of Chemistry, University of Maine, Orono, ME 04469
chemistry.umeche.maine.edu/CHY251/IR-Table.html
5/5
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Characteristic Infrared Absorption Bands of Functional GroupsDokument1 SeiteCharacteristic Infrared Absorption Bands of Functional GroupszzozzoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Characteristic Infrared Absorption BandsDokument1 SeiteCharacteristic Infrared Absorption BandsSuta VijayaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Functional Class Range (NM) Intensity Assignment Range (NM) Intensity AssignmentDokument6 SeitenFunctional Class Range (NM) Intensity Assignment Range (NM) Intensity AssignmentdubstepoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Spec IR Table For Common Chemical SymbolsDokument4 SeitenSpec IR Table For Common Chemical SymbolsYoussef LatashNoch keine Bewertungen
- 05 IR Chart PDFDokument1 Seite05 IR Chart PDFojasvapal singhNoch keine Bewertungen
- 05 IR Chart PDFDokument1 Seite05 IR Chart PDFKonstantina MsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Spectroscopy Infrared SpectraDokument51 SeitenSpectroscopy Infrared SpectraAakshi JairathNoch keine Bewertungen
- Infrared Spectroscopy: IR Absorptions For Representative Functional GroupsDokument3 SeitenInfrared Spectroscopy: IR Absorptions For Representative Functional GroupsSaleem BashaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Spectroscopy Infrared SpectraDokument51 SeitenSpectroscopy Infrared Spectrathanasa08Noch keine Bewertungen
- Spec Ir NMR Spectra TablesDokument15 SeitenSpec Ir NMR Spectra TablesMah NovaesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Infrared SpectrosDokument51 SeitenInfrared SpectrosDrHamdy KhameesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Capitolo 13 - Cumulated Double Bonds PDFDokument11 SeitenCapitolo 13 - Cumulated Double Bonds PDFAntonino GiuffridaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Spektrometri IRDokument51 SeitenSpektrometri IRClarion 642Noch keine Bewertungen
- 424 Spectra TablesDokument19 Seiten424 Spectra TablespradeepiitdNoch keine Bewertungen
- Adobe Scan 31 May 2023Dokument1 SeiteAdobe Scan 31 May 2023Imuu IsmuuNoch keine Bewertungen
- NMR 13C 13 QuesDokument52 SeitenNMR 13C 13 QuesgussalimNoch keine Bewertungen
- Infrared Spectroscopy IR Absorptions For Representative Functional GroupsDokument6 SeitenInfrared Spectroscopy IR Absorptions For Representative Functional GroupsChandra ReddyNoch keine Bewertungen
- CHMBD 449 - Organic Spectral: AnalysisDokument43 SeitenCHMBD 449 - Organic Spectral: AnalysisIleana ManciuleaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Spektro IRDokument64 SeitenSpektro IRAnonymous NSK4nvH4ufNoch keine Bewertungen
- Spectroscopy of Aldehydes and KetonesDokument12 SeitenSpectroscopy of Aldehydes and KetonesCristina SimaNoch keine Bewertungen
- IR-freq CO BondDokument3 SeitenIR-freq CO BondRD's AcademyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Common I R Absorption SDokument1 SeiteCommon I R Absorption SVisakha SureshNoch keine Bewertungen
- Frequency Table For IR & NMRDokument6 SeitenFrequency Table For IR & NMRYogesh PingleNoch keine Bewertungen
- M.SC NMR SpectrosDokument72 SeitenM.SC NMR SpectrosShweta BishtNoch keine Bewertungen
- Infrared Spectroscopy: Conformational IsomersDokument7 SeitenInfrared Spectroscopy: Conformational IsomersRiyan NazarudinNoch keine Bewertungen
- Table - 1: Characteristic Infrared Absorptions of Functional GroupsDokument1 SeiteTable - 1: Characteristic Infrared Absorptions of Functional GroupsAJIT CHAUDHARINoch keine Bewertungen
- 13C NMRDokument28 Seiten13C NMRArjun MaharajNoch keine Bewertungen
- Infrared Spectroscopy: Gives Information About The Functional Groups in A MoleculeDokument17 SeitenInfrared Spectroscopy: Gives Information About The Functional Groups in A Moleculesonico197710Noch keine Bewertungen
- Spectroscopy RangeDokument4 SeitenSpectroscopy Rangematt_drakul4860Noch keine Bewertungen
- 13C NMR Spectroscopy Power Point PresentationDokument34 Seiten13C NMR Spectroscopy Power Point PresentationOti DeeaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Table of IR Absorptions: Functional Group Characteristic Absorption(s) (CM NotesDokument2 SeitenTable of IR Absorptions: Functional Group Characteristic Absorption(s) (CM NoteskeenakinkinNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2230L 08 IR Spectra InterpretationDokument11 Seiten2230L 08 IR Spectra Interpretationvennilaj23Noch keine Bewertungen
- IR&NMR ProblemsDokument43 SeitenIR&NMR ProblemsAndrew Ronaldi Tandio100% (2)
- ASS Instrumental OrganicDokument17 SeitenASS Instrumental OrganicMohamed SakrNoch keine Bewertungen
- GCE Chemistry Data Sheet: Table B Table C Table ADokument2 SeitenGCE Chemistry Data Sheet: Table B Table C Table AcalebNoch keine Bewertungen
- Spectroscopic Studies On /3-Cyclodextrin: Short CommunicationDokument3 SeitenSpectroscopic Studies On /3-Cyclodextrin: Short CommunicationManu VelascoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Table 1. Characteristic IR Absorption Peaks of Functional Groups Vibration Position (CM) Intensity Notes Alkanes AlkenesDokument6 SeitenTable 1. Characteristic IR Absorption Peaks of Functional Groups Vibration Position (CM) Intensity Notes Alkanes AlkenesBag VatiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Table of IR Absorptions: Functional Group Characteristic Absorption(s) NotesDokument2 SeitenTable of IR Absorptions: Functional Group Characteristic Absorption(s) NotesMuhammad Khairuna SyahPutraNoch keine Bewertungen
- 13C NMRDokument40 Seiten13C NMRKrishna BurakaNoch keine Bewertungen
- IR SlideshowDokument22 SeitenIR SlideshowHafiz Shoaib SarwarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Alkynes and Compounds Containing C C GroupsDokument21 SeitenAlkynes and Compounds Containing C C GroupsMani PillaiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Elimination ContinuumDokument12 SeitenElimination ContinuumMinwoo KimNoch keine Bewertungen
- IR SpectrosDokument44 SeitenIR SpectrosVansh YadavNoch keine Bewertungen
- FullDokument10 SeitenFullAbdul Wahab KhanNoch keine Bewertungen
- CHE 320 Test 1-2011-12Dokument3 SeitenCHE 320 Test 1-2011-12PdomNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chemical ShiftsDokument2 SeitenChemical ShiftsErica CouzensNoch keine Bewertungen
- IR Spectroscopy (Solutions)Dokument4 SeitenIR Spectroscopy (Solutions)LakshayNoch keine Bewertungen
- Infrared (IR) Spectroscopy: Structure, Purity, and IdentityDokument16 SeitenInfrared (IR) Spectroscopy: Structure, Purity, and IdentityDiana KowsariNoch keine Bewertungen
- Spectrochemical Method of Analysis (CHM 580) EXPERIMENT 1:qualitative Analysis of Aspirin Phenacetin Caffeine and Sample Using FTIR and NMRDokument9 SeitenSpectrochemical Method of Analysis (CHM 580) EXPERIMENT 1:qualitative Analysis of Aspirin Phenacetin Caffeine and Sample Using FTIR and NMRbatrisyia hazirahNoch keine Bewertungen
- Infrared Spectroscopy: WWU ChemistryDokument34 SeitenInfrared Spectroscopy: WWU ChemistryTrung HoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Characteristic Infrared Absorption FrequenciesDokument1 SeiteCharacteristic Infrared Absorption Frequencies0312_kalpanaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 2 (Part 2)Dokument82 SeitenChapter 2 (Part 2)MELVINDO JACOBNoch keine Bewertungen
- Infrared Spectroscopy: Concepts and TheoriesDokument55 SeitenInfrared Spectroscopy: Concepts and Theoriesdead_knightNoch keine Bewertungen
- Table 2 Table 3 Table 1: GCE Chemistry Data SheetDokument0 SeitenTable 2 Table 3 Table 1: GCE Chemistry Data SheetSusan FarhangNoch keine Bewertungen
- Guide For Infrared SpectrosDokument22 SeitenGuide For Infrared SpectrosSuta VijayaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 13-C NMR-09Dokument27 Seiten13-C NMR-09M Nur M. MahmudNoch keine Bewertungen
- Table of Characteristic IR AbsorptionsDokument4 SeitenTable of Characteristic IR Absorptionsأمالي أريفينNoch keine Bewertungen
- Reviews in Computational Chemistry, Volume 31Von EverandReviews in Computational Chemistry, Volume 31Abby L. ParrillNoch keine Bewertungen
- 424 Spectra TablesDokument19 Seiten424 Spectra TablespradeepiitdNoch keine Bewertungen
- Al Mathurat PDFDokument6 SeitenAl Mathurat PDFGti GirlzNoch keine Bewertungen
- Al Mathurat PDFDokument6 SeitenAl Mathurat PDFGti GirlzNoch keine Bewertungen
- Blog Paper Toy Mini Ryu Template Gus SantomeDokument1 SeiteBlog Paper Toy Mini Ryu Template Gus Santomekrajan77Noch keine Bewertungen
- (Asce) PS 1949-1204 0000381Dokument11 Seiten(Asce) PS 1949-1204 0000381Hop Minh NguyenNoch keine Bewertungen
- Grade 3 Energy Summary Grade 3 Learning Standards (From Bced Curriculum)Dokument4 SeitenGrade 3 Energy Summary Grade 3 Learning Standards (From Bced Curriculum)Akbar KurniawanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Carbon Nanotubes, Inorganic Nanowires and FunctionalizationDokument68 SeitenCarbon Nanotubes, Inorganic Nanowires and FunctionalizationFrancisco Javier Delgado MartínezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Yhfe Fix York 2022 FolletoDokument6 SeitenYhfe Fix York 2022 FolletoDvid451Noch keine Bewertungen
- Chemical Composition of Callisia Fragrans Juice 1. Phenolic CompoundsDokument2 SeitenChemical Composition of Callisia Fragrans Juice 1. Phenolic CompoundsLeTienDungNoch keine Bewertungen
- HPLCDokument2 SeitenHPLCApoorva ChaudharyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Classification of Economic: DR S e eDokument2 SeitenClassification of Economic: DR S e ekishan kumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Monte Carlo Simulation of 1D Heisenberg ModelDokument12 SeitenMonte Carlo Simulation of 1D Heisenberg Modelt_sairamNoch keine Bewertungen
- Formulae and Oxidation NumbersDokument14 SeitenFormulae and Oxidation NumbersDoc_CrocNoch keine Bewertungen
- Biochemistry: Molecular and Cell BiochemistryDokument7 SeitenBiochemistry: Molecular and Cell BiochemistryKHIENT CARLO MARTINNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ch02 QuestionsDokument8 SeitenCh02 QuestionsAdliNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fluid I - Lec 3 and 4 - ProductionDokument34 SeitenFluid I - Lec 3 and 4 - Productionamr mohamedNoch keine Bewertungen
- DR FCC PDFDokument7 SeitenDR FCC PDFAle SanzNoch keine Bewertungen
- Accelerated Atmospheric Corrosion Testing Using A Cyclic Wet/Dry Exposure Test: Aluminum, Galvanized Steel, and SteelDokument8 SeitenAccelerated Atmospheric Corrosion Testing Using A Cyclic Wet/Dry Exposure Test: Aluminum, Galvanized Steel, and SteelTito MuñozNoch keine Bewertungen
- Thermodynamics 2018 (Repaired)Dokument15 SeitenThermodynamics 2018 (Repaired)carolNoch keine Bewertungen
- PoliMac Coated Gabion Mattress SpecDokument2 SeitenPoliMac Coated Gabion Mattress SpecworkatarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Revision SPM 2018 Paper 2Dokument70 SeitenRevision SPM 2018 Paper 2Azie Nurul Akhtar75% (4)
- Unit Test 3 Paper 1 Compile - SolutionDokument9 SeitenUnit Test 3 Paper 1 Compile - Solutionyashi84480Noch keine Bewertungen
- Stainless SteelDokument6 SeitenStainless Steelkarioke mohaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chem HSSC 1 Model PaperDokument8 SeitenChem HSSC 1 Model PaperPikoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Heat Exchangers ReportDokument15 SeitenHeat Exchangers ReportBigNoch keine Bewertungen
- EJ 4131 Revised Manuscript FDokument14 SeitenEJ 4131 Revised Manuscript FSantiago GaitanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Glide 6.7. User Manual. Schrödinger PressDokument138 SeitenGlide 6.7. User Manual. Schrödinger PressKevin Mego De La CruzNoch keine Bewertungen
- Flotation Assessment Report of XYZ - 7th April 2023 - 230409 - 052526Dokument9 SeitenFlotation Assessment Report of XYZ - 7th April 2023 - 230409 - 052526LopezNgelekaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chemistry Project - BilalDokument6 SeitenChemistry Project - Bilalmetrotigers377Noch keine Bewertungen
- Science 7 3rd Quarter Edited LeaPDokument18 SeitenScience 7 3rd Quarter Edited LeaPcristine joy hirangNoch keine Bewertungen
- CH 20-21 Answers (All)Dokument36 SeitenCH 20-21 Answers (All)Thục NghiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Heat Transfer: Mechanical EngineeringDokument10 SeitenHeat Transfer: Mechanical EngineeringVenkatasairamreddy KandulaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Outstanding Absolute Electromagnetic Interference Shielding Effectiveness of Cross-Linked PEDOT:PSS FilmDokument5 SeitenOutstanding Absolute Electromagnetic Interference Shielding Effectiveness of Cross-Linked PEDOT:PSS FilmamithgnNoch keine Bewertungen
- OrbitsDokument2 SeitenOrbitsPantsik GrifoiNoch keine Bewertungen