Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Advanced Physics 1st Semester Review 2012
Hochgeladen von
a_gellerCopyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Advanced Physics 1st Semester Review 2012
Hochgeladen von
a_gellerCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Advanced Physics 1st Semester Review
1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. 11. 12. 13. TOPICS COVERED Units + Measurement Vectors/Scalars Constant Velocity 1D Motion Motion Graphs Constant Acceleration/Freefall 2D Motion (launched horizontally and at angles) Forces and Newtons Laws Momentum and Conservation Circular Motion Gravitation Work, Energy, Power Conservation of Energy
Equations You Should Know:
What You Should Be Able to Do:
1. 2. 3. 4. Units/Measurement Identify units for various physical quantities (Mass, Length, Force, etc.) Convert between English and SI units (feet to meters, mph to m/s, etc.) Metric Conversions (grams to kilograms, KHDBDCM) Add, Subtract, Multiply and Divide numbers in scientific notation Vectors/Scalars: Explain the difference between vectors and scalars Explain the difference between distance and displacement and speed and velocity Use the Pythagorean theorem and different angle notations to draw vectors Find the x and y components of a known vector, and use them to find a resultant vector Add vectors using the tip to tail method 1D Motion: Solve constant velocity problems for an unknown variable using kinematics equations Solve constant acceleration problems using the core four kinematics equations Identify key features of each type of motion graph (DT, VT, AT graphs) With a given motion graph, generate the other two graphs (d vs. t, v vs. t, a vs. t) Solve free fall problems using a = 9.8 m/s2 along with the core four kinematic equations
1. 2. 3. 4. 5.
1. 2. 3. 4. 5.
2D Motion: 1. Identify key features of projectile motion (independence of x and y components) 2. Solve projectile problems for objects launched both horizontally and at an angle. 3. Be comfortable using trigonometry and vectors to solve for horizontal and vertical components of motion Forces: Given a scenario where forces are acting, draw a free body diagram of an object State Newtons Laws from memory Use Newtons First Law to solve problems where forces are balanced Use Newtons Second Law to solve net force problems or problems where forces are unbalanced Be Familiar with Newtons Third Law and how to apply it to a situation or scenario Determine the weight of an object and explain the difference between mass and weight Momentum: State the law of conservation of momentum Define Elastic and Inelastic Collisions and how they are similar/different Explain recoil of a projectile launcher (gun) Calculate the change in velocity of a thrown object during and after the time it is acted on by a force Explain how Impulse and time of impact are related to change in momentum Apply conservation of momentum to solve simple collision problems. Circular Motion/Gravitation: Distinguish between rotation and revolution Explain the difference between centripetal force and centrifugal force Describe the forces on an object that is moving in a circular fashion (car on a circular track, satellite in orbit) Predict how the gravitational force between objects changes when the distance between them changes Calculate forces, masses, or distance, given any three of these quantities (Law of Universal Gravitation)
1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6.
1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6.
1. 2. 3. 4. 5.
Mechanical Energy, Work, Power Compare work done in different situations and calculate work done on an object Explain the relationship between work and energy, and explain for form of energy in given situations Calculate KE or PE in a simple system using the formulas for KE and PE (pendulum, roller coaster, etc) Calculate impact speed of an object dropped from a specific height 5. Calculate maximum height reached by an object, given initial vertical velocity 1. 2. 3. 4.
Units and Measurement 1. How fast is 65 mi/hr in m/s? 2. I swam 40 lengths (20 laps) of a 33 yard pool (length). Calculate how far I swam in yards, miles, meters, kilometers, and millimeters. 3. If light travels at 3 x 108 m/s, how long does it take to travel the 1.5 x 1011 m from the sun to Earth? 4. Convert the distance a runner travels in a standard marathon (26.2 miles) to feet 5. How many square centimeters are there in 1 square kilometer? 6. The height of Mount Everest is 6.9 x 10-2 percent of the earths radius (6.37 x 106 m). What is the height of Mount Everest in feet?
Vectors/Scalars 1. A dog searching for a bone walks 3.5 meters south, then 8.2 meters at an angle of 30 north of east, and finally 15 meters west. Find the dogs resultant displacement. 2. A quarterback takes the ball from the line of scrimmage, runs backward for 10.0 yards, and then runs parallel to the line of scrimmage for 15.0 yards. At this point, he throws the ball down the field 50.0 yards. What is the resultant displacement of the football? 3. Given the three vectors below, determine the fourth vector that will make the resultant zero (i.e. find the vector that gets you back to the beginning). A = 5 meters at 30 B = 9 meters at 160 C = 7 meters at 230 D = ???
1.
2.
3.
4.
1D Motion A tsunami caused by an earthquake occurring in Alaska in 1946 consisted of several huge waves which were found to travel at the average speed of 790 km/hr. The first of the waves reached Hawaii 4 hours 34 minutes after the earthquake occurred. From this data, calculate how far the origin of the tsunami was from Hawaii. The Space Shuttle travels at a speed of about 7.20 x 103 m/s. The blink of an astronaut's eye lasts about 96.4 ms. How many football fields (length = 91.4 m) does the Space Shuttle cover in the blink of an eye? A ball is dropped from rest from the top of a cliff that is 22.7 m high. From ground level, a second ball is thrown straight upward at the same instant that the first ball is dropped. The initial speed of the second ball is exactly the same as that with which the first ball eventually hits the ground. In the absence of air resistance, the motions of the balls are just the reverse of each other. Determine how far below the top of the cliff the balls cross paths. Create a displacement vs. time graph with the data table below and then use the d vs. t graph to create a velocity vs. time graph. Describe the motion of the object. d (m) -2 2 2 3 1 4
t (s) 0 1 2 3 4 5
1.
2.
3.
4.
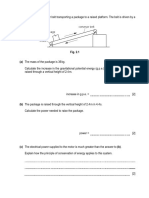
2D Motion A ham sandwich (on wheat) is shot into the air with a big sling-shot. Its launched at an angle of 30 degrees with respect to the ground. The whole flight takes 6 seconds and the sandwich travels a horizontal distance of 45 meters. Find the initial horizontal velocity of the sandwich, the initial vertical velocity of the sandwich, initial (resultant) velocity of the sandwich, and the maximum height that the sandwich reaches. A hiker comes across a waterfall and quickly notes that the falls are 73.5 meters in height. The hiker also observes that the water is landing 8 meters out from the base of the falls. The curious hiker can tell that water is shooting off the top horizontally and wants to know what the velocity of the water at the top is. Determine this velocity. A Ballard physics student is tossing water balloons at their friend. If the student releases the balloons from a height of 1.8 meters and throws a balloon with a velocity of 11 m/s at an angle of 40 degrees, what is the range of the balloon? Florence Griffith-Joyner of the United States set the women's world record for the 200 m run by running with an average speed of 9.28 m/s. Suppose Griffith-Joyner wants to jump over a river. She runs horizontally from the river's higher bank at 9.28 m/s and lands on the edge of the opposite bank. If the difference in height between the two banks is 2.00 m, with the far bank having the lower height, how wide is the river?
1. 2. 3. 4.
5.
6.
Forces What is the mass of a person weighing 150 lbs? What is the force of gravity on that person? A 6.4 kg box is sliding down an incline at a constant velocity. If the slope of the incline is 20 degrees, what is the coefficient of friction between the box and the ramp? A 9.5 kg box slides down a 250 incline. If the coefficient of friction is 0.20, what is the acceleration of the box? Brett, the 72.0 kg star quarterback of the Green Bay Packers football team, collides with James, a stationary left tackle, and is brought to a bone crushing stop with an acceleration of -20.0 m/s2. What force does James exert on Brett? An average size woman has a mass of about 60 kg. The average size elephant has a mass of about 1500 kg. The area of a typical spiked heel in contact with the floor is 0.40 cm2. The typical elephants foot has an area of 0.25 m2. Find the pressure exerted by each when they stand on only one foot. Who exerts the greater force? Who exerts the greater pressure? Who is more dangerous to a nice marble floor? A 945-kg car traveling rightward at 22.6 m/s slams on the brakes and skids to a stop (with locked wheels). If the coefficient of friction between tires and road is 0.972, determine the distance required to stop.
1. 2.
3. 4.
5.
Momentum A 0.150-kilogram baseball traveling with a horizontal speed of 4.50 m/s is hit by a bat and then moves with a speed of 34.7 m/s in the opposite direction. What is the change in the balls momentum? To get off a frozen, frictionless lake, an 85-kilogram person throws a 0.30-kilogram object horizontally, directly away from the shore, with a speed of 2.5 m/s. If the person is 12 m from the shore, how long does it take for him to reach it? A bullet with a mass of 0.005 kg is loaded into a gun with a mass of 0.52 kg. The bullet is fired causing the gun to recoil at a velocity of 2.1 m/s. What is the velocity of the bullet? Two cars of equal mass collide on a horizontal frictionless surface. Before the collision, car A is at rest while car B has a constant velocity of 12 m/s. After the collision, the two bodies are stuck together. What is the speed of the composite body (A + B) after the collision? Explain why air bags and crumple zone in cars save lives. What physics principle is at work here?
1. 2.
3. 4. 5.
Circular Motion/Gravitation How long does it take a plane, traveling at a constant speed of 193 m/s, to fly once around a circle whose radius is 1870 m? At an amusement park there is a ride in which cylindrically shaped chambers spin around a central axis. People sit in seats facing the axis, their backs against the outer wall. At one instant the outer wall moves at a speed of 2.66 m/s, and an 89.0-kg person feels a 352-N force pressing against his back. What is the radius of a chamber? What is the acceleration due to gravity on the moon? (Mmoon = 7.36 x 1022 kg, Rmoon = 1737.4 km) How fast must a satellite be traveling to stay in orbit if it is 700 km above the Earths surface? A student on a roller coaster is moving at 18.9 m/s over the top of a hill which has a radius of curvature of 12.7 m. Use Newton's second law to determine the magnitude of the applied force of the track pulling down upon the 621 kg roller coaster car.
1. 2. 3.
4.
5.
6. 7. 8.
Energy/Work/Power When doing a chin-up, a physics student lifts her 42.0-kg body a distance of 0.25 meters in 2 seconds. What is the power delivered by the student's biceps? How many joules of energy are you buying from LG&E for the 9 cents it costs for each kilowatt-hour? Ben Travlun carries a 200-N suitcase up three flights of stairs (a height of 10.0 m) and then pushes it with a horizontal force of 50.0 N at a constant speed of 0.5 m/s for a horizontal distance of 35.0 meters. How much work does Ben do on his suitcase during this entire motion? When Sir Edmund Hillary and Tenzing Norgay climbed to the top of Mt. Everest, they expended a great deal of energy. Assume Sir Hilliary weighs approx. 150 lb. and did 4.35 million ft-lb of work in his tortuous ascent. How high did he climb? The first hill of a roller coaster is 100 meters high. It travels down the hill and then up the second hill. If the second hill is 40 meters high, what is the speed of the coaster when it gets to the top of the second hill? A 2.00-kg metal sled slides down a 10.0-meter high slope. At the bottom its speed is 8.50 m/s. Find the magnitude of the work done by friction A car weighing 10000 N is traveling with a speed of 17 m/s. When the brakes on the car lock up a friction force of 3000 N acts on the car, what distance does it skid? Mrs. Eschels has just completed her shopping at Kroger. She accidentally bumps her 42.5-kg cart, setting it in motion from rest down a hill inclined at 14.9 degrees. Upon descending a distance of 9.27 meters along the inclined plane, the cart hits a tree stump (which was placed in the parking lot for the sole purpose of this problem). A 0.295-kg can of tomato soup is immediately hurled from the moving cart and heads towards Ms. Dixon's brand new Lexus. Upon striking the Lexus, the tomato soup can creates a dent with a depth of 3.16 cm. Noah Formula, who is watching the entire incident and fixing to do some physics, attempts to calculate the average force which the Lexus applies to the soup can. Assume negligible air resistance and friction forces and help Noah out.
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Advanced ThermodynamicsDokument21 SeitenAdvanced ThermodynamicsYash KrishnanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Some Problems of Chemical Kinetics and Reactivity: Volume 1Von EverandSome Problems of Chemical Kinetics and Reactivity: Volume 1Noch keine Bewertungen
- Advanced Mathematics Group 2 SyllabusDokument5 SeitenAdvanced Mathematics Group 2 Syllabusgeneral674100% (1)
- Physics 1922 – 1941: Including Presentation Speeches and Laureates' BiographiesVon EverandPhysics 1922 – 1941: Including Presentation Speeches and Laureates' BiographiesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chemistry and Physics QuestionsDokument5 SeitenChemistry and Physics QuestionsRuel CedeñoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Answer Problem Sheet-05 Me201 2nd LawDokument9 SeitenAnswer Problem Sheet-05 Me201 2nd LawshantanuNoch keine Bewertungen
- DiffusionDokument10 SeitenDiffusionprofjayakaran0% (2)
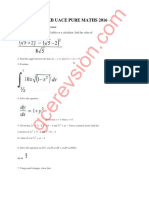
- UNEB UACE PURE MATHS 2016 solutionsDokument4 SeitenUNEB UACE PURE MATHS 2016 solutionsGilbert MutaiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Physical Chemistry An Advanced TreatiseVon EverandPhysical Chemistry An Advanced TreatiseWilhelm JostBewertung: 1 von 5 Sternen1/5 (1)
- Chemical Energetics NotesDokument7 SeitenChemical Energetics NotesSalwa Ag Akbar100% (1)
- Heat Transfer Applications for the Practicing EngineerVon EverandHeat Transfer Applications for the Practicing EngineerNoch keine Bewertungen
- New Age' Caatalogue PDFDokument25 SeitenNew Age' Caatalogue PDFajitphadkuleNoch keine Bewertungen
- Physics Books NeededDokument4 SeitenPhysics Books NeededShams ShamsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Thermochemical Data of Elements and Compounds PDFDokument942 SeitenThermochemical Data of Elements and Compounds PDFJulio Hernandez MartinezNoch keine Bewertungen
- NEW AGE - Physics Catalogue 2014 - 2015Dokument7 SeitenNEW AGE - Physics Catalogue 2014 - 2015Pradeep ChauhanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Unit 6 Summary: Physics Grade 9Dokument23 SeitenUnit 6 Summary: Physics Grade 9AhmedNoch keine Bewertungen
- 07a30802 Chemical Process CalculationsDokument8 Seiten07a30802 Chemical Process CalculationsAshwin Nandagiri100% (1)
- Physics FormulasDokument23 SeitenPhysics FormulasViral AssassinNoch keine Bewertungen
- Grade 10 Physics Chapter 3 Revision Problems - Answer Key: Multiple Choice Questions. Q1Dokument6 SeitenGrade 10 Physics Chapter 3 Revision Problems - Answer Key: Multiple Choice Questions. Q1NONO0% (1)
- Revision Notes PDFDokument7 SeitenRevision Notes PDFrafeekherNoch keine Bewertungen
- ChemistryDokument14 SeitenChemistryraennieNoch keine Bewertungen
- Practice Test/Thermochemistry/Ap Chemistry: Combustion F F FDokument3 SeitenPractice Test/Thermochemistry/Ap Chemistry: Combustion F F FMaria GinzburgNoch keine Bewertungen
- Test - Series and Parallel CircuitsDokument4 SeitenTest - Series and Parallel CircuitsMinor100% (1)
- Ce6306 Som PDFDokument55 SeitenCe6306 Som PDFHemakumar ManoharanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chemistry Final Study Guide Multiple Choice QuestionsDokument22 SeitenChemistry Final Study Guide Multiple Choice Questionssrahimi@verizon.netNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2-Chem 1101 The The Properties of Gases & Solutions (Text)Dokument55 Seiten2-Chem 1101 The The Properties of Gases & Solutions (Text)Tmmp SmileNoch keine Bewertungen
- SPH4U 1.6 - Relative MotionDokument14 SeitenSPH4U 1.6 - Relative MotionMatthew GreesonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chem Quiz BeeDokument4 SeitenChem Quiz BeeAdrimar AdrianoNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2ND TERM S3 PHYSICS BorrowedDokument46 Seiten2ND TERM S3 PHYSICS BorrowedAlvan MmaduwubaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Exam 3 Material Science MATS 2001 UMN Fall 2012Dokument7 SeitenExam 3 Material Science MATS 2001 UMN Fall 2012Zaki Smn100% (1)
- Pressure and Manometers-Worked Examples For Fluid MechanicsDokument6 SeitenPressure and Manometers-Worked Examples For Fluid MechanicsLuvin RajNoch keine Bewertungen
- Separating Mixtures TechniquesDokument2 SeitenSeparating Mixtures TechniquesHenry TuganoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Worksheet 01 MechanicsDokument10 SeitenWorksheet 01 MechanicsImran Mirza0% (1)
- Homework Problems on Forces, Motion and EnergyDokument7 SeitenHomework Problems on Forces, Motion and EnergyQuinnNgo100% (1)
- Chemistry SSC-I (3rd Set)Dokument5 SeitenChemistry SSC-I (3rd Set)Amaan KareemNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chemistry Form 5 Chapter 1 - Rate of ReactionDokument63 SeitenChemistry Form 5 Chapter 1 - Rate of ReactionSiti Nursyafiqah100% (7)
- Solution For General Physics - Worksheet - OneDokument15 SeitenSolution For General Physics - Worksheet - OnesadNoch keine Bewertungen
- Question Bank in Chemistry Class ADokument81 SeitenQuestion Bank in Chemistry Class AiliasNoch keine Bewertungen
- ChemistryDokument27 SeitenChemistryFatmawati MnNoch keine Bewertungen
- NUCLEAR CHEMISTRY KEY TERMS AND CONCEPTSDokument10 SeitenNUCLEAR CHEMISTRY KEY TERMS AND CONCEPTSUday Prakash SahuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Polyurethane ChemistryDokument15 SeitenPolyurethane Chemistryyoga nayagi punichelvana100% (1)
- General Chemistry - Practice - Final - ExamDokument7 SeitenGeneral Chemistry - Practice - Final - ExamReyes Ilagan MyrnaNoch keine Bewertungen
- All Physics Formula and Glossary - GCE Study Buddy - The Best O Level Revision ResourceDokument13 SeitenAll Physics Formula and Glossary - GCE Study Buddy - The Best O Level Revision ResourceVei Adoptante100% (2)
- Practice Exam With Answers PDFDokument38 SeitenPractice Exam With Answers PDFPaigeNoch keine Bewertungen
- 11 Physics WorksheetsDokument31 Seiten11 Physics WorksheetssbatrabatraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Plane Curvilinear Motion:: DisplacementDokument18 SeitenPlane Curvilinear Motion:: Displacementyalexca100% (1)
- CHEM 121 Midterm Practice Questions 2013Dokument13 SeitenCHEM 121 Midterm Practice Questions 2013Kathryn CruzNoch keine Bewertungen
- Units: Basic MathematicsDokument38 SeitenUnits: Basic MathematicsGraham MooreNoch keine Bewertungen
- H2 Jun Holiday Assignment 2013 AnswersDokument12 SeitenH2 Jun Holiday Assignment 2013 AnswersKaitlyn HoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Thermal ExpansionDokument27 SeitenThermal ExpansionVijay AgarwalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ode GreenDokument1.125 SeitenOde GreenSumalinog G. Gelson100% (1)
- Chemical Kinetics: Practice ExamplesDokument31 SeitenChemical Kinetics: Practice ExamplesJudith Del Valle MorejonNoch keine Bewertungen
- 12 Physics Handbook PDFDokument143 Seiten12 Physics Handbook PDFtranhuutuongNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mineralogy & Crystallography Exit ExamDokument14 SeitenMineralogy & Crystallography Exit ExamAmanuel Buzuna100% (1)
- Physics Paper II Exam ReviewDokument12 SeitenPhysics Paper II Exam ReviewSoniyaKanwalG100% (1)
- Laws of Motion QuestionsDokument4 SeitenLaws of Motion QuestionsRajesh DeyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Physics Final Project SlideDokument13 SeitenPhysics Final Project Slideapi-348201239Noch keine Bewertungen
- 0625 s17 QP 42Dokument20 Seiten0625 s17 QP 42Ved AsudaniNoch keine Bewertungen
- Balancing Theory of M/C PDFDokument6 SeitenBalancing Theory of M/C PDFSandip GhoshNoch keine Bewertungen
- VOL1 Hitagi Crab PDFDokument88 SeitenVOL1 Hitagi Crab PDFMauricio LópezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Modern Chemistry Homework 22-1Dokument7 SeitenModern Chemistry Homework 22-1afefjetcm100% (1)
- Project 1Dokument10 SeitenProject 1partoNoch keine Bewertungen
- ME 3507: Theory of Machines: Dr. Faraz JunejoDokument45 SeitenME 3507: Theory of Machines: Dr. Faraz JunejoArsal AbbasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Her DrearyDokument3 SeitenHer DrearyMiera Yushira Yusoff67% (6)
- Electric Charges and Fields Bank of Board QuestionsDokument11 SeitenElectric Charges and Fields Bank of Board QuestionsNishy GeorgeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Physics - XI - AE - 2020-21 (Ques)Dokument4 SeitenPhysics - XI - AE - 2020-21 (Ques)Ghost AnkanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lab 106 Static and Kinetic FrictionDokument5 SeitenLab 106 Static and Kinetic FrictionAbdulahad Malik0% (1)
- Energy, Work & Power ERDokument6 SeitenEnergy, Work & Power EREman Gurmani100% (2)
- A Brief History of TimeDokument101 SeitenA Brief History of Timeaadil86% (21)
- General Relativity For Pedestrians - First 5 LecturesDokument11 SeitenGeneral Relativity For Pedestrians - First 5 LecturesBir HanuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Important Questions (Applied Mechanics)Dokument2 SeitenImportant Questions (Applied Mechanics)Saurabh Prasad Gupta100% (1)
- Chapter 2 Forces and Motion (Exercise)Dokument44 SeitenChapter 2 Forces and Motion (Exercise)xiaokia100% (3)
- Scientiæ Baccalaureus: A Physics Research TextDokument258 SeitenScientiæ Baccalaureus: A Physics Research TextPerry Lee GordonNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Mass OrnamentDokument13 SeitenThe Mass OrnamentYalda PilehchianNoch keine Bewertungen
- Complementary Relativity - Beyond The Lorentz Transformations - Eng+ItaDokument39 SeitenComplementary Relativity - Beyond The Lorentz Transformations - Eng+ItaLeonardo RubinoNoch keine Bewertungen
- 7 Momentum and ImpulseDokument16 Seiten7 Momentum and ImpulseJohn Angelo RamosNoch keine Bewertungen
- Traffic Accident ReconstructionDokument58 SeitenTraffic Accident Reconstructionsandeepsamarth100% (2)
- Sample Detailed Lesson PlanDokument11 SeitenSample Detailed Lesson PlanppNoch keine Bewertungen
- Abbreviations Medication Administration RoutesDokument4 SeitenAbbreviations Medication Administration Routesvinila7967% (3)
- S-T V-T Graphs SDokument31 SeitenS-T V-T Graphs SYeap Joo YunNoch keine Bewertungen
- MEEN208 - 2018 Tutorials - 2019Dokument65 SeitenMEEN208 - 2018 Tutorials - 2019Abdulmujeeb simpaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Physics Coursework 2016/2017 STPMDokument13 SeitenPhysics Coursework 2016/2017 STPMShi JieNoch keine Bewertungen
- PHYSICS 2421 HW#1 SolutionsDokument4 SeitenPHYSICS 2421 HW#1 Solutionsmalonz030% (1)
- CHP 5 SolutiomsDokument2 SeitenCHP 5 SolutiomsSana AshfaqNoch keine Bewertungen
- Torques and Rotational EquilibriumDokument5 SeitenTorques and Rotational EquilibriumHopia QuintelNoch keine Bewertungen
- "To Find The Charge Induced On Styro Foam Balls Using Coulomb's Law" Physics Investigatory ProjectDokument22 Seiten"To Find The Charge Induced On Styro Foam Balls Using Coulomb's Law" Physics Investigatory ProjectShivendra Tripathi85% (20)
- The Things We Make: The Unknown History of Invention from Cathedrals to Soda CansVon EverandThe Things We Make: The Unknown History of Invention from Cathedrals to Soda CansNoch keine Bewertungen
- Crossings: How Road Ecology Is Shaping the Future of Our PlanetVon EverandCrossings: How Road Ecology Is Shaping the Future of Our PlanetBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (10)
- Summary of Neil Postman's Amusing Ourselves to DeathVon EverandSummary of Neil Postman's Amusing Ourselves to DeathBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (2)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureVon EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (474)
- Cable Supported Bridges: Concept and DesignVon EverandCable Supported Bridges: Concept and DesignBewertung: 5 von 5 Sternen5/5 (1)
- To Engineer Is Human: The Role of Failure in Successful DesignVon EverandTo Engineer Is Human: The Role of Failure in Successful DesignBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (137)
- Piping and Pipeline Calculations Manual: Construction, Design Fabrication and ExaminationVon EverandPiping and Pipeline Calculations Manual: Construction, Design Fabrication and ExaminationBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (18)
- The Great Bridge: The Epic Story of the Building of the Brooklyn BridgeVon EverandThe Great Bridge: The Epic Story of the Building of the Brooklyn BridgeBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (59)
- The Things We Make: The Unknown History of Invention from Cathedrals to Soda CansVon EverandThe Things We Make: The Unknown History of Invention from Cathedrals to Soda CansBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (21)
- Shallow Foundations: Discussions and Problem SolvingVon EverandShallow Foundations: Discussions and Problem SolvingBewertung: 5 von 5 Sternen5/5 (1)
- Methodology for Estimating Carbon Footprint of Road Projects: Case Study: IndiaVon EverandMethodology for Estimating Carbon Footprint of Road Projects: Case Study: IndiaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Principles of Forensic Engineering Applied to Industrial AccidentsVon EverandPrinciples of Forensic Engineering Applied to Industrial AccidentsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Introducing Structures: A Textbook for Students of Civil and Structural Engineering, Building and ArchitectureVon EverandIntroducing Structures: A Textbook for Students of Civil and Structural Engineering, Building and ArchitectureBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (11)
- Transportation Engineering: Theory, Practice, and ModelingVon EverandTransportation Engineering: Theory, Practice, and ModelingNoch keine Bewertungen
- Safety and Intelligent Transport Systems Development in the People’s Republic of ChinaVon EverandSafety and Intelligent Transport Systems Development in the People’s Republic of ChinaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Climate Adaptation Engineering: Risks and Economics for Infrastructure Decision-MakingVon EverandClimate Adaptation Engineering: Risks and Economics for Infrastructure Decision-MakingNoch keine Bewertungen
- Field Book for Quality Control in Earthwork Operations: Project Construction Management BookVon EverandField Book for Quality Control in Earthwork Operations: Project Construction Management BookNoch keine Bewertungen