Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
SR Classification
Hochgeladen von
api-246811319Originaltitel
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
SR Classification
Hochgeladen von
api-246811319Copyright:
Verfügbare Formate
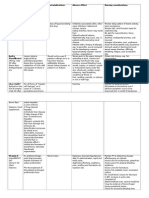
Classification Anti-Infective Agents
Penicillin penicillin V (Betapen) amoxicillin (Amoxil) ampicillin (Omnipen) cloxacillin (Tegopen) PO/IV/IM
Mechanism of Action
Indications
Contraindications Adverse Effects Nursing Considerations
Inhibition of cell wall synthesis
Mitral Valve Stenosis Endocarditis Sinusitis Pneumonia Gram-negative bacteria
Allergy Oral contraceptives (decreases OC efficacy) Kidney failure
Rash Pruritis N/V/D Allergic reaction** **Cephalosporins should also be used with caution**
Assess for history of allergy Post administration: clients can have an allergic reaction within 0- 30 minutes Pen. V and amoxicillin should be taken with food. All other penicillins should be taken medication with water, 1 hour before or 2 hours after meals Avoid taking with acidic fruit juices Clients must complete full course of treatment Use with caution in neonates r/t immature kidney function slowing elimination Hypernatremia and hyperkalemia are possible, but uncommon
Sulfonamide sulfamethoxazoletrimethoprim (Septra) sulfisoxazole (Generic) PO/IV/IM
Do not directly destroy bacteria; however they interfere with their growth by preventing the synthesis of folic acid (required to make the nucleus of DNA)
Sinusitis Pyelonephritis Meningitis Urinary Tract Infection Otitis Media Gram-negative bacteria Gram-positive bacteria Sinusitis Pyelonephritis Meningitis Urinary Tract Infection Skin Infections Gram-negative
Allergy Children under the age of 2 months Renal failure
Rash Photosensitivity N/V/D Allergic reaction
Assess for history of allergy Post administration: clients can have an allergic reaction within 0- 30 minutes Clients must complete full course of treatment Encourage fluids to produce a urine output of 1,200-1,500mL/day to avoid crystalluria (drug crystals in the urine
Cephalosporin cephalexin (Keflex) cefprozil (Cefzil) cefazolin (Cefazolin) ceftriaxone (Rocephin) PO/IV/IM
Inhibition of cell wall synthesis
Allergy Alcohol Oral contraceptives (decreases OC efficacy)
Rash Pruritis N/V/D Allergic reaction
Assess for history of allergy Post administration: clients can have an allergic reaction within 0- 30 minutes Clients must complete full course of treatment Used cautiously because immature
bacteria Gram-positive bacteria
kidney function slows elimination Dosages must be reduced by the prescriber in the presence of renal impairment Allergy Pregnancy Not to be given to children under the age of 8 (r/t permanent discoloration of teeth) Oral contraceptives (decreases OC efficacy) Allergy Warfarin use (increases serum concentration) Liver disease N/V/D Overgrowth of nonsusceptible organisms (i.e. Candidiasis) Discoloration of teeth Photosensitivity Avoid taking with antacids, dairy products, iron preparations, or antidiarrheal medications ( levels) Avoid exposure to sunlight Clients must complete full course of treatment
Tetracyclines doxycycline (Vibramycin) minocycline (Minocin) tetracycline (Achromycin) PO/IV
Inhibition of bacterial protein synthesis
Pyelonephritis Meningitis Urinary Tract Infection Otitis Media Pneumonia Gram-negative bacteria Gram-positive bacteria
Macrolide azithromycin (Zithromax) clarithromycin (Biaxin) erythromycin (Generic) PO Fluoroquinolones ciprofloxacin (Cipro) levofloxacin (Levaquin) moxifloxacin (Avelox) PO/IV
Inhibition of bacterial protein synthesis
Pyelonephritis Urinary Tract Infection Pneumonia Gram-positive bacteria
N/V/D Rash Palpitations
Clients must complete full course of treatment Avoid taking with fruit juices
Inhibition of bacterial enzymesstops DNA synthesis in the cell
Pyelonephritis Urinary Tract Infection Pneumonia Gram-negative bacteria Gram-positive bacteria
Liver disease Kidney disease Warfarin use (increases serum concentration) Not to be used in children under the age of 18 (safety has not been established) Allergy Kidney disease Pregnancy (can cause congenital bilateral deafness in
N/V/D Candidiasis Photosensitivity Tendon injury (tendonitis r/t apoptosis and decreased collagen synthesis in a tendon
Clients must complete full course of treatment Encourage fluids to produce a urine output of 1,200-1,500mL/day to avoid crystalluria (drug crystals in the urine) Avoid exposure to sunlight
Aminoglycoside gentamicin sulfate (Gentamicin) tobramicin sulfate (Tobramycin)
Inhibit cell wall synthesis
VRE Skin infections (folliculitis) Gram-negative bacteria
Nephrotoxicity Ototoxicity Skin rash Headache Dizziness
Monitor blood levels of the medication Assess for toxicity (i.e. hearing loss/tinnitus, kidney failure) Preferred choice for VRE infections
IV
children if taken during pregnancy) Inhibits DNA synthesis of a cell C. Diff Bacterial Vaginosis Trichomonas Alcohol use Liver disease Dizziness GI upset Headache Neurotoxicity (seizures) N/V Dizziness Headache Encourage client to take with food/milk Alcohol should not be consumed during, and for at least 24 hours after last dose Clients must complete full course of treatment Increase fluids to 1,200-1,500 mL/day
Nitroimidazole metronidazole (Flagyl) PO/IV
Nitrofuran nitrofurnantoin (MacroBID) PO
Interferes with the activity of enzymes that regulate bacteria metabolism and disrupts cell wall synthesis Binds to the cell wall and produces inhibition of cell wall synthesis
Urinary Tract Infection
Allergy Kidney disease
Glycopeptide vancomycin (Vancocin) IV/PO
MRSA C. Diff
Kidney disease Hearing loss
Ototoxicity Kidney failure Skin rash Hypotension Flushing of the skin
Monitor blood levels of the medication Assess for toxicity (i.e. hearing loss, kidney failure) Preferred choice for MRSA infections
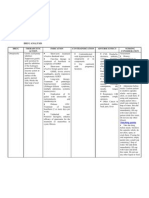
Laxatives
Stimulant bisacodyl (Dulcolax) senna (Senokot) sennosides (Ex-Lax; USA) PO/PR Irritates intestinal smooth muscle + colonic intramural plexus increased peristalsis Promotes some water into stool Constipation Bulk Forming psyllium (Metamucil) methylcellulose (Entrocel, Citrucel) PO Increase size and softness of stool triggering peristalsis Absorbs water into stool Constipation IBS **Has shown to lower LDL in Hypercholesteremia Allergy Acute abdomen Intestinal obstruction Undiagnosed abdo pain Appendicitis Electrolyte imbalance Renal failure Children < 6 years Diarrhea Abdo cramping Electrolyte imbalances Dizziness Assess fluid and electrolytes Increase dietary fibre (whole grain, bran, fruit, greens) Increase water intake Long-term use (7d+) results in low bowel tone = dependency May interact with milk/juices/antacids
same
Constipation Abdo cramping Flatulence
Assess fluid and electrolytes Increase dietary fibre (whole grain, bran, fruit, greens) Increase water intake Long-term use (7d+) results in low
bowel tone = dependency May interact with milk/juices/antacids Usually taken hs; onset = 6-8 hrs (mineral oil) or 24-72 hr (docusate sodium) Assess fluid and electrolytes Increase dietary fibre (whole grain, bran, fruit, greens) Increase water intake Long-term use (7d+) results in low bowel tone = dependency Safe in pregnancy docusate should not be taken within 2 hrs of mineral oil r/t mineral oil absorbed by the body May interact with milk/juices/antacids 30 min 3 hr onset Assess fluid and electrolytes Increase dietary fibre(whole grain, bran, fruit, greens) Increase water intake Long-term use (7d+) results in low bowel tone = dependency Safe in pregnancy May interact with milk/juices/antacids
Emollient docusate sodium (Colace) mineral oil (Fleet* mineral oil enema) *sodium phosphate/Fleet is the more common saline enema* PO/PR
Lubricates intestinal wall Promotes water and fat into stool
Constipation Diagnostic preparations (i.e. colonoscopy)
Others are same Caution in pregnancy
Cramping Diarrhea
BP Diarrhea Abdo cramping Electrolyte imbalances Muscle cramping Dizziness
Saline Laxative magnesium sulfate (Epsom Salts) magnesium citrate (Citro-Mag) magnesium hydroxide (Milk of magnesia/MOM; Diovol) sodium phosphate (Fleet) PO (liquid or tablet) Hyperosmotic glycerin (Glycerin supp.) Lactulose (APOLactulose) sorbitol polyethylene glycol; PEG (Restoralax, PegLyte)
Increases osmotic retention of fluid Increases peristalsis
Constipation Diagnostic preparations (i.e. colonoscopy)
same Children < 2 years
Increases stool water content Promotes peristalsis **Lactulose can be used to decrease serum ammonia; seen in portal systemic encephalopathy**
Constipation Diagnostic preparations (i.e. colonoscopy)
same Diabetes (lactulose contains lactose)
BP Diarrhea Abdo cramping Electrolyte imbalances Belching & flatulence
Assess fluid and electrolytes Increase dietary fibre(whole grain, bran, fruit, greens) Increase water intake Long-term use (7d+) results in low bowel tone = dependency Safe in pregnancy May interact with milk/juices/antacids
PO
Diabetes
Insulin Rapid Acting NovoRapid Humalog Short Acting Humulin R Novolin ge Toronto Intermediate Acting Novolin ge NPH Long Acting Lantus IV/SC
Insulin is a hormone Acts on cells in pancreas Helps to metabolize proteins, fats and carbohydrates Helps to store glucose in the liver Moves glucose from blood to cells
Type 1 Diabetes Type 2 Diabetes
Allergy Hypoglycemia Corticosteroids (increases glucose) Diuretics (increases glucose) Birth control (increases glucose)
Hypoglycemia
Insulins differ in onset and duration of action Insulin can not be given orally; must be given subcutaneously or IV (regular insulin) Insulin can be stored at room temperature or in the fridge Injection sites can not be used more than once a month (must move at least inch from previous site) Effective management requires a consistent schedule of meals, snacks, exercise, injections and blood glucose monitoring Impaired vision may result in inaccurate dosages Should not be taken at bedtime Should be taken no more than 30 minutes prior to eating Meals and snacks should be taken routinely
Sulfonylureas glyburide (Diabeta) gliclazide (Diamicron) glimepiride (Amaryl) PO
Stimulate the pancreas to produce more insulin (therefore ineffective if cells of the pancreas can no longer function) Acts by decreasing the hepatic production of glucose (gluconeogenesis) Helps to decrease intestinal absorption of glucose Helps to improve insulin receptor sensitivity Does not increase insulin secretion, thus does not cause hypoglycemia
Type 2 Diabetes
same Alcohol (lowers glucose)
Hypoglycemia Weight gain Hemolytic anemia Nausea
Biguanides metformin (Glucophage) PO
Type 2 Diabetes
Allergy Hypoglycemia Some antacids Iodine containing contrast mediums
Diarrhea Nausea Metallic taste in mouth Anorexia
Must be taken with meals Must stop medication 48 hours prior to iodine radiological studies
Thiazolidinediones pioglitazone (Actos) rosiglitazone (Avandia) PO
Helps to enhance the sensitivity of insulin receptors Helps to stimulate glucose storage Inhibits glucose production in the liver
Type 2 Diabetes
Allergy Hypoglycemia
Edema Weight gain Liver failure
Can be taken with or without food
Meglitinides repaglinide (GlucoNorm) nateglinide (Starlix)
Stimulates the pancreas to produce more insulin (therefore ineffective if cells of the pancreas can no longer function)
Type 2 Diabetes
Antifungal medications (lowers glucose) Nonsteroidal antiinflammatory medications (NSAIDS) (lowers glucose) Anti-seizure medications (increases glucose)
Hypoglycem ia Headache Dizziness
Must be taken 0 to 30 minutes before meals If a meal is skipped, the dose should be skipped. If a meal added, then a dose should be added
Respiratory
Antitussive Non-opioid dextromethorphan (Benylin/Buckleys/Rob itussin) Opioid Hydrocodone/Codeine PO Suppress cough reflex by numbing stretch receptors in resp. tract cough reflex not initiated or Suppress the cough reflex; medulla Cough (nonproductive only!) URTI (viral and bacterial Allergy Opioid dependency Children <6 years of age Risk for respiratory depression Drowsiness/sedation Dizziness N/V Constipation (opioids) Adequate respiratory assessment Avoid driving, operating heavy machinery Push fluid intake
Decongestants Adrenergic Agonist pseudoephedrine (Sudafed) oxymetazoline (Vicks/Dristan/Dimeta pp) xylometazoline (Otrivin/Triaminic) Corticosteroid budesonide
Vasoconstriction of arterioles of nasal mucosa Anti-inflammatory effect
Allergies URTI (viral and bacterial) Rhinitis Sinusitis
Allergy HTN Diabetes Hyperthyroidism
Mucosal dryness/irritation Palpitations Insomnia Tremors
Potential for rebound congestion (rhinitis medicamentosa); if used >5 days nasal passage damage Avoid caffeine Report fever, productive cough, etc. lasting >5-7d
(Pulmicort/Symbicort) mometasone furoate (Nasonex) PO/INH Antihistamine (H1) diphenhydramine (Benadryl) cetirizine (Reactine) loratadine (Claritin) PO/IV/IM Compete with histamine for specific receptor sites **Remember: Histamine causes constriction of smooth muscles, increased body secretions, and vasodilatation** Dilates airways by stimulating 2-adrenergic receptors in lung tissue (bronchodilation) Rhinitis Anaphylaxis Allergies in general Glaucoma Pregnancy Heart disease Kidney disease Asthma Bronchitis COPD Allergy Cardiac dysrhythmia Hypertension (medications cause vasoconstriction) Under the age of 6 is limited Beta-blocker use (inhibits bronchodilation) Allergy Not recommended in children under the age of 12 Drowsiness (side effect) Anticholinergic effects Tachycardia Restlessness Dilated pupils Decreased salivation Urinary retention Tachycardia Insomnia Tremors Hyperglycemia May experience paradoxical excitement May cause confusion, dizziness, and hypotension diphenhydramine is sometimes used as a sleeping aid for occasional use Avoid driving and use of heavy machinery
Beta-adrenergic Agonist (2-Agonist) salbutamol (Ventolin) salmeterol (Serevent) terbutaline (Bricanyl) PO/INH
Preferred medication for acute respiratory symptoms Cardiac and respiratory assessments Hold breath for 5-10 seconds post inhalation Use a spacer or Aero chamber for administration Wait 2 minutes between inhalations Rinse mouth after inhalation (metallic taste) Do not use medication to terminate an acute attack Hold breath for 5-10 seconds post inhalation Use a spacer or Aero chamber for administration Wait 2 minutes between inhalations Rinse mouth after inhalation
Anticholinergic ipratropium bromide (Atrovent) INH
Block ACh (acetylcholine) receptors to prevent bronchoconstricti on **RememeberACh comes from the PSNS and causes bronchial constriction** Medications work in the same manner as naturally occurring steroid hormones
Asthma Bronchitis COPD
Anticholinergic effects Tachycardia Restlessness Dilated pupils Decreased salivation Urinary retention
Corticosteroids cortisone (Cortistan) hydrocortisone (Cortef)
Addisons Disease Asthma Inflammatory Bowel Disease
Allergy Cataracts Glaucoma Peptic ulcer disease
Impaired wound healing Masking of infections
(decrease absorption & increase excretion of calcium) Long-term use may cause Cushings disease/syndrome
methylprednisolone (Medrol) prednisone (Winpred) dexamethasone (Decadron) fluticasone (Flovent) PO/IV/IM/TOPICAL/I NH 1.
Xanthines theophylline (TheoDur) aminophylline (Somophylline) PO/IV
Gonadocorticoids: (androgens) contribute to onset of puberty Mineralocorticoids: recall function of aldosterone Glucocorticoids: (cortisol) Increase blood glucose by inhibiting insulin secretion and promoting gluconeogenesis 2. Breakdown lipids and proteins 3. Suppress the inflammatory response Influence CNS to affect mood Causes bronchodilation Acts on the CNS medulla to enhance respiratory drive
Rhinitis Pruritis Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease Hodgkins Disease Leukemias Sinusitis
Psychiatric problems Systemic infections
Hypokalemia Peptic ulcers Edema Sodium/fluid retention Nausea Anxiety Weight gain Heart failure Increased intraocular pressure Fragile skin Candidiasis (inhaler use)
Oral glucocorticoids should be given in the morning to decrease amount of adrenal suppression Oral glucocorticoids should be given with milk or food to decrease GI upset Growth retardation is possible. Thus, smaller doses should be considered and accurate weekly height and weight must be documented Corticosteroids often aggravate other conditions (i.e. hypertension, CHF, diabetes, infection) Rinse mouth after inhaled use to prevent candidiasis
Asthma Bronchitis COPD
Allergy Cardiac dysrhythmia Seizure disorders Antibiotic use (increases serum levels of xanthine) Caffeine
N/V Anorexia Cardiac dysrhythmia
Limit caffeine intake Report s/s of toxicity (anorexia, N/V, hypotension, seizure) Limit cigarette smoking (reduces therapeutic effect of xanthines) Between 6 months and 16 years of age may need increased doses r/t rapid metabolization Under the age of 6 months have prolonged elimination r/t immature liver Very unpredictable r/t drug interactions, renal and hepatic impairment Monitor liver function tests (especially during early course of treatment) Do not use medication to terminate an acute attack
Antileukotrines montelukast sodium (Singulair) zafirlukast (Accolate) PO
Prevent smooth muscle contraction of the bronchi Decreases mucus secretion Decreases
Asthma
Allergy Allergy to lactose (inactive ingredient in antileukotrines) Liver disease
N/D Headache Liver failure
inflammation in lungs by preventing mobilization and migration of WBCs into the lungs
Cardiovascular
Anticoagulants Heparin dalteparin (Fragmin)(LMWH) enoxaprin (Lovenox)(LMWH) warfarin (Coumadin) PO/IV/IM/SC
Prevents thrombus formation Inhibits clotting factors in intrinsic pathway (Xa, IX, X, XI, XII & VIII) Inhibits prothrombin to thrombin & fibrinogen to fibrin
Venous Thrombosis Pulmonary Embolism Atrial Fibrillation CVA Thrombosis MI
Allergy Thrombocytopenia Active internal ( platelet count) Bleeding bleeding Severe hypertension HematuriaNausea Bleeding disorders Local irritation ASA/NSAIDS ( (preferably anticoagulant effect) injected SC into abdomen) Trauma Intracranial hemorrhage
Prophylaxis use only (they do not work on clots that have already formed) Monitor blood work, values such as aPTT (heparin use) and INR (warfarin use) Check for bleeding especially in gums and stool Heparin (20 min onset) usually starts therapy, followed by Warfarin (36h onset) Vitamin K is used to reverse effects of warfarin toxicity Protamine sulfate is used to reverse heparin effects Heparin containing benzyl alcohol must not be given to neonates (fatal reactions have been reported) When warfarin is used, all care providers should be informed to avoid unnecessary physical trauma More likely to experience bleeding complications dalteparin and enoxaparin can cause renal failure
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- The Renal Diet Kitchen: 60+ Quick and Delicious Renal Diet Recipes to Improve Kidney FunctionVon EverandThe Renal Diet Kitchen: 60+ Quick and Delicious Renal Diet Recipes to Improve Kidney FunctionNoch keine Bewertungen
- Drug CardsDokument16 SeitenDrug Cardsp_dawg100% (7)
- Naplex Complete Study Outline A Topic-Wise Approach DiabetesVon EverandNaplex Complete Study Outline A Topic-Wise Approach DiabetesBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (2)
- Drug Therapy For GI Disorders PDFDokument5 SeitenDrug Therapy For GI Disorders PDFmeeraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lecture 1 Gastrointestinal Pharmacology (Powerpoint)Dokument30 SeitenLecture 1 Gastrointestinal Pharmacology (Powerpoint)j.doe.hex_87100% (2)
- Drug OrderDokument8 SeitenDrug OrderRiezza BalicaoNoch keine Bewertungen
- GI Disorders Note - 221206 - 074045Dokument48 SeitenGI Disorders Note - 221206 - 074045Shabnam SajidaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Diarrhoea in Children: An ApproachDokument78 SeitenDiarrhoea in Children: An ApproachNP SinghNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pharmacotherapy of DiarhheaDokument29 SeitenPharmacotherapy of DiarhheaFahril LabuduNoch keine Bewertungen
- Drugs GCDokument7 SeitenDrugs GCJharene BasbañoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Drugs Affecting The Gastrointestinal TractDokument61 SeitenDrugs Affecting The Gastrointestinal TractSameera DahamNoch keine Bewertungen
- Gastrointestinal DrugsDokument45 SeitenGastrointestinal DrugsCindy MaslagNoch keine Bewertungen
- Drugs Affecting The Gastrointestinal System & NutritionDokument26 SeitenDrugs Affecting The Gastrointestinal System & NutritionNur Faza RosliNoch keine Bewertungen
- Printed Material Module 7 Gastrointestinal System Drugs - PDFDokument45 SeitenPrinted Material Module 7 Gastrointestinal System Drugs - PDFShang MacarayonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bowel PreparationDokument22 SeitenBowel Preparationbashiruaminu100% (1)
- 27 Pendekatan Klinis DiareDokument41 Seiten27 Pendekatan Klinis DiareEks TraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Gastroenteritis Dan MalabsorptionDokument62 SeitenGastroenteritis Dan MalabsorptionDandi PremaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Farmakoterapi Sistem Pencernaan Diare Konstipasi HepatitisDokument77 SeitenFarmakoterapi Sistem Pencernaan Diare Konstipasi HepatitisRefika FahruNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nichols GI 09Dokument59 SeitenNichols GI 09marviecute22Noch keine Bewertungen
- Diare Noninfeksi.2017Dokument34 SeitenDiare Noninfeksi.2017Tim IrmaNoch keine Bewertungen
- AmoxicillinDokument5 SeitenAmoxicillinKyle DelrosarioNoch keine Bewertungen
- Therapy of ConstipationDokument37 SeitenTherapy of ConstipationBishal ChauhanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Drug Study AGEDokument9 SeitenDrug Study AGECherry Jani OlmedoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Drug StudyDokument14 SeitenDrug StudyLovely Saad TubañaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cues Nursing DX Objectives Nursing Interventions RationaleDokument5 SeitenCues Nursing DX Objectives Nursing Interventions RationaleJamie IcabandiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Drug Therapuetic Action Indication Contraindication Adverse Effect Nursing ConsiderationDokument5 SeitenDrug Therapuetic Action Indication Contraindication Adverse Effect Nursing ConsiderationDan DomingoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Parenteral FeedingDokument7 SeitenParenteral Feeding4gen_7Noch keine Bewertungen
- Side Effects of AmoxicillinDokument4 SeitenSide Effects of AmoxicillinAphro DhiteNoch keine Bewertungen
- Diarrhoea in Children::-Professor Dulari Gandhi HOD Department of PediatricsDokument34 SeitenDiarrhoea in Children::-Professor Dulari Gandhi HOD Department of PediatricsDrbhupeshwari GourNoch keine Bewertungen
- Katzung LaxativesDokument6 SeitenKatzung LaxativesLonnieAllenVirtudesNoch keine Bewertungen
- T HypoidDokument22 SeitenT HypoidDeddy ShangrelaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Kuliah TK IV Fkui DiarrhoeaDokument41 SeitenKuliah TK IV Fkui DiarrhoeaYosi Rizal JrNoch keine Bewertungen
- Laxatives and Anti-DiarrhealDokument28 SeitenLaxatives and Anti-DiarrhealimnasNoch keine Bewertungen
- DR/ Mohammad Abdul Baset Badr: Prepared byDokument75 SeitenDR/ Mohammad Abdul Baset Badr: Prepared byamrharidi446Noch keine Bewertungen
- Management of DiarrhoeaDokument16 SeitenManagement of Diarrhoeasunday danielNoch keine Bewertungen
- Anti DiarrhoealsDokument37 SeitenAnti DiarrhoealsCrome operatorNoch keine Bewertungen
- Drugs Used in The Treatment of Gastrointestinal DiseasesDokument52 SeitenDrugs Used in The Treatment of Gastrointestinal DiseasesWidia Isa Aprillia SujanaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Drug Therapy For ConstipationDokument25 SeitenDrug Therapy For ConstipationRiddhi JainNoch keine Bewertungen
- Gastrointestinal Pharmacology: Learning ObjectivesDokument54 SeitenGastrointestinal Pharmacology: Learning Objectivesamr ahmedNoch keine Bewertungen
- Study Guide - Pharmacology: Agonist vs. AntagonistDokument4 SeitenStudy Guide - Pharmacology: Agonist vs. Antagonistb2ktookie9455Noch keine Bewertungen
- PDF Module 10 Urinary System DrugsDokument7 SeitenPDF Module 10 Urinary System DrugsAJ VitangculNoch keine Bewertungen
- w15 - Drug StudyDokument4 Seitenw15 - Drug StudyGeneva LatorreNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pharma Review FinalsDokument31 SeitenPharma Review FinalsLanz Andrei MatociñosNoch keine Bewertungen
- Antidiarrhoeals and Laxatives PDFDokument34 SeitenAntidiarrhoeals and Laxatives PDFKumar SaurabhNoch keine Bewertungen
- Antidiarrheal DrugsDokument7 SeitenAntidiarrheal Drugsmwaithira71682Noch keine Bewertungen
- Patofisiologi DiareDokument45 SeitenPatofisiologi DiareAngela Kristiana Intan100% (1)
- Esomeprazole MagnesiumDokument3 SeitenEsomeprazole Magnesiumapi-3797941100% (1)
- 14 Antidiarrhead Laxatives UpdDokument52 Seiten14 Antidiarrhead Laxatives Updone_nd_onlyuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pathophysiology of Pyelonephritis: How It HappensDokument6 SeitenPathophysiology of Pyelonephritis: How It HappensReno Jun NagasanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Drug Study - LeptospirosisDokument19 SeitenDrug Study - LeptospirosisCamille PinedaNoch keine Bewertungen
- GI Tract - Nutrition/EliminationDokument51 SeitenGI Tract - Nutrition/Eliminationnick_nock08Noch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter - 2 - C - V-B Infectious - Diarrhea PPT AmnaDokument47 SeitenChapter - 2 - C - V-B Infectious - Diarrhea PPT AmnaEmmaNoch keine Bewertungen
- PrimDokument2 SeitenPrimapi-3797941Noch keine Bewertungen
- DiarrheaDokument2 SeitenDiarrheajanna_3Noch keine Bewertungen
- Drugs Used To Treat Digestive Problems: Classification: AntidiarrhealsDokument68 SeitenDrugs Used To Treat Digestive Problems: Classification: AntidiarrhealsTom-tom LunaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Drug Study (FINAL)Dokument31 SeitenDrug Study (FINAL)iamjenivicNoch keine Bewertungen
- Anti DiarrheaDokument40 SeitenAnti DiarrheaNofilia Citra CandraNoch keine Bewertungen
- DiarrheaDokument92 SeitenDiarrheaWilliams Emmanuel AdeyeyeNoch keine Bewertungen
- gddrg0035 25948 63478Dokument6 Seitengddrg0035 25948 63478Jemima DzitseNoch keine Bewertungen
- Care of Puppies Birth To 10 Days Sept 2015Dokument2 SeitenCare of Puppies Birth To 10 Days Sept 2015Annelle GeldenhuysNoch keine Bewertungen
- Septic Shock Rapid Recognition and Initial Resuscitation inDokument19 SeitenSeptic Shock Rapid Recognition and Initial Resuscitation inCristian Villarroel SNoch keine Bewertungen
- ATSP (Asked To See Patient) BookletDokument24 SeitenATSP (Asked To See Patient) BookletCindy WongNoch keine Bewertungen
- 17 Nrcme Practice TestDokument19 Seiten17 Nrcme Practice Testdr_milan100% (1)
- Part 1 Sample Questions MRCPDokument33 SeitenPart 1 Sample Questions MRCParvindNoch keine Bewertungen
- Diabetes in School Powerpoint PresentationDokument16 SeitenDiabetes in School Powerpoint Presentationmaria sarojiniNoch keine Bewertungen
- Treatment of Type 2 DibetesDokument4 SeitenTreatment of Type 2 DibetesAnonymous ysrxggk21cNoch keine Bewertungen
- CBG RetdemDokument7 SeitenCBG Retdemadd.bdrcNoch keine Bewertungen
- BIOCHEMISTRY: Laboratory DiscussionDokument7 SeitenBIOCHEMISTRY: Laboratory DiscussionNorman Vryne CaduaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ran CadDokument6 SeitenRan CadSameer JadhavNoch keine Bewertungen
- OET-Preparation-Book - Reading-Sub-Test - Volume-1-Anna-HartfordDokument57 SeitenOET-Preparation-Book - Reading-Sub-Test - Volume-1-Anna-HartfordGeorgianNeagu100% (1)
- Diabetes in Elderly Adults: Graydon S. Meneilly and Daniel TessierDokument9 SeitenDiabetes in Elderly Adults: Graydon S. Meneilly and Daniel Tessierdita prameswariNoch keine Bewertungen
- Gestational Diabetes Case Study With Questions For The Undergraduate NurseDokument46 SeitenGestational Diabetes Case Study With Questions For The Undergraduate NurseAndrea Donmyer100% (1)
- Diabetes PathophysiologyDokument6 SeitenDiabetes PathophysiologyKatelyn CherryNoch keine Bewertungen
- Practical Approach To A Person Who Is Unconscious: Nagarajan VenkataramanDokument5 SeitenPractical Approach To A Person Who Is Unconscious: Nagarajan VenkataramanIlam PrabhuNoch keine Bewertungen
- 04 GTTDokument15 Seiten04 GTTAshish TuraleNoch keine Bewertungen
- Student Notes: Clinchem1: Davao Doctors College Medical Laboratory Science DepartmentDokument9 SeitenStudent Notes: Clinchem1: Davao Doctors College Medical Laboratory Science DepartmentMelody Jane PardilloNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pone 0163350Dokument14 SeitenPone 0163350alifandoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Metformin GlucophageDokument1 SeiteMetformin GlucophageENoch keine Bewertungen
- Vinaya Self - Amritha Institute of Medical Science Amritha Institute of Medical Science Sample Collected atDokument1 SeiteVinaya Self - Amritha Institute of Medical Science Amritha Institute of Medical Science Sample Collected atBipin RethinNoch keine Bewertungen
- Prevalence of Refractive Errors in Type 2 Diabetic Patients in Northern IndiaDokument8 SeitenPrevalence of Refractive Errors in Type 2 Diabetic Patients in Northern IndiaRagni MishraNoch keine Bewertungen
- NCLEX Questions - OB MATERNITY QUESTIONS PDFDokument17 SeitenNCLEX Questions - OB MATERNITY QUESTIONS PDFAnneRaquelTalentoNoch keine Bewertungen
- IVMS Physiology and Pathophysiology Flash FactsDokument4.648 SeitenIVMS Physiology and Pathophysiology Flash FactsMarc Imhotep Cray, M.D.Noch keine Bewertungen
- Guided by Asso Prof DR Sunil K Agarawalla Presented by DR Minakhi Kumari Sahu (JR-1)Dokument45 SeitenGuided by Asso Prof DR Sunil K Agarawalla Presented by DR Minakhi Kumari Sahu (JR-1)Gobinda Pradhan100% (1)
- Crash Course in Dental Management of The Medically Compromised PatientDokument30 SeitenCrash Course in Dental Management of The Medically Compromised Patientmazen bokhari100% (1)
- Endocrine System (Pathophysiology)Dokument18 SeitenEndocrine System (Pathophysiology)roselle legson100% (1)
- Mortality Report April 25th 2019Dokument12 SeitenMortality Report April 25th 2019ramotNoch keine Bewertungen
- Manejo HiperglicemiaDokument28 SeitenManejo HiperglicemiaLya Mylene VillarroelNoch keine Bewertungen
- Invisible Minerals Part II by DR Carolyn DeanDokument46 SeitenInvisible Minerals Part II by DR Carolyn Deanlihu74100% (1)