Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Diffusion and Osmosis
Hochgeladen von
Mera FunportalOriginalbeschreibung:
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Diffusion and Osmosis
Hochgeladen von
Mera FunportalCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
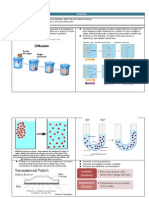
Diffusion is the chemical process when molecules from a material move from an area of high concentration (where there
are lots of molecules) to an area of low concentration (where there are fewer molecules). This happens through otherwise random movement. Diffusion usually happens in a gas although it can happen in a liquid. It is possible to see diffusion happening when two liquids are mixed in atransparent container. It describes the constant movement of particles in all liquids and gases.These particles move in all directions bumping into each other. Diffusion can only work with gases and liquids. Here are some examples of diffusion: A sugar cube is left in a beaker of water for a while. The smell of ammonia spread from the front of the classroom to the back of the room. Fumes of perfume rises from the bottle when the top is removed. Food coloring dropped on the beaker causing to spread out. Adding of sugar in water!
One of the most important things about diffusion is that molecules tend to move from places of high concentration to places of low concentration, just by moving randomly. Therefore, this is not the most effective way of moving in and out of cells, however there are many examples where diffusion takes place but is adapted so it is efficient. For example, there is more oxygen in a lung than there is oxygen in the blood so oxygen molecules will tend to move into the blood. Similarly, there is more carbon dioxide molecules in the blood than in the lung so carbon dioxide molecules will tend to move into the lung. Diffusion can be considered to arise from probability alone - areas of high density are, due to the random movement of fluid molecules, likely to spread out within their boundary until they can do so no longer. Diffusion is also connected to Entropy.
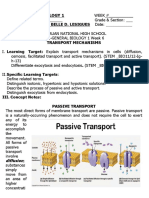
Osmosis is the movement of water through a plasma membrane from a region of [1] low solute concentration to a region of high concentration. It is a type of diffusion. Osmosis is passive transport, meaning it does not require energy to be applied. What causesosmotic pressure is different concentrations of solutes on the two sides of the membrane. When osmosis happens, water moves from the side of the membrane with a lower amount of osmotic pressure to the side of the membrane with the higher amount. An important example of osmosis is the movement of liquid (solvent) molecules across a cell membrane into a cell with a higher solute concentration. Osmosis is a fundamental part of cell biochemistry, but also has mechanical applications and usages.
Hypotonic, isotonic, and hypertonic
Hypotonic describes the less concentrated solution. An isotonic solution is when the concentration is equal on both sides of the membrane. Hypertonic describes the more concentrated solution. The usual cell biology situation is: hypotonic solution outside the cell, and hypertonic solution inside.
Cell membranes[change | edit source]
The plasma membrane of a cell is semi-permeable, which means it lets small molecules pass through, but blocks larger molecules. However, the membrane has special gateways which allow certain kinds of macromolecules to get though. This is not passive transport, but requires energy, and is selective.
nn
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Biochem Laboratory Activity 2Dokument4 SeitenBiochem Laboratory Activity 2Kristine PangahinNoch keine Bewertungen
- Diffusion Vs OsmosisDokument3 SeitenDiffusion Vs OsmosisK TanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Diffusion: AND ExplanationDokument2 SeitenDiffusion: AND ExplanationTaimoor QadeerNoch keine Bewertungen
- Diffusion and OsmosisDokument3 SeitenDiffusion and Osmosisshaniah100% (1)
- Diffusion and OsmosisDokument6 SeitenDiffusion and OsmosisCharlesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cell Transport NotesDokument10 SeitenCell Transport NotesReyad BarbarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Gene103Lab DiffusionandOsmosisDokument5 SeitenGene103Lab DiffusionandOsmosisbodurr571Noch keine Bewertungen
- Research PaperDokument9 SeitenResearch PaperNifemi OlutayoNoch keine Bewertungen
- DiffusionDokument32 SeitenDiffusionAce Mhac TeñidoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Osmosis and Semipermeable MembranesDokument4 SeitenOsmosis and Semipermeable MembranesAarhan KhanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Diffusion, Osmosis AND Active TransportDokument18 SeitenDiffusion, Osmosis AND Active TransportScience,Physical Education And Sports VideosNoch keine Bewertungen
- Osmosis: Diffusion Is The Process Where Molecules of Two or More Substances Move AboutDokument3 SeitenOsmosis: Diffusion Is The Process Where Molecules of Two or More Substances Move AboutizzahNoch keine Bewertungen
- Water Ang Ingon Sa Isa Ka Source: Semipermeable MembraneDokument1 SeiteWater Ang Ingon Sa Isa Ka Source: Semipermeable MembranemarielNoch keine Bewertungen
- (Original Size) Movement in and Out of CellsDokument8 Seiten(Original Size) Movement in and Out of CellshridanshhirparaNoch keine Bewertungen
- BioCLab Mod3Dokument11 SeitenBioCLab Mod3Samantha BolanteNoch keine Bewertungen
- In and Out of CellsDokument3 SeitenIn and Out of CellsA personNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chemistry ProjectDokument16 SeitenChemistry ProjectGokul100% (1)
- Movement in and OutDokument35 SeitenMovement in and OutzefanyaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Las-Q3-Wk6.1 2Dokument12 SeitenLas-Q3-Wk6.1 2Jhude JosephNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 5: Homeostasis and Transport Lesson 5.2: Cell Transport-Passive and ActiveDokument10 SeitenChapter 5: Homeostasis and Transport Lesson 5.2: Cell Transport-Passive and ActiveVanshika VermaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Personal NotesDokument7 SeitenPersonal NoteslayshengNoch keine Bewertungen
- 19031121-Abeto-Difusi Molekul Di Dalam AirDokument29 Seiten19031121-Abeto-Difusi Molekul Di Dalam AirZhafiraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Class Notes (1) CHP 3 Movement Into and Out of The CellDokument8 SeitenClass Notes (1) CHP 3 Movement Into and Out of The CellRahil ShahNoch keine Bewertungen
- Notes Movement in & Out of CellsDokument6 SeitenNotes Movement in & Out of CellsddddddffdfdfNoch keine Bewertungen
- Diffusion Osmosis and Active TransportDokument18 SeitenDiffusion Osmosis and Active TransportThompson Ta Ta JevonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Biology Diffusion: Examples of Diffusion in The BodyDokument2 SeitenBiology Diffusion: Examples of Diffusion in The BodydonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Osmosis: From Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaDokument6 SeitenOsmosis: From Wikipedia, The Free Encyclopediaallanlopez_2009Noch keine Bewertungen
- Movement of Particles NoteDokument2 SeitenMovement of Particles NoteSabita SinghNoch keine Bewertungen
- 5.7 Cell TransportDokument6 Seiten5.7 Cell TransportMonica B. BautistaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Gases - Diffusion and EffusionDokument5 SeitenGases - Diffusion and EffusionLovely RamNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 1 Doc 4Dokument4 SeitenChapter 1 Doc 4Enju ChipepeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Laporan Physio ExDokument13 SeitenLaporan Physio ExsolideoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Assignment Topic Osmotic Pressure and Its ApplicationDokument8 SeitenAssignment Topic Osmotic Pressure and Its ApplicationSohail JihadiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Movement Across The Cell MembraneDokument3 SeitenMovement Across The Cell MembraneUmi Zaheera AzharNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mechanism: Osmosis Is The Spontaneous Net Movement ofDokument4 SeitenMechanism: Osmosis Is The Spontaneous Net Movement ofm bilalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Osmosis, Diffusion PresentationDokument19 SeitenOsmosis, Diffusion PresentationRahul YadavNoch keine Bewertungen
- Passive TransportDokument3 SeitenPassive Transportirnumambreen15Noch keine Bewertungen
- Diffusion Final NotesDokument16 SeitenDiffusion Final NotesBalakrishnan MarappanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bio Lab IntroDokument2 SeitenBio Lab Introapi-327731714Noch keine Bewertungen
- Diffusion Across The Cell MembraneDokument3 SeitenDiffusion Across The Cell Membranetoro toroNoch keine Bewertungen
- Untitled DocumentDokument3 SeitenUntitled Documenttoro toroNoch keine Bewertungen
- Osmosis, Diffusion PresentationDokument19 SeitenOsmosis, Diffusion PresentationmefunNoch keine Bewertungen
- 3 Diffusion & OsmosisDokument27 Seiten3 Diffusion & OsmosisnasserkhanNoch keine Bewertungen
- BIOLOGY SUMMARY TOPIC 3 IgcseDokument5 SeitenBIOLOGY SUMMARY TOPIC 3 IgcsesameehaNoch keine Bewertungen
- B3 Movement Into and Out of Cells SlidesDokument52 SeitenB3 Movement Into and Out of Cells SlidesMinh Hoàng ĐứcNoch keine Bewertungen
- DiffusionDokument4 SeitenDiffusionROBERTO SHERWIN JR TANDASNoch keine Bewertungen
- Diffusion 222Dokument3 SeitenDiffusion 222jinky_julianNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cell Transport: by Felipe Hoffmann, Juan Felipe Canal, Juan Sebastian Lopez, Nicolas Castrillon and Simon KnudsenDokument6 SeitenCell Transport: by Felipe Hoffmann, Juan Felipe Canal, Juan Sebastian Lopez, Nicolas Castrillon and Simon KnudsenSimon KnudsenNoch keine Bewertungen
- Osmosis: For Other Uses, SeeDokument4 SeitenOsmosis: For Other Uses, SeeMisrai FaraukNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cell TransportDokument23 SeitenCell Transport7104Noch keine Bewertungen
- Osmosis: Osmosis Is The Spontaneous Net Movement of SolventDokument3 SeitenOsmosis: Osmosis Is The Spontaneous Net Movement of SolventCHIEF VISHAAL 45Noch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 7Dokument20 SeitenChapter 7criselledalipe12Noch keine Bewertungen
- 04 NotesDokument6 Seiten04 NotesAirus SamaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Diffusion and Osmosis - IGCSEDokument37 SeitenDiffusion and Osmosis - IGCSEJohnnie ZhangNoch keine Bewertungen
- CELLSDokument5 SeitenCELLSJermaine CorpuzNoch keine Bewertungen
- Osmosis, Diffusion PresentationDokument19 SeitenOsmosis, Diffusion PresentationLee KaiYangNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chemlab Report2Dokument15 SeitenChemlab Report2Czarriel F. Flores100% (1)
- Science SpeechDokument2 SeitenScience SpeechzaraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lecture 2 - Diffusion and OsmosisDokument11 SeitenLecture 2 - Diffusion and Osmosiskinza yasirNoch keine Bewertungen
- Was The Congress Attitude The Most Important Factor Why Muslim League Was Formed in 1906Dokument6 SeitenWas The Congress Attitude The Most Important Factor Why Muslim League Was Formed in 1906Mera FunportalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Quiad InformationDokument11 SeitenQuiad InformationShahid ImranNoch keine Bewertungen
- Was The Congress Attitude The Most Important Factor Why Muslim League Was Formed 1906 PDFDokument6 SeitenWas The Congress Attitude The Most Important Factor Why Muslim League Was Formed 1906 PDFMera FunportalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Why Were Morley Minto Reforms IntroducedDokument1 SeiteWhy Were Morley Minto Reforms IntroducedMera FunportalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Was The Congress Attitude The Most Important Factor Why Muslim League Was Formed in 1906 PDFDokument6 SeitenWas The Congress Attitude The Most Important Factor Why Muslim League Was Formed in 1906 PDFMera FunportalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Theory and Research Methods in SociologyDokument99 SeitenTheory and Research Methods in SociologyMera FunportalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Could Not Read and WriteDokument1 SeiteCould Not Read and WriteMera FunportalNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2052Dokument1 Seite2052Mera FunportalNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2052Dokument1 Seite2052Mera FunportalNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2052Dokument1 Seite2052Mera FunportalNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2052Dokument1 Seite2052Mera FunportalNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2015 Paper IslDokument1 Seite2015 Paper IslMera FunportalNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2052Dokument1 Seite2052Mera FunportalNoch keine Bewertungen
- J2052 Find One That Is ValuableDokument1 SeiteJ2052 Find One That Is ValuableMera FunportalNoch keine Bewertungen
- DeedDokument2 SeitenDeedMera FunportalNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Mosque GreenHall PublicationsDokument2 SeitenThe Mosque GreenHall PublicationsMera FunportalNoch keine Bewertungen
- 02 How To Pray SalahDokument47 Seiten02 How To Pray Salahrazanym100% (1)
- Various ArtsDokument4 SeitenVarious ArtsMera FunportalNoch keine Bewertungen
- 538 A-1Dokument22 Seiten538 A-1Mera FunportalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Q1: How Did Allama Iqbal Argue The Need For A Separate Muslim State? Discuss in The Light of Allahabad Address of 1930Dokument24 SeitenQ1: How Did Allama Iqbal Argue The Need For A Separate Muslim State? Discuss in The Light of Allahabad Address of 1930Mera Funportal100% (1)
- DeedDokument2 SeitenDeedMera FunportalNoch keine Bewertungen
- DeedDokument2 SeitenDeedMera FunportalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Downloaded LicensesDokument1 SeiteDownloaded LicensesMera FunportalNoch keine Bewertungen
- LDL HDL Blood TestDokument2 SeitenLDL HDL Blood TestMera FunportalNoch keine Bewertungen
- DeedDokument2 SeitenDeedMera FunportalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Paletine IssueDokument2 SeitenPaletine IssueMera FunportalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Strategic ElementsDokument7 SeitenStrategic ElementsMera FunportalNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2059 w15 Ms 2 PDFDokument15 Seiten2059 w15 Ms 2 PDFMera FunportalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Palestine 1Dokument2 SeitenPalestine 1Mera FunportalNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2059 w15 Ms 2 PDFDokument15 Seiten2059 w15 Ms 2 PDFMera FunportalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Exponential Smoothing - The State of The ArtDokument28 SeitenExponential Smoothing - The State of The ArtproluvieslacusNoch keine Bewertungen
- MCQ Floyd ElexDokument87 SeitenMCQ Floyd ElexnicoleNoch keine Bewertungen
- Truss-Design 18mDokument6 SeitenTruss-Design 18mARSENoch keine Bewertungen
- Newsletter 1-2021 Nordic-Baltic RegionDokument30 SeitenNewsletter 1-2021 Nordic-Baltic Regionapi-206643591100% (1)
- I Pmtea 2020 HandoutDokument94 SeitenI Pmtea 2020 HandoutAbhijeet Dutta100% (1)
- 9881 enDokument345 Seiten9881 enSaid BenNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fake News Infographics by SlidesgoDokument33 SeitenFake News Infographics by SlidesgoluanavicunhaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Marion Nicoll: Life & Work by Catharine MastinDokument147 SeitenMarion Nicoll: Life & Work by Catharine MastinArt Canada InstituteNoch keine Bewertungen
- Unit 2 - Industrial Engineering & Ergonomics - WWW - Rgpvnotes.inDokument15 SeitenUnit 2 - Industrial Engineering & Ergonomics - WWW - Rgpvnotes.inSACHIN HANAGALNoch keine Bewertungen
- European Construction Sector Observatory: Country Profile MaltaDokument40 SeitenEuropean Construction Sector Observatory: Country Profile MaltaRainbootNoch keine Bewertungen
- Java Complete Collection FrameworkDokument28 SeitenJava Complete Collection FrameworkkhushivanshNoch keine Bewertungen
- Oceanarium: Welcome To The Museum Press ReleaseDokument2 SeitenOceanarium: Welcome To The Museum Press ReleaseCandlewick PressNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nfpa 1126 PDFDokument24 SeitenNfpa 1126 PDFL LNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bioinformatics Computing II: MotivationDokument7 SeitenBioinformatics Computing II: MotivationTasmia SaleemNoch keine Bewertungen
- Vygotsky EssayDokument3 SeitenVygotsky Essayapi-526165635Noch keine Bewertungen
- Liquitex Soft Body BookletDokument12 SeitenLiquitex Soft Body Booklethello belloNoch keine Bewertungen
- What You Need To Know About Your Drive TestDokument12 SeitenWhat You Need To Know About Your Drive TestMorley MuseNoch keine Bewertungen
- Green Dot ExtractDokument25 SeitenGreen Dot ExtractAllen & UnwinNoch keine Bewertungen
- Natural Cataclysms and Global ProblemsDokument622 SeitenNatural Cataclysms and Global ProblemsphphdNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sheltered 2 Item Recycle ListDokument5 SeitenSheltered 2 Item Recycle ListRachel GNoch keine Bewertungen
- CAREDokument11 SeitenCARELuis SementeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Digital Electronics Chapter 5Dokument30 SeitenDigital Electronics Chapter 5Pious TraderNoch keine Bewertungen
- Paul Spicker - The Welfare State A General TheoryDokument162 SeitenPaul Spicker - The Welfare State A General TheoryTista ArumNoch keine Bewertungen
- LFF MGDokument260 SeitenLFF MGRivo RoberalimananaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Amritsar Police StationDokument5 SeitenAmritsar Police StationRashmi KbNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1.co - Deb4113 - Industrial ManagementDokument10 Seiten1.co - Deb4113 - Industrial ManagementrohaizadNoch keine Bewertungen
- Algorithms For Automatic Modulation Recognition of Communication Signals-Asoke K, Nandi, E.E AzzouzDokument6 SeitenAlgorithms For Automatic Modulation Recognition of Communication Signals-Asoke K, Nandi, E.E AzzouzGONGNoch keine Bewertungen
- CCDokument5 SeitenCCnazmulNoch keine Bewertungen
- Women Are Better Managers Than MenDokument5 SeitenWomen Are Better Managers Than MenCorazon ValdezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lightning Protection Measures NewDokument9 SeitenLightning Protection Measures NewjithishNoch keine Bewertungen