Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Unit 2
Hochgeladen von
V V Satyanarayana PasupuletiOriginaltitel
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Unit 2
Hochgeladen von
V V Satyanarayana PasupuletiCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
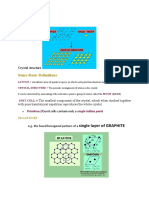
CRYSTAL STRUCTURES
Crystalline Solids:in a solid, if the atoms are arranged regularly in three dimensions and the environment about any atom is same then that solid is called crystalline solid Or A crystal is defined as a periodic three dimensional array of atoms. This 3D array is called the lattice and it can be generated from its unit cell Amorphous solid: If the atoms are arranged irregularly in three dimensions and environment about any atom is not same that type of solids is called Amorphous Solids. COMPARISION BETWEEN CRYSTALINE AND AMARPHOUS SOLIDS: CRYSTALINE SOLIDS 1. Crystalline solids have regular arrangement of atoms 2. Crystalline materials have very sharp melting point. 3. Crystalline materials have different properties in different directions. i.e., they are anisotropic. 4. The cooling curve of crystalline material has breaks. 5. Crystalline materials have long range order of interactions. 6. Example for crystalline materials are Si, Ge, Nacl,CsCl etc AMORPHOUS SOLIDS 1. Amorphous solids have random arrangement of atoms. 2. These materials are not having sharp melting point. 3. Amarphous solids show same properties in different directions. i.e., they are Isotropic. 4. The cooling curve of amorphous solids is smooth curve. 5. Amorphous materials have short range, i.e., limited to few atomic distances. 6. Example for Amorphous solids is Glass.
Lattice Point: An Imaginary point which represents the position of an atom or molecule in a crystal. Each lattice point in the crystal will have the same environment as the other lattice point. Space Lattice: The Geometrical representation of the crystal structure in terms of imaginary points in the space is called Space lattice. Basis or (Motif): The Basis is the atom or molecule which replaces the lattice point. To represent Crystal we associate every lattice point with identical atoms or molecules called Basis. Lattice Point + Basis = Crystal structure Unit Cell: The unit cell is the smallest geometrical figure, the repetition of which in three dimensions will give the actual crystal structure. Primitive Cell: The Primitive cell is an unit cell which contains lattice points at the corners only or The primitive cell is an unit cell which contains only one atom inside the unit . Non-Primitive Cell: Non primitive cell contains more than one lattice point or one atom inside the unit cell. Ex: Body centered Cubic (BCC), Face Centered cubic (FCC) and Base Centered Cubic (C).
PEC
Name of the Faculty: P.V.V.Satyanarayana
Lattice Parameters: The lines drawn parallel to the lines of intersection of any three faces of the unit cell which do not lie in the same plane are called crystallographic axes. A unit cell can be completely described by three fundamental vectors a, b and c called lattice vectors. The angle between b and c is , the angle between c and a is and the angle between a and b is . These angle , , and are called interfacial angles. The lattice vectors (a b, c) and inter facial angles (, , and ) are called Lattice parameters. This is shown in the figure.
Where a, b, and c are Primitives along X, Y, and Z axis and , , and are Interfacial angles subtended by bc, ca and ab respectively.
Bravais Lattice: If all the atoms at lattice points are identical the lattice is called as Bavais Lattice Crystal systems and Bravais Lattices in three Dimensional: Depending upon variations of Lattice Parameters i.e., (a, b, and c) & (, , and ) we can classify the crystal systems into Seven different ways. Further in 1848, on the base of possible Primitives and Non-Primitives Bravais showed that there are 14 different types of space lattices in three Dimensions.
For Hexagonal: Zinc (Zn), Cadmium (Cd), and Quartz (SiO2) For Trigonal: Calcite (CaCo3), Arsenic (As), Bismuth (Bi)
Gypsum (CaSO4. 2H2O)
Potassium Chromate (K2CrO7)
PEC
Name of the Faculty: P.V.V.Satyanarayana
Examples
NaCl, Ag, Au,Cu, Zinc Sulfide etc..
PEC
Name of the Faculty: P.V.V.Satyanarayana
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Crystal Structures - Unit IDokument16 SeitenCrystal Structures - Unit Isanjay sNoch keine Bewertungen
- Unit V Crystal PhysicsDokument7 SeitenUnit V Crystal Physicssmileofsun4656Noch keine Bewertungen
- Engg Physics R20 - Unit-5Dokument18 SeitenEngg Physics R20 - Unit-5manchikatlahimanshu.13Noch keine Bewertungen
- Bravaise Lattice Structure - PPTX 1Dokument77 SeitenBravaise Lattice Structure - PPTX 1cipet imphal100% (1)
- CP1Dokument10 SeitenCP1prabhumaluNoch keine Bewertungen
- EEM Part3Dokument76 SeitenEEM Part3MD MamnunNoch keine Bewertungen
- Notes, Unit 1Dokument42 SeitenNotes, Unit 1Srisailam ChintuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Crystal Structure PDFDokument19 SeitenCrystal Structure PDFJunior Paul BalenNoch keine Bewertungen
- C2710 Introduction To Solid State Chemistry 2023Dokument8 SeitenC2710 Introduction To Solid State Chemistry 2023sispulieNoch keine Bewertungen
- Crystal GeometryDokument17 SeitenCrystal GeometryNeel PatelNoch keine Bewertungen
- Section-A: Some Basic DefinitionsDokument81 SeitenSection-A: Some Basic DefinitionsappliedphyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Elements of X-Ray Diffraction 3rd Ed TQW - Darksiderg 42Dokument1 SeiteElements of X-Ray Diffraction 3rd Ed TQW - Darksiderg 42Nipunika JainNoch keine Bewertungen
- Unit IDokument133 SeitenUnit IShubhamNoch keine Bewertungen
- Crystal Lattices: 2.1 The LatticeDokument10 SeitenCrystal Lattices: 2.1 The LatticeBridget GwenNoch keine Bewertungen
- Crystal Structure - Delivery NotesDokument35 SeitenCrystal Structure - Delivery NotesAninda LahiriNoch keine Bewertungen
- Solid State Chemistry - IntroductionDokument27 SeitenSolid State Chemistry - Introductionmithunesh 07Noch keine Bewertungen
- 2.space, Lattice and BasisDokument4 Seiten2.space, Lattice and BasisAshutosh SinghNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 1 - Delivery NotesDokument30 SeitenChapter 1 - Delivery NotesSrushtiNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Structure of Crystalline SolidsDokument18 SeitenThe Structure of Crystalline SolidsAkshay BundhooNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lecture 2Dokument18 SeitenLecture 2sgab cANoch keine Bewertungen
- CrystallographyDokument39 SeitenCrystallographypoornachandhu022Noch keine Bewertungen
- Crystallography: Categories of Solids Based On The Solid PackDokument21 SeitenCrystallography: Categories of Solids Based On The Solid PackSomnath SahaNoch keine Bewertungen
- SSP Unit 1Dokument44 SeitenSSP Unit 1kavithavenkatesanNoch keine Bewertungen
- EMG 1204 Lecture 3Dokument15 SeitenEMG 1204 Lecture 3James musambakiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Unit Cell Vs Primitive Cell: Symmetry OperationsDokument48 SeitenUnit Cell Vs Primitive Cell: Symmetry OperationsMohammad Anas SaiyedNoch keine Bewertungen
- Physics Notes Unit 2 (Solid State)Dokument33 SeitenPhysics Notes Unit 2 (Solid State)ch215109152 B.Sc. ChemistryNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2 Crystal StructureDokument32 Seiten2 Crystal StructureHesh JayatissaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nearly Free ElectronDokument15 SeitenNearly Free ElectronJohnNoch keine Bewertungen
- Crystal Structure and CrystallographyDokument41 SeitenCrystal Structure and CrystallographyannapoornaavulaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Crystal StructuresDokument30 SeitenCrystal StructuresMilton Chandro SarkerNoch keine Bewertungen
- Crystal Structure Mod-4Dokument24 SeitenCrystal Structure Mod-4Syed ShaNoch keine Bewertungen
- "Crystal Physics": Submitted By:-Roll No.: - ClassDokument29 Seiten"Crystal Physics": Submitted By:-Roll No.: - Classsabitri beheraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lecture 3Dokument30 SeitenLecture 37pnqmtty84Noch keine Bewertungen
- Engineering Physics (PH22101) : ObjectivesDokument59 SeitenEngineering Physics (PH22101) : ObjectivesSK crushNoch keine Bewertungen
- Unit-I 2Dokument21 SeitenUnit-I 2Nivishna RNoch keine Bewertungen
- PhysicsDokument152 SeitenPhysicsRajani GadalaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 5208Dokument53 Seiten5208Aditya ParabNoch keine Bewertungen
- Unit Ii Crystal StructureDokument24 SeitenUnit Ii Crystal StructureHarshit KhuranaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Crystalline StructureDokument8 SeitenCrystalline StructureAdeolu AdelekeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Crystal StructureDokument7 SeitenCrystal StructureSREERAGHAV KNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lecture 1Dokument27 SeitenLecture 1sgab cANoch keine Bewertungen
- MaterialDokument2 SeitenMaterialAtif AhmadNoch keine Bewertungen
- Semi Conductor PhysicsDokument89 SeitenSemi Conductor Physicstrishandewanji2004Noch keine Bewertungen
- Unit I:Crystal StructureDokument51 SeitenUnit I:Crystal Structuresamurai7_77Noch keine Bewertungen
- ADARSH SOLID UploadedDokument49 SeitenADARSH SOLID Uploadedalamarif3546Noch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 2Dokument59 SeitenChapter 2Temesgen Zeleke100% (1)
- Imp 002Dokument7 SeitenImp 002rafey314Noch keine Bewertungen
- Crystal StructureDokument14 SeitenCrystal StructureMahesh Lohith K.S100% (4)
- Chapter - 1 Crystal PhysicsDokument136 SeitenChapter - 1 Crystal PhysicsAmeyNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Structure of Crystalline SolidsDokument40 SeitenThe Structure of Crystalline SolidsAsif AliNoch keine Bewertungen
- Unit III Crystal StructureDokument25 SeitenUnit III Crystal Structurejitendra kumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Struktur KristalDokument22 SeitenStruktur KristalReza AditiyaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Structure of MetalsDokument29 SeitenStructure of Metalsps4haris.ch3534Noch keine Bewertungen
- 3Dokument67 Seiten3Louise UmaliNoch keine Bewertungen
- Basic Concepts of Crystalline StructureDokument60 SeitenBasic Concepts of Crystalline StructureKhen Mehko Ojeda100% (1)
- Solid State ChemistryDokument6 SeitenSolid State ChemistryAravindan B BabuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Magnetic Effects of CurrentsDokument41 SeitenMagnetic Effects of CurrentsV V Satyanarayana PasupuletiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Innovation IN Civil and Structural EngineeringDokument10 SeitenInnovation IN Civil and Structural EngineeringV V Satyanarayana PasupuletiNoch keine Bewertungen
- two-Dimensional Arays in CDokument4 Seitentwo-Dimensional Arays in CV V Satyanarayana PasupuletiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Women AtrocityDokument4 SeitenWomen AtrocityV V Satyanarayana Pasupuleti100% (1)
- Fiber Optics: Basic Principle of Opticle Fibers or Principle of Total Internal ReflectionDokument10 SeitenFiber Optics: Basic Principle of Opticle Fibers or Principle of Total Internal ReflectionV V Satyanarayana PasupuletiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Introduction To GIMPDokument30 SeitenIntroduction To GIMPV V Satyanarayana PasupuletiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ban Plastic Bags: An Awful Load of RubbishDokument10 SeitenBan Plastic Bags: An Awful Load of RubbishV V Satyanarayana PasupuletiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Crystal Structures and X-Ray DiffractionDokument5 SeitenCrystal Structures and X-Ray DiffractionV V Satyanarayana PasupuletiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ultrasonics NDT TestingDokument68 SeitenUltrasonics NDT TestingV V Satyanarayana PasupuletiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Polymorphism NotesDokument6 SeitenPolymorphism NotesFrozen FlameNoch keine Bewertungen
- Exam 3-2022Dokument8 SeitenExam 3-2022Afif FikriNoch keine Bewertungen
- Advanced Materials - 2017 - Susner - Metal Thio and Selenophosphates As Multifunctional Van Der Waals Layered MaterialsDokument40 SeitenAdvanced Materials - 2017 - Susner - Metal Thio and Selenophosphates As Multifunctional Van Der Waals Layered MaterialsRC XNoch keine Bewertungen
- 12th Science HSC Chemistry NumericalsDokument23 Seiten12th Science HSC Chemistry NumericalsAliNoch keine Bewertungen
- Test Planner - Lakshya NEET 3.0 2024Dokument2 SeitenTest Planner - Lakshya NEET 3.0 2024pj9482Noch keine Bewertungen
- 半导体物理与器件第四版课后习题答案1Dokument6 Seiten半导体物理与器件第四版课后习题答案1David100% (1)
- Atomic and Ionic Arrangement-1Dokument7 SeitenAtomic and Ionic Arrangement-1Joseph MuhoroNoch keine Bewertungen
- Solution Manual For Physical Metallurgy Principles 4th Edition Reza Abbaschian Robert e Reed Hill 2Dokument28 SeitenSolution Manual For Physical Metallurgy Principles 4th Edition Reza Abbaschian Robert e Reed Hill 2accidie.fapan7923100% (46)
- Following Materials: (A) Csi, (B) Nio, (C) Ki, and (D) Nis. Justify Your SelectionsDokument12 SeitenFollowing Materials: (A) Csi, (B) Nio, (C) Ki, and (D) Nis. Justify Your SelectionsIngi Abdel Aziz SragNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Metrical Matrix in Teaching MineralogyDokument12 SeitenThe Metrical Matrix in Teaching Mineralogyindependent_mindNoch keine Bewertungen
- LammpsDokument21 SeitenLammpsFernandoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Crystal Structure - 複本Dokument75 SeitenCrystal Structure - 複本劉宇哲Noch keine Bewertungen
- John E. Greedan - Geometrically Frustrated Magnetic MaterialsDokument17 SeitenJohn E. Greedan - Geometrically Frustrated Magnetic MaterialsGravvol100% (1)
- Spring 07 - EE 221 Problem Set 1 SolutionDokument5 SeitenSpring 07 - EE 221 Problem Set 1 SolutionSaket KaushalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Diluted Magnetic SemiconductorsDokument37 SeitenDiluted Magnetic SemiconductorsEnzo Victorino Hernandez AgressottNoch keine Bewertungen
- SuperconductorDokument216 SeitenSuperconductorscribdkkkNoch keine Bewertungen
- CMS II-4: Band Theory, Band Structure, K-Point Sampling, and Density of StateDokument37 SeitenCMS II-4: Band Theory, Band Structure, K-Point Sampling, and Density of StateManjeet BhatiaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 4.1 Bonding and Structure (Answers)Dokument10 Seiten4.1 Bonding and Structure (Answers)Deeyana DeenNoch keine Bewertungen
- Solid State TutorialDokument12 SeitenSolid State TutorialMohamed WaelNoch keine Bewertungen
- ATOICV1 6 0 Crystal StructuresDokument34 SeitenATOICV1 6 0 Crystal Structures20tamilselvi-ugcheNoch keine Bewertungen
- Atomic Packing Factor and Theor Density PDFDokument14 SeitenAtomic Packing Factor and Theor Density PDFanirudh zodeNoch keine Bewertungen
- 10688919Dokument30 Seiten10688919Anuj SoniNoch keine Bewertungen
- Structure Factors & Fourier TransformsDokument32 SeitenStructure Factors & Fourier TransformsAsrafulNoch keine Bewertungen
- University of Dhaka Department of Theoretical Physics Four Year BS CoursesDokument31 SeitenUniversity of Dhaka Department of Theoretical Physics Four Year BS CoursesJanus MalikNoch keine Bewertungen
- Engineering Geology Unit - IIDokument73 SeitenEngineering Geology Unit - IIsivabharathamurthyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Unit-1 Solids: Questions Carrying One MarkDokument159 SeitenUnit-1 Solids: Questions Carrying One MarkGahan Gowda SNoch keine Bewertungen
- Oym Test Planner - Phase 02Dokument5 SeitenOym Test Planner - Phase 02ManishNoch keine Bewertungen
- Solid State Physics: Unit IVDokument20 SeitenSolid State Physics: Unit IVReddyvari VenugopalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Phase Transformations and Heat Treatments of SteelDokument34 SeitenPhase Transformations and Heat Treatments of Steeljayson marquezNoch keine Bewertungen
- MSE203 Structure and Characterization of Materials: L-2 10-1-17, TuesdayDokument32 SeitenMSE203 Structure and Characterization of Materials: L-2 10-1-17, Tuesdaymohit kumarNoch keine Bewertungen