Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Chapter 4 Outline
Hochgeladen von
api-241411885Originaltitel
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Chapter 4 Outline
Hochgeladen von
api-241411885Copyright:
Verfügbare Formate
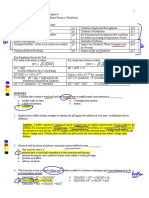
Chapter 4 Outline Reactions in Aqueous solutions I. 4.1 General Properties of Aqueous solutions A.
Solution- a homogenous mixture of two or more substances 1. Solute- the substance present in a smaller amount 2. Solvent- the substance present is a larger amount B. Aqueous solution1. The solute initially is a liquid or solid 2. the solvent is water C. Electrolytic properties (solutes that dissolve in water categories) 1. Electrolyte- a substance that, when dissolved in water, results in a solution that ca conduct electricity 2. Nonelectrolyte- does not conduct electricity when dissolved in water 3. Electrolytes a. Strong electrolytes- ionic compounds (metal bonded to a nonmetal) b. Weak electrolytes- Has a hydrogen in front (CH3OOH, HF, H2O, ect) c. Non electrolyte- No Hydrogen in front, or OH at the end (base) 4. Hydration- an ion is surrounded by water molecules arranged in a specific manner
II.
Precipitation reactions A. Precipitation Reaction- formation of an insoluble product (precipitate) B. Metathesis reaction reaction that involves the exchange in parts between parts in two compounds C. Solubility maximum amount of solute that will dissolve in a given quantity of solvent at a specific temperature 1. CASH N G1A C is chlorates A is acetates S is sulfates (except: Ca, Ba, Sr.....just remember the tv network CBS) H is halogens( except: Ca, Ba, Sr (CBS) Hg Ag Pb (HAPPY) ) N is Nitrates, G1a is Group I A metals. ---> THESE ARE ALL SOLUBLE, XCEPT
2. CCOPS Carbonates Chromates OH Ba(OH)2 Phosphates Sulfides D. Molecular Equations, Ionic Equations, Net Ionic Equations Molecular Equation- formulas of the compounds are written as tough the species existed as molecules or whole units. identifies reagents (Lead(ii) sulfide) KNO3(aq) + HCl(aq) KCl(aq) + HNO3(aq)
III.
Acid- Base Reactions A. Acids 1. Sour taste (vinegar acetic acid, lemons, citrus fruits with citric acid) 2. Color changes in plant dyes- litmus from blue to red 3. Acids react with certain metals-- zinc, magnesium, &iron-- to produce hydrogen gas 4. Acids react with carbonates and bicarbonates-- such as Na2CO3, CaCO3, and NaNCO3--to produce carbon dioxide gas 5. Aqueous(aq) acid solutions conduct electricity B. Bases 1. Bitter taste 2. Slippery feeling(soap contains bases) 3. Litmus paper changes from red to blue
4. Aqueous(aq) base solutions conduct electricity
C. Bronsted acids and bases 1. Bronsted acid- proton donor (H+) 2. Bronsted base- Proton acceptor (OH)
3. Diprotic Acid- each unit gives up 2 H= protons 4. Triprotic Acids- yields 3 H+ ions
5. Acid Base reaction (neutralization) Acid + Base salt +water
IV.
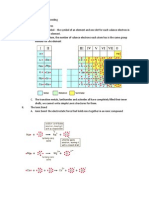
Oxidation Reduction Reactions A. oxidation-reduction, or redox, reactions are considered electron transfer reactions (ex. fossil fuels & bleach)
B. Oxidation number 1. Also known as oxidation state 2. # of charges the atoms wound have in an ionic compound or molecule if electrons were transferred completely
C. Types of Redox Reactions 1. Combination Reaction
2. Decomposition Reaction
3. Combustion Reaction (reacts with oxygen)
4. Displacement Reactions a. Hydrogen displacement
b. Metal displacement (above) c. Halogen displacement 5. Disproportionation Reaction- an element in one oxidation state is simultaneously oxidized and reduced
V.
Concentration of solutions A. Concentration of Solution- the amount of solute present in a given amount of solvent, or solution B. Molarity
C. Dilution the procedure for preparing a less concentrated solution from a more concentrated one
VI.
VII.
D. Quantitative analysis determination of the amount or concentration of a substance in a sample. E. Gravimetric analysis an analytical technique based on the measurement of mass Acid-Base Titrations A. Titration- a solution of an accurately know concentration B. Standard solution- added gradually to another solution of an unknown concentration , until the chemical reaction between the two is complete C. Equivalence point- the point at which an acid has completely with or has been neutralized by a base D. Indicators- substances that have different colors in acidic or basic media Redox titrations
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryVon EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (231)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Von EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Bewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (119)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItVon EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (838)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaVon EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (265)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingVon EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (399)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceVon EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (587)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyVon EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (2219)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeVon EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (5794)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnVon EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (234)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeVon EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (537)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerVon EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (271)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreVon EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (1090)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesVon EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (821)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersVon EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (344)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceVon EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (890)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureVon EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (474)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaVon EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (45)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Von EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Bewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (98)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealVon EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (73)
- Hydraulic FluidsDokument20 SeitenHydraulic FluidsRamirez Indeleble100% (1)
- HuckelDokument167 SeitenHuckelShivansh BhatnagarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Test3 Ch17b Buffer Titration Equilibrium Practice Problems Answers Full 2015Dokument18 SeitenTest3 Ch17b Buffer Titration Equilibrium Practice Problems Answers Full 2015Anas SaadNoch keine Bewertungen
- VII - Chemistry KAT Worksheet - I PDFDokument3 SeitenVII - Chemistry KAT Worksheet - I PDFSahithi100% (2)
- Advanced Materials and StructuresDokument244 SeitenAdvanced Materials and StructuresCarlos LlanoNoch keine Bewertungen
- A Chapter 7 NotesDokument10 SeitenA Chapter 7 Notesapi-241411885Noch keine Bewertungen
- Synopses of HowDokument2 SeitenSynopses of Howapi-241411885Noch keine Bewertungen
- A Chemistry 1305 Chapter 9Dokument7 SeitenA Chemistry 1305 Chapter 9api-241411885Noch keine Bewertungen
- Chem Chapter 3 NotesDokument5 SeitenChem Chapter 3 Notesapi-241411885Noch keine Bewertungen
- Eliminate 7 Billion Tons of Co2 ADokument3 SeitenEliminate 7 Billion Tons of Co2 Aapi-241411885Noch keine Bewertungen
- Aaathe Chapter 5 Outline 1Dokument6 SeitenAaathe Chapter 5 Outline 1api-241411885Noch keine Bewertungen
- Energy of FormationDokument2 SeitenEnergy of Formationapi-241411885Noch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 6 Thermochemistry OutlineDokument7 SeitenChapter 6 Thermochemistry Outlineapi-241411885Noch keine Bewertungen
- During The 19th Century Industrial Revolutions Took Place Throughout The WorldDokument2 SeitenDuring The 19th Century Industrial Revolutions Took Place Throughout The Worldapi-241411885Noch keine Bewertungen
- An Inconvenient Truth SynopsisDokument2 SeitenAn Inconvenient Truth Synopsisapi-241411885Noch keine Bewertungen
- NRDC Global Warming SolutionsDokument2 SeitenNRDC Global Warming Solutionsapi-241411885Noch keine Bewertungen
- American Food Production ReportDokument13 SeitenAmerican Food Production Reportapi-241411885Noch keine Bewertungen
- BrochureDokument2 SeitenBrochureapi-241411885Noch keine Bewertungen
- The Dangers of Processed Food - 1-1Dokument3 SeitenThe Dangers of Processed Food - 1-1api-241411885Noch keine Bewertungen
- Lab Report-11: Environmental Chemistry (ENE-213) Course Instructor: Dr. Sofia BaigDokument7 SeitenLab Report-11: Environmental Chemistry (ENE-213) Course Instructor: Dr. Sofia BaigHaniya SiddiqueNoch keine Bewertungen
- Me 598 - Lecture 1 - Overview of Materials Characterization Techniques.20110215.4d5ad7e0f3d0e6.28002081Dokument57 SeitenMe 598 - Lecture 1 - Overview of Materials Characterization Techniques.20110215.4d5ad7e0f3d0e6.28002081Saad SalmanNoch keine Bewertungen
- PT PresentationDokument18 SeitenPT Presentationahmed titoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Enhanced Efficiency and Stability of N-I-P Perovskite Solar Cells by Incorporation of Fluorinated Graphene in The Spiro-OMeTAD Hole Transport LayerDokument11 SeitenEnhanced Efficiency and Stability of N-I-P Perovskite Solar Cells by Incorporation of Fluorinated Graphene in The Spiro-OMeTAD Hole Transport Layer北科大-洪珮倫Noch keine Bewertungen
- En Tds A-80Dokument3 SeitenEn Tds A-80cnotebookNoch keine Bewertungen
- RuO2 AltermagnetsmDokument27 SeitenRuO2 AltermagnetsmAybüke GülkayaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lecture 7Dokument5 SeitenLecture 7Abhijeet BhagavatulaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Effect of Temperature To The Speed of SoundDokument26 SeitenEffect of Temperature To The Speed of SoundCecilia Sarita100% (1)
- Compost 1Dokument20 SeitenCompost 1YassertahlawyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Materials Science & Engineering B: SciencedirectDokument10 SeitenMaterials Science & Engineering B: SciencedirectMuhammad BramansyahNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pipe Terms With AnswerDokument23 SeitenPipe Terms With AnswerTIKTOK COMPILATIONNoch keine Bewertungen
- Calculus of Variation 1Dokument56 SeitenCalculus of Variation 1Enny MurwaningtyasNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Crystal and Molecular Structure of Naphthalene. I. X-Ray MeasurementsDokument6 SeitenThe Crystal and Molecular Structure of Naphthalene. I. X-Ray MeasurementsRudolf KiraljNoch keine Bewertungen
- Preformulation MaterialDokument10 SeitenPreformulation MaterialRajesh NayakNoch keine Bewertungen
- Spe 115 G PDFDokument14 SeitenSpe 115 G PDFJuan SantosNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chemistry RevisionDokument3 SeitenChemistry RevisionIram GulfarazNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 18. Entropy, Free Energy, and EquilibriumDokument41 SeitenChapter 18. Entropy, Free Energy, and EquilibriumEUNAH LimNoch keine Bewertungen
- Week 3Dokument7 SeitenWeek 3shmyeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chemistry Criterion B and C Lab ReportDokument7 SeitenChemistry Criterion B and C Lab ReportBRIGHTON ONYANGONoch keine Bewertungen
- Graphene Oxide and Its Application As An Adsorbent For Wastewater Treatment PDFDokument33 SeitenGraphene Oxide and Its Application As An Adsorbent For Wastewater Treatment PDFThanh Nguyen100% (1)
- Chemistry 206 Advanced Organic Chemistry: Olefin Addition Reactions: Part-2Dokument17 SeitenChemistry 206 Advanced Organic Chemistry: Olefin Addition Reactions: Part-2eraborNoch keine Bewertungen
- Student Exploration: Periodic TrendsDokument9 SeitenStudent Exploration: Periodic TrendsAnger50% (2)
- ConductivitySensor BrochureDokument4 SeitenConductivitySensor BrochureJames TakeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Differential Thermal Analysis & Differential Scanning CalorimetryDokument51 SeitenDifferential Thermal Analysis & Differential Scanning CalorimetryBesma Hamdi100% (1)
- J Eurpolymj 2020 109485Dokument63 SeitenJ Eurpolymj 2020 109485MZeeshanAkramNoch keine Bewertungen