Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
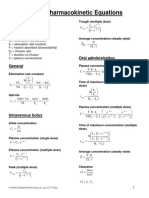
Pharmacokinetic Equations
Hochgeladen von
Nana BonsuCopyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Pharmacokinetic Equations
Hochgeladen von
Nana BonsuCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Equations/Useful_pharmacokinetic_equ_5127 1
Useful Pharmacokinetic Equations
Symbols
D =dose
t =dosing interval
CL =clearance
Vd =volume of distribution
k
e
=elimination rate constant
k
a
=absorption rate constant
F =fraction absorbed (bioavailability)
K
0
=infusion rate
T =duration of infusion
C =plasma concentration
General
Elimination rate constant
( ) ( )
k
CL
Vd
C
C
t t
C C
t t
e
= =
|
\
|
.
|
ln
ln ln
1
2
2 1
1 2
2 1
Half-life
t
Vd
CL k k
e e
1 2
0693 2 0693
/
. ln( ) .
=
= =
Intravenous bolus
Initial concentration
C
D
Vd
0
=
Plasma concentration (single dose)
C C e
k t
e
=
0
Plasma concentration (multiple dose)
( )
C
C e
e
k t
k
e
e
=
0
1
t
Peak (multiple dose)
( )
C
C
e
k
e
max
=
0
1
t
Trough (multiple dose)
( )
C
C e
e
k
k
e
e
min
=
0
1
t
t
Average concentration (steady state)
Cp
D
CL
ss
=
t
Oral administration
Plasma concentration (single dose)
( )
( )
C
F D k
Vd k k
e e
a
a e
k t k t
e a
=
Time of maximum concentration (single
dose)
( )
t
k
k
k k
a
e
a e
max
ln
=
|
\
|
.
|
Plasma concentration (multiple dose)
( )
( ) ( )
C
F D k
Vd k k
e
e
e
e
a
a e
k t
k
k t
k
e
e
a
a
=
|
\
|
.
|
|
1 1
t t
Time of maximum concentration (multiple
dose)
( )
( )
( )
t
k e
k e
k k
a
k
e
k
a e
e
a
max
ln
=
|
\
|
.
|
|
1
1
t
t
Average concentration (steady state)
C
F D
CL
=
t
Clearance
AUC
F Dose
Cl
=
d e
V k Cl =
Equations/Useful_pharmacokinetic_equ_5127 2
Constant rate infusion
Plasma concentration (during infusion)
( )
C
k
CL
e
k t
e
=
0
1
Plasma concentration (steady state)
C
k
CL
=
0
Calculated clearance (Chiou equation)
( )
( )
( ) ( )
CL
k
C C
Vd C C
C C t t
=
+
+
+
2 2
0
1 2
1 2
1 2 2 1
Short-term infusion
Peak (single dose)
( )
C
D
CL T
e
k T
e
max( ) 1
1 =
Trough (single dose)
( )
C C e
k T
e
min( ) max( ) 1 1
=
t
Peak (multiple dose)
( )
( )
C
D
CL T
e
e
k T
k
e
e
max
=
1
1
t
Trough (multiple dose)
( )
C C e
k T
e
min max
=
t
Calculated elimination rate constant
k
C
C
t
e
=
|
\
|
.
|
-
-
ln
max
min
A
with C
max
*
=measured peak and C
min
*
=
measured trough,
measured over the time interval At
Calculated peak
C
C
e
k t
e
max
max
=
-
-
with C
max
*
=measured peak, measured at time
t
*
after the end of the infusion
Calculated trough
C C e
k t
e
min min
=
-
-
with C
min
*
=measured trough, measured at
time t
*
before the start of the next infusion
Calculated volume of distribution
( )
)] ( [
1
min max
T
e
k
T
e
k
e e C C
e
T k
D
Vd
=
Calculated recommended dosing interval
t =
|
\
|
.
|
+
ln
max( )
min( )
C
C
k
T
desired
desired
e
Calculated recommended dose
( )
( )
D C k V T
e
e
desired e
k
k T
e
e
=
max( )
1
1
t
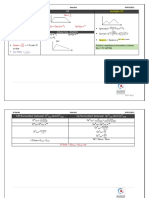
Two-Compartment-Body Model
C a e b e
t t
= - + -
o |
AUC a b
= + / / o |
Vd Vd Vc
area ss
> >
Creatinine Clearance
CL male
age weight
Cp
creat
creat
( )
( )
=
-
-
140
72
CL female
age weight
Cp
creat
creat
( )
( )
=
-
-
140
85
With weight in kg, age in years, creatinine plasma conc.
in mg/dl and CL
creat
in ml/min
Equations/Useful_pharmacokinetic_equ_5127 3
K
e
for aminoglycosides
K
e
=0.00293(CrCL) +0.014
Metabolic and Renal Clearance
E
H
=
Cl fu
Q Cl fu
b
H b
int
int
+
Cl
H
= E Q
H H
=
Q Cl fu
Q Cl fu
H b
H b
+
int
int
F
H
=
b H
H
fu Cl Q
Q
+
int
Cl
ren
= RBFE =
in
out in
C
C C
GFR
Cl
ren
=
ion concentrat plasma
excretion of rate
Cl
ren
=
(
+
ion concentrat Plasma
on reabsorpti of Rate - secretion of Rate
GFR fu
Cl
ren
=
ion concentrat Plasma
ion concentrat urine flow Urine
Ideal Body Weight
Male
IBW =50 kg +2.3 kg for each inch over 5ft in
height
Female
IBW =45.5 kg +2.3 kg for each inch over 5ft in
height
Obese
ABW =IBW +0.4*(TBW-IBW)
Volume of Distribution
P T P
K V V V + =
T
T P
fu
fu
V V V + =
Clearance
AUC
Dose
Cl =
d e
V k Cl =
Last modified 2010
C:\Current Data\pha5127_Dose_Opt_I\equations\5127-28-equations.doc
For One Compartment Body Model
If the dosing
involves the use
of I.V. bolus
administration:
For a single I.V. bolus administration:
V
D
C =
0
t k
e
e C C
=
0
For multiple I.V. bolus administration:
( )
( )
t k
k
nk
e
e
e
e
e
e
V
D
t Cn
=
t
t
1
1
) (
at peak: t =0; at steady state n
at trough: t =t
) e (
V
D
C
e
k
ss
t
=
1
1
max
t
e
k
ss ss
e C C
=
max min
If the dosing
involves the use
of I.V. infusion:
For a single short-term I.V. infusion:
Since t =t for C
max
( )
T k
e
e
e
T Vk
D
C
= 1
max
) (
max min
T k
e
e C C
=
t
For multiple short-term I.V. infusion at steady state:
( )
( )
t
e
e
k
T k
e e
e
T Vk
D
C
=
1
1
max
) (
max min
T k
e
e C C
=
t
Last modified 2010
C:\Current Data\pha5127_Dose_Opt_I\equations\5127-28-equations.doc
If the dosing
involves a I.V.
infusion (more
equations):
( )
t k T k
e
t
e e
e e
T Vk
D
C
= 1 (most general eq.) during infusion t =T so,
( )
t k
e
t
e
e
T Vk
D
C
= 1 (during infusion) at steady state t , e
-k
e
t
,
t 0 so,
CL
k
Vk
k
T Vk
D
Cpss
e e
0 0
= = = (steady state) remembering
T
D
k =
0
and
e
k V CL =
If the dosing
involves oral
administration:
For a single oral dose:
( )
( )
t k t k
e a
a
a e
e e
k k V
k D F
C
=
( )
e a e
a
k k k
k
t
=
1
ln
max
For multiple oral doses:
( )
( ) (
t
a
a
e
e
k
t k
k
t k
e a
a
e
e
e
e
k k V
k D F
C
1 1
( )
( )
( )
e a
k
e
k
a
k k
e k
e k
t
a
e
(
(
1
1
1
ln
max
t
t
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Pharmacokinetic ConceptsDokument28 SeitenPharmacokinetic ConceptsAmy Yuen100% (1)
- ONE Compartment Open ModelDokument29 SeitenONE Compartment Open ModelNOORUDDINNoch keine Bewertungen
- FA 2016 Step 1 - Reference ValuesDokument2 SeitenFA 2016 Step 1 - Reference ValuesJUSASBNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pharmacotherapy For SchizophreniaDokument17 SeitenPharmacotherapy For SchizophreniaNadya SaptarinaNoch keine Bewertungen
- BASIC PHARMACOKINETICS - CHAPTER 11: Multicompartment ModelDokument65 SeitenBASIC PHARMACOKINETICS - CHAPTER 11: Multicompartment ModelDrHeba100% (1)
- Intravenous Infusion 1Dokument20 SeitenIntravenous Infusion 1كسلان اكتب اسمي100% (1)
- Applied Pharmacokinetics Exercises DraftDokument18 SeitenApplied Pharmacokinetics Exercises DraftMINANI TheobaldNoch keine Bewertungen
- Practice ProblemsDokument2 SeitenPractice ProblemsShemaj GurchumaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cal Pharmaspirit PH Cal Q ADokument49 SeitenCal Pharmaspirit PH Cal Q AAriadne BalmacedaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Clinical PharmacokineticsDokument36 SeitenClinical PharmacokineticsWalaa YousefNoch keine Bewertungen
- Clin PK 1-4Dokument105 SeitenClin PK 1-4Klye SahagunNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1: Clinical PharmacokineticsDokument18 Seiten1: Clinical PharmacokineticsJalal AlbadriNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1important DefinitionsDokument3 Seiten1important DefinitionsBest VideoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pharmacotherapy of UTI and STDDokument36 SeitenPharmacotherapy of UTI and STDDr.U.P.Rathnakar.MD.DIH.PGDHMNoch keine Bewertungen
- S02 Dispensing CalculationDokument15 SeitenS02 Dispensing CalculationJoe BlackNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mechanism of Drug ActionDokument41 SeitenMechanism of Drug ActionEryanda Dinata100% (1)
- Pharmacology: Pharmacokinetic & Dose: Ana Khusnul Faizah Farmasi FK Uht 2018Dokument27 SeitenPharmacology: Pharmacokinetic & Dose: Ana Khusnul Faizah Farmasi FK Uht 2018Aulia rahmawatiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Introduction To Biopharmaceutics and PharmacokineticsDokument40 SeitenIntroduction To Biopharmaceutics and PharmacokineticsSyeda Eshaal JavaidNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pharmacokinetic Calculations - FormulasDokument1 SeitePharmacokinetic Calculations - FormulasVijendra RNoch keine Bewertungen
- Clinical PharmacokineticsDokument31 SeitenClinical PharmacokineticsArdiyanti Puspitasari100% (1)
- Non Linear PharmacokineticsDokument64 SeitenNon Linear PharmacokineticsMoganaa LakshmiNoch keine Bewertungen
- PHARM CARE PD SLE NewDokument58 SeitenPHARM CARE PD SLE NewbrevmanaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 07 Dosage RegimenDokument44 Seiten07 Dosage Regimenzetttttttttt100% (3)
- 08 Noncompartmental ModelsDokument17 Seiten08 Noncompartmental ModelsNishNoch keine Bewertungen
- Final Answer of PharmacologyDokument45 SeitenFinal Answer of Pharmacologynidhhu100% (1)
- 4-Pharmacokinetics IDokument88 Seiten4-Pharmacokinetics IMarc Imhotep Cray, M.D.Noch keine Bewertungen
- Pharmacy Study PlanDokument158 SeitenPharmacy Study PlanaleksandraNoch keine Bewertungen
- 124Dokument20 Seiten124chem_dream00Noch keine Bewertungen
- Application of PK in Clinical SitutionDokument42 SeitenApplication of PK in Clinical Situtionsafia mehmood100% (1)
- Prof Henny Lucida PHD Apt Calculation of DosespptDokument27 SeitenProf Henny Lucida PHD Apt Calculation of DosespptWella CitraersyaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Oxytocin BioassayDokument17 SeitenOxytocin BioassayPhArMaCyGrAdUaTeS100% (4)
- APHA-Chapter-34 - Patient Assessment Laboratory: REVIEW OF SYSTEMS - Physical Assessment, Vital Signs& ObservationsDokument13 SeitenAPHA-Chapter-34 - Patient Assessment Laboratory: REVIEW OF SYSTEMS - Physical Assessment, Vital Signs& ObservationsDrSamia El WakilNoch keine Bewertungen
- Clinical PharmacokineticsDokument36 SeitenClinical PharmacokineticsDr.U.P.Rathnakar.MD.DIH.PGDHM80% (5)
- Vancomycin ReviewDokument26 SeitenVancomycin Reviewkhangsiean89Noch keine Bewertungen
- Pedia Stickers PDFDokument8 SeitenPedia Stickers PDFAshNoch keine Bewertungen
- IV PO Conversion CAPDokument3 SeitenIV PO Conversion CAPdamondouglasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Principles of PharmacotherapyDokument40 SeitenPrinciples of Pharmacotherapyjunitria13Noch keine Bewertungen
- PK-PD of Antimicrobial Therapy-Lecture12 Oct11Dokument37 SeitenPK-PD of Antimicrobial Therapy-Lecture12 Oct11Idrissou FmsbNoch keine Bewertungen
- نم هدمتعم و هعجارم اهنل اهب قوثوم لخادلاب تامولعملا Certified fromDokument20 Seitenنم هدمتعم و هعجارم اهنل اهب قوثوم لخادلاب تامولعملا Certified fromMedhat EyadaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pharmacokinetic Exercises ListDokument5 SeitenPharmacokinetic Exercises ListVijendra R100% (1)
- Applied Biopharmacy Exercises by MteDokument19 SeitenApplied Biopharmacy Exercises by MteMINANI TheobaldNoch keine Bewertungen
- Basic Pharmacokinetic CalculationsDokument7 SeitenBasic Pharmacokinetic CalculationsShoaib Biradar100% (1)
- Introduction To BiopharmaceuticsDokument34 SeitenIntroduction To BiopharmaceuticsMd. Yasir Galib 1721609649100% (1)
- Kinetics Review 2Dokument37 SeitenKinetics Review 2filenotfoundNoch keine Bewertungen
- OSCE (Objective Structured Clinical Examination)Dokument2 SeitenOSCE (Objective Structured Clinical Examination)balamuruganNoch keine Bewertungen
- To Study The Effect of Various Tranquilizers and Sedatives On Motor Co-Ordination by Rotarod Test in Mice PDFDokument2 SeitenTo Study The Effect of Various Tranquilizers and Sedatives On Motor Co-Ordination by Rotarod Test in Mice PDFSuman DahalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Abdullah M. Kharbosh, B.SC., PharmDokument27 SeitenAbdullah M. Kharbosh, B.SC., PharmsrirampharmaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pharmacokinetics - Exam 3 SPR 2012 Answer KeyDokument6 SeitenPharmacokinetics - Exam 3 SPR 2012 Answer KeyCharlie BravoNoch keine Bewertungen
- UntitledDokument10 SeitenUntitledOmar EldemiriNoch keine Bewertungen
- Kuliah MKDU-3Dokument121 SeitenKuliah MKDU-3SuryaAtmajayaNoch keine Bewertungen
- TDM EquationsDokument4 SeitenTDM EquationsMohammed AbdulrahmanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Methods of Determining Absorption Rate ConstantDokument42 SeitenMethods of Determining Absorption Rate ConstantFilip Ilievski50% (2)
- Pharmacokinetics L6Dokument89 SeitenPharmacokinetics L6Indira ButkoonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Daftar Rumus Farmakokinetika Klinik-TDMDokument1 SeiteDaftar Rumus Farmakokinetika Klinik-TDMFatiha CitraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Useful Pharmacokinetic Equations: SymbolsDokument3 SeitenUseful Pharmacokinetic Equations: SymbolsAngga SantosoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Multi - Dimensional Problems: NPTEL IIT Kharagpur: Prof. K.P. Sinhamahapatra, Dept. of Aerospace EngineeringDokument5 SeitenMulti - Dimensional Problems: NPTEL IIT Kharagpur: Prof. K.P. Sinhamahapatra, Dept. of Aerospace EngineeringArun YogaNoch keine Bewertungen
- PHA 5128 First Exam Spring 2009Dokument16 SeitenPHA 5128 First Exam Spring 2009Ali JavedNoch keine Bewertungen
- Practical CL PK 2023 Part OneDokument14 SeitenPractical CL PK 2023 Part OneAdel MohamedNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ans VancomycinDokument10 SeitenAns VancomycinPratiwi Asih AyuNoch keine Bewertungen
- PkineticsDokument8 SeitenPkineticsmlbranham2753Noch keine Bewertungen
- Dispelling Myths About Drinking Distilled WaterDokument6 SeitenDispelling Myths About Drinking Distilled WaterPau StraitNoch keine Bewertungen
- Practice Guidelines For Telemental HealthDokument51 SeitenPractice Guidelines For Telemental HealthNataanatiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Surgery TCVS SGD Guide KKDokument7 SeitenSurgery TCVS SGD Guide KKFu Xiao ShanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Surgical SkillsDokument47 SeitenSurgical SkillsSamah SuhailNoch keine Bewertungen
- Emphasis On Non-Pharmacologic Aspect: Key Principles: o Gate Control & Neuromatrix Theory of PainDokument3 SeitenEmphasis On Non-Pharmacologic Aspect: Key Principles: o Gate Control & Neuromatrix Theory of PainJudy Ignacio EclarinoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pharmaceutics IntroductionDokument9 SeitenPharmaceutics IntroductionVIJAY KUMAR TIRUKKACHINoch keine Bewertungen
- Therapeutic CommanalitiesDokument8 SeitenTherapeutic CommanalitiesRoshni TripathyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Life History of Dr.J.T. KentDokument13 SeitenLife History of Dr.J.T. KentPrathibha MadikiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Metabolic Encephalopathies and Delirium: Panayiotis N. Varelas, MD, PHDDokument34 SeitenMetabolic Encephalopathies and Delirium: Panayiotis N. Varelas, MD, PHDjorge_suoNoch keine Bewertungen
- X PROCEDURAL SKILLS AND OTHERSDokument9 SeitenX PROCEDURAL SKILLS AND OTHERSWilson Ong Ying FaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Vicky Sawyer: Misusing and Abusing 'Science' in The Cause of Transgenderism and HomosexualityDokument4 SeitenVicky Sawyer: Misusing and Abusing 'Science' in The Cause of Transgenderism and HomosexualityRogerWilliamsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Stress Burnout - Georgeann RoudebushDokument45 SeitenStress Burnout - Georgeann RoudebushVinnyYusrainiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Prevention of Hypotension After Spinal Anaesthesia For Caesarean SectionDokument13 SeitenPrevention of Hypotension After Spinal Anaesthesia For Caesarean SectionANGELICANoch keine Bewertungen
- Methods Used in EpidemologyDokument53 SeitenMethods Used in EpidemologySameera banuNoch keine Bewertungen
- EXSA - Gold Award Recipients 2009Dokument1 SeiteEXSA - Gold Award Recipients 2009applebarrelNoch keine Bewertungen
- Evidence Based PracticeDokument28 SeitenEvidence Based Practiceraghad awwadNoch keine Bewertungen
- Medical Terminology Medical PrefixesDokument5 SeitenMedical Terminology Medical PrefixesRicky Rhenzs Gultia Villafuerte100% (6)
- PIN1287 Lumbar Sympathetic BlockDokument3 SeitenPIN1287 Lumbar Sympathetic BlockBob AdleNoch keine Bewertungen
- Challenges in Care of Adult CF Patients - The Specialist Cystic Fibrosis TeamDokument4 SeitenChallenges in Care of Adult CF Patients - The Specialist Cystic Fibrosis TeamjuniorebindaNoch keine Bewertungen
- A Nursing Case Study On: Alzheimer's DiseaseDokument22 SeitenA Nursing Case Study On: Alzheimer's DiseaseJesslee Llanes100% (4)
- OmphaloceleDokument3 SeitenOmphaloceleAnonymous uI8yHXobYNoch keine Bewertungen
- 27Dokument2 Seiten27Helen UgochukwuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Buku BacaanDokument329 SeitenBuku BacaanNurhasni FebrianiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Case Study Intestinal ObstructionDokument36 SeitenCase Study Intestinal ObstructionMamta Parmar100% (1)
- 50 Nursing Mnemonics and Acronyms You Need To Know NowDokument29 Seiten50 Nursing Mnemonics and Acronyms You Need To Know Nowtandz100% (19)
- Abscess Incision and Drainage NEJMDokument4 SeitenAbscess Incision and Drainage NEJMMarcela CharryNoch keine Bewertungen
- Antenatal Diet PlanDokument7 SeitenAntenatal Diet PlanSunija Selvam100% (3)
- Hypertension CASE STUDYDokument30 SeitenHypertension CASE STUDYKaloy Kamao100% (7)
- Student Nurses' Community: Nursing Care Plan PneumoniaDokument2 SeitenStudent Nurses' Community: Nursing Care Plan PneumoniaJhasmine MocnanganNoch keine Bewertungen
- Recent Patents On Biotechnology 2009, 3, 166-174Dokument10 SeitenRecent Patents On Biotechnology 2009, 3, 166-174TehMarianNoch keine Bewertungen