Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Dynamics Syllabus
Hochgeladen von
Vanu VamalaiCopyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Dynamics Syllabus
Hochgeladen von
Vanu VamalaiCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
1.
THEORY OF VIBRATIONS 9 Concept of inertia and damping Types of Damping Difference between static forces and dynamic excitation Degrees of freedom SDOF idealisation Equations of motion of SDOF system for mass as well as base excitation Free vibration of SDOF system Response to harmonic excitation Impulse and response to unit impulse Duhamel integral 2. MULTIPLE DEGREE OF FREEDOM SYSTEM 9 Two degree of freedom system Normal modes of vibration Natural frequencies - Mode shapes Introduction to MDOF systems Decoupling of equations of motion Concept of mode superposition (No derivations). 3. ELEMENTS OF SEISMOLOGY 9 Causes of Earthquake Geological faults Tectonic plate theory Elastic rebound Epicentre Hypocentre Primary, shear and Raleigh waves Seismogram Magnitude and intensity of earthquakes Magnitude and Intensity scales Spectral Acceleration - Information on some disastrous earthquakes 4. RESPONSE OF STRUCTURES TO EARTHQUAKE 9 Response and design spectra Design earthquake concept of peak acceleration Site specific response spectrum Effect of soil properties and damping Liquefaction of soils Importance of ductility Methods of introducing ductility into RC structures. 5. DESIGN METHODOLOGY 9 IS 1893, IS 13920 and IS 4326 Codal provisions Design as per the codes Base isolation techniques Vibration control measures Important points in mitigating effects of earthquake on structures. TOTAL : 45 TEXT BOOKS 1. Arya, A.S., ed., Earthquake Engineering, Jai Krishna 60th Birthday Anniversary Commemoration Volume, ISET, Sarita Prakashan, Meerut, 1974. 2. Chopra, A.K., Dynamics of Structures Theory and Applications to Earthquake Engineering, Second Edition, Pearson Education, 2003.
REFERENCES 1. Biggs, J.M., Introduction to Structural Dynamics, McGrawHill Book Co., N.Y., 1964 2. Dowrick, D.J., Earthquake Resistant Design, John Wiley & Sons, London, 1977 3. Paz, M., Structural Dynamics Theory & Computation, CSB Publishers & Distributors, Shahdara, Delhi, 1985 4. NPEEE Publications - See more at: http://topengineeringcollegesintamilnadu.blogspot.in/2010/05/ce1403-basics-ofdynamics-and-aseismic.html#sthash.JXa6X4NG.dpuf
GE6353 ENGINEERING MECHANICS L T P C 3104 OBJECTIVES To develop capacity to predict the effect of force and motion in the course of carrying out the design functions of engineering UNIT I BASICS AND STATICS OF PARTICLES 12 Introduction Units and Dimensions Laws of Mechanics Lamis theorem, Parallelogram and triangular Law of forces Vectorial representation of forces Vector operations of forces -additions, subtraction, dot product, cross product Coplanar Forces rectangular components Equilibrium of a particle Forces in space Equilibrium of a particle in space Equivalent systems of forces Principle of transmissibility . UNIT II EQUILIBRIUM OF RIGID BODIES 12 Free body diagram Types of supports Action and reaction forces stable equilibrium Moments and Couples Moment of a force about a point and about an axis Vectorial representation of moments and couples Scalar components of a moment Varignons theorem Single equivalent force -Equilibrium of Rigid bodies in two dimensions Equilibrium of Rigid bodies in three dimensions UNIT III PROPERTIES OF SURFACES AND SOLIDS 12 Centroids and centre of mass Centroids of lines and areas - Rectangular, circular, triangular areas by integration T section, I section, - Angle section, Hollow section by using standard formula Theorems of Pappus - Area moments of inertia of plane areas Rectangular, circular, triangular areas by integration T section, I section, Angle section, Hollow section by using standard formula Parallel axis theorem and perpendicular axis theorem Principal moments of inertia of plane areas Principal axes of inertiaMass moment of inertia mass moment of inertia for prismatic, cylindrical and spherical solids from first principle Relation to area moments of inertia. UNIT IV DYNAMICS OF PARTICLES 12
Displacements, Velocity and acceleration, their relationship Relative motion Curvilinear motion -Newtons laws of motion Work Energy Equation Impulse and Momentum Impact of elastic bodies. UNIT V FRICTION AND ELEMENTS OF RIGID BODY DYNAMICS 12 Friction force Laws of sliding friction equilibrium analysis of simple systems with sliding friction wedge friction-. Rolling resistance -Translation and Rotation of Rigid Bodies Velocity and acceleration General Plane motion of simple rigid bodies such as cylinder, disc/wheel and sphere. TOTAL: 60 PERIODS 9 TEXT BOOKS: 1. Beer, F.P and Johnston Jr. E.R., Vector Mechanics for Engineers (In SI Units): Statics and Dynamics, 8th Edition, Tata McGraw-Hill Publishing company, New Delhi (2004). 2. Vela Murali, Engineering Mechanics, Oxford University Press (2010) REFERENCES: 1. Hibbeller, R.C and Ashok Gupta, Engineering Mechanics: Statics and Dynamics, 11th Edition, Pearson Education (2010). 2. Irving H. Shames and Krishna Mohana Rao. G., Engineering Mechanics Statics and Dynamics, 4th Edition, Pearson Education (2006) 3. Meriam J.L. and Kraige L.G., Engineering Mechanics- Statics - Volume 1, Dynamics- Volume 2, Third Edition, John Wiley & Sons,(1993) 4. Rajasekaran S and Sankarasubramanian G., Engineering Mechanics Statics and Dynamics, 3rd Edition, Vikas Publishing House Pvt. Ltd., (2005). 5. Bhavikatti, S.S and Rajashekarappa, K.G., Engineering Mechanics, New Age International (P) Limited Publishers, (1998). 6. Kumar, K.L., Engineering Mechanics, 3rd Revised Edition, Tata McGrawHill Publishing company, New Delhi (2008)
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeVon EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (537)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeVon EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (5794)
- Estimation and Costing Textbook by BN Dutta PDFDokument156 SeitenEstimation and Costing Textbook by BN Dutta PDFSumayya Kareem60% (10)
- BS1192-4 Collaborative Production of Information Part 4Dokument58 SeitenBS1192-4 Collaborative Production of Information Part 4Fábio PinhoNoch keine Bewertungen
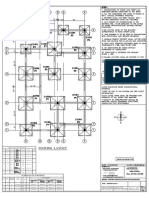
- A B C D E F A B C D E F C: Footing LayoutDokument1 SeiteA B C D E F A B C D E F C: Footing LayoutVanu VamalaiNoch keine Bewertungen
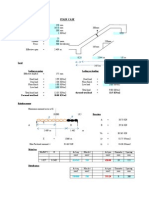
- SpillwayDokument5 SeitenSpillwayVanu VamalaiNoch keine Bewertungen
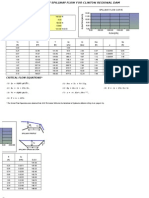
- Aa Consultants: Project Number: Project Name: DataDokument4 SeitenAa Consultants: Project Number: Project Name: DataVanu VamalaiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Staircase Design 1Dokument365 SeitenStaircase Design 1Vanu VamalaiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Stair CaseDokument19 SeitenStair CaseVanu VamalaiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Annexure I 2013.1.1 NewDokument715 SeitenAnnexure I 2013.1.1 NewVanu VamalaiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Appendix: Various Location of Natural Soil ProfileDokument6 SeitenAppendix: Various Location of Natural Soil ProfileVanu VamalaiNoch keine Bewertungen
- UNIT III FINITE ELEMENT METHOD 12 Introduction - Discretisation of A Structure - Displacement Functions - Truss Element - Beam Element - Plane Stress and Plane Strain - Triangular ElementsDokument1 SeiteUNIT III FINITE ELEMENT METHOD 12 Introduction - Discretisation of A Structure - Displacement Functions - Truss Element - Beam Element - Plane Stress and Plane Strain - Triangular ElementsVanu VamalaiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Is SP 16 1980 PDFDokument255 SeitenIs SP 16 1980 PDFshantanu pande100% (3)
- Slab ReinforcementDokument1 SeiteSlab ReinforcementVanu VamalaiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tunnel Design ManualDokument571 SeitenTunnel Design ManualVanu Vamalai100% (15)
- Teachers Manual Diploma Hydropower EngineeringDokument270 SeitenTeachers Manual Diploma Hydropower EngineeringVanu Vamalai60% (5)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceVon EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (895)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Von EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Bewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (98)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceVon EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (588)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingVon EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (400)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerVon EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (271)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItVon EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (838)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyVon EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (2259)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealVon EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (74)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureVon EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (474)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryVon EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (231)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnVon EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (234)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaVon EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (266)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersVon EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (345)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaVon EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (45)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreVon EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Von EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Bewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (121)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesVon EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (821)
- (WWW - Asianovel.com) - Quan Zhi Gao Shou Chapter 051 - Chapter 100Dokument310 Seiten(WWW - Asianovel.com) - Quan Zhi Gao Shou Chapter 051 - Chapter 100Exile0105Noch keine Bewertungen
- Bio-Rad D-10 Dual ProgramDokument15 SeitenBio-Rad D-10 Dual ProgramMeesam AliNoch keine Bewertungen
- 31. (NÂNG CAO) Đề soạn theo cấu trúc minh họa 2021 - Tiếng Anh - Đề 31 - DươngDokument15 Seiten31. (NÂNG CAO) Đề soạn theo cấu trúc minh họa 2021 - Tiếng Anh - Đề 31 - DươngNguyễn Quế Anh100% (1)
- Rajiv Gandhi University of Health Sciences Exam Result: PrintDokument1 SeiteRajiv Gandhi University of Health Sciences Exam Result: PrintAbhi NavNoch keine Bewertungen
- (Rect-15) Experimental Study On Partial Replacement of Cement With Coconut Shell Ash in ConcreteDokument3 Seiten(Rect-15) Experimental Study On Partial Replacement of Cement With Coconut Shell Ash in Concretefrancis dimakilingNoch keine Bewertungen
- An Adaptive Power Oscillation Damping Controllerby STATCOM With Energy StorageDokument10 SeitenAn Adaptive Power Oscillation Damping Controllerby STATCOM With Energy StorageChristian EmenikeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Aoc f22sDokument43 SeitenAoc f22sJoao Jose Santos NetoNoch keine Bewertungen
- 500 Word LIST Synonim of TOEFLDokument22 Seiten500 Word LIST Synonim of TOEFLNurul JulinarNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1 s2.0 S0956713515002546 Main PDFDokument9 Seiten1 s2.0 S0956713515002546 Main PDFIfwat ThaqifNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lesson 2 Arts of East AsiaDokument21 SeitenLesson 2 Arts of East Asiarenaldo ocampoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Attacks On Cryptosystems PDFDokument18 SeitenAttacks On Cryptosystems PDFUjjayanta BhaumikNoch keine Bewertungen
- Industrial Training Report (Kapar Power Plant)Dokument40 SeitenIndustrial Training Report (Kapar Power Plant)Hakeemi Baseri100% (2)
- History of DiamondsDokument21 SeitenHistory of Diamondssilvernitrate1953Noch keine Bewertungen
- Greyhound Free Patt.Dokument14 SeitenGreyhound Free Patt.claire_garlandNoch keine Bewertungen
- Linear Predictor: Nature of Linear PredictionDokument9 SeitenLinear Predictor: Nature of Linear PredictionkvNoch keine Bewertungen
- Complex Sentences For IELTS SpeakingDokument16 SeitenComplex Sentences For IELTS SpeakingWill Go NalamNoch keine Bewertungen
- 300.91C - Fire Alarm System Pre-Test and Acceptance Test Checklist 3-27-14Dokument2 Seiten300.91C - Fire Alarm System Pre-Test and Acceptance Test Checklist 3-27-14mthuyaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Air Cooler With Checking DoorDokument2 SeitenAir Cooler With Checking DoorSuraj KumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Techno Enviro EconomicanalysisofintegrateddirectchemicalloopingDokument14 SeitenTechno Enviro EconomicanalysisofintegrateddirectchemicalloopingAhmad SyauqiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Carriages and Mounts SeriesDokument92 SeitenCarriages and Mounts Seriessudhirm16Noch keine Bewertungen
- Igorot Village: Get To Know..Dokument11 SeitenIgorot Village: Get To Know..Elain RagosNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2nd Quarter - Summative Test in TleDokument2 Seiten2nd Quarter - Summative Test in TleRachelle Ann Dizon100% (1)
- Xu 2020Dokument11 SeitenXu 2020Marco A. R. JimenesNoch keine Bewertungen
- QuestionsDokument6 SeitenQuestionsRomeo martinezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Vision For Mobile Robot Navigation - A Survey PDFDokument31 SeitenVision For Mobile Robot Navigation - A Survey PDFtes donlodNoch keine Bewertungen
- Flap Designs For Flap Advancement During Implant Therapy A Systematic Review 2016 PDFDokument8 SeitenFlap Designs For Flap Advancement During Implant Therapy A Systematic Review 2016 PDFRohit ShahNoch keine Bewertungen
- Omyacarb 1t TNDokument1 SeiteOmyacarb 1t TNGİZEM DEMİRNoch keine Bewertungen
- Responsible Living: Mantri DevelopersDokument15 SeitenResponsible Living: Mantri Developersnadaf8Noch keine Bewertungen
- Static CMOS and Dynamic CircuitsDokument19 SeitenStatic CMOS and Dynamic CircuitsAbhijna MaiyaNoch keine Bewertungen
- SMA - Core 1 - IEC62109-2 - 0 Test ReportDokument6 SeitenSMA - Core 1 - IEC62109-2 - 0 Test ReportFurqan HamidNoch keine Bewertungen