Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
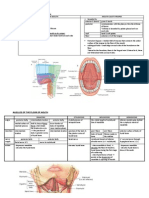
#Lung
Hochgeladen von
ameerabestOriginalbeschreibung:
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
#Lung
Hochgeladen von
ameerabestCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
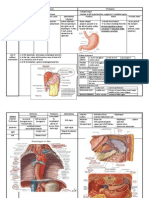
TB Surgical indications in pulmonary TB: 1. Diagnosis (wedge excision of solitary peripheral nodule [tuberculoma]) 2.
Massive hemoptysis (lobectomy, pneumonectomy) 3. BPF w/ tuberculous empyema (pleuropneumonectomy) 4. Trapped lung following empyema (decortications, thoracoplasty) 5. Persistent localized infection in destroyed lung or distal to bronchostenosis (lobectomy, pneumonectomy) 6. An open, culture-negative cavity (>2cm) in young patient (lobectomy) 7. Localized disease resulting from atypical multidrug resistant organism (lobectomy)
PULMONARY INFECTIONS BRONCHIECTASIS etiology = suppurative lung disease characterized by bronchial dilatation 1. Congenital (Kartagener syndrome) 2. Infection 3. Bronchial obstruction - intrinsic = FB, mucus plug, tumor - extrinsic = enlarged LN 1. Plain CXR & CT scan = dilated bronchi 2. Bronchoscopy LOBECTOMY 1. Failure medical treatment 2. Hemoptysis 3. Isolated lobar bronchiectasis LUNG CYSTS CONGENITAL LOBAR EMPHYSEMA = idiopathic hyperinflation of one lobe usually left upper dt intrinsic weakness of bronchial supporting cartilage - severe respiratory distress in infancy
LUNG ABSCESS 1. Complicating necrotizing pneumonia 2. Aspiration 3. Staph lung abscess in 1st yr of life 4. Systemic sepsis 5. Pulmonary infarction 6. On top of carcinoma or parasitic infection
investigations surgical indications
1. CXR = well-delineated cavity with fluid level 2. CT = differentiate benign & malignant abscess LOBECTOMY 1. Failure medical treatment 2. Massive hemoptysis 3. Malignant abscess
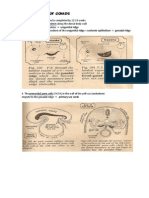
BRONCHOGENIC CYST Develop from aberrant buds from the primitive tracheo-bronchial tree - if separates early hilar/mediastinal cyst - if separates later intrapulmonary lower lobe cyst C/P - pulmonary cyst recurrent infection - mediastinal cyst airway obstruction - may communicate with bronchial lumen - may be single, multiple or multiloculated Investiga tion
SEQUESTRATION = segments of non-functional lung that have no bronchial communication w/ the airway - arterial supply : aorta - VR : pulmonary veins Extralobar Asymptomatic *detected incidentally as triangular shadow in posterior costophrenic angle adjacent to aorta & esophagus excision Intralobar recurrent pneumonia, abscess * in lower lobe * sequelae of high BF to pulmonary system = hemoptysis, CHF
HYDATID CYST
BULLAE = air-filled space within the lung parenchyma - results from intrinsic destruction of alveolar tissue - has fibrous wall - may communicate (open) or not (closed) with bronchial tree - dyspnea (bulla enlarges progressively and compresses normal lung) - complications of bulla (pneumothorax, infection, hemoptysis) 1. CXR, CT 2. V/Q lung scanning 3. PFT
- breathlessness - cough - of expectoration watery fluid or grape-like skin (cyst rupture)
CXR = overinflation of a lobe, mediastinal shift
treatme nt
excision
lobectomy
lobectomy
1. CXR = spherical, well defined opacity w/ or w/o air cap, water lily appearance 2. CT chest 3. Casoni test 4. Serological test - enucleation & capetonage - lobectomy (very large cyst)
- bullectomy - lobectomy (when whole lung is replaced by a large bulla)
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- #Chest TraumasDokument4 Seiten#Chest Traumasameerabest100% (3)
- Review of Session 2003-2004Dokument246 SeitenReview of Session 2003-2004The Royal Society of Edinburgh0% (1)
- The Neurological ExamDokument88 SeitenThe Neurological ExamsanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Approach To The Patient With Endocrine DisordersDokument17 SeitenApproach To The Patient With Endocrine Disordersseun williamsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cardiovascular Shoutouts: When She Says You SayDokument7 SeitenCardiovascular Shoutouts: When She Says You SayGbotemi AlaladeNoch keine Bewertungen
- # Diseases of ConjunctivaDokument4 Seiten# Diseases of Conjunctivaameerabest100% (1)
- Bates Chapter 8 Lung and ThoraxDokument15 SeitenBates Chapter 8 Lung and ThoraxAdrian CaballesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Physical Diagnosis Information OverviewDokument119 SeitenPhysical Diagnosis Information OverviewNarcis PopaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mechanism of Drug Action PDFDokument1 SeiteMechanism of Drug Action PDFraviomjNoch keine Bewertungen
- Dse Pathogenesis/ Causes Diagnosis Complications TX Prognosis NotesDokument5 SeitenDse Pathogenesis/ Causes Diagnosis Complications TX Prognosis NotesLuka Desabelle- JustoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pulmonary Diseases - Dental ManagementDokument45 SeitenPulmonary Diseases - Dental Managementfilyouth4life100% (3)
- PEDIA Clerks Revalida Review 2023Dokument106 SeitenPEDIA Clerks Revalida Review 2023Raven EvangelistaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Abdominal PXDokument60 SeitenAbdominal PXabinadivegaNoch keine Bewertungen
- EndoDokument8 SeitenEndoSheryl Layne Lao-SebrioNoch keine Bewertungen
- How To Read A CTGDokument31 SeitenHow To Read A CTGAbdullah As'ad100% (1)
- Drug Toxicity and PoisoningDokument12 SeitenDrug Toxicity and PoisoningPAULA MARIE MERCADO LLIDONoch keine Bewertungen
- Study Notes On Anemia in Pediatrics (2014-2015) by Remedios C. Ong, M.D. Generalities On AnemiaDokument13 SeitenStudy Notes On Anemia in Pediatrics (2014-2015) by Remedios C. Ong, M.D. Generalities On AnemiaWILLIAM BERNARD ONGNoch keine Bewertungen
- Signs in ObgyDokument2 SeitenSigns in ObgyAnnapurna DangetiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Surgery QuestionsDokument19 SeitenSurgery QuestionsdocaliNoch keine Bewertungen
- Physio Ob ReviewDokument368 SeitenPhysio Ob ReviewMark LopezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pathophysiology of AgingDokument5 SeitenPathophysiology of AgingRemelou Garchitorena AlfelorNoch keine Bewertungen
- Gynecology: Recurrent Pregnancy LossDokument6 SeitenGynecology: Recurrent Pregnancy LossDawn Marco100% (1)
- Heart MurmursDokument48 SeitenHeart MurmursAhmed T Al-MomtinNoch keine Bewertungen
- Clinical Abstract TEMPLATEDokument3 SeitenClinical Abstract TEMPLATEDiannesa April GolosindaNoch keine Bewertungen
- GIT Examination - Clinical Skills With DRDokument8 SeitenGIT Examination - Clinical Skills With DRNaveen KovalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Rheumatic Heart Disease and Infective EndocarditisDokument10 SeitenRheumatic Heart Disease and Infective Endocarditisapi-19840404Noch keine Bewertungen
- Differential DiagnosisDokument10 SeitenDifferential DiagnosisRhaffy Bearneza RapaconNoch keine Bewertungen
- Management For HypertensionDokument8 SeitenManagement For HypertensionSugimoto Karla Erika100% (1)
- IM 3A PE Cardiology Dr. JumangitDokument12 SeitenIM 3A PE Cardiology Dr. JumangitCzara DyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Approach To A Child With Cough and Difficulty in BreathingDokument23 SeitenApproach To A Child With Cough and Difficulty in BreathingKashif Burki100% (2)
- Polycystic Kidney DiseaseDokument9 SeitenPolycystic Kidney DiseaseCésar Aguilar ContrerasNoch keine Bewertungen
- ENT Quick ReviewDokument6 SeitenENT Quick ReviewWade100% (1)
- Internal Medicine Sample Osce Examination Component Questions eDokument2 SeitenInternal Medicine Sample Osce Examination Component Questions eFajar ChampionNoch keine Bewertungen
- Disorder of Sex DevelopmentDokument40 SeitenDisorder of Sex DevelopmentAndi AdityaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Harrison-Principals of Internal Medicine 20th. Ed. Prt.7-11Dokument707 SeitenHarrison-Principals of Internal Medicine 20th. Ed. Prt.7-11Choi DongYiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Menstrual Cycle Made SimpleDokument6 SeitenMenstrual Cycle Made SimpleNurul Nabilah AzraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Kamal KV 500 Q CollectionsDokument13 SeitenKamal KV 500 Q CollectionsBeta ReaderNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cranial Fossa Notes - HelpfulDokument4 SeitenCranial Fossa Notes - HelpfulKo HakuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Dengue Virus: DescriptionDokument12 SeitenDengue Virus: Descriptionpedia blue bookNoch keine Bewertungen
- Part IIDokument64 SeitenPart IIhussainNoch keine Bewertungen
- PEDIA para 08AMDokument17 SeitenPEDIA para 08AMpedia blue bookNoch keine Bewertungen
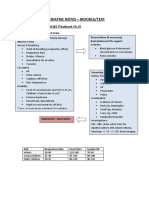
- Paediatric Notes - Moodle/Text: Paediatric Emergencies (Textbook Ch.5)Dokument6 SeitenPaediatric Notes - Moodle/Text: Paediatric Emergencies (Textbook Ch.5)Jana AldourNoch keine Bewertungen
- Gemp3 Paediatric Clinical Examination SkillsDokument13 SeitenGemp3 Paediatric Clinical Examination SkillsAnna-Tammy HumanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pedia Bacte Table 08amDokument25 SeitenPedia Bacte Table 08ampedia blue bookNoch keine Bewertungen
- Questions For OSCE Exam - Model AnswersDokument9 SeitenQuestions For OSCE Exam - Model AnswersFarah FarahNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lung Pathology Flow ChartsDokument6 SeitenLung Pathology Flow ChartsZagros MotamedNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lower Respiratory Tract InfectionDokument9 SeitenLower Respiratory Tract InfectionNamrah AfzalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Management of Acute Appendicitis in Adults - UpToDateDokument28 SeitenManagement of Acute Appendicitis in Adults - UpToDateaulia rachman100% (1)
- Case Presentation: NeurologyDokument19 SeitenCase Presentation: NeurologySydrex SarmientoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Legal Medicine and Medical Jurisprudence Comprehensive Exam ReviewerDokument17 SeitenLegal Medicine and Medical Jurisprudence Comprehensive Exam ReviewerYeshua Tura100% (1)
- Topnotch Waiver Oath and Checklist April 2015 PDFDokument2 SeitenTopnotch Waiver Oath and Checklist April 2015 PDFRalph JuicoNoch keine Bewertungen
- OB-GYN Patient History and PEDokument4 SeitenOB-GYN Patient History and PEAngelique TongsonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Approach To A Neonate With CyanosisDokument56 SeitenApproach To A Neonate With CyanosispaanarNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1-Ammar Notes (Med & Pedia)Dokument23 Seiten1-Ammar Notes (Med & Pedia)anmar alkhudhri100% (1)
- Problem-based Approach to Gastroenterology and HepatologyVon EverandProblem-based Approach to Gastroenterology and HepatologyJohn N. PlevrisNoch keine Bewertungen
- Buzz Words MRCPDokument74 SeitenBuzz Words MRCPKyrillos G FahmyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Most Common Nelsons 16th EdDokument32 SeitenMost Common Nelsons 16th EdRegine PanaliganNoch keine Bewertungen
- Headache History: Introduction - WIPPPDokument4 SeitenHeadache History: Introduction - WIPPPAmjad_2020Noch keine Bewertungen
- @acute Nephritic SyndromeDokument3 Seiten@acute Nephritic Syndromeameerabest100% (1)
- @ovary Cyst ComparisonDokument2 Seiten@ovary Cyst ComparisonameerabestNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cme Bronchial AsthmaDokument28 SeitenCme Bronchial AsthmaameerabestNoch keine Bewertungen
- @tumors of The Breast 1Dokument2 Seiten@tumors of The Breast 1ameerabestNoch keine Bewertungen
- Semen AnalysisDokument3 SeitenSemen Analysisameerabest80% (5)
- OSCE DermaDokument8 SeitenOSCE DermaameerabestNoch keine Bewertungen
- Genital EmbryologyDokument6 SeitenGenital EmbryologyameerabestNoch keine Bewertungen
- Parotid Gland Submandibular Gland Sublingual GlandDokument5 SeitenParotid Gland Submandibular Gland Sublingual GlandameerabestNoch keine Bewertungen
- PleuraDokument6 SeitenPleuraameerabest100% (1)
- Extracorporial Circulation (Ecc) Heart Lung Machine Cardio-Pulmonary Bypass (CPB)Dokument2 SeitenExtracorporial Circulation (Ecc) Heart Lung Machine Cardio-Pulmonary Bypass (CPB)ameerabestNoch keine Bewertungen
- #MediastinumDokument4 Seiten#Mediastinumameerabest100% (1)
- PharynxDokument2 SeitenPharynxameerabest0% (1)
- Mouth Cavity, Palate, TongueDokument8 SeitenMouth Cavity, Palate, Tongueameerabest100% (1)
- Oesophagus & StomachDokument3 SeitenOesophagus & StomachameerabestNoch keine Bewertungen
- Home-Made HBsAgDokument1 SeiteHome-Made HBsAgsomchaisNoch keine Bewertungen
- Homeostasis and The Excretory SystemDokument21 SeitenHomeostasis and The Excretory Systemmark smithNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ketogenic DietDokument8 SeitenKetogenic DietzabedahibrahimNoch keine Bewertungen
- 3637 Technical Bulletin MTD Isa 760 vg4536718630311562122Dokument1 Seite3637 Technical Bulletin MTD Isa 760 vg4536718630311562122Thảo ThảoNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Vaccine Adverse Event Reporting System (VAERS) (2) 091621Dokument475 SeitenThe Vaccine Adverse Event Reporting System (VAERS) (2) 091621jb_uspuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Physiotherapy AssessmentDokument8 SeitenPhysiotherapy Assessmentみ にゅきゅ100% (2)
- Vestibular Function TestsDokument11 SeitenVestibular Function TestsM. Arief Purnanta0% (1)
- Chief Complaints: Sl. Medicine Name Dosage Freq. Duration InstructionsDokument4 SeitenChief Complaints: Sl. Medicine Name Dosage Freq. Duration InstructionstejaminnikantiNoch keine Bewertungen
- XN-1500 10p ENDokument5 SeitenXN-1500 10p ENHarika PutraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Medication Administration Nursing PracticeDokument34 SeitenMedication Administration Nursing PracticeSWATNoch keine Bewertungen
- Normal Spontaneous DeliveryDokument4 SeitenNormal Spontaneous Deliveryvivian magnoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Comparative Study of Posterior Stabilizing VS Cruciate Retaining Prosthesis in Total Knee ReplacementDokument15 SeitenComparative Study of Posterior Stabilizing VS Cruciate Retaining Prosthesis in Total Knee ReplacementIJAR JOURNALNoch keine Bewertungen
- Rashi - Effusion CytDokument56 SeitenRashi - Effusion CytShruthi N.RNoch keine Bewertungen
- NSG ProcessDokument6 SeitenNSG ProcessJay-Dee Evangelista PacionNoch keine Bewertungen
- SB 3 Flu VaccineDokument2 SeitenSB 3 Flu VaccineBIANNE KATRINA GASAGASNoch keine Bewertungen
- HemostasisDokument5 SeitenHemostasisPadmavathi C100% (1)
- MICP211 Midterm ReviewerDokument39 SeitenMICP211 Midterm ReviewerKrista CruzNoch keine Bewertungen
- 03 NCP 5 Pulmonary Tuberculosis LalitDokument17 Seiten03 NCP 5 Pulmonary Tuberculosis Lalitamit100% (2)
- High Altitude TrainingDokument6 SeitenHigh Altitude TrainingALEX SNEHANoch keine Bewertungen
- Renr Practice Test 9 FinalDokument12 SeitenRenr Practice Test 9 FinalTk100% (2)
- Pathological Condition in Buffalo GenitalsDokument3 SeitenPathological Condition in Buffalo GenitalsgnpobsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pathology Supplement Handout Nov 2018Dokument25 SeitenPathology Supplement Handout Nov 2018Zak Kaz100% (2)
- Physical Assessment Head To ToeDokument4 SeitenPhysical Assessment Head To ToeFely Theresa Lanes Loreno95% (43)
- Role of Gingival Tissue Biotype in Perio PDFDokument4 SeitenRole of Gingival Tissue Biotype in Perio PDFMedstudNoch keine Bewertungen
- Marc A. Levitt: AuthorDokument16 SeitenMarc A. Levitt: AuthorAlonso Rodriguez EscobedoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Author Book TitleDokument13 SeitenAuthor Book TitlejenniferxarmstrongNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nursing Care Plan FinalDokument2 SeitenNursing Care Plan FinalRy LlanesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Gases Arteriales - BE NEJMDokument10 SeitenGases Arteriales - BE NEJMalexsr36Noch keine Bewertungen
- KalingaDLL-scientific Literacy & Critical ThinkingDokument4 SeitenKalingaDLL-scientific Literacy & Critical ThinkingMary Joy Lucob TangbawanNoch keine Bewertungen
- A Special Interview With Dr. Meryl Nass by Dr. Joseph MercolaDokument9 SeitenA Special Interview With Dr. Meryl Nass by Dr. Joseph MercolaJonathan Robert Kraus (OutofMudProductions)Noch keine Bewertungen