Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
PERLIS-answer PHYSICS P1 P2 P3-Trial SPM 2009
Hochgeladen von
kamalharmozaOriginalbeschreibung:
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
PERLIS-answer PHYSICS P1 P2 P3-Trial SPM 2009
Hochgeladen von
kamalharmozaCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
· .;.
"
SULIT 4531 Physics August 2009
4531
PEPERIKSAAN PERCUBAAN nERSAMA SIJIL PELAJARAN MALAYSIA 2009
ANJURAN
PERSIDANGAN KEBANGSAAN PENGETUA-PENGETUA SEKOLAH MENENGAH MALAYSIA CAW ANGAN PERLIS
PHYSICS
PERATURAN PEMARKAHAN
4531
Peraturan pemarkahan ini mengandungi 14 halaman bercetak
SULIT
2
PAPERl
1. D 11. ~ 21. D 31. D 41. C
2. D 12. 22. e 32. A 42. D
3. e 13. e 23. A 33. D 43. A
4. A 14. e 24. D 34. B 44. B
5. C 15. A 25. D 35. A 45. D
6. C 16. B 26. C 36. D 46. B
7. e 17. B 27. B 37. A 47. A
8. C 18. C 28. e 38. e 48. e
9. D 19. C 29. D 39. B 49. e
10. e 20. B 30. A 40. B 50. B PAPER 2
Section A
NO
MARKING CRITERIA
MARK
5
SUB TOTAL
7
1 (a)(i) The air pack acceleratellconstant acceleration
(ii) 40 images
(b)(i) O.ls
(ii) 50 ems"
(iii)
decreases
2(a)(i) smaller
(ii) biggerllfaster
(iii) lower
(b) Bernoulli (principle)
(d) 0> E D>F F>E
(c)
4531
(any two corrects)
2
SULIT
3
NO MARKING CRITERIA
MARK
7
2
SUB TOTAL
6
3. (a) The amount of heat energy required to increase I kg of substance by 1°C.
4(a) (b)
(ii)
9000 9000000
or
3.36xlOs 3.36xlOs
0.027 kg (with unit) or 27 g (with unit)
4000 4000000
or
3.36xlOs 3.36xlOs
0.012 kg (with unit) or 12 g (with unit)
Convex lens
"'l"""~ 1 (correct ray and image) (~
(c)(i) 0.1 x 900 x 100 or 100 x 900 x 100
(c) Virtual/upright / magnified / on the same side as the object (anyone correct)
4531
- 7.5 cm (with unit)
SULIT
4
NO MARKING CRITERIA MARK
SUB TOTAL
5(a) Diffraction 1
III ~)))
(b)
~))) D ) J J J V· 2
D
Diagram 1.1 Diagram 1.2 (c)(i) (Region X) is deeper (so the wavelength), A shorter
II (Region X) is shallower (so the wavelength), A longer.
[ 1 ] [ 1 ]
(ii) Wavelength I A
24 (d) 5 x 8 II 5 x 3
-,
40 i'M"(with unit) emS
8
(ii) The direction of the induced current in a solenoid is such that its magnetic effect always opposes the change producing it
6(a)
(b )(i)
(iii)
P: North Q: South
~ -j-fl- -ff· -J. --fs-n
• ~ ~ 1_ •• -- -- -J~;---
I
• Stronger magnet
• Increases number oftums of the solenoid
• Increases the speed of movement of magnet into solenoid (any two corrects)
2
8
(d)(i) Direct current
(ii) Magnitude and direction of current will remain constant
4531
SULIT
5
MARK
NO MARKING CRITERIA
SUB TOTAL
7(a) Electron gun
(b )(i)
A positive v~
~C:::::=::::'::====:JI
(ii) a. Bigger deflection upward//increase deflection upward
b. less deflection II Increase brightness
c. Electron will be deflected downward
(c )(i)
(c)(ii) (a) P : Diode
Change a.c to d.c II as rectifier
Q : Capasitor
Smooth the current
10
8(a) m=4
n=4
(b) Proton = 84 Neutron = 126
(c) 3.5 X 10-20 x(3 X 108 i
3.15 X 10-3 J (with unit)
(d) 3Ty,
YJ hourll 0.33 hour (with unit)
9
156
SULIT
4531
6
SECTIONB
NO
MARKING CRITERIA
MARK
4
SULIT
SUB TOTAL
(b)
(c)
9(a) The distance between the focal point, F, and the pole of the spherical mirror
(d)(i) Convex mirror.
To provide a wider field view (of the activities taking place in the shopping area).
(ii) A bigger size of mirror.
To enable a wider view and a sharper image.
(iii) Hung the mirror at the corner of the supermarket ceiling.
Easier to look at II It won't disturb the pathway of the customer.
Mirror in diagram 9.1 is more curve than the mirror in diagram 9.2 II Mirror in diagram 9.2 is less/fewer curve than 9.1.
(S4~) ..
fhe rays in diagram 9.1 is bent more than the rays in diagram 9.2 II Rays in diagram 9.2 bent less than 9.1.
Focal length in diagram 9.1 less than in diagram 9.2 II Focal length in diagram 9.2 more than in diagram 9.1.
The more the curve of the mirror, the less/fewer the focal length II The less/fewer the curve of the mirror, the more the focal length.
5
6
4531
bulb
Concave mirror
Choose the correct materials i.e. I bulb, 1 concave mirror.
Correct arrangement and reflected ray. Diagram: Correct arrangement and label
Correct label focal point, F I I label focal length, f
Explanation:
The bulb is placed at focal point in front of a concave mirror. The light ray will be reflected in parallel.
7
NO MARKING CRITERIA MARK
SUB TOTAL
Place: a bending road II sharp road comers II dangerous bend 1
Reason: To minimize the occurrence of accidents II 1
To enable the motorist to see the oncoming traffic.
Place: in a car, as a rearview mirror 1
Reason: it can provide a wider field of view than plane mirror. 1 4
20
I~(a) Supply 9 Joule electric energy for each coulomb of charge transfer from 1 1
one point to another point within a material
(b)(i) Electrical energy ~ Light energy + Heat energy I 1
(ii) Diagram 4.2 is brighter II Diagram 4.1 is dimmer 1
The brighter bulb has larger amount of current 1/ 1
The dimmer bulb has smaller amount of current
The brighter the bulb, the higher the current flows 1
and
Internal resistance of dry cell is lower Ilotherwise 1 4
( c)(i) Lead-acid accumulator 1 1
(ii) No 1
8 dry cells are arranged in serial so the total internal resistance is
8xO.5 =4 Q 1
Current flow, I = VIR = 12/4 = 3 A 1 3
This small current cannot start the engine.
(d) Modification Explanation
Use the fluorescent lamp Consume less power and economic 2
Use a more efficient It brightens the room more clearly and
fluorescent lamp thoroughly and prevents wastage 2
Use a more energy Helps the temperature in the room to be
efficient fluorescent lamp not too hot due to less energy loss in 2
form of heat energy.
Fuses should be To prevent overheating of lamps might
connected to the cause the fluorescent lamp to blowout. 2
fluorescent lamp
Two or more fluorescent If one lamp blows the rest are still
lamp are arrange in functioning. 2 10
~arallel.
20 4531
SULIT
8 SECTIONC
NO MARKING CRITERIA MARK
SUB TOTAL
11 (a)(i) The weight of an object 1 1
(ii)
Characteristic Explanation
A Dynamic type of rope It is softer and could prevent 2
injury
A lower density It is lighter 2 ,.~ - ... ........
Strong snapping force So that the ro~e will not snap 2
A rope with smaller diameter It will occupy less space 2
The best choice is rope Q because it is a dynamic rope, of lower 2 10
density, bi~er snapping force and less diameter
(b)(i) weight of the parachutist 1
weight of parachute 1
air resistant 1 3
\eI'\S~t'l 0+ rare-.
(ii) weight of parachutist + weight of the parachute = air resistant 2 2
(c) 8 x 10 II 5 x 10 II 80 II 50 ~ -I .:8-( 2..J I) 1
30 1 ~ ~ _~l;l· 3/J 1
80 - 50 = 13a II -
13 - ~ '·S.;)./V -
-
-
.
a= 2.31 ms" 2 4 -<>.~...,
20
12(a)(i) An beta particle consist an electron and negatively charge 2 2
(ii)
Characteristics Reason
Physical state is solid It can be conveniently placed at the tip 2
of the lig!lJning conductor.
Ionize Power is high Easy for the medium to conductor 2
electricity and cause the lightning to
divert to the place of higher ionization.
Half life must be long The substance will be active for a long
time 2 6
P is suitable because it is a solid, it has high ionize and very long half 2 2
life. 4531
SULIT
9
NO MARKING CRITERIA MARK
SUB TOTAL
(b) Half life of6 hour is a short half life. Within one day almost all of the 1
substance injected into the body will have lost its activity.
It can then be safely excreted from the body without causing 1
unnecessary damage to the tissues.
Since it is a gamma emitter, the radiation can come out of the body 1
because gamma is very penetrating. Hence it can be traced from the
outside using the detector.
Since it is low energy gamma radiation will not do much damage to the 1
tissues while it is going through the body
Hence this is very suitable for use in medical diagnosis. 1 5
(c)(i) 1200 - 600 - 300 - 150 - 75 = 4 T1/2 1
T y, = 15 minutes 1 2
(ii) 5 g - 2.5 g ( 15 minutes) - 1.25 g ( 30 minutes) - 5/8 g (45 minutes) 1
5 - 5/8 g 1
35/8 g 1 3
20 4531
SULIT
I
10 PAPER 3
SECTION A
NO
MARKING CRITERIA
MARK
1
1 1 1 1 2 1
SUB TOTAL
Uniform scale at both axes 1
1 (a)(i)
State the correct manipulated variable Mass,m
(ii) State the correct responding variable height, h
(iii) State one fixed variable
Cross sectional area II type of the liquid II density of the liquid
(b) Tabulate m], m, and h correctly
50.0 100.0 1.6
100.0 150.0 2.4 +
:====1~5~0.~0====:====2~0~0.~0====:=====~3.~2====:_ 0.,.
200.0 250.0 4.0
250.0 300.0 4.8
mi, m, and h shown in table with correct units. Value ofm] shown in a table
All value of m correct
All value of ml and m consistent to 1 d.p. All value of h correct
All value of h consistent to 1 d.p.
(c) Draw correctly a graph of a against h
h at the y-axis, m at the x-axis and correct units at both axes
Best straight line
5 points plotted correctly [Note: 3 or 4 points plotted correctly givel m] 2
(d) States the correct relationship based on the straight line drawn Height of the liquid is directly proportional to the mass
Lb~~~ U"'" 1''''~ }.y~ oj.
4531
16
SULIT
7
5
11
NO
MARKING CRITERIA
MARK
2
State the correct relationship between V and x V increases linearly with x
(ii) Draws the intrapolation line from x = 1.0 m to the graph and from 1
the graph to the V - axis
2(a)(i)
SUB TOTAL
(b )(i) Draw large triangle
Showing the correct calculation Answer with correct unit 1.0Vm-1
States the correct value and its unit of the resistance l.1V
(ii) Showing the correct calculation 1.0
100 x 1.5 x to-5
Answer with correct unit 1.65 x 10-7 V m
(iii) Answer with correct unit 0.50
(iv) Showing the correct calculation
1 1 0.5
-+- -
0.5 o.s or 2
Answer with correct unit 0.250
(d) State one suitable precaution
All wire connections must be tightly fixed II turned off the switch while not taking any reading
1 1
1
3
2
2
1
12
4531
SULIT
12
SECTIONB
NO
MARKING CRITERIA
MARK
SUB TOTAL
3(a) Making the right inference
The temperature of the gas affects the volume.
(b) Building an appropriate hypothesis
The volume of a fixed mass of gas at constant pressure increases when its temperature is increased.
(c )(i) Stating the aim of the experiment
To investigate the relationship between the temperature, T and the volume, V of a gas at constant pressure (to verify Charles' law)
(ii) Stating the correct variables
Manipulated variable: temperature of trapped air, 0 Responding variable: length of air column, x
Fixed variable: atmospheric pressure@ mass of trapped air
(iii) List of appropriate apparatus and material
Capillary tube, tall beaker, thermometer, Bunsen burner, tripod stand,
wire gauze, retort stand, mercury or concentrated sulphuric acid, stirrer, ruler, and ice.
4531
(iv) Describing set up of the apparatus
Draws a labeled and functional diagram of the set up of the apparatus
(v) State how the manipulated variable is controlled
• The air sample under investigation is trapped inside the capillary tube by a bead of concentrated sulphuric acid which acts as an index.
• The capillary tube is mounted on a 30cm ruler such that the bottom end of the column of air is aligned with the '0' mark on the ruler.
• Water and ice are poured into the beaker until the column of air is fully immersed under water. The water is stirred until the water temperature falls to 0 °C.
State how the responding variable is measured
The length of the air column, x is measured with the ruler and recorded.
SULIT
13
NO
MARKING CRITERIA
MARK
10
SUB TOTAL
State how the procedure is repeated to obtain at least 5 sets of results
The water is heated and continuously stirred for the values of temperature, (} 1
= 20 "C, 40 "C, 60 "C and 80 "C
(vi) Tabulating data
Show table with (} and X as headings
(vii) Analysing data ..THRf1NIiI'YH;
~~"
4531
Temperature, (} rOC) Length of air column, X (cm)
o
20
40
60
80
12
L... • l:e/9g.U4 6ffilj,. e9I1j~r<I, ¥(~m)
fa~f<Zr~·
4(a) Making the right inference
The distance between two spherical dippers affects the distance between 1 1
two constructive / destructive interference
(b) Building an appropriate hypothesis ~cr ~ .
The distance between two constructive / destructive interference ~es 1 1
when the distance between two spherical dippers.
(c)(i) Stating the aim of the experiment
To investigate the relationship between the distance between two spherical 1 .. '",,'Y"" .A"'.T~·"'~_
dippers and the distance between two constructive / destructive
interference
(ii) Stating the correct variables
Manipulated variable: The distance between two spherical dippers 1
Responding variable: The distance between two constructive / destructive
interference
Fixed variable: Depth of the water II speed of the motor II the perpendicular 1
distance between the two spherical dippers and the place where the interference
pattern is observed.
(iii) List of appropriate apparatus and material
Ripple tank with its accessories, power supply, white paper and ruler. 1 SULIT
14
NO
MARKING CRITERIA
MARK
SUB TOTAL
10
(iv) State a functional arrangement of the apparatus
Draws a labeled and functional diagram of the set up of the apparatus
State how the procedure is repeated to obtain at least 5 sets of results
Repeat the previous step by increasing the distance between two spherical dippers, a = 6.0 em, 7.0 em, 8.0 em and 9.0 em
(vi) Tabulating data
Show table with (} and X as headings
(vii) Analysing data x/em
(v) State how the manipulated variable is controlled
• Two spherical dippers are attached to the water
• The distance between spherical dippers on the screen are adjusted to a = 5.0 cm
State how the responding variable is measured
The distance between two constructive / destructive interference on the screen, x is measured with the ruler and recorded.
a/em x/cm
5.0
6.0
7.0
8.0
9.0 12
PERATURANPEMARKAHANTAMAT
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Skema K2 Set A JUJ Pahang 2014 Physics SPMDokument7 SeitenSkema K2 Set A JUJ Pahang 2014 Physics SPMCikgu FaizalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Perak-Answer Physics-Trial SPM 2008Dokument21 SeitenPerak-Answer Physics-Trial SPM 2008kamalharmoza50% (2)
- Terangganu-Answer Physics P2-Trial SPM 2007Dokument15 SeitenTerangganu-Answer Physics P2-Trial SPM 2007kamalharmoza100% (1)
- Trial Pahang Answers For Physics Paper 1 Trial 2010Dokument16 SeitenTrial Pahang Answers For Physics Paper 1 Trial 2010lilysuhanyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Johor-Answer P2-Trial SPM 2007Dokument8 SeitenJohor-Answer P2-Trial SPM 2007kamalharmozaNoch keine Bewertungen
- PAHANG-Answer Physics P1 P2 P3-Trial SPM 2009Dokument16 SeitenPAHANG-Answer Physics P1 P2 P3-Trial SPM 2009kamalharmozaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pre PSPM Computer Science Subject (Sc015) Kolej Matrikulasi Labuan (2019/2020)Dokument8 SeitenPre PSPM Computer Science Subject (Sc015) Kolej Matrikulasi Labuan (2019/2020)Veshal RameshNoch keine Bewertungen
- Trial MRSM SPM 2014 Physics K2 No SkemaDokument36 SeitenTrial MRSM SPM 2014 Physics K2 No SkemaCikgu Faizal83% (6)
- Kimia Kertas 2 Set 2 (Soalan)Dokument25 SeitenKimia Kertas 2 Set 2 (Soalan)kimia chemistryNoch keine Bewertungen
- Physics Paper 1, 2, 3 Trial SPM 2010 MRSMDokument100 SeitenPhysics Paper 1, 2, 3 Trial SPM 2010 MRSMrenuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Question Score A Chapter 1Dokument14 SeitenQuestion Score A Chapter 1Dee -AdilaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Jawapan Kertas Soalan Ramalan Biologi SPM 2022Dokument15 SeitenJawapan Kertas Soalan Ramalan Biologi SPM 2022kubendran saravanan100% (1)
- Physics P2 SPM 2014 MelakaDokument9 SeitenPhysics P2 SPM 2014 MelakaLeeZiangNoch keine Bewertungen
- Skema Fizik SPM Trial Perak 2009Dokument16 SeitenSkema Fizik SPM Trial Perak 2009fizmie100% (2)
- KIMIA K2 SkimaDokument7 SeitenKIMIA K2 SkimaTay Poh Leng0% (1)
- Chemistry (The Mole)Dokument44 SeitenChemistry (The Mole)Aisya AnwarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Trial SPM SBP 2010 Chemistry Marking SchemeDokument18 SeitenTrial SPM SBP 2010 Chemistry Marking SchemeFain Sudais100% (1)
- Skema Jawp Soalan Objektif Gerak Gempur 2Dokument1 SeiteSkema Jawp Soalan Objektif Gerak Gempur 2SK Pos TenauNoch keine Bewertungen
- 7 Skema Kimia K1 & K2 Trial SPM Terengganu MPP3 2019Dokument13 Seiten7 Skema Kimia K1 & K2 Trial SPM Terengganu MPP3 2019SaravananNoch keine Bewertungen
- MRSM-ANSWER PHYSICS-Trial SPM 2008Dokument20 SeitenMRSM-ANSWER PHYSICS-Trial SPM 2008kamalharmoza100% (3)
- Formula Dan Jadual Taburan NormalDokument4 SeitenFormula Dan Jadual Taburan NormalCekgi IntanNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2018 - Modul Kimia JKD Sains Tulen (Kimia) Mersing18 PDFDokument24 Seiten2018 - Modul Kimia JKD Sains Tulen (Kimia) Mersing18 PDFSiti Hajar Abd HamidNoch keine Bewertungen
- 04 Fakta Kimia SPM 2016Dokument23 Seiten04 Fakta Kimia SPM 2016haninadiaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Form 4 - Salts (+experiment)Dokument4 SeitenForm 4 - Salts (+experiment)kanryu_zonasNoch keine Bewertungen
- SPM Percubaan 2007 SBP Physics Paper 2 Marking SchemeDokument8 SeitenSPM Percubaan 2007 SBP Physics Paper 2 Marking SchemeChinWynn.com100% (2)
- Kertas 2 Pep. Set 4 SPM 2016Dokument17 SeitenKertas 2 Pep. Set 4 SPM 2016Siti Hasmah MohamadNoch keine Bewertungen
- Paper 2 Form 4 2020Dokument28 SeitenPaper 2 Form 4 2020Yusfalina Mohd YusoffNoch keine Bewertungen
- SPM Percubaan 2008 SBP Chemistry AnswersDokument19 SeitenSPM Percubaan 2008 SBP Chemistry AnswersChinWynn.com94% (16)
- Modul Biologi 2016 t4 SkemaDokument65 SeitenModul Biologi 2016 t4 SkemaIsmaliza IshakNoch keine Bewertungen
- Physics MRSM (Q and A)Dokument109 SeitenPhysics MRSM (Q and A)Patrick ChunNoch keine Bewertungen
- Add Math SPM Trial 2018 SBP P1&Ans PDFDokument25 SeitenAdd Math SPM Trial 2018 SBP P1&Ans PDFKataba MyTutorNoch keine Bewertungen
- 12.8 Bab 1 - 2 Ting. 4Dokument10 Seiten12.8 Bab 1 - 2 Ting. 4izrulNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2.9 Analysing Forces in Equilibrium: Chapter 2 Forces and MotionDokument16 Seiten2.9 Analysing Forces in Equilibrium: Chapter 2 Forces and MotionPauling ChiaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 7 Electricity Paper 2 SPMDokument12 SeitenChapter 7 Electricity Paper 2 SPMNor Hanisa100% (2)
- SPM 4531 2005 Physics p2 BJWPDokument30 SeitenSPM 4531 2005 Physics p2 BJWPpss smk selandar100% (1)
- KEDAH-Answer Physics-Trial SPM 2008Dokument17 SeitenKEDAH-Answer Physics-Trial SPM 2008kamalharmozaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chemistry SkemaMara2009Dokument13 SeitenChemistry SkemaMara2009spm_victim2010Noch keine Bewertungen
- Physics P1,2,3 Melaka 08 SkemaDokument13 SeitenPhysics P1,2,3 Melaka 08 SkemaMohd Khairul Anuar100% (4)
- With The Help A Brieo) Junction Half-Wave: S Shee (Ydrogen SolidDokument6 SeitenWith The Help A Brieo) Junction Half-Wave: S Shee (Ydrogen SolidRoy DeepeshNoch keine Bewertungen
- Skema Fizik Tingkatan 5 Kertas 2 Pep Percubaan SPM SBP 2011Dokument8 SeitenSkema Fizik Tingkatan 5 Kertas 2 Pep Percubaan SPM SBP 2011Chin Shee YanNoch keine Bewertungen
- PHYS12SQPDokument3 SeitenPHYS12SQPShreeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Peperiksaan Percubaan SPM Kelantan 2010 Peraturan Pemarkahan Physics Paper 1Dokument14 SeitenPeperiksaan Percubaan SPM Kelantan 2010 Peraturan Pemarkahan Physics Paper 1nik mohamad solehinNoch keine Bewertungen
- Solved PapersDokument284 SeitenSolved PapersAlfiya PathanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Attempt All QuestionsDokument7 SeitenAttempt All QuestionsNirupan neupaneNoch keine Bewertungen
- SPM Trial 2011 Physics A PerakDokument24 SeitenSPM Trial 2011 Physics A PerakKer HerNoch keine Bewertungen
- Physics QPDokument3 SeitenPhysics QPThemistocles AthensNoch keine Bewertungen
- Thakur International School PHYSICS 2020Dokument4 SeitenThakur International School PHYSICS 2020Study in an easy wayNoch keine Bewertungen
- QP of Xii Phy II TermDokument3 SeitenQP of Xii Phy II TermDêêpák Sîñgh ÑîtwálNoch keine Bewertungen
- 270000313-Sample Paper 7Dokument6 Seiten270000313-Sample Paper 7sithur2305Noch keine Bewertungen
- CBSE Class 12 Physics Sample Paper Term 2 For 2021 22Dokument4 SeitenCBSE Class 12 Physics Sample Paper Term 2 For 2021 22SUBHAM WORLDNoch keine Bewertungen
- Physics SQP Term2Dokument4 SeitenPhysics SQP Term2Aastha ShreeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Physics Advanced Level Problem Solving (ALPS-12) - PaperDokument13 SeitenPhysics Advanced Level Problem Solving (ALPS-12) - PaperAnanmay ChauhanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pre-Term-Ii: (For CBSE Board) Class-Xii PhysicsDokument3 SeitenPre-Term-Ii: (For CBSE Board) Class-Xii PhysicsBadAss GamingNoch keine Bewertungen
- Modul Skor A+ Fizik - Radioaktif - SkemaDokument5 SeitenModul Skor A+ Fizik - Radioaktif - SkemaCikita IsmailNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2011 SBP Fizik SkemaDokument14 Seiten2011 SBP Fizik SkemaAimi LiyanaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Answer Section B and C and Paper 3Dokument21 SeitenAnswer Section B and C and Paper 3Adnan ShamsudinNoch keine Bewertungen
- Skema Modul 6Dokument14 SeitenSkema Modul 6nik mohamad solehinNoch keine Bewertungen
- Physics SSC-II (2nd Set)Dokument7 SeitenPhysics SSC-II (2nd Set)Maryam KhanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Kendriya Vidyalaya Sangathan Kolkata Region Pre-Board Examination 2020-21 Class - Xii Subject:PhysicsDokument7 SeitenKendriya Vidyalaya Sangathan Kolkata Region Pre-Board Examination 2020-21 Class - Xii Subject:PhysicsShivankar PandeyNoch keine Bewertungen
- 5054 On 2021 P22Dokument14 Seiten5054 On 2021 P22Raahin RahimNoch keine Bewertungen
- IGCSE Physics ExamDokument24 SeitenIGCSE Physics Examkamalharmoza100% (3)
- SPM Trial 2013 Physics Qa SBPDokument92 SeitenSPM Trial 2013 Physics Qa SBPkamalharmozaNoch keine Bewertungen
- KS3 Physics: 8L Sound and HearingDokument36 SeitenKS3 Physics: 8L Sound and HearingkamalharmozaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Analisa Fizik SPMDokument1 SeiteAnalisa Fizik SPMkamalharmozaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ramalan Fizik SPM 2009Dokument1 SeiteRamalan Fizik SPM 2009kamalharmozaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ramalan Physics SPM 2010Dokument1 SeiteRamalan Physics SPM 2010kamalharmozaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Physics SPMDokument23 SeitenPhysics SPMkamalharmoza100% (4)
- 10 JPNT Trial FZK k1Dokument30 Seiten10 JPNT Trial FZK k1Siti Aziah HalilanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Strategy To Answer & Physics Tips: For SPM CandidatesDokument28 SeitenStrategy To Answer & Physics Tips: For SPM CandidateskamalharmozaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Answering Technique-Physics SPMDokument3 SeitenAnswering Technique-Physics SPMkamalharmozaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Skema Paper 1 Set 2Dokument1 SeiteSkema Paper 1 Set 2kamalharmozaNoch keine Bewertungen
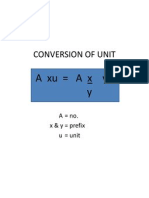
- Conversion of Unit-Physics SPMDokument6 SeitenConversion of Unit-Physics SPMkamalharmozaNoch keine Bewertungen
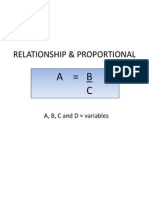
- Relationship-Physics SPMDokument7 SeitenRelationship-Physics SPMkamalharmozaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Motion Graph-Physics SPMDokument1 SeiteMotion Graph-Physics SPMkamalharmozaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nota Padat Fizik F5 ElectronicDokument21 SeitenNota Padat Fizik F5 Electronicslokkro100% (24)
- MRSM SPM Trial 2009 Phy Paper 1Dokument39 SeitenMRSM SPM Trial 2009 Phy Paper 1nursuhailahNoch keine Bewertungen
- MRSM-Physics P2-Trial SPM 2009Dokument36 SeitenMRSM-Physics P2-Trial SPM 2009kamalharmoza100% (3)
- Skema p3 Set 1 Trial 2010Dokument4 SeitenSkema p3 Set 1 Trial 2010kamalharmozaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ujian Selaras F4 2008Dokument21 SeitenUjian Selaras F4 2008kamalharmozaNoch keine Bewertungen
- MRSM Fizik K3 SPM 09Dokument21 SeitenMRSM Fizik K3 SPM 09Norfadila Mat JusofNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 9-Electronics (Teacher's Guide)Dokument36 SeitenChapter 9-Electronics (Teacher's Guide)kamalharmoza90% (10)
- Ujian Selaras F4 2009Dokument18 SeitenUjian Selaras F4 2009kamalharmozaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 5 Light Teacher's GuideDokument38 SeitenChapter 5 Light Teacher's Guidekamalharmoza80% (5)
- Chapter 8 TeacherDokument46 SeitenChapter 8 TeachercsteeeeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 6 Waves (Teacher's Guide)Dokument35 SeitenChapter 6 Waves (Teacher's Guide)Ahmad Zaidi63% (8)
- Chapter 7 - Electricity (Teacher's Guide)Dokument60 SeitenChapter 7 - Electricity (Teacher's Guide)kamalharmoza90% (21)
- Sekolah Berasrama PenuhDokument55 SeitenSekolah Berasrama PenuhPrince AceNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 10 Radioactivity Teacher Guide1Dokument29 SeitenChapter 10 Radioactivity Teacher Guide1Hazrol Fazly Husin100% (1)
- Physics Chapter 4 Heat Teacher S GuideDokument33 SeitenPhysics Chapter 4 Heat Teacher S Guideaiman48Noch keine Bewertungen