Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
C CALC Project
Hochgeladen von
Vijay KanugaOriginalbeschreibung:
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
C CALC Project
Hochgeladen von
Vijay KanugaCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
C Programming Project
C Programming
CALC Project
C Programming Project
Project 1
Making Calc
Description: This Assignment is divided into section each lecture will complete a portion of the CALC Lecture 1: Printf command, declaring variable We will be using printf command to display messages like #include <stdio.h> #include <conio.h> void main() { int a=5; printf(the value of a is %d, a); getch(); }
C Programming Project
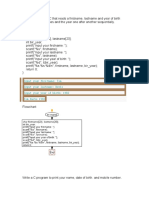
Lecture 2: Operators For performing mathematical calculation in CALCULATOR will have to use Operators as shown in the example #include <stdio.h> #include <conio.h> void main() { int a,b,c; printf(Enter the value of a\n); scanf(%d,&a); printf(Enter the value of b\n); scanf(%d,&b); c=a+b; printf(Sum of a and b is %d,c); getch(); } Lecture 3: if else, switch In the program there are four basic operations to be done sum, subtraction, multiplication, division depending upon the selection #include <stdio.h> #include <conio.h> void main() { int opr; float a,b,c; printf(enter value of a); scanf(%f,&a); printf(enter value of b); scanf(%f,&b); printf(Enter your choice for operation to be done); scanf(%d,&opr); switch(opr) { case 1: c=a+b; break; case 2: c=a-b; break; case 3: c=a*b; break; case 4: 3
C Programming Project
c=a/b; break; default: c=0; } printf(ans is %f,c); getch(); } Lecture 4: Loops Using loops we can repeat a similar task in cycle like in CALC there are buttons on it with different co-ordinates on x & y axis. Value of x & y co-ordinates can be incremented using loop as shown below #include <stdio.h> #include <conio.h> void main() { int x=0,y=0; for(x=1;x<=3;x++) { for(y=0;y<=4;y++) { printf((x,y)=(%d,%d),x,y); } printf(\n); } getch(); } Lecture 5: Preprocessors Using Preprocessors we declare some constants for convenience in lecture 3 example instead of comparing integer value with choice i.e. 1 for sum, 2 for subtraction, 3- multiplication, 4 for division we can use constants declared using preprocessor #include <stdio.h> #include <conio.h> #define sum 1 #define sub 2 #define prod 3 #define div 4 void main() { int opr; float a,b,c; printf(enter value of a); 4
C Programming Project
scanf(%f,&a); printf(enter value of b); scanf(%f,&b); printf(Enter your choice for operation to be done); scanf(%d,&opr); switch(opr) { case sum: c=a+b; break; case sub: c=a-b; break; case prod: c=a*b; break; case div: c=a/b; break; default: c=0; } printf(ans is %f,c); getch(); } Lecture 6 & 7: Arrays For creating button labels on CALC we will use two dimensional Array. The structure of this is shown as follows 7 4 1 0 #include <stdio.h> #include <conio.h> void main() { char buttons[][]={7,8,9,/}, {4,5,6,x}, {1,2,3,-}, int i,j; for(i=0;i<4;i++) { for(j=0;j<4;j++) { printf(%c\t,buttons[i][j]); 5 8 5 2 . 9 6 3 = / X +
{0,.,=,+};
C Programming Project
} Printf(\n); } getch(); }
Lecture 9: structures Co-ordinates of a point can be represented with the help of structure #include <stdio.h> #include <conio.h> struct coord { int x; int y; } void main() { struct coord point1; point1.x=250; point1.y=300; printf(point1(%d,%d),point1.x,point1.y); getch(); }
C Programming Project
Lecture 10: Union In the example the use of Union REGS and also shows how to move cursor position #include <stdio.h> #include <conio.h> #include <dos.h> #define VIDEO 0x10 void movetoxy(int x, int y) { union REGS regs; /* The union REGS is used to pass information to and from these functions*/ regs.h.ah = 2; /* set cursor position */ regs.h.dh = y; regs.h.dl = x; regs.h.bh = 0; /* video page 0 */ int86(VIDEO, ®s, ®s); } int main(void) { clrscr(); movetoxy(35, 10); printf(Hello\n); getch(); return 0; } Lecture 11: string functions Using string functions we can manipulate a string like displaying a text in UPPER CASE #include <stdio.h> #include <conio.h> #include <string.h> void main() { char heading=calculator; printf(%s,strupr(heading)); getch(); }
C Programming Project
Lecture 14: functions For repetitive use of any logic we can use functions like in calc arithmetic calculation logic used again & again #include <stdio.h> #include <conio.h> #include <string.h> #include <stdlib.h> #define sum 1 #define sub 2 #define prod 3 #define div 4 void operation(int) float a,b; void main() { int choice; while(1) { printf(enter value a\n); scanf(%f%,&a) ; printf(enter value b\n); scanf(%f%,&b) ; printf(enter choice for operation 1.sum, 2.substration, 3.product, 4.division a\n); scanf(%d%,&choice) ; operation(choice); printf(continue using calc[y/n]?); if(getch()!=y) { exit(0); } } } void operation(int opr) { switch(opr) { case sum: c=a+b; break; case sub: c=a-b; break; case prod: c=a*b; break; case div: c=a/b; break; default: c=0; 8
C Programming Project
} printf(ans is %f,c); getch(); } Lecture 15 & 19: In the following example pointer are used to trace the mouse pointer button status and x, y coordinates #includegraphics.h #includedos.h #includestdio.h #includemath.h union REGS i,o; void showmouseptr(); void main() { int gd=DETECT,gm,x1,x2,y1,y2,i,j,maxx,maxy,x,y,button; char *s; initgraph(&gd,&gm,c:/tc/bgi); showmouseptr(); while(1) { getmousepos(&button,&x,&y); sprintf(s,button status=%d, x=%d, y=%d,button,x,y); setcolor(1); outtextxy(50,50,s); if(button==1) { exit(0); } } getch(); } void showmouseptr() { i.x.ax=1; int86(0x33,&i,&o); return 0; } getmousepos(int *button,int *x,int *y) { i.x.ax=3; int86(0x33,&i,&o); *button=o.x.bx; *x=o.x.cx; *y=o.x.dx; 9
C Programming Project
return 0; } Complete Code
#includegraphics.h #includedos.h #includestdio.h #includemath.h union REGS i,o; char *text[]={ 7,8,9,*, 4,5,6,/, 1,2,3,+, 0,00,.,-, M,M+,M-,+/-, MR,MC,x^2,sr, OFF,AC,CE,=}; int k=0,pass,op,prop,newnum=1,bt,memo=1,d=0,sq; long double num=0,accum,m; void normalbutton(int ,int ,int ,int,char**); void main() { int gd=DETECT,gm,x1,x2,y1,y2,i,j,maxx,maxy,x,y,button; char *text1[]={\,T,o, ,K,n,o,w, ,a,b,o, u,t, ,m,e, ,l,o,g,o,n, ,:}; char *text2[]={w,w,w,.,g,e,o,c,i,t,i,e,s, .,c,o,m,/,t,a,l,k,d,e,e,p, e,s,h}; initgraph(&gd,&gm,c:/tc/bgi); if(initmouse()==0) { closegraph(); restorecrtmode(); printf(Mouse driver not loded); exit(1); } showmouseptr(); // x=y=50; movemouseptr(&x,&y); setbkcolor(11); setcolor(1); rectangle(198,140,417,163); 10
C Programming Project
rectangle(199,141,418,164); rectangle(197,139,416,162); rectangle(185,130,430,450); rectangle(184,129,431,451); rectangle(182,127,433,454); rectangle(181,126,434,453); //setfillstyle(SOLID_FILL,3); //bar(200,142,415,161); outtextxy(200,50,A Calculator Project); outtextxy(200,100,Press OFF button to exit....); y1=140; y2=160; for(j=0;j<7;j++) { x1=200; x2=235; y1+=40; y2+=40; for(i=0;i<4;i++) { normalbutton(x1,x2,y1,y2,text); x1+=60; x2+=60; } } while(1) { getmousepos(&button,&x,&y); y1=140; y2=160; /* { if( (x>400&&x<450) && (y>400&&y<420) ) if((button & 1)==1) { sound(500); delay(5); exit(); }
} */ for(j=0;j<7;j++) { x1=200; x2=235; y1+=40; 11
C Programming Project
y2+=40; for(i=0;i<4;i++) { if((x<x2&&x>x1)&&(y<y2&&y>y1)) { if((button & 1)==1) { gotoxy(28,10); // printf(%d,ch=*text[j*4+i]); // printf(char is %c,ch); bt=j*4+i; printf(char is %d,j*4+i); setcolor(11); outtextxy(x1+12,y1+7,text[j*4+i]); if(num>pow(10.0,18)) exit(); sound(500);delay(10);nosound(); delay(250); sound(400);delay(10); nosound(); switch (bt) { case 8 : addnum(1); break; case 9 : addnum(2); break; case 10 : addnum(3); break; case 4 : addnum(4); break; case 5 : addnum(5); break; case 6 : addnum(6); break; case 0 : addnum(7); break; case 1 : addnum(8); break; case 2 : addnum(9); break; case 12 : addnum(0); break; 12
//
C Programming Project
case 11 : // plus operation(1); break; case 15 : // minus operation(2); break; case 3 : // multiplication operation(3); break; case 7 : // division operation(4); break; case 13: doublezero(); break; case 14 : decimal(); break; case 16: mem(); break; case 20: recallmem(); break; case 19: plusminus(); break; case 17: plusm(); break; case 18: minusm(); break; case 21: clearm(); break; case 22 : square(); break; case 23: sqroot(); break; case 24: // OFF hidemouseptr(); setcolor(1); for(j=0;j<20;j++) 13
C Programming Project
{ for(i=75;i<481;i+=20) line(0,0+i+j,640,j+0+i); delay(100); } setcolor(14); outtextxy(225,200,Thanks for using it !); delay(2000); setcolor(13); for(j=0;j<20;j++) { for(i=0;i<640;i+=20) line(0+i+j,0,j+0+i,640); delay(100); } setcolor(1); for(i=0;i<25;i++) { outtextxy(75+10*i,200,text1[i]); sound(3000); delay(50); nosound(); } for(i=0;i<29;i++) { outtextxy(125+10*i,225,text2[i]); sound(3000); delay(50); nosound(); } // outtextxy(200,225,www.saintangelos.com); delay(2500); sound(5000); delay(10); nosound(); exit(); break; case 25: allclear(); break; case 26: clear(); break; case 27: // equalto operation(5); 14
C Programming Project
break;
} setcolor(1); outtextxy(x1+12,y1+7,text[j*4+i]); } } x1+=60; x2+=60; } } } nosound(); } void normalbutton(int x1,int x2,int y1,int y2,char **text) { setcolor(15); rectangle(x1-2,y1-2,x2+1,y2+1); rectangle(x1-1,y1-1,x2+2,y2+2); setcolor(7); rectangle(x1,y1,x2+2,y2+2); rectangle(x1,y1,x2+1,y2+1); setfillstyle(SOLID_FILL,14); bar(x1,y1,x2,y2); setcolor(1); outtextxy(x1+12,y1+7,text[k]); k++; } /* initmouse */ initmouse() { i.x.ax=0; int86 (0x33,&i,&o); return(o.x.ax); } hidemouseptr() { i.x.ax=2; int86(0x33,&i,&o); } /* displays mouse pointer */ showmouseptr() { 15
C Programming Project
i.x.ax=1; int86(0x33,&i,&o); return 0; } /*gets mouse coordinates and button status*/ getmousepos(int *button,int *x,int *y) { i.x.ax=3; int86(0x33,&i,&o); *button=o.x.bx; *x=o.x.cx; *y=o.x.dx; return 0; } /* Move mouse ptr to x,y */ movemouseptr(int *x,int *y) { i.x.ax=4; int86(0x33,&i,&o); o.x.cx=*x; o.x.dx=*y; return 0; } addnum(int pass) { if(sq) newnum=1; if(newnum) { if(d) { num=pass/(pow(10.0,d)); d++; newnum=0; } else { num=pass; newnum=0; } } else { /* if(num==0) { if(d) { num=num+pass/(pow(10.0,d)); d++; } else num=pass; } */ 16
C Programming Project
// { {
else if(d)
if(num<0) num=num-pass/(pow(10.0,d)); else num=num+pass/(pow(10.0,d)); d++; } else { num=num*10+pass; } } } printf(%25.5Lf,num); } operation(int opr) { long double pnum; pnum=num; if(newnum && (prop != 5) && memo) { } else { newnum=1; d=0; sq=0; switch(prop) { case 1: accum=accum+pnum; break; case 2: accum=accum-pnum; break; case 3: accum=accum*pnum; break; case 4: accum=accum/pnum; break; default: accum=pnum; } } prop=opr; num=accum; printf(%25.5Lf,num); } allclear() { 17
C Programming Project
sq=0; accum=0; num=0; d=0; newnum=1; printf(%25.5Lf,num); } mem() { m=num; } recallmem() { memo=0; printf(%25.5Lf,m); num=m; } plusminus() { if(num!=0) { num*=-1; printf(%25.5Lf,num); } } plusm() { m+=num; } minusm() { m-=num; } clearm() { m=0; } decimal() { if(!d) {d=1; if(newnum==1) { num=0; } printf(%25.5Lf,num); } } square() { sq=1; num*=num; printf(%25.5Lf,num); 18
C Programming Project
// newnum=1; } sqroot() { sq=1; num=pow(num,0.5); printf(%25.5Lf,num); // newnum=1; } doublezero() { if(d) { // num=num+pass/(pow(100.0,d)); d++; d++; } else num*=100; printf(%25.5Lf,num); } clear() { num=0; printf(%25.5Lf,num); }
19
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Int Int Int Int: Main P P Malloc PDokument11 SeitenInt Int Int Int: Main P P Malloc PArunNoch keine Bewertungen
- Puzzels On CDokument14 SeitenPuzzels On CUjjwal VaddepatiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Rdinaz PDFDokument18 SeitenRdinaz PDFvaishnaviNoch keine Bewertungen
- C QuestionDokument41 SeitenC QuestionrajeevsahaniNoch keine Bewertungen
- C QuestionsDokument57 SeitenC QuestionsSuman RavuriNoch keine Bewertungen
- C Programming MCQDokument206 SeitenC Programming MCQBikram DeNoch keine Bewertungen
- C-Program-SolutionsDokument40 SeitenC-Program-SolutionssampurnakumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bisection Method Program in CDokument24 SeitenBisection Method Program in CAnshumanSrivastavNoch keine Bewertungen
- Intro Programming CDokument11 SeitenIntro Programming CKoffiNoch keine Bewertungen
- CS Lab File-1Dokument115 SeitenCS Lab File-1Muhammad Khursheed Aqueeb SiddiquiNoch keine Bewertungen
- C PROGRAMMES - SET-1 - GECR GEEK - UpdatedDokument8 SeitenC PROGRAMMES - SET-1 - GECR GEEK - Updatedyash gamingNoch keine Bewertungen
- CPU Lab Manual 2014-15: Practical Set-01Dokument46 SeitenCPU Lab Manual 2014-15: Practical Set-01EmrebelNoch keine Bewertungen
- C Program Output for Memory, Pointers, Bitwise, MacrosDokument53 SeitenC Program Output for Memory, Pointers, Bitwise, MacrosKalyan Kotha100% (1)
- Program to Find Sum of Individual DigitsDokument101 SeitenProgram to Find Sum of Individual Digitsgdayanand4uNoch keine Bewertungen
- Let Us CDokument19 SeitenLet Us CSajjad RizviNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lab#5Dokument17 SeitenLab#5zainabsaleem2004444Noch keine Bewertungen
- C Debugging QuizDokument5 SeitenC Debugging QuizRickyNoch keine Bewertungen
- #Include #Include Int Main Int A, B, C Double X, Y, DDokument22 Seiten#Include #Include Int Main Int A, B, C Double X, Y, DChinnaraoNoch keine Bewertungen
- CPE Laboratory ExercisesDokument21 SeitenCPE Laboratory ExercisesNicoles JavaNoch keine Bewertungen
- C Programming Code Examples: 12 Fundamental C ProgramsDokument297 SeitenC Programming Code Examples: 12 Fundamental C ProgramsSachin Saini0% (1)
- CG Programs - Learn Graphics Programming in CDokument11 SeitenCG Programs - Learn Graphics Programming in CChandu KumareNoch keine Bewertungen
- PPS All Units 2 MarksQuestions With AnswersDokument33 SeitenPPS All Units 2 MarksQuestions With AnswersHARIKRISHNA SATVIKNoch keine Bewertungen
- Checklist: I. Q & A II. Ôn tập QuizzesDokument19 SeitenChecklist: I. Q & A II. Ôn tập QuizzesLê Hoàng Minh ThưNoch keine Bewertungen
- C Program Debugging ExamplesDokument12 SeitenC Program Debugging ExamplesShreeji ShethNoch keine Bewertungen
- Array CDokument6 SeitenArray Camitghimire102Noch keine Bewertungen
- C programming questions and answersDokument7 SeitenC programming questions and answersPragadesh KumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sample C ProgramDokument9 SeitenSample C Programritesh patelNoch keine Bewertungen
- C Coding Examples 1Dokument11 SeitenC Coding Examples 1Sarthak RoyNoch keine Bewertungen
- C Programming Complete Lab 1-17Dokument41 SeitenC Programming Complete Lab 1-17MURALI KARTHIK REDDYNoch keine Bewertungen
- AST 131 C Lec-7Dokument21 SeitenAST 131 C Lec-7TarikulNoch keine Bewertungen
- C Lab ProgramsDokument51 SeitenC Lab Programssowmya8929Noch keine Bewertungen
- C Programming Lab ProgramsDokument39 SeitenC Programming Lab Programsans_h2003Noch keine Bewertungen
- CDokument31 SeitenCratulray2006100% (3)
- C Programming Interview QuestionsDokument12 SeitenC Programming Interview QuestionsdeepanjankoulNoch keine Bewertungen
- Board Question C Program SolveDokument33 SeitenBoard Question C Program SolvedfdasfNoch keine Bewertungen
- C Programming Lab Subject Code: 20UCA1CC2P/20UIT1CC2P Class: BCA/BSC IT Programs InsideDokument12 SeitenC Programming Lab Subject Code: 20UCA1CC2P/20UIT1CC2P Class: BCA/BSC IT Programs InsideHajiram Beevi100% (1)
- Mimansa Pathania, CG Lab File, 500091628Dokument26 SeitenMimansa Pathania, CG Lab File, 500091628Divyansh SinghNoch keine Bewertungen
- Question:1 Write A Program To Generate Fibonacci Series, Using RecursionDokument9 SeitenQuestion:1 Write A Program To Generate Fibonacci Series, Using RecursionPiyush BhardwajNoch keine Bewertungen
- CD (KCS - 552) Lab FileDokument41 SeitenCD (KCS - 552) Lab FileVashu GuptaNoch keine Bewertungen
- C Programming ExercisesDokument26 SeitenC Programming Exercisestanjim1100% (2)
- C Programming Lab Manual ExercisesDokument49 SeitenC Programming Lab Manual ExercisesDixit JainNoch keine Bewertungen
- C Program Output SolutionsDokument34 SeitenC Program Output SolutionschirusagarNoch keine Bewertungen
- SAUMYA GUPTA'S IT ASSIGNMENTDokument17 SeitenSAUMYA GUPTA'S IT ASSIGNMENTSaumyaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Programs Arrays StringsDokument30 SeitenPrograms Arrays StringsumamaheshsjcetNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1.C Program Without Using Semicolon (At Least Do Addition of Two Numbers)Dokument5 Seiten1.C Program Without Using Semicolon (At Least Do Addition of Two Numbers)prabhusctNoch keine Bewertungen
- Practice Question CPDokument6 SeitenPractice Question CPGourav SharmaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Prepared by Bushemmy Page 1 of 9Dokument9 SeitenPrepared by Bushemmy Page 1 of 9Bushahiro EmmyNoch keine Bewertungen
- 25 Programs of C-1Dokument31 Seiten25 Programs of C-1Azeem026Noch keine Bewertungen
- C Practical FileDokument16 SeitenC Practical FileAmanpreet SinghNoch keine Bewertungen
- C ProgrammingDokument24 SeitenC ProgrammingshielaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tip#5) - Some Cool SCANF Tricks: Find Out Some of The Unheard Scanf Tricks That You Must KnowDokument17 SeitenTip#5) - Some Cool SCANF Tricks: Find Out Some of The Unheard Scanf Tricks That You Must KnowGauri BansalNoch keine Bewertungen
- StudyDokument12 SeitenStudytrxxx.axxNoch keine Bewertungen
- Department of Electrical and Electronics Engineering: Lab ManualDokument53 SeitenDepartment of Electrical and Electronics Engineering: Lab ManualgdeepthiNoch keine Bewertungen
- BCSL 058 Computer Oriented Numerical Techniques Lab Solved Assignment 2019 20Dokument9 SeitenBCSL 058 Computer Oriented Numerical Techniques Lab Solved Assignment 2019 20Ambed Kant DinkarNoch keine Bewertungen
- 200 ObjectiveType QuestionsDokument33 Seiten200 ObjectiveType QuestionsKaushal KishoreNoch keine Bewertungen
- Practical Assignment-28Dokument24 SeitenPractical Assignment-28kulkarnivishal907Noch keine Bewertungen
- 2.manage Input and Output: 1) Using OperatorDokument13 Seiten2.manage Input and Output: 1) Using OperatorMELKY ABISHAKE RNoch keine Bewertungen
- Projects With Microcontrollers And PICCVon EverandProjects With Microcontrollers And PICCBewertung: 5 von 5 Sternen5/5 (1)
- 20483Dokument9 Seiten20483Anonymous iUW0JL6O5Noch keine Bewertungen
- MCQ Java Multiple Choice QuestionsDokument7 SeitenMCQ Java Multiple Choice QuestionsJitendra TekwaniNoch keine Bewertungen
- Kotlin DocsDokument187 SeitenKotlin DocsRocky MehtaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Samkoon HMI User Manual (HmiVietNam - Com)Dokument422 SeitenSamkoon HMI User Manual (HmiVietNam - Com)Minh Nguyễn100% (1)
- Project ReportDokument9 SeitenProject Reportapi-307821649Noch keine Bewertungen
- Sppa T3000Dokument22 SeitenSppa T3000sina20795100% (2)
- Embedded Systems - Fs 2018: Figure 1: Simplified Task States Diagram in FreertosDokument8 SeitenEmbedded Systems - Fs 2018: Figure 1: Simplified Task States Diagram in FreertosPhạm Đức HuyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Learning Python - Unit 16, EmbeddingDokument23 SeitenLearning Python - Unit 16, EmbeddingkrishaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Python For Mathematics Students PDFDokument115 SeitenPython For Mathematics Students PDFLakshmi RajNoch keine Bewertungen
- Dum OCPDokument55 SeitenDum OCPHenry Aulia RahmanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Unit 3 Test (CH 4 5 6) 11-6-2013 KEYDokument31 SeitenUnit 3 Test (CH 4 5 6) 11-6-2013 KEYOsama MaherNoch keine Bewertungen
- Letusc (By Yashvant Kanetkar) Chapter 1 SolutionDokument20 SeitenLetusc (By Yashvant Kanetkar) Chapter 1 Solutiontooba mukhtarNoch keine Bewertungen
- IS 28640-Random Variate Generation Methods PDFDokument58 SeitenIS 28640-Random Variate Generation Methods PDFzilangamba_s4535Noch keine Bewertungen
- Mplab C18 ReadmeDokument24 SeitenMplab C18 ReadmeWellinton MarcioNoch keine Bewertungen
- 101-235 Questions C#Dokument31 Seiten101-235 Questions C#Lương Anh Sơn100% (1)
- Sample Question Paper of PRogramming in 'C'Dokument4 SeitenSample Question Paper of PRogramming in 'C'vikassolankeNoch keine Bewertungen
- 3BUA000156-510 C en System 800xa 5.1 Post InstallationDokument230 Seiten3BUA000156-510 C en System 800xa 5.1 Post InstallationJose MellaNoch keine Bewertungen
- F.Y.B.Sc. Computer Science Exam 2010: C Programming and File Organization QuestionsDokument76 SeitenF.Y.B.Sc. Computer Science Exam 2010: C Programming and File Organization QuestionsAmarjeet DasNoch keine Bewertungen
- 10 Sending Data Through Usb Using A Queue: What You Will Learn in This ChapterDokument5 Seiten10 Sending Data Through Usb Using A Queue: What You Will Learn in This ChapterOussama TarkhaniNoch keine Bewertungen
- C Basic ExercisesDokument7 SeitenC Basic ExercisesAngelo MartinNoch keine Bewertungen
- Syllabus IBMDokument28 SeitenSyllabus IBMManas KhareNoch keine Bewertungen
- 312303-Programming in C 271223Dokument8 Seiten312303-Programming in C 271223ts6071270Noch keine Bewertungen
- Menu - 634641194757402500 - CS6106 Compiler Design Lab AssignmentsDokument3 SeitenMenu - 634641194757402500 - CS6106 Compiler Design Lab AssignmentsKarthik Sara MNoch keine Bewertungen
- System Programming Lab: LEX: Lexical Analyser GeneratorDokument33 SeitenSystem Programming Lab: LEX: Lexical Analyser GeneratorDivya D GowdaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Kurukshetra University Syllabus for First Year 2015-16Dokument54 SeitenKurukshetra University Syllabus for First Year 2015-16RiyaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Printing - Creating A Macro - HM-8000Dokument8 SeitenPrinting - Creating A Macro - HM-8000api-19817003Noch keine Bewertungen
- An Integrated Data Flow Visual Language and Software Development EnvironmentDokument30 SeitenAn Integrated Data Flow Visual Language and Software Development EnvironmentBoban CelebicNoch keine Bewertungen
- MATLAB-Manual RTW GsDokument136 SeitenMATLAB-Manual RTW GsTanNguyễnNoch keine Bewertungen
- Python built-in functions guideDokument27 SeitenPython built-in functions guidevinaykumar460Noch keine Bewertungen
- PPLADokument55 SeitenPPLAdreamafonNoch keine Bewertungen