Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
ARI E c4 Topol
Hochgeladen von
catalin_giana8622Originalbeschreibung:
Originaltitel
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
ARI E c4 Topol
Hochgeladen von
catalin_giana8622Copyright:
Verfügbare Formate
1.
4 Network Topologies
A network topology = physical arrangement of the various network elements and their interactions (links, nodes, etc.); (topology = graph). A network topology (redundancy) influences its performances. Types of network topologies (as graphs, topologies differ only in the way nodes and arcs are arranged):
point-to-point; bus; ring; star; mesh; mixed.
Nodes in a network topology may be interconnecting devices or terminals, while arcs may be physical connections (direct or indirect) or logical.
1.4.1 Point-to-point Topology (P2P)
the simplest topology, with the minimum redundancy (redundancy = 0, i.e., there is no spare/backup link) reduced reliability; Advantage: simple management; use: in long-haul networks (when redundancy is expensive);
in networks with 2 terminals, over small distances (where the redundancy is useless).
1.4.2 Bus Topology
A linear topology = a multipoint communications link (in LAN Ethernet, rare use nowadays). Advantages:
network homogeny; low cost media and couplings; no medium access control (MAC - LAN) implemented in nodes.
Disadvantages:
MAC problems = collisions, if random access is used; a cable interruption of a segment 2 unusable segments (redundancy = 0).
1.4.3 Ring Topology
All nodes are connected in a succesive manner (in pairs), a loop closes with last node connecting the first node; Each node relays the message received on one port to the other port, copying it if is the destination; The message can be eliminated from loop (ring) by the source node or by another node (= ring monitor); a MAC mechanism can be used, based on a token, i.e., a transmission permit; such a network is called Token ring;
1.4.3 Ring Topology (contin.)
A short-circuit mechanism is introduced at each node, in order to avoid the ring interruption in case of a node failure; A double ring solution (one ring for each transmission way; ex.: FDDI) advantage: close the loop to form a new ring, from 2 broken rings; Use: LAN Token Ring (IEEE 802.5) and FDDI (IEEE 802.6); SONET/SDH.
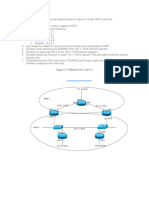
DAS3 - primary ring interconnects stations - secondary ring = backup - Single attachment station (SAS) PCs - Dual attachment station (DAS) Servers - Concentrators DAS1 N1 = SAS1
N2
DAS2
1.4.3 Ring Topology (contin.)
Advantages :
no need for central management.
Disadvantages :
redundancy = 0 (for a single ring) or redundancy = 1 (double ring); sensitive to interruptions (short-circuits) failures; network capacity increase (new stations) high propagation delays (larger ring).
1.4.4 Star Topology
A central node (CN) is used to connect each terminal node; in fact, each node is physically connected to CN by a point-to-point link; The information transfer:
point-to-point (P2P), when CN = switch (layer 2); point-to-multipoint (PTMP), when CN = HUB Host-Unit Broadcast (layer 1).
Used in LAN (IEEE 802.3): 10BASE-T Ethernet, Fast Ehernet, and Gigabit Ehernet.
1.4.4 Star Topology (contin.)
Advantages : almost all software is concentrated in CN; terminal nodes need a simple SW;
easy net extension (if there are enough spare ports in CN); facile installation and management; a link / equipment failure eliminates only one node, the rest are operational; cheap and fast switches development; increased redundancy for extended stars.
Disadvantages : a bottleneck (congestion) due to intense traffic CN failure;
the net reliability depends mostly on CN; net capacity is limited by the number of the available ports in CN .
1.4.5 Mesh Topology
(full-)mesh topology = most complex topology, having the maximum redundancy (i.e., at least two links are available between any pair of nodes in the network (one direct link and one indirect link); Use: core networks (ex. WDM). Advantages:
a larke number of links (redundancy) high reliability; for N nodes N (N-1) / 2 links
Disadvantage :
high costs (links/cables and devices).
1.4.6 Mixed (Hybrid) Topologies
a network extension of elementary topologies (any of the above); A mixed net is composed by a core (backbone) net, which interconnects other networks. Examples of mixed topologies: the tree topology combines the P2P and the star topologies; a full mesh core + stars for access networks.
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceVon EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (895)
- Home Wireless Network DesignDokument14 SeitenHome Wireless Network DesignSai Rohit PaturiNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeVon EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (5794)
- Router Introduction 1Dokument45 SeitenRouter Introduction 1Vo Ngoc HoangNoch keine Bewertungen
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeVon EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (537)
- Cisco ATA Guide - Support Centre For Kiwi VoIPDokument10 SeitenCisco ATA Guide - Support Centre For Kiwi VoIPMarianna MorozovaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceVon EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (588)
- Canon - Inkjet Manuals - IJ Network Device Setup Utility - Status CodesDokument3 SeitenCanon - Inkjet Manuals - IJ Network Device Setup Utility - Status CodespaluckNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Von EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Bewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (98)
- KLMDokument1 SeiteKLMbrahim_603Noch keine Bewertungen
- Entclass Full Paste Update VPNDokument48 SeitenEntclass Full Paste Update VPNAbiolu Victor100% (3)
- IOT Network Architecture and DesignDokument32 SeitenIOT Network Architecture and DesignMegha ShreeNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingVon EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (400)
- DDoS Secure Operation Guide R13 (16.1.50) PDFDokument78 SeitenDDoS Secure Operation Guide R13 (16.1.50) PDFdame koffiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItVon EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (838)
- CCNA Study NotesDokument60 SeitenCCNA Study Notesapi-3800455Noch keine Bewertungen
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureVon EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (474)
- Huawei SingleSDB Feature ListDokument22 SeitenHuawei SingleSDB Feature Listelectrico servicesNoch keine Bewertungen
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryVon EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (231)
- Ospf Labs With AnswersDokument10 SeitenOspf Labs With AnswersformycandyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Untuk Setting GPRSDokument5 SeitenUntuk Setting GPRSdhyantNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerVon EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (271)
- Huawei S5720-LI Series Switches BrochureDokument15 SeitenHuawei S5720-LI Series Switches BrochureMurillo SilvaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1 About Packet Tracer: Instructor FAQ 2004, Cisco Systems, IncDokument4 Seiten1 About Packet Tracer: Instructor FAQ 2004, Cisco Systems, IncUdaya Sri KariyawasamNoch keine Bewertungen
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaVon EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (266)
- Tplink Ap EAP110 - V1 - Datasheet PDFDokument5 SeitenTplink Ap EAP110 - V1 - Datasheet PDFiraudyNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersVon EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (345)
- Bacnet Protocol Implementation Conformance StatementDokument7 SeitenBacnet Protocol Implementation Conformance StatementCassio José Matos De SouzaNoch keine Bewertungen
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealVon EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (74)
- International School of Management and TechnologyDokument5 SeitenInternational School of Management and TechnologyAthl SNoch keine Bewertungen
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyVon EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (2259)
- ACI Remote Leaf Fabric Discovery v1.0 PDFDokument24 SeitenACI Remote Leaf Fabric Discovery v1.0 PDFdelplayNoch keine Bewertungen
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnVon EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (234)
- ISDN User PartDokument7 SeitenISDN User Partomjaijagdish.raiNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaVon EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (45)
- Lab - Configuring Switch Security Features: TopologyDokument9 SeitenLab - Configuring Switch Security Features: TopologybobNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreVon EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (1090)
- TCP Variations: Tahoe, Reno, New Reno, Vegas, Sack: Paul D. Amer, ProfessorDokument50 SeitenTCP Variations: Tahoe, Reno, New Reno, Vegas, Sack: Paul D. Amer, Professordennismenace007Noch keine Bewertungen
- Practice Lab #2 - Mpls L3Vpn + Mpls Atom + Mpls Te + Internet AccessDokument17 SeitenPractice Lab #2 - Mpls L3Vpn + Mpls Atom + Mpls Te + Internet AccessJe RelNoch keine Bewertungen
- 8.1.2.5 Lab - Configuring Basic DHCPv4 On A Switch WBDokument9 Seiten8.1.2.5 Lab - Configuring Basic DHCPv4 On A Switch WBShaRonNoch keine Bewertungen
- 04 MPLS Te PDFDokument69 Seiten04 MPLS Te PDFlamvan tuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hydra SetDokument73 SeitenHydra SetAllangmrNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lab 2Dokument13 SeitenLab 2Vũ PhướcNoch keine Bewertungen
- Install The SSH Server (Optional)Dokument16 SeitenInstall The SSH Server (Optional)leomer7697Noch keine Bewertungen
- Transport Layer Security (TLS)Dokument22 SeitenTransport Layer Security (TLS)wachelokNoch keine Bewertungen
- Netkiller Cisco IOS 手札Dokument144 SeitenNetkiller Cisco IOS 手札Neo ChenNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Von EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Bewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (121)
- EECS 489: Final Exam, Fall 2018: Duration: 70 MinutesDokument7 SeitenEECS 489: Final Exam, Fall 2018: Duration: 70 MinutesTayyaba AsifNoch keine Bewertungen
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesVon EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (821)